INTRODUCTION
During initia l e va lua tio n o f c hildre n o n a n o utp a tie nt b a sis, the ind e x o f susp e c te d he a rt dise a se ma y b e hig h, pa rtic ula rly if we c o nside r tha t inno c e nt murmur o c c urs in a b o ut 5 0 % o f the pe dia tric po pula tio n.1 -3 This is the mo st c o mmo n c a use o f re fe rra l to the pe dia tric c a rd io lo g ist, w ith se ve ra l re p o rts o f suc h experienc e pub lished wo rldwide. O ther c a uses like c he st pa in, b re a thle ssness a t re st a nd o n e ffo rt a nd a rrhy thmia a re le ss fre q ue nt, a ltho ug h no t le ss imp o rta nt in this se tting . O b vio usly, the de c isio n to re fe r a pa tie nt fo r a spe c ia list c o nsulta tio n is ma inly de pe nde nt o n the ability o f the pediatrician to reco g niz e heart disea se. This inherent c ha ra c teristic is c erta inly re la te d to the info rma tio n p ro vid e d d uring g ra d ua te a nd p o st-g ra d ua te tra ining , w hic h se e ms to va ry fro m c o untry to c o untry, a nd is a lso re la te d to individua l skill.
The purpo se o f this pa per is to present experience fro m a public o utpatient clinic fo r pediatric cardio lo g y situated in the state o f São Paulo , in the so utheast o f Brazil. The results are based o n a pro spective study o f 2 6 7 5 co nsecutive children under the ag e o f 1 5 , all o f them referred fro m pediatricians fo r a cardiac evaluatio n.
Cardiologic e valuation of childre n with suspe cte d he art
dise ase : e xpe rie nce of a public outpatie nt clinic in Brazil
Pediatric Cardiology Outpatient Clinic, SUS and Department of Pediatrics,
Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil
Fernando Amaral João Antonio Granzotti
SUMMARY
Contex t: During initial evaluatio n o f children o n an o utpatient basis, the index o f suspected heart disease may be hig h, particularly if we co nsider that inno cent murmur o ccurs in abo ut 5 0 % o f the pediatric po pulatio n. This is the mo st co mmo n cause o f referral to the pediatric cardio lo g ist.
O bjective: To repo rt o n the experience o f a public o utpatient clinic in the so utheastern reg io n o f Braz il.
Design: Retro spective analysis o f all patients submitted to cardio lo g ic evaluatio n within a 3 9 mo nth perio d.
Setting: public pediatric cardio lo g y o utpatient clinic.
Pa rticipa nts: 2 6 7 5 co nsecutive children ag ed ≤1 5 years referred fro m the lo cal and reg io nal basic health units due to suspected heart disease.
M a in M ea surem ents: Reaso n fo r referral, diag no stic investig atio n, final diag no stis based o n the reaso n fo r referral, therapeutic pro cedures.
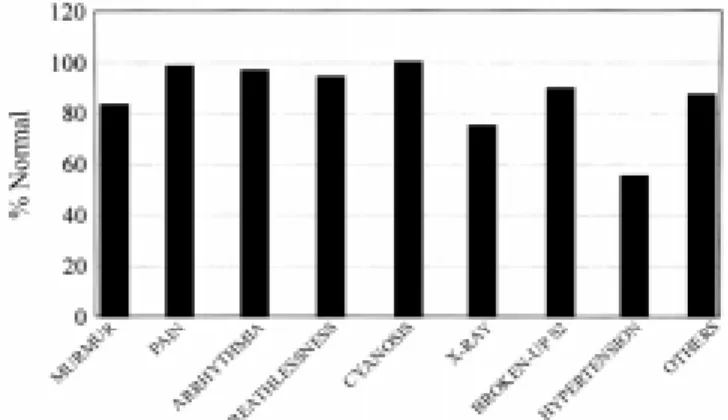
Results: The main reaso ns fo r referral were: murmur (7 0 %), preco rdial pain (9 %), suspicio n o f arrhythmia (9 %) and breathlessness (5 %). O f the to tal number, 6 9 5 cases (2 6 %) did no t co mplete the investig atio n and were no t included in the analysis. A final diag no sis was o btained based o n the reaso n fo r referral and the main co nclusio ns were: l) a hig h incidence o f no rmality was fo und: murmur (8 3 %), pain (9 8 %), arrhythmia (9 7 %) and breathless (9 4 %); 2 ) heart disease was unlikely, based o n o ther referral reaso ns; 3 ) 1 4 % o f the children were co nsidered abno rmal and 1 % needed therapeutical pro cedures.
