ORIGINAL RESEARCH EFFECTS OF AN AQUATIC VERSUS NON-AQUATIC RESPIRATORY EXERCISE PROGRAM ON THE RESPIRATORY MUSCLE STRENGTH IN HEALTHY AGED PERSONS
Texto
Imagem
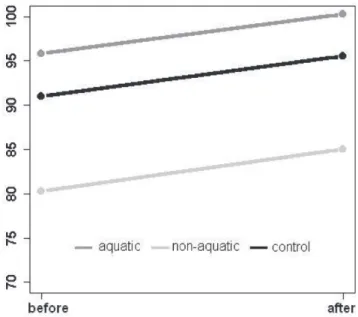
Documentos relacionados
Foi relatado também por docentes, em relação ao conhecimento que cada profissional da área da saúde deve ter quanto aos seus limites de conhecimentos, não devendo intervir em
showed a decrease in postoperative respiratory muscle strength, when compared to the pre values , however, it was found no relation between preoperative dysfunc- tion of
CONCLUSION: The preoperative inspiratory muscle training increased the inspiratory muscle strength (maximal inspiratory pressure) and attenuated the negative postoperative effects
In the study group, mouth breathing children had a higher rate of altered neck posture and decreased respiratory muscle strength compared to nose breathing
Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate the inluence of inspiratory muscle training on functional capacity submaximal and inspiratory muscle strength in patients
point, however, was a reduction in the number of steps across days in group 1 like the non-demyelinated animals, suggesting a better motor performance in the group with
3 Como aconteceria na situação em que um doente desse entrada num serviço de urgência, com indicação para cirurgia urgente, optando o médico por não a fazer depois de o filho
Objective: Evaluate the interaction between high-intensity inspiratory muscle training (IMT) and aerobic exercise on physical capacity, respiratory muscle strength, peripheral muscle