H VM BI OFLUX
H u m a n & V e t e r in a r y M e dicin e
I n t e r n a t ion a l Jou r n a l of t h e Bioflu x Socie t y
Pr ope r t ie s of na t u r a l ze olit e s in be n e fit of
n u t r it ion a n d h e a lt h
I rina Sm ical
Facult y of Environm ent al Science, Babeş- Boly ai Univ ersit y Cluj - Napoca, 30 Fânt ânele St reet , Cluj - Napoca Cit y, Cluj Count y , Rom ania, European Union;
e- m ail: irinadan2003@y ahoo. com
Abst r a ct. Due t o t heir r em ar kable pr oper t ies, nat ur al zeolit es have com e t o t he at t ent ion of m edicine r esear cher s t o find new ways of t r eat ing various diseases and ensur e an im pr oved supply of m iner als in nut r it ion. The r esear ch r esult s have shown t he beneficial effect s of applicat ion of var ious t ypes of nat ur al zeolit es in healing or am elior at ing especially gast r oint est inal and diarr hea disease and cancer disease, as well. Because nat ur al zeolit es have a ver y good abilit y as ion exchanger s t hey ar e lar gely used in nut r it ion for supplying t he essent ial m iner als in nut r it ion of anim als.
Ke y W or ds: nat ur al zeolit e, ion exchange, adsor pt ion, nut r it ion, m edicine.
I n t r odu ct ion. Zeolit es are hy drat ed alum inosilicat es especially of calcium and sodium from t ect osilicat es class. They are charact erized by a cry st alline st ruct ure consist ing of t hree- dim ensional net w orks represent ed by alum inium t et rahedra, silicon and ox y gen, w it h large channel gaps w hich are usually filled w it h w at er m olecules t hat can be easily rem ov ed by heat ing gradually and w hich can be again absorbed or replaced by m olecules of ot her subst ances ( Fig. 1) ( Coom bs et al 1998) .
Nat ural zeolit es are t he m ost im port ant inorganic ion ex changers showing high ion ex change capacit y , select ivit y and com pat ibilit y w it h t he nat ural env ironm ent ( Nicula et al 2010; Sm ical et al 2010ab; Sm ical 2011) . Their applicat ions are based on one or m ore of t he following propert ies: ion ex change, adsorpt ion and m olecular siev e, cat alyst , high m oist ure and easy dehy drat ion, low densit y and large v olum e of v oids when dehy drat ed, lat t ice st abilit y aft er dehy drat ion, m olecular sized channels in t he dried cry st als ( Christ ie et al 2002; Ack ley et al 1991; Pansini 1996; Mum pt on 1999; Hugon et al 2000; Woinarski et al 2003) .
From t hese propert ies, in applying of nat ural zeolit es in m edicine, t he m ost im port ant are: m olecular adsorpt ion and ion ex change.
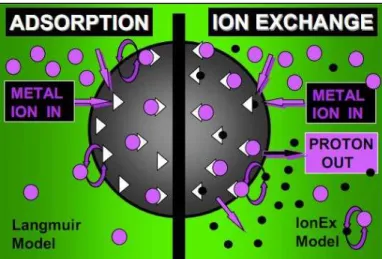
M ole cula r Adsor pt ion. Adsorpt ion process carried out by nat ural zeolit es can be bot h phy sical and chem ical by ion exchange being called in t his case chem osorpt ion, as w ell ( Fig. 2) . Phy sical adsorpt ion is achiev ed w hen t he dissolved cont am inant s in w at er
adhere and becom e im m obilized on t he surface of zeolit e part icles wit hout dest roying t he at om ic st ruct ure of t he zeolit e.
Large cav it ies and channels of input of nat ural zeolit es are generally filled wit h w at er m olecules form ing hy drat ion spheres around changing cat ions. I f t he w at er is rem ov ed, t he sm all enough in diam et er m olecules t o pass t hrough t he input channels are rapidly adsorbed on t he surfaces of dehy drat ed cent ral cavit ies rings. The av ailable area for adsorpt ion can be up t o sev eral hundred square m et ers per gram ( Mum pt on 1983) .
I on Ex ch a n ge. I on ex change capacit y is prim arily a funct ion of t he degree of subst it ut ion of silicon by alum inum in t he st ruct ure of t he net w ork . I n zeolit e st ruct ures, negat iv e charge is giv en by subst it ut ion Si4 + by Al3 + in t et rahedron, generat ing a deficit of posit iv e charge on t he net w ork. This negat iv e charge is balanced by div alent cat ions and m onov alent ( Na+, K+, Mg2 +, Sr2 + and Ba2 +) t hat are locat ed in channels. The great er subst it ut ion is t he m ore pronounced deficiency of charge is and also t he great er num ber of cat ions required t o elect rical neut ralize is.