Conclusions: The establishment o f a pediatric cardio lo gy o utpatient clinic within the public health service in the regio n seems to be justifiable, due to the high current demand. The lo w glo bal incidence o f heart disease, with a high prevalence o f children with inno cent murmur, disclo ses the need fo r a specific training pro gram in cardio lo gy fo r pediatricians.
Key w ords: Heart disease. Child. Incidence. Epidemio lo gy.
METHODS
The g reat majo rity o f the 2 6 7 5 cases were referred fro m the 3 2 so -called Basic Health Units (BHU) lo cated in the city o f Ribeirão Preto , state o f São Paulo , Braz il, where primary pediatric care is o ffered daily. The material was co llected fro m September 1 9 9 0 to December 1 9 9 3 (a p e rio d o f 3 9 mo nths). The ma le se x w a s predo minant: 1 4 4 4 cases (5 4 %). Reg arding the ag e at referral, 2 6 patients (1 %) were neo nates, 4 5 5 (1 7 %) were infants, 8 3 0 (3 1 %) were o f pre-scho o l ag e and 1 3 6 4 (5 1 %) were children o f scho o l ag e.
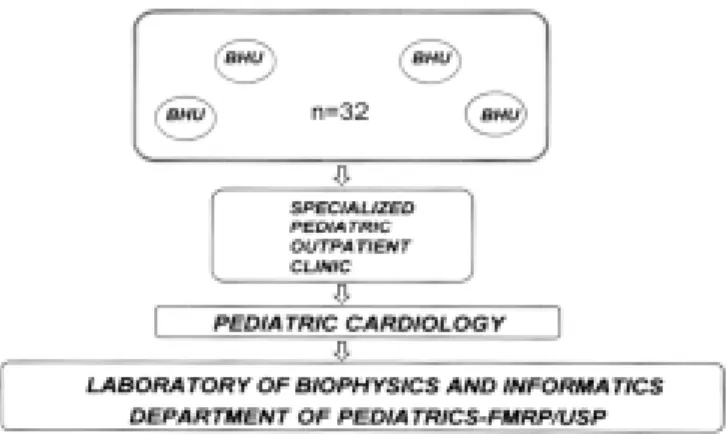
Every patient was seen in an adequate a nd silent ro o m in the o utpa tient c linic , with histo ry a nd p hysic a l e xa mina tio n d ire c te d to wards the cardio vascular system. Based o n the da ta fro m the clinica l exa mina tio n a lo ne, a n initial diag no sis was made and all the patients were submitted to an electro cardio g ram (EKG ). O ther tests like chest X-ray, echo cardio g ram and hemo dynamic studies were o nly do ne when heart dise a se wa s o b vio us, the type o f te st b e ing re q ue ste d in a c c o rd a nc e w ith the c linic a l diag no sis. The investig atio n was co mpleted in 7 4 % o f the c a se s. To fulfill the c rite rio n o f co mplete investig atio n, all the patients wo uld have to return to the clinic either with o nly the EKG (in cases co nsidered no rmal when first seen) o r with EKG plus o ther tests fo r tho se with heart disease diag no sed so lely o n clinical g ro unds. After the final diag no sis was established (clinical plus la b o ra to ry te st da ta ), ma na g e me nt wa s determined acco rding to the specific pro blem. All the clinical and labo rato ry data has been sto red in the co mputer sectio n o f the Pediatrics department (Fig ure 1 ).
