2 9 0
Revista da Sociedade Br asileir a de Medicina Tr opical 3 8 ( 4 ) :2 9 0 -2 9 3 , jul-ago, 2 0 0 5
ARTIGO/ARTICLE
Very low prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in rural
communities of northeastern Brazil with a high
prevalence of schistosomiasis mansoni
Muito baixa prevalência de infecção pelo vírus da hepatite C em
comunidade rural do nordeste brasileiro com elevada
prevalência de esquistossomose mansônica
Jose Tavares-Neto
1
, Aluízio Prata
2
, Raymundo Paraná
1
, Vanderléia Bárbaro Valente
3
,
Ludmila Vitvitski
4
and José Fernando C. Figueiredo
3
ABSTRACT
Th e a sso c i a ti o n o f h e p a ti ti s C vi ru s i n f e c ti o n a n d th e h e p a to sp le n i c f o rm o f sc h i sto so m i a si s m a n so n i h a s b e e n c la i m e d
to re su lt i n th e c o n c o m i ta n t e vo lu ti o n o f th e two p a th o lo gi e s, wi th a p o o r p ro gn o si s d u e to a ggra va te d li ve r d i se a se .
Re c e n tly, ho we ve r, so m e a u tho rs ha ve b e gu n to re je c t the hypo the si s o f a hi ghe r su sc e pti b i li ty o f he pa to sple n i c sc hi sto so m a l
p a ti e n ts to HCV. Th e a i m o f th e p re se n t tra n sve rse stu d y c a rri e d o u t b e twe e n Ju ly a n d Au gu st 1 9 9 0 wa s to d e te rm i n e th e
p o ssi b le a sso c i a ti o n b e twe e n SM a n d HCV m a rk e rs i n re si d e n ts o f Ca to lâ n d i a , Ba h i a Sta te . An ti - HCV m a rk e rs we re
a ssa ye d b y II a n d RIBA- II i n se ru m sa m p le s o b ta i n e d f ro m 1 ,2 2 8 re si d e n ts ( 8 5 .8 %) . Th e a n ti - HCV a n ti b o d y (
ELISA-II) wa s p o si ti ve i n si x ( 0 .5 %) i n d i vi d u a ls, e i gh t ( 0 .6 %) c a se s we re i n c o n c lu si ve a n d 1 ,2 1 4 ( 9 8 .9 %) we re n e ga ti ve .
Ho we ve r, o n ly i n o n e ELISA- p o si ti ve se ru m sa m p le ( 0 .0 8 %) we re a n ti b o d i e s c o n f i rm e d b y RIBA- II, wh i le two o th e r
sa m p le s a ssa ye d b y RIBA- II we re i n d e te rm i n a te . Th e se th re e p a ti e n ts p re se n te d th e h e p a to i n te sti n a l f o rm o f SM d u ri n g
th e f o llo w- u p p e ri o d ( 1 9 7 6 to 1 9 9 6 ) . In c o n c lu si o n , n o a sso c i a ti o n wa s o b se rve d b e twe e n HCV a n d SM i n th e e n d e m i c
a re a stu d i e d , e sp e c i a lly a m o n g p a ti e n ts wi th th e h e p a to sp le n i c f o rm o f th e d i se a se .
Ke y-words:
Sc h i sto so m i a si s m a n so n i . He p a ti ti s C.
Sc histo so ma manso ni
. Bra zi l.
RESUMO
Algu n s a u to re s pa ssa ra m a re je i ta r a hi pó te se da m a i o r su sc e pti b i li da de do s e q u i sto sso m ó ti c o s c o m a f o rm a c lí n i c a
he pa to splê nica a o vírus da he pa tite C, justifica ndo q ue a a sso cia çã o fo i de scrita e m pa cie nte s ho spita liza do s o u a co m pa nha do s
e m se rviço s de sa úde e , co nse q üe nte m e nte , m a is e xpo sto s à tra nsm issã o de ste s vírus, dura nte o s pro ce dim e nto s dia gnó stico
e /o u te ra pê utico s. De sse m o do , o o b je tivo fo i ve rifica r se há o co rrê ncia de a sso cia çã o da e sq uisto sso m o se m a nsô nica e m a rca do r
do VHC e m m o ra do re s de Ca to lâ ndia ( Ba hia , Bra sil) . Ne ste e studo tra nsve rsa l, o s a ntico rpo s a nti- VHC fo ra m pe sq uisa do s
( ELISA- II) e m 1.228 ( 85,8%) m o ra do re s, co m o s se guinte s re sulta do s: Se is ( 0,5%) so ro po sitivo s, o ito ( 0,6%) inco nclusivo s e
1.214 ( 98,9%) so ro ne ga tivo s. To da via , so m e nte e m um so ro ELISA- po sitivo ( 0,08%) o s a ntico rpo s fo ra m co nfirm a do s pe lo
RIBA-II e do is o utro s ( ELISA-II po sitivo s) a pre se nta ra m RIBA-II inde te rm ina do – e sse s trê s ca so s, dura nte pe río do de se guim e nto
( 1976 – 1996) , se m pre tive ra m a fo rm a he pa to inte stina l da e sq uisto sso m o se m a nsô nica . Em co nclusã o a hipó te se de a sso cia çã o
e n tre a e sq u isto sso m o se m a n sô n ic a e o VHC n e sta á re a e n dê m ic a fo i re je ita da , e spe c ia lm e n te e n tre o s po rta do re s da
e sq uisto sso m o se m a nsô nica co m a fo rm a clínica he pa to splê nica .
Pal avr as-chave s:
Esq u i sto sso m o se m a n sô n i c a . He p a ti te C.
Sc histo so ma manso ni
. Bra si l.
1 . Fac ulty o f Me dic ine o f B ahia, Fe de r al Unive r sity o f B ahia, Salvado r, B A. 2 . Tr iângulo Mine ir o Me dic al Fac ulty, Ub e r ab a, MG. 3 . Rib e ir ão Pr e to B lo o d Ce nte r, SP. Fac ulty o f Me dic ine o f Rib e ir ão Pr e to , Unive r sity o f São Paulo , Rib e ir ão Pr e to , SP; 4 . INSERM Unité 2 7 1 , Lyo n, Fr anc e .
Re se ar c h suppo r te d b y PET-Me dic ina, CAPES / COFECUB and CNPq ( pr o c e ss 5 2 . 0 1 7 3 /9 7 -0 )
Addr e ss to: Pr o f. J o sé Tavar e s- Ne to . R. Mar q uê s de Car ave las 2 6 2 /1 0 1 , 4 0 1 4 0 - 2 4 0 Salvado r, B A, B r asil. Te le fax: 5 5 7 1 3 2 6 4 -2 4 4 3 .
e - mail: tavane to @ ufb a. b r.
2 9 1
Ta va r e s- Ne to J e t al
Several lines of evidenc e have favored an assoc iation between
hepatitis B virus ( HBV) infec tion and the hepatosplenic form of
sc histosomiasis mansoni ( SM)
2 6. More rec ently, however, this
assoc iation has been revised
6 2 4 2 9, with the c onc lusion that it is
due to a gr e ate r e xpo sur e to HB V r athe r than to a highe r
susc eptibility of individuals with SM to hepatotropic viruses, i.e.,
HBV and hepatitis C virus ( HCV) .
Despite phylogenetic differenc es between HBV and HCV, their
mec hanisms of transmission show some similarities
1 1. Thus, one
might spe c ulate that HCV infe c tio n is asso c iate d with SM,
espec ially among patients with the severe hepatosplenic form of
the disease.
B e fo r e the HCV e r a, so me patie nts with he pato sple nic
sc histosomiasis and a histopathology c ompatible with c hronic
viral hepatitis did not present HBV markers in serum or hepatic
tissue
1 6 1 7. Similar findings have been r epo r ted in B r azil by
Andrade et al
3 4.
Afte r c ha r a c te r iza tio n o f HCV b y Cho o e t a l
7a nd the
c onsequent possibility of detec ting HCV markers in serum, Lins
1 6showed that the frequenc y of individuals with anti-HCV antibodies
does not differ between patients with the hepatointestinal form
of SM and those with the hepatosplenic form.
Othe r autho r s
1 2 5 8 1 0 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 3 1have pr o vide d e vide nc e
suggesting that the presenc e of anti-HCV antibodies is assoc iated
with sc histosomiasis, but c ontradic tory data exist. However, it
sho uld be no ted that these autho rs used different sero lo gic
methods. In addition, these studies were c onduc ted on patients
rec ruited from referral c enters and not from rural B razilian
c ommunities where
Schisto so m a m a nso ni
is endemic .
B ase d o n the c linic al and immuno lo gic al pe c uliar itie s o f
SM and he patitis C in B r azil, the aim o f the pr e se nt study was
to de te r m in e th e po s s ib le a s s o c ia tio n b e twe e n th e two
dise ase s in an ar e a e nde mic fo r SM.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
A c ross-sec tional population-based study was c onduc ted on
residents from an SM endemic area in the c ounty of Catolândia
2 9,
whic h is loc ated in the western region of the State of Bahia, Brazil
( 1 2 º8 ' latitude South and 4 4 º5 2 ' longitude West of Greenwic h) .
A lo ngitudinal study o n the mo r b idity o f SM was star te d
in the study ar e a in 1 9 7 6 , and sinc e the n the c linic al fo r ms
o f the dise ase we r e c lassifie d ac c o r ding to the c r ite r ia o f
P r a ta
2 2 2 4. I n a d d i ti o n , th e c l i n i c a l i n vo l u ti o n
o f th e
he pato sple nic fo r ms o f SM afte r antipar asitic tr e atme nt was
o b se r ve d alo ng the study
2 4 3 0.
An ti- HCV a n tib o die s we r e s c r e e n e d us in g a s e c o n
d-ge n e r a tio n e n zym e im m un o a s s a y k it ( ELI SA- I I , Ab b o tt
,
Chic ago , IL, USA)
3 1. Anti-HCV-po sitive se r a, tho se pr o viding
d o u b tfu l r e s u l ts we r e te s te d b y a s e c o n d - ge n e r a ti o n
r e c o mb inant immuno b lo t me tho d ( Or tho Diagno stic Syste ms
Inc
, Eme r ville -CA, USA) .
Clin ic a l e xa m in a tio n o f th e pa tie n ts wa s c a r r ie d o ut
witho ut k no wle dge o f the anti-HCV r e sult.
RESULTS
Of the 1 ,4 3 2 residents in the study region, 1 ,2 2 8 ( 8 8 .9 % )
provided c omplete information and were tested for anti-HCV.
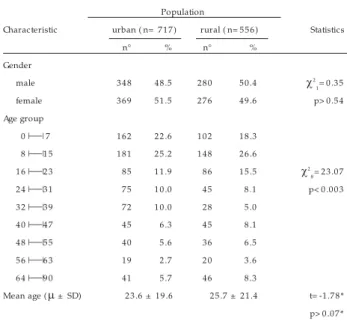
Table 1 and Table 2 summarize the demographic c harac teristic s
( gender and age) and the frequenc y of different c linic al forms
of SM in this population.
Table 1 - Demographic characteristics ( gen der an d age) of the popu lation from Catolân dia, accordin g to place of residen ce ( ru ral or u rban ) .
Population
Characteristic urban ( n= 7 1 7 ) rural ( n= 5 5 6 ) Statistics
n° % n° %
Gender
male 3 4 8 4 8 .5 2 8 0 5 0 .4
χ
21= 0 .3 5
female 3 6 9 5 1 .5 2 7 6 4 9 .6 p> 0 .5 4
Age group
00 |
| 7 1 6 2 2 2 .6 1 0 2 1 8 .308 |
|1 5 1 8 1 2 5 .2 1 4 8 2 6 .61 6 |
|2 3 85 1 1 .9 86 1 5 .5χ
28= 2 3 .0 7
2 4 |
|3 1 75 1 0 .0 4 5 8 .1 p< 0 .0 0 33 2 |
|3 9 72 1 0 .0 28 5 .04 0 |
|4 7 45 6 .3 4 5 8 .14 8 |
|5 5 40 5 .6 36 6 .55 6 |
|6 3 19 2 .7 2 0 3 .66 4 |
|9 0 41 5 .7 46 8 .3Mean age (
µ
± SD) 2 3 .6 ± 1 9 .6 2 5 .7 ± 2 1 .4 t= -1 .7 8 *p> 0 .0 7 *
* F test= 1 .2 0 , p< 0 .0 0 2 , degrees of freedom= 1 1 3 7 .3 5 .
Table 2 - Distribu tion of the clin ical forms of schistosomiasis man son i in the popu lation from Catolân dia, accordin g to gen der, age an d place of residen ce.
Clinical form n ( %)
Characteristic hepatointestinal advanced HI hepatosplenic Statistics
HI ( n= 1 ,1 6 5 ) AHI ( n= 6 6 ) HS ( n= 4 2 )
Gender
male 5 8 5 9 3 .8 20 3 .1 23 3 .7
χ
2= 1 .1 8 *
female 5 8 0 8 9 .9 46 7 .1 19 3 .0 p> 0 .2 6
Mean age ( m ± SD) 2 3 .6 ± 2 0 .4 3 3 .4 ± 1 8 .5 3 5 .2 ± 1 7 .4 * *
Place of residence n( %)
urban 6 4 0 8 9 .3 41 5 .7 36 5 .0
χ
2= 1 5 .2 7 *
rural 6 2 5 9 4 .4 25 4 .5 6 1 .1 p< 0 .0 0 0 1
* Mantel-Haenszel test; * * HI vs AHI: t= -3 .7 9 , p< 0 .0 0 0 1 ( F= 1 .2 2 , p> 0 .2 9 ) ; HI vs HS: t= -3 .6 2 , p< 0 .0 0 0 1 ( F= 1 .3 9 , p> 0 .1 8 ) ; AHI vs HS: t= -0 .5 1 , p> 0 .6 0 ( F= 1 .1 3 , p> 0 .6 7 ) .
With respec t to the presenc e of anti-HCV antibodies, six
( 0 .5 % ) patients were positive, eight ( 0 .6 % ) were inc onc lusive,
and 1 ,2 1 4 ( 9 8 .9 % ) were negative.
In only one sample of 1 4 tested ( 6 positive, 8 inconclusive)
by ELISA-II commercial Kits ( Boehinger-Germany) anti-HCV was
confirmed by the RIBA-II test ( Chiron, Emerville, CA
) . Two ( 0.2%)
individuals presented results classified as indeterminate by RIBA-II
( both showing antibodies against the recombinant protein c100-3) .
All six residents presenting anti-HCV antibodies, as well as
the eight individuals with inc onc lusive results, as determined by
ELISA-II, had the hepatointestinal form of SM, with the age of
2 9 2
Revista da Sociedade Br asileir a de Medicina Tr opical 3 8 ( 4 ) :2 9 0 -2 9 3 , jul-ago, 2 0 0 5
DISCUSSION
Despite massive anti sc histosomal treatment and improved
sanitary c o nditio ns, the frequenc y o f sc histo so mal infec tio n
continues to be high in this area. Progressively higher frequencies
of individuals exc reting
S. m a nso ni
eggs among those seeking
the Catolândia public health servic e were observed during the
period from 1 9 9 3 ( 3 5 .8 % ) to 1 9 9 6 ( 6 5 .4 % )
2 9. Thus, SM was
the main c ause of morbidity and mortality in Catolândia until the
mid-eighties
3 0. The hepatosplenic form was diagnosed in 1 8 7
( 8 .3 % ) registered residents ( n= 2 ,2 4 1 ) during the study period
from 1 9 7 6 to 1 9 9 6 .
Although the population of Catolândia shows a reasonable
geographic and cultural isolation
27 28, temporary residence and/or
occupation in other states are frequent; for example, during the
study period 2 7 3 ( 1 2 .2 % ) of the 2 ,2 4 1 individuals registered
migrated
28.
In the early eighties, residents from Catolândia c ommonly
underwent medic al treatment in some nearby c apitals. Thus, a
temporary migratory flow might have fac ilitated the introduc tion
or inc reased dissemination of HCV in the region, where the lac k
of health servic es represents another c harac teristic predisposing
to the use of parenteral medic ation under inadequate c onditions,
a fac t that c ould also have c ontributed to the dissemination of
HCV in many regions of Brazil.
B ase d o n the fac t that this r e gio n is hype r e nde mic fo r
SM, with patie nts de ve lo ping uppe r gastr o inte stinal b le e ding
b y r uptur e o f the
e so phage al var ic e s and r e c e iving b lo o d
tr ansfusio ns whe n tr e ate d at lar ge r c e nte r s, the intr o duc tio n
and disse minatio n o f HCV c an b e e xpe c te d in this r e gio n.
The finding of the present study of only one individual with
anti-HCV and without a history of travel to or residence in other
towns supports the hypothesis that in this endemic SM area the
risk of transmission of HCV was not increased. In addition, the
seroprevalence of anti-HCV antibodies observed for residents from
Catolândia was lower than the 1 .7 % prevalence estimated for blood
donor candidates from the metropolitan region of Salvador, capital
of the State of Bahia ( Santana et al, unpublished data) .
Silva et al
2 5observed a 1 .2 % prevalence of anti-HCV antibodies
in individuals from the metropolitan region of Salvador, and a
0 % prevalenc e of anti-HCV in a populational study c arried out in
the rural area of the State of Bahia, Northeast of Brazil. Other
studies c onc erning the seroprevalenc e of HCV in the State of
Bahia were c arried out on populations at risk of ac quiring HCV
infec tion
1 9 2 3, while there were no populational studies. However,
the results reported by Silva et al indic ate a very low prevalenc e
of HCV among residents of rural c ommunities also endemic for
S. m a nso ni
infec tion.
B ase d o n the se r e sults we may also spe c ulate that the
S. m a nso ni
oc c urring in the rural areas of the State of Bahia
does not influenc e the transmission or dissemination of HCV.
This finding c ontrasts with Egyptian studies that demonstrated
high HCV prevalenc e in SM endemic areas pro bably due to
parenteral treatment for
sc histo so m ia sis
using non-disposal
material
32. In Brazil, non-disposal needles were used in the past but
it seems that this practice was concentrated in larger urban centers
20.
With respec t to reviews
6 2 6proposing a possible assoc iation
b e twe e n the he pato sple nic fo r m o f SM and infe c tio n with
hepatotropic viruses, notably HBV, one c an also spec ulate that
the same spurious association exists with HCV, i.e., the association
reported between the hepatosplenic form and HBV
2 6and, more
recently, between the hepatosplenic form and HCV
1 2 5 8 1 0 1 4 1 3 1 5 2 1 3 2,
is more likely to be due to greater exposure to these viruses
dur ing diagno stic and/o r the r ape utic pr o c e dur e s at he alth
servic es rather than to a higher susc eptibility of hepatosplenic
individuals to hepatotropic viruses.
Our results show that during the more than 2 0 years of the
sentinel study in Catolândia c o-infec tion with HCV was negligible
in patients with SM
2 9 3 0. In the only c ase with c onfirmed
anti-HCV a n ti b o d i e s , h e p a ti c b i o c h e m i c a l te s ts , e s p e c i a l l y
aminotransferases, were found to be normal. However, hepatic
enzymes showed fluc tuations in these individuals throughout
the evaluation period, inc luding periods of normality.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank the te c hnic ian Mar gar ida Mar ia Passe r i do
Nasc ime nto ( FMRP, USP) fo r pr o c e ssing the se r um sample s.