The ion ex change process m ay be present ed by t he following equat ion:
A B AB z
z B z
s A z
s B Z
z
A
B
z
A
z
B
z
A
z
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )Where:
A
z
andz
B represent the A şi B exchangeable ion charges and the coefficient z and sreffers t o zeolit e and t o solut ion, respect iv ely . The react ion runs up t o t he equilibrium is est ablished.
Ex changeable cat ions of nat ural zeolit es are usually represent ed by : Mg2 +, Ca2 + and Na+. Such t heoret ical cat ion ex change capacit y ( TCEC) is t he sum of free cat ions of
zeolite (Table 1) (Tsitsishvili et al 1992; Çulfaz & Yağız 2004) .
Na
K
Mg
Ca
TCEC
,
,
,
Table 1 Cat ion ex change capacit y of zeolit es ( Pabalan & Bert et t i 2001)
Nr. Crt .
Zeolit e nam e Form ula CEC ( m eq/ g)
1 Analcim e Na16( Al16Si32O96) 16H2O 4.5
2 Chabazit e Ca2( Al4Si8O2 4) 12H2O 3.9
3 Clinopt ilolit e ( Na,K)6 Si30 Al6 O72 20H2O 2.2
4 Heulandit e ( Ca)4 ( Si2 8 Al8 O7 2) 24H2O 3.2
5 Laum ont it e Ca4( Al8Si16O48) 16H2O 4.3
6 Nat rolit e Na16 ( Al16 Si2 4 O80)∙16H2O 5.3
7 Morden it e Na2KCa2( Al8Si40O96) 28H2O 2.2
8 Phillipsit e K2( Ca0. 5 Na)4( Al6Si10O32) 12H2O 4.5
I n t he case of a pure zeolit e, it s chem ical form ula can be used t o det erm ine t he ideal cat ionic ex change capacit y . I n Table 2 t he ideal cat ionic exchange capacit ies are present ed based on t he pure species form ula. I deal ex change capacit y , est im at ed at 100% for clinopt ilolit e- rich rock s of t he chem ical form ula w as report ed t o be 2. 32 ± 0. 12 ( Cerri et al 2002) .
Tabel 2 I deal cat ionic exchange capacit y of nat ural zeolit es ( Mu m pt on 1999)
Nr. crt .
Zeolit e nam e Cat ionic exchange capacit y ( m eq/ g)
1 Chabazit e 3.84
2 Clinopt ilolit e 2.16
3 Erion it e 3.12
4 Ferr ierit e 2.33
5 Heulandit e 2.91
6 Laum ont it e 4.25
7 Morden it e 2.29
8 Phillipsit e 3.31
9 Fauj asit e 3.39
The real ex change capacit y is represent ed by t he ( negat iv e) charging of t he zeolit e net w ork , so t o det erm ine t he real exchange capacit y is t o est im at e all zeolit e cat ions t hat could be ex changed from solid phase. This m eans t hat t he zeolit e cations should be com plet ely ex changed. I n ot her w ords, t he negat iv e charge of t he zeolit e should be balanced by an equiv alent am ount of ions t hat int eract s wit h zeolit e. This t ot al exchange could be achiev ed by : repeat ed balancing in bat ch sy st em s wit h periodic renew al of t he solut ion ( Cerri et al 2002; Nik ashina et al 1995; Mier et al 2001) .
I m por t a n ce of Ze olit e s in N u t r it ion. According t o Mum pt on & Fishm an ( 1977) , since 1965 t he Japanese researchers had t ried t o use zeolit es as supplim ent in nut rit ion of anim als ( poult ry , swine and cat t le) .
The successful result s conduct ed t o and encourage zeolit e use, especially clinopt ilolit e and m ordenit e, in nut rit ion for a larger scale of anim als. This kind of feed not only assures a gain of w eight of anim als but also im prov ed t heir healt h wit hout negat iv e effect s.
The research m ade by Loughbrough ( 1993) hav e show n t hat zeolit es can be used as binding agent s in anim al feeds. They also appear t o act as a buffer in t he anim als digest iv e sy st em , st oring nit rogen in t he form of am m onium and releasing it gradually by ion ex change w it h sodium and pot assium . The anim al receiv es great er benefit from t he sam e quant it y of feed.
On t he ot her hand, w as not iced t he abilit y of nat ural zeolit es, applied t o rum inant s, t o t ak e up t he NH4+ from t he rum en and slowly release it w hich allow ed rum en m icroorganism s t o sy nt hesize cellular prot ein cont inuously for easy assim ilat ion int o t he digest iv e syst em of anim als (Mum pt on & Fishm an 1977) .
Posit ive effect of com bined feed wit h zeolit e on digest ibilit y of nut rient s; balance of nit rogen, calcium and phosphorous, and av er age daily increase of w eight of heifers has been not iced ( Kirolov e et al 1995) . Moreov er, zeolit e is com m only used in dairy cow rat ions t o reduce t he im pact of m y cot oxins in t he feed, and it is also effect ive for am eliorat ing t he negat ive im pact of m old produced t ox ins in anim al feeds.
Ze olit e s Applica t ion in Me dicine. Phy siological effect s of zