Genetic analysis for water use efficiency traits, yield and yield attributes in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.)
Texto
Imagem
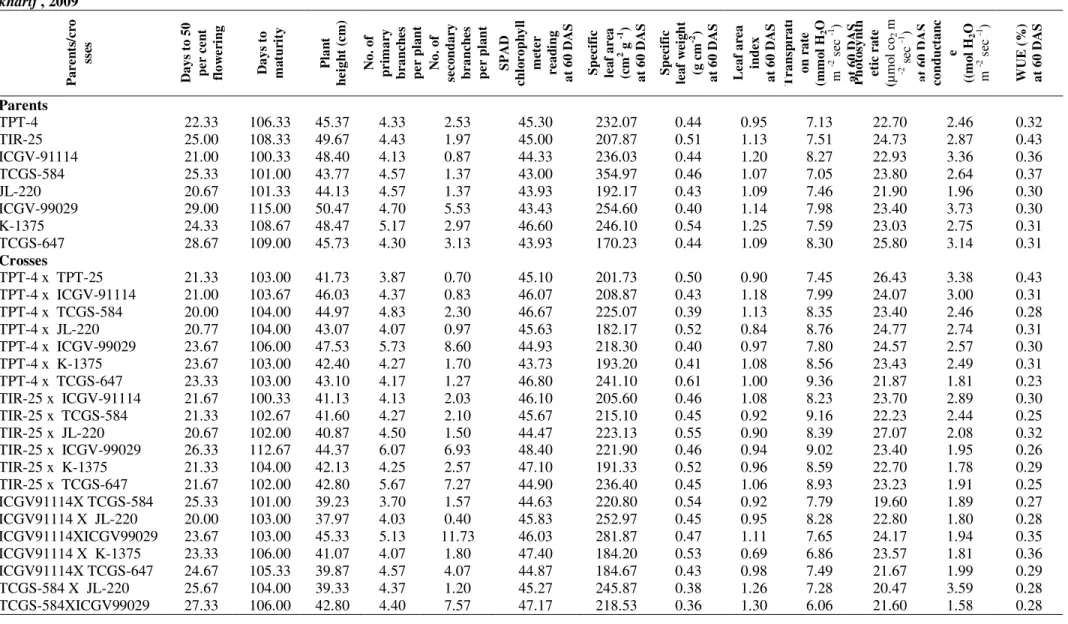
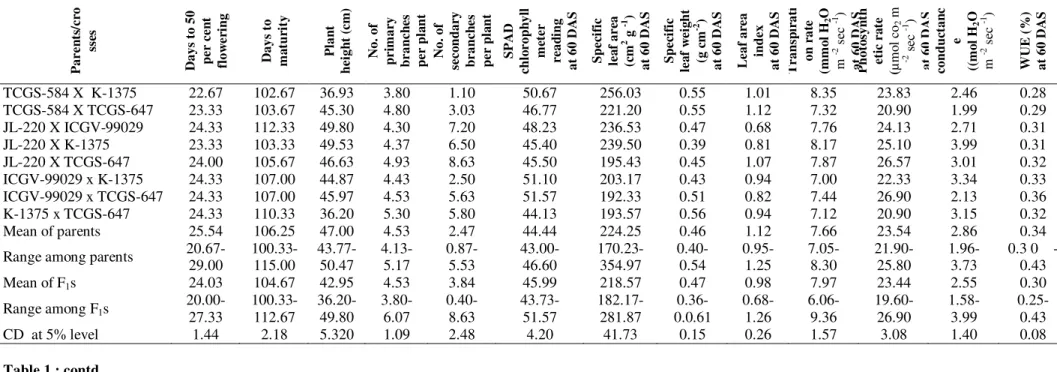
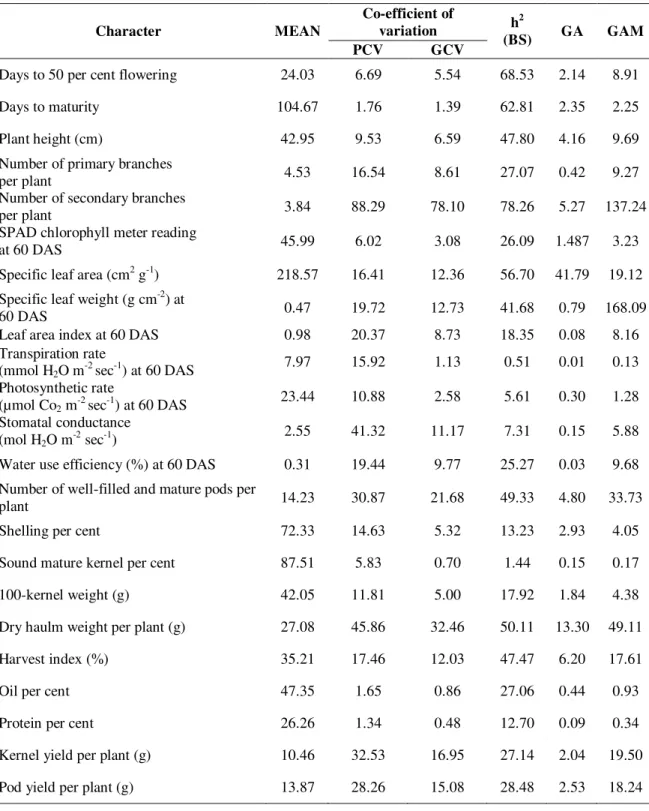
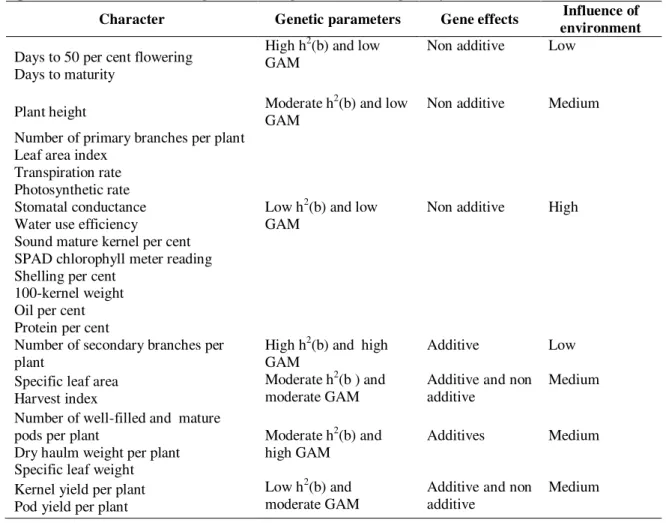
Documentos relacionados
Five agronomic traits (plant cycle, number of seeds per pod, number of pods per plant, weight of 100 seeds, and grain yield), five morphological traits (growth habit, plant
Summary of variance analysis total yield (TY), commercial head yield (CHY), plant height (PH), commercial head circumference (CHC) and water use efficiency (WUE)
Positive effects of irrigation were observed for number of grains per spike, number of days to anthesis and plant height, while a negative effect was present for grain yield, number
Genetic variation for dry matter yield, seed yield, fertility index, harvest index, plant height, plant spread, crude protein, neutral detergent fiber and acid detergent fiber,
It was observed that yield, total biomass, filled spikelet, 1000grain weight, total panicle, tillers mortality, plant height and number of tillers reduced with
An increase in plant population reduced the number of pods per plant and the contribution of branches to the grain yield, independently of N fertilization, but the effects on
Moderate heritability and genetic advance were observed as the percent of the mean observed for the number of grains per panicle (39.96% and 16.59%, respectively) and the number
Analysis was performed for crop injury, Soil and Plant Analyzer Development (SPAD) index, as well as variables related to agronomic performance (height, number of pods per