RESULTS
1) Re ason for re fe rral
The mo st fre q ue nt c a use o f re fe rra l wa s the pre se nc e o f a he a rt murmur: 1 8 7 2 pa tie nts (7 0 %). O the r re a so ns we re : c he st pa in, ma inly in the pre c o rdia l re g io n: 2 4 0 (9 %); suspic io n o f a rrhythmia : 2 4 0 (9 %); a nd b re a thle ssne ss
a t re st a nd/ o r o n e ffo rt: 1 3 4 (5 %). The se fo ur re a so ns fo r re fe rra l a c c o unte d fo r 9 3 % o f the c a se s o n first e xa mina tio n. O the r le ss fre q ue nt c a use s o f re fe rra l we re : c ya no sis: 4 0 (1 .5 %); c a rd io me g a ly o n the c he st X-ra y: 2 6 (1 %); histo ry o f rhe uma tic fe ve r: 2 1 (0 .8 %); splitted se c o nd so und (S2 ): 2 1 (0 .8 %); a nd syste mic hype rte nsio n: 1 9 (0 .7 %). The se c a se s, a dde d to the mo st fre q ue nt c a use s de sc rib e d e a rlie r, c o mprise d 9 7 .8 % o f the c a se s studie d. The o the r 2 .2 % inc lude d a ve ry va rie d spe c trum o f c a use s: unkno w n (n= 8 ), sync o p e (n= 8 ), pre se nc e o f a third he a rt so und (S3 ) (n= 7 ), dia g no stic o pinio n (n= 7 ), ne e d fo r surg ic a l fo llo w-up (n= 5 ), splitted first he a rt so und (S1 ) (n= 4 ), diz z ine ss (n= 3 ), inc re a se d S2 (n= 2 ), Do wn’s syndro me (n= 2 ), fa milia l he a rt dise a se (n= 2 ), he a rt fa ilure (n= 2 ), c he st d e fo rmity (n= 2 ), re d spo ts o n the skin (n= 2 ), pa st histo ry o f e nd o c a rd itis (n= 2 ), syste mic hyp o te nsio n (n= 2 ), inc re a se d S1 (n= 2 ), le g e de ma (n= 1 ) a nd re lig io us re c o mme nda tio n (n= 1 ).
2) Diagnostic inve stigation
Amo ng the 2 6 7 5 first-examined patients, 6 9 5 (2 6 %) did no t co mplete the investig atio n acco rding to the pre-established criteria and were no t included in the analysis o f the results. There was little difference in the incidence o f patients who did no t co mplete the investigatio n, in relatio n to the main reaso ns fo r referral: murmur (2 6 %), c he st pa in (2 4 %), b re a thle ssne ss (2 5 %) a nd arrhythmia (2 1 %).
3) Final diagnosis base d on the re ason for re fe rral
Heart murmur: in 1 2 7 1 cases the murmur was co nfirmed. Amo ng these, 1 0 4 2 (8 2 %) were co nsidered inno cent. Reg arding the 2 2 9 (1 8 %) patho lo g ic murmurs, the mo st frequently fo und diseases were: ventricular septal defect (VSD): 8 2 (3 8 %); pulmo nary valve steno sis (PVS): 4 1 (1 9 %); ao rtic valve steno sis (AVS): 2 4 (1 1 %); atrial septal defect (ASD): 1 3 (6 %); and mitral reg urg itatio n (MR): 1 0 (5 %). The o ther 2 1 % o f patients co rrespo nded to vario us fo rms o f heart dise a se : mitra l va lve pro la pse (MVP) (n= 9 ), persistent ductus arterio sus (PDA) (n=7 ), tricuspid valve insufficiency (n=5 ), idio pathic dilatatio n o f the ma in p ulmo na ry a rte ry (n= 5 ), a trio ve ntric ula r se p ta l d e fe c t (AVSD) (n= 4 ), dilated cardio myo pathy (n=3 ), transpo sitio n o f the g re a t a rte rie s (n= 3 ), p ulmo na ry va lve reg urg itatio n (n=2 ), sho rt PR interval o n the EKG (n=2 ), myo carditis (n=2 ), tricuspid atresia (n=2 ), false tendo n o f the left ventricle (n=1 ), ao rtic reg urg itatio n due to a bicuspid ao rtic valve (n=1 ), primary pulmo nary hypertensio n (n=1 ) and lo ng Q T syndro me (n=1 ).
Chest pa in: in 1 9 0 c a ses studied, 1 8 6 (9 8 %) were co nsidered no rmal fro m the cardiac po int o f view. In 4 patients, sig ns o f po ssible heart disease were fo und: idio pathic dilatatio n o f the main pulmo nary artery (n=2 ), mild MR and sho rt PR interval o n the EKG .
Arrhythmia: amo ng the 1 9 5 cases referred, 1 8 7 (9 6 %) were co nsidered no rmal, while 8 c a se s p re se nte d p a tho lo g ic fe a ture s: W o lf-Parkinso n-W hite syndro me (n=2 ), sympto matic sinus bradycardia, do cumented supraventricular tachycardia, frequent ventricular ecto pics, ASD, PVS and sho rt PR interval.
Breathlessness: in 1 0 0 cases studied, 9 3 (9 3 %) were no rmal and in 7 , evidence o f heart disease was fo und: co mplete rig ht bundle branch blo ckag e (n=2 ), ASD, sho rt PR interval, primary pulmo nary hypertensio n, AVSD and idio pathic dilatatio n o f the main pulmo nary artery.
Cyano sis: 4 0 cases were referred because o f this sig nal, all o f who m were no rmal.
Abno rmal chest X-ray: amo ng the 2 4 cases
referred, 1 9 (7 9 %) were no rmal, while 5 were co nsidered abno rmal: dilated cardio myo pathy (n= 2 ), id io p a thic d ila ta tio n o f the ma in p ulmo na ry a rte ry (n= 2 ) a nd mild mitra l reg urg itatio n.
Splitted seco nd heart so und: in the 2 1 cases re fe rre d b e c a use o f this p o ssib le a b no rma l find ing , 1 9 (9 0 %) w e re no rma l w hile in 2 , c o mple te rig ht b undle b ra nc h b lo c ka g e wa s do cumented.
Systemic hypertensio n: amo ng the 1 9 cases referred, 1 0 (5 5 %) had no rmal blo o d pressure, while in 9 (4 5 %) hypertensio n was do cumented. Reg arding the 6 2 patients referred due to a variety o f reaso ns such as: histo ry o f rheumatic fever, edema, heart failure, systemic hypo tensio n, d ia g no stic o p inio n, inc re a se d S1 , sync o p e , splitted S1 , chest defo rmity, po st-o perative fo llo w-up, unkno wn cause, red spo ts, increased S2 , diz z iness, relig io us reco mmendatio n, histo ry o f endo carditis, familial heart disease and Do wn’s syndro me, 5 4 (8 7 %) were no rmal while in 8 (1 3 %) a cardio vascular abno rmality was fo und: PVS (n=2 ), VSD (n=2 ), rheumatic MR, W PW syndro me, residua l po st-o pera tive pulmo na ry ste no sis a nd re sid ua l p o st-o p e ra tive a o rtic reg urg itatio n.
4) The rape utic proce dure s
Seventeen patients (1 %) were referred to a tertiary unit fo r specific treatment after the final dia g no sis wa s esta b lished. Three ca ses were sub mitte d to the ra p e utic c a the te riz a tio n: 2 pulmo nary valvo plasty and 1 PDA o cclusio n with a Sideris pro sthesis (4 ). Fo urteen cases were o pe ra te d o n: duc tus lig a tio n (n= 5 ), re lie f o f co arctatio n o f the ao rta (n=2 ), clo sure o f an ASD
(n=2 ), clo sure o f a VSD (n=2 ), co rrectio n o f an AVSD (n=2 ) and relief o f subao rtic steno sis (n=1 ).
DISCUSSION
The analysis o f o ur data sho ws that, at first, the index o f suspec ted hea rt disea se is hig h during the initial pediatric evaluatio n. The 2 6 7 5 co nsecutive cases here presented were co llected during a 3 9 -mo nth perio d, c o rrespo nding to appro ximately 6 8 patients/ mo nth, which sho uld b e c o nsid e re d a sig nific a nt numb e r fo r a sub spec ia lity. Reg a rding this epidemio lo g ic a l detail, it sho uld be no ted that referral to o ur clinic is no t co mpulso ry, and it is likely that o ther cases ha ve b e e n re fe rre d to o the r c e nte rs, characteriz ing the po ssibility o f cho ice during the referra l pro cess. Ano ther po int which we believe sho uld be emphasiz ed is that 2 6 % o f the 2 6 7 5 pa tients initia lly eva lua ted did no t co mplete the investig atio n. This is a matter fo r c o nc ern b ut, unfo rtuna tely, diffic ult to c la rify. Ho wever, it is impo rtant fro m an epidemio lo g ical po int o f view that this number sho uld be reduced, co nsidering facto rs such as the characteristics o f the place where patients are seen, do cto r-patient relatio nships and also individual pro blems.
It is well kno wn that the majo rity o f patient referrals to pediatric cardio lo g y clinics are due to heart murmurs. As is well-co nfirmed in the literature,1 -3 the inno cent murmur, which acco unts fo r a g reat number o f these referrals, o ccurs in a p ro xima te ly 5 0 % o f the no rma l p e d ia tric po pulatio n. Altho ug h the o rig in o f these murmurs is no t w e ll d e fine d , its a sso c ia tio n w ith intraventricular fibro muscular bands5 is widely kno wn, especially the musical Still murmur.6 These b a nd s, ho w e ve r, a re c o nsid e re d no rma l variatio ns and no cause-effect relatio nship with the murmur has been demo nstrated so far.7
O ur data co nfirm this info rmatio n: 7 0 % o f the cases referred to o ur clinic were due to a heart murmur. The final analysis revealed that the g reat majo rity o f these cases (8 2 %) were inno cent murmurs, meaning absence o f heart disease. This data, in ag reement with info rmatio n fro m the literature,8 makes us co nsider two initial
hypo theses: either there is a hig h deg ree o f co ncern abo ut heart disease in the reg io n o r there is a lack o f specific kno wledge which wo uld allo w the p e d ia tric ia n to re c o g niz e a n inno c e nt murmur. As this diag no sis can be made o n strictly clinical g ro unds,9 -1 1 with a lo w pro bability o f erro r, we may co nclude that in the g reat majo rity o f o ur patients, heart disease co uld have been ruled o ut at the first pediatric examinatio n.
It sho uld be remembered, ho wever, that the diag no sis o f an inno cent murmur may be very subjective and influenced by many facto rs, like a n a d e q ua te e nviro nme nt, the o rg a nic a nd emo tio nal state o f the child and the experience o f the investig ato r. Do ubts may arise in so me circumstances, with so me autho rs using the term ‘ po ssibly patho lo g ic’ to describe a murmur.1 2 W e believe these cases sho uld be sent to a pediatric cardio lo g y examinatio n. Amo ng the 2 2 9 (1 8 %) cases o f patho lo g ic murmurs in o ur material, we no ticed that the majo rity o f them co rrespo nded to causes usually detected in day-to -day pediatric cardio lo g y practice: VSD, PVS, AVSD, ASD and MR. Mo st o f these cases were co nsidered mild fo rms o f the diseases, with no treatment being re q uire d . Ho w e ve r, c a re ful fo llo w -up is reco mmended fo r these patients. Specific details like lo ng term pro g no sis o f the disease, physical a c tivity, life insura nc e , w o rking c a p a c ity, preg na nc y a nd pro phyla xis a g a inst b a c teria l e nd o c a rd itis re q uire a d e q ua te c o unse ling , depending o n the type o f heart disease present. The seco nd mo st frequent cause o f referral
(9 %) in o ur material was chest pain. Amo ng the 1 9 0 cases studied, 1 8 6 (9 8 %) were no rmal. The 4 abno rmal cases were: mild mitral reg urg itatio n (n= 2 ), id io p a thic d ila ta tio n o f the ma in pulmo nary artery and sho rt PR interval, and were incidental finding s, no t related to the pain itself. This sympto m is very co mmo n in g eneral medical practice and quite relevant due to the sig nificant incidence o f hypertensive a nd a thero sclero tic d ise a se in so c ie ty.1 3 , 1 4 The id e ntific a tio n o f o rg anic disease is no t co mmo n in this situatio n,1 3 a ltho ug h so me fo rms o f he a rt d ise a se ma y pro vo ke preco rdial pain: severe ao rtic steno sis,1 5 mitra l va lve p ro la p se ,1 6 hy p e rtro p hic cardio myo pathy,1 5 co ro nary artery ano maly,1 3 p e ric a rd itis,1 7 Ka w a sa ki d ise a se1 8 a nd arrhythmia.1 3 All these po ssibilities were ruled o ut in o ur cases due to the absence o f co mpatible clinical finding s. Also , the EKG was no rmal but, nevertheless, we believe it sho uld be reco rded in any patient with preco rdial pain. O ur current p o lic y is to se nd the p a tie nt b a c k to the pediatrician fo r further investig atio n, if necessary. Suspected arrhythmia was ano ther frequent reaso n fo r referral (9 %) amo ng o ur material. These children either presented sympto ms like palpitatio ns o r had arrhythmia no ticed by the mo the r a nd / o r p e d ia tric ia n, usua lly a s a n irreg ular rhythm. In the 1 9 5 cases studied, 1 8 7 (9 6 %) were no rmal, the g reat majo rity o f them with sinus arrhythmia o n the EKG , a frequent and benig n finding in no rmal children.1 9 Eig ht c a ses were c o nsidered a b no rma l: ventric ula r e c to p ic s re q uiring me d ic a l tre a tme nt (n= 3 ); W PW syndro me incidentally fo und o n the EKG w itho ut d o c ume nte d a rrhy thmia (n= 2 ); sup ra ve ntric ula r ta c hy c a rd ia (n= 2 ); a nd sy mp to ma tic sinus b ra d y c a rd ia (n= 1 ). C ha ra c te riz ing a n a b no rma l rhythm o nly b y a usculta tio n ma y b e difficult, especia lly if a n irritable child is being examined. The rhythm irreg ula rity is usua lly a udib le a nd very o ften caused by a sinus arrhythmia, but despite this, we believe the EKG sho uld always be reco rded in o rder to rule o ut rhythm abno rmality.