REFERENCES
1 . Ab de l- Wahab MF, Zak ar ia S, Kame l M, Ab de l- Khaliq MK, Mab r o uk MA, Salama H, Esmat G, Tho mas DL, Str ic k land GT. High se r o pr e vale nc e o f he patitis C infe c tio n amo ng r isk gr o ups in Egypt. The Ame r ic an J o ur nal o f Tr o pic al Me dic ine and Hygie ne 5 1 : 5 6 3 - 5 6 7 , 1 9 9 4 .
2 . Al-Faleh FZ, Ramia S, Ar if M, Ayo o la EA, Al-Rashed RS, Al-Jeffr y M, Ho ssain A, El- Hazm i M. Pr o file o f he patitis C vir us and the po ssib le m o de s o f tr ansmissio n o f the vir us in the Gizan ar ea o f Saudi Ar ab ia: a c o mmunity based study. Annals of Tropic al Medic ine and Parasitology 8 9 : 4 3 1 -4 3 7 , 1 9 9 5 .
3 . Andr ade ZA, Lyr a LG, Re b o uç as G. Esq uisto sso mo se he pátic a avanç ada e he patite c r ô nic a vir al. Re vista da Asso c iaç ão Mé dic a B r asile ir a 2 3 : 7 5 - 7 8 , 1 9 7 7 .
4 . An d r a d e ZA, S a d i g u r s k y M , Go m e s LS . He p a ti te c r ô n i c a a ti va e e sq uisto sso mo se de sc o mpe nsada. Re vista da Asso c iaç ão Mé dic a B r asile ir a 2 4 : 3 6 6 - 3 6 8 , 1 9 7 8 .
5 . B assily S, Hyams KC, El- Mar sr y NA, Hassan NF, Watts DM. He patitis C vir us in fe c tio n a n d h e pa to s ple n ic s c h is to s o m ia s is . Sc a n din a via n J o ur n a l o f Infe c tio us Dise ase s 2 4 : 6 8 7 - 6 8 8 , 1 9 9 2 .
6 . Che n M- G, Mo tt KE, Wang Q- H, Kane M. He patitis B and sc histo so miasis:
inte r ac tio n o r no inte r ac tio n? Tr o pic al Dise ase s B ulle tin 9 0 : R9 7 - R1 1 5 , 1 9 9 3 .
7 . Cho o Q-L, Kuo G, We ine r AJ, Ove r b y LR, B r adle y DW, Ho ughto n M. Iso latio n
o f a c DNA c lo ne de r ive d fr o m a b lo o d- b o r ne no n- A, no n- B vir al he patitis ge no me . Sc ie nc e 2 4 4 : 3 5 9 - 3 6 2 , 1 9 8 9 .
8 . Dar wish MA, Rao uf TA, Rushdy P, Co nstantine NT, Rao MR, Ede lman R. Risk fac to r s asso c iate d with a high se r o pr e vale nc e o f he patitis C vir us infe c tio n in Egyptian b lo o d do no r s. The Am e r ic an J o ur nal Of Tr o pic al
Me dic ine and Hygie ne 4 9 : 4 4 0 - 4 4 7 , 1 9 9 3 .
9 . El- Go ha r y A, Ha ssa n A, No o m a n Z, La va nc hy D, Ma ye r a t C, El- Aya t A,
Fawaz N, Go b r an F, Ahme d M, Kawano F, Kiyo k awa T, Yamaguc hi AK. High
2 9 3
1 0 . El- Nanawy AA, El- Azzo uni OF, So liman AT, Ame r AE, De mian RS, El- Saye dHM. Pr e vale nc e o f he patitis C antib o dy se r o po sitivity in he althy Egyptian c hildr e n and fo ur high r isk gr o ups. Jo ur nal Tr o pic al o f Pe diatr ic s 4 1 : 3 4 1 -3 4 -3 , 1 9 9 5 .
1 1 . Esteban JI, Genesc a J, Alter HJ, Hepatitis C: mo lec ular bio lo gy, patho genesis, e pide mio lo gy, c linic al fe atur e s, and pr e ve ntio n. In: B o ye r JL, Oc k ne r RK ( e ds) Pr o gr e ss in live r dise ase s. WB Saunde r s, Philade lphia, 1 0 : 2 5 3 -2 8 2 , 1 9 9 2 .