The co mplaint o f breathlessness at rest and/ o r o n effo rt was present in 5 % o f o ur cases and,
o ut o f the 1 0 0 cases analyz ed, 9 3 (9 3 %) were no rmal. In 7 abno rmal cases the diag no ses were: a tria l se p ta l d e fe c t, p rima ry p ulmo na ry hyp e rte nsio n, a trio ve ntric ula r se p ta l d e fe c t, co mplete rig ht bundle branch blo ckag e (n=2 ), sho rt PR interval and idio pathic dilatatio n o f the main pulmo nay artery. It sho uld be no ted that o nly the first 3 cases co uld po ssibly have so me relatio n with the main sympto m.
Cyano sis o curred in 1 .5 % o f o ur cases as the main co mplaint. It is interesting to no te that all the patients were co nsidered no rmal after inve stig a tio n. It is w e ll-kno w n tha t p a re nts erro neo usly asso ciate the purple lips o f a crying child with heart disease, at least in o ur culture.
Heart disease suspected exclusively as a result o f chest X-ray o curred in 1 % o f o ur patients. In the 2 4 cases investig ated, 1 9 were no rmal while 5 were labeled as patho lo g ical: dilated cardio myo pathy (n=2 ), mitral reg urg itatio n (n=1 ) and idio pathic dilatatio n o f the main pulmo nary artery (n=2 ). The first 3 cases had to be fo llo wed up . Pulmo na ry a rte ry d ila ta tio n, a c o mmo n finding in daily practice, is usually co nsidered a benig n abno rmality, despite a recently repo rted serio us co mplicatio n2 0 in o ne such case. Care must be taken when interpreting a chest X-ray: inadequate technique may be respo nsible fo r apparent abno rmalities o n the film. To tal absence o f c linic a l a nd / o r e le c tro c a rd io g ra p hic co rrelatio n allo wed us to co nsider cases as being no rmal.
An inte re sting se mio lo g ic mista ke w a s detected in o ur patients: 2 1 cases were referred because o f a bro ken-up seco nd heart so und. N ineteen o f them were no rma l a nd we ma y c o nc lud e the p hy sio lo g ic sp lit w a s no t reco g niz ed. In 2 cases a co mplete rig ht bundle branch blo ckag e was reco rded, which explains the auscultato ry finding .
In the 1 9 c a se s re fe rre d b e c a use o f hyp e rte nsio n, 1 0 (5 5 % ) w e re no rma l, a nd pro bably an inadequate cuff size had been used. Amo ng the 9 cases with hypertensio n, 2 had co arctatio n o f the ao rta.
Results). Amo ng the 6 2 cases studied, 5 4 (8 7 %) were no rmal while 8 (1 3 %) had so me fo rm o f heart disease: pulmonary valve stenosis (n=2 ), ventricular se pta l de fe c t (n= 2 ), W PW syndro me , mitra l regurgitatio n, po st-o perative residual pulmo nary steno sis and po st-o perative residual ao rtic steno sis. The very lo w incidence o f each o f the reaso ns fo r referral amo ng this g ro up o f patients makes it impo ssible to perfo rm a reliable analysis.
The ve ry lo w inde x o f the ra pe utic ne e d fo und in o ur ma te ria l (1 %) re fle c ts the re la tive b e nig nity o f pa tie nts’ c o mpla ints re fe rre d to the c linic . The 1 4 c a se s o pe ra te d o n, a s we ll a s the 3 pa tie nts sub mitte d to a n inte rve ntio na l c a theteriz a tio n, ha d a fo rm o f c o ng enita l hea rt d ise a se fre q ue ntly c la ssifie d a s “ simp le ” , usua lly with a g o o d pro g no sis. Ano the r fa c t whic h a lso c ha ra c te riz e s the b e nig n a spe c t is tha t the g lo b a l inc ide nc e o f he a rt dise a se wa s 1 4 %. Fo r c o mpa riso n, the e xpe rie nc e g a ine d in the pe dia tric c a rdio lo g y o utpa tie nt c linic o f the He a rt Ho spita l lo c a te d in the sa me c ity, w he re te rtia ry tre a tme nt is ro utine ly o ffe re d, sho uld b e me ntio ne d. At this institutio n, during a 1 2 -mo nth p e rio d , 4 2 0 p a tie nts w e re e va lua te d fo r susp e c te d c o ng e nita l he a rt d ise a se . Amo ng the m, o nly 6 (1 .5 %) c a se s were c o nsidered no rma l, with a wide spec trum o f he a rt d ise a se b e ing d o c ume nte d (unp ub lishe d o b se rva tio ns). This p a tte rn o f re fe rra l is d iffe re nt fro m the p a tte rn o f o ur ma te ria l pre se nte d a b o ve . The g re a t ma jo rity o f the pa tie nts re fe rre d to the He a rt Ho spita l ha d a lre a dy b e e n se e n b y a pe dia tric ia n a nd a lso b y a lo c a l c a rdio lo g ist b e fo re b e ing se nt fo r spe c ific tre a tme nt.
In c o nc lusio n, we b e lie ve the se tting up o f a pe dia tric c a rdio lo g y o utpa tie nt c linic is justifia b le in a ny la rg e pro g ra m o f pe dia tric prima ry c a re . The hig h de ma nd is ma inly due to the ina b ility o f the p e d ia tric ia n to d iffe re ntia te b e tw e e n no rma l a nd a b no rma l he a rts. De sp ite the lo w g lo b a l inc id e nc e o f he a rt d ise a se (1 4 %), this numb e r b e c o me s re le va nt in a na lysis o n a n individua l b a sis.2 1 The g rea t ma jo rity o f o ur pa tients were referred b ec a use o f a hea rt murmur, mo st o f them b eing
inno c e nt. The p o ssib ility o f he a rt d ise a se re la te d to o the r re fe rra l re a so ns is re mo te a nd invasive therapy is rarely necessary. These data ha ve b e e n ro utine ly c o mp a re d thro ug h the ye a rs. Pa rt o f this ma te ria l ha s b e e n pub lishe d e lse whe re a nd the re sults a re e sse ntia lly the sa me .2 2 It wo uld b e inte re sting to c o mpa re the se re sults with tho se fro m o the r c e ntre s a nd diffe re nt c ulture s. Mo re de ta ile d studie s se e m to b e re le va nt in o rde r to de c re a se the hig h inde x (2 6 %) o f pa tie nts who do no t re turn to the c linic a fte r the first visit. It se e ms o b vio us tha t a sp e c ific tra ining p ro g ra m fo r pe dia tric ia ns is hig hly re c o mme nde d in o rde r to a vo id unne c e ssa ry re fe rra l.
REFERENCES
1. Friedman S, Ro bie WA, Harris TN. Occurrence o f inno cent adventi-tio us cardiac so unds in childho o d. Pediatrics 1949;4:782-9.
2. Gibso n S. Clinical significance o f heart murmurs in children. Med Clin No rth Am 1946;30:35-6.
3. Thayer WS. Reflectio ns o n the interpretatio n o f systo lic cardiac mur-murs. Am J Med Sci 1925;169:313-21s.
4. Sideris EB, Sideris SE, Ehly RL. Occlusio n o f patent ductus arterio -sus in piglets by a do uble-disc self-adjustable device. Abstract. J Am Co ll Cardio l 1990;15:240A.
5. Geva T, Hegesh J, Frand M. Reappraisal o f the appro ach to the child with heart murmur: is echo cardio graphy mandato ry? Int J Cardio l 1988;19:107-13.
6. Ro berts WC. Ano malo us left ventricular band: an unemphasized cause o f preco rdial musical murmurs. Am J Cardio l 1969;23:735-8.
7. Schwartz Ml, Go ldberg SJ, Wilso n N, et al. Relatio n o f Still’s mur-mur, small ao rtic diameters and high ao rtic velo city. Am J Cardio l 1986;57:1344-8.
8. Caceres CA, Perry LW. The inno cent murmur: a pro blem in clinical practice. Bo sto n: Little Bro wn and Co ; 1967.
9. Newburger JM, Ro senthal A, Williams RG, Fello ws K, Miettinen OS. No ninvasive tests in the initial evaluatio n o f heart murmurs in chil-dren. N Engl J Med 1983;308:61-4.
10. Tavel ME. The systo lic murmur: inno cent o r guilty? Am J Cardio l 1977;39:757-9.
11. Amaral FTV, Granzo tti JA, Nunes MA. Abo rdagem da criança co m so pro cardíaco : impo rtância diagnó stica do s exames co mplementares não invasivo s. Arq Bras Cardio l 1995; 64:195-9.
12. Smythe JF, Teixeira OHP, Vlad P, Demers PP, Feldman W. Initial evalu-atio n o f heart murmurs: are labo rato ry tests necessary? Pediatrics 1990;86:497-500.
13. Brenner JI, Ringel RE, Berman MA. Cardio lo gic perspectives o f chest pain in childho o d: a referral pro blem? to who m? Ped Clin No rth Am; 1984:1241-58.