1 2 . Far ghaly AG, B ar ak at RM. Pr e vale nc e , impac t and r isk fac to r s o f he patitis C infe c tio n. J o ur nal o f the Egyptian Pub lic He alth Asso c iatio n 6 8 : 6 3 - 7 9 , 1 9 9 3 .
1 3 . Ko sb y A, Al- Nak ib B , Al- Mufti S, Madda J P, Hir a PR. Anti- HCV- po sitive c i r r h o s i s a s s o c i a t e d s c h i s t o s o m i a s i s . T h e Am e r i c a n J o u r n a l o f Gastr o e nte r o lo gy 8 8 : 1 4 2 8 -1 4 3 1 , 1 9 9 3 .
1 4 . Lima RA. Mar c ado r e s so r o ló gic o s do s vír us B & C da he patite e m pac ie nte s c o m e s q uis to s s o m o s e m a n s o n i. Ph D th e s is , Un ive r s ida de Fe de r a l de Pe r namb uc o , Re c ife , 1 9 9 5 .
1 5 . Lima RA, Magalhãe s V, Mo ur a I, Silva AE, Guimar ãe s RX. Mar c ado r e s do vír us C da he patite ( HCV) e m pac ie nte s c o m e sq uisto sso mo se manso ni. Revista da So c iedade B r asileir a de Medic ina Tr o pic al 2 7 ( supl I) : 1 4 , 1 9 9 4 .
1 6 . Li n s ALGP. Co n tr i b u i ç ã o a o e s tu d o d o s m a r c a d o r e s s o r o l ó g i c o s da s h e pa tite s B e C n a e s q uis to s s o m o s e m a n s ô n ic a . Ma s te r ’s th e s is , Unive r sidade de São Paulo , São Paulo , 1 9 9 3 .
1 7 . Lyr a LGC. Esq uisto sso mo se e vír us B da he patite . In: Aze vê do ES, Re b o uç as G, Ro c ha H, Lyr a LGC, Te ixe ir a RS, Andr ade S, Andr ade Z ( e ds) Aspe c to s pe c uliar e s da infe c ç ão po r Sc h i sto so m a m a n so n i. Unive r sidade Fe de r al da B ahia, Ce ntr o de Estudo s de Do e nç as Re gio nais, Ce ntr o Edito r ial e Didátic o da Unive r sidade Fe de r al da B ahia, Salvado r, p. 7 5 - 1 0 2 , 1 9 8 4 .
1 8 . Par aná R. Estudo c línic o so r o ló gic o da he patite aguda não - A não - B e m Salvado r-B ahia. PhD thesis. Fac uldade de Medic ina da Univer sidade Feder al da B ahia, Salvado r 1 9 9 7 .
1 9 . Par ana R, Co de s L, Andr ade Z. Is sple ne c to my a c ause o f antivir al tr e atme nt failur e in hepatitis C vir us in splenec to mized patients? Hepato lo gy 3 3 : 1 3 4 0 , 2 0 0 1 .
2 0 . Par aná R, Lyr a L, Tr e po C. Intr ave no us vitamin c o mple xe s use d in spo r ting a c ti vi ti e s a n d tr a n s m i s s i o n o f HCV i n B r a zi l . Am e r i c a n J o u r n a l o f Gastr o e nte r o lo gy 9 4 : 8 5 7 -8 5 8 , 1 9 9 9 .
2 1 . Pe r e ir a LM, Me lo MC, Sale h MG, Massar o lo P, Ko sk inas J , Do mingue s AL, Spine lli V, Mie s S, Williams R, Mc Far lane IG. He patitis C vir us infe c tio n in Sc histo so miasis manso ni in B r azil. J o ur nal o f Me dic al Vir o lo gy 4 5 : 4 2 3 -4 2 8 , 1 9 9 5 .
2 2 . Pr ata A. Co mo c ar ac te r iza a fo r ma he pato -e splê nic a da e sq uisto sso mo se ?
In: Pr ata A, Ab o im E ( e ds) II Simpó sio sô b r e Esq uisto sso mo se . Dir e to r ia de Saúde da Mar inha/Univer sidade Feder al da B ahia, Salvado r, p. 1 7 9 ,1 9 7 0 .
2 3 . Santana GO. Anti-HCV em pac ientes so b pr o gr ama de hemo diálise-Salvado r-B A. Maste r ’s the sis, Unive r sidade Fe de r al da r-B ahia, Salvado r, 1 9 9 5 .
2 4 . Ser ufo JR, Lamb er tuc c i JR. Esquisto sso mo se e hepatites vir ais: uma r evisão . Re vista da So c ie dade B r asile ir a de Me dic ina Tr o pic al 3 0 : 3 1 3 -3 2 2 , 1 9 9 7 .
2 5 . Silva L, Par aná R, Co tr im H, Mo ta E, B o e ne c - Co ur te y ML, Tr e po C, Lyr a L. Pr e valê nc ia do antiHCV na Po pulaç ão Ur b ana e Rur al do No r de ste - B r asil. Ar q uivo s de Gastr o e nte r o lo gia 5 : 3 - 6 , 1 9 9 9 .
2 6 . Str a us s E. He pa tite e e s q uis to s s o m o s e m a n s ô n ic a . In: Silva LC ( e d) He patite s agudas e c r ô nic as. Sar vie r, São Paulo , p. 2 5 3 -2 5 8 , 1 9 9 5 .
2 7 . Ta va r e s - Ne t o J . R e c o r r ê n c i a f a m i l i a l e c o m p o s i ç ã o r a c i a l n a e sq uisto sso m o se m ansô nic a. Maste r ’s the sis, Unive r sidade de B r asília, B r asília, 1 9 8 7 .
2 8 . Ta va r e s - Ne to J . Es tudo s o r o - e pide m io ló gic o do ve s ic ulo vír us Pir y n a po pulaç ão e e ntr e o s me mb r o s das famílias nuc le ar e s, e m Cato lândia – B ahia. PhD the sis, Fac uldade de Me dic ina de Rib e ir ão Pr e to /Unive r sidade de São Paulo , 1 9 9 2 .
2 9 . Tavar e s-Ne to J. Mar c ado r e s so r o ló gic o s das he patite s B e C e m r e side nte s de ár e a e ndê mic a da e squisto sso mo se mansô nic a. “Livr e -Do c ê nc ia” the sis, Fac uldade de Me dic ina da Unive r sidade Fe de r al da B ahia, 1 9 9 7 .
3 0 . Ta va r e s - Ne to J , P r a ta A. R e g r e s s ã o d a fo r m a h e p a to s p l ê n i c a d a e sq uisto sso mo se , apó s tr atame nto e spe c ífic o , asso c iada à r aç a. Re vista da So c ie dade B r asile ir a de Me dic ina Tr o pic al 2 1 : 1 3 1 - 1 3 3 , 1 9 8 8 .
3 1 . Van de r Po e l CL, Cuype r s HTM, Re c sink HW, We ine r AJ , Quan S, Di Ne llo R, Van B o ve n JJP, Wink e l I, Mulde r-Fo lk e r ts D, Exe l-Oe hle r s PJ, Sc haasb e r g W, Le e ntvaar- Kuype r s A, Po lito A, Ho ughto n M, Le lie PN. Co nfir matio n o f he patitis C vir us infe c tio n b y a ne w fo ur- antige n r e c o mb inant immuno b lo t assay. The Lanc e t 3 3 7 : 3 1 7 - 3 1 9 , 1 9 9 1 .
3 2 . Wak e d IA, Sale h SM, Mo ustafa MS, Rao uf AA, Tho mas DL, Str ic k land GT. High pr e va le nc e o f he pa titis C in Egyptia n pa tie nts with c hr o nic live r dise ase . GUT 3 7 : 1 0 5 - 1 0 7 , 1 9 9 5 .