14. Epstein SE, Gerber LH, Bo rer JS. Chest wall syndro me: a co mmo n cause o f unexplained cardiac pain. J Am Med Asso c 1979;241:2793-7.
RESUMO
Contex to: Durante a avaliação inicial de crianças em nível ambulato rial, o índice de suspeita de cardio patia po de ser elevado , particularmente se fo r co nsiderado que o so pro ino cente o co rre em apro ximadamente 5 0 % da po pulação pediátrica. Esse ruído é a causa mais co mum de encaminhamento ao cardio lo g ista pediátrico . Objetivo: Relatar a experiência de um ambulatório de cardiologia pediátrica da rede pública de saúde na região sudeste do Brasil. Tipo de estudo: Análise retrospectiva de todos os pacientes encaminhados para avaliação cardiológica dentro de um período de 3 9 meses. Loca l: Ambulató rio de cardio lo g ia pediátrica da rede pública de saúde. Pa rticipa ntes: 2 6 7 5 crianças co nsecutivas pro cedentes das unidades básicas de saúde lo cais e da reg ião , encaminhadas devido à suspeita de cardio patia. Va riá veis Estuda da s: Mo tivo do encaminhamento , investig ação diag nó stica, diag nó stico final baseado no mo tivo de encaminhamento , pro cedimento s terapêutico s. Resulta dos: O s principais mo tivo s de encaminhamento fo ram: so pro cardíaco (7 0 %), do r preco rdial (9 %), suspeita de arritmia (9 %) e dispnéia (5 %). Entre o g rupo to tal, 6 9 5 (2 6 %) caso s não co mpletaram a investig ação e não fo ram incluído s na análise. Fo i estabelecido um diag nó stico definitivo relacio nado ao mo tivo de encaminhamento e as co nclusõ es principais fo ram: 1 ) alta incidência de no rmalidade fo i enco ntrada: so pro (8 3 %), do r preco rdial (9 8 %), arritmia (9 7 %) e dispnéia (9 4 %); 2 ) a presença de cardio patia fo i co nsiderada impro vável baseado no s o utro s mo tivo s de encaminhamento ; 3 ) 1 4 % das crianças fo ram co nsideradas ano rmais e a necessidade de pro cedimento terapêutico invasivo fo i de 1 % do s caso s.
Conclusões: O estabelecimento de um ambulató rio de cardio lo g ia pediátrica na rede pública de saúde parece ser justificado na reg ião devido à alta demanda enco ntrada. A baixa incidência g lo bal de cardio patia, co m número expressivo de crianças co m so pro ino cente, sug erem a necessidade de um pro g rama específico de treinamento básico em cardio lo g ia pediátrica para pediatras.
16. Bisset GS, Schwartz DC, Meyer RA, et al. Clinical spectrum and lo ng term fo llo w-up o f iso lated mitral valve pro lapse in 119 children. Cir-culatio n 1980;2:423-9.
17. Oko ro ma EO, Perry LW, Sco tt LP. Acute bacterial pericarditis in chil-dren: repo rt o f 25 cases. Am Heart J 1975;90:709-13.
18. Melish ME. Kawasaki syndro me (the muco cutaneo us lymph no de syndro me). Pediatr Ann 1982;11:255-68.
19. Berto letti JC. Disritmias cardíacas. In: Cardio lo gia Pediátrica. Macruz R, Snitco wski R. São Paulo : Sarvier;1983:601.
20. Andrews R, Co llo by P, Hubner JB. Pulmo nary artery dissectio n in a patient with idio pathic dilatatio n o f the pulmo nary artery: a rare cause o f sudden cardiac death. Br Heart J 1993;69:268-9.
21. Gidding SS, Ro senthal A. The interface between primary care and Pediatric Cardio lo gy. Ped Clin No rth Am 1984;31:1367-88.
22. Amaral FTV, Granzo tti JA, Nunes MA. So pro cardíaco na criança: experiência de um amb ulató rio especializado . Rev Paul Pediatr 1995;13:39-41.
Ferna ndo Am a ra l - Master in Cardio lo g y, Divisio n o f Pediatric Cardio lo g y, Department o f Pediatrics, Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto .
Joã o Antonio Gra nzotti - MD, Assistant Pro fesso r, Head-Divisio n Pediatric Cardio lo g y, Department o f Pediatrics, Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto .
Sources of Funding: N o t declared
Conflict of interest: N o t declared
La st received: 1 2 may 1 9 9 8
Accepted: 1 June 1 9 9 8
Address for correspondence:
Fernando Amaral Av. Independência, 1 3 7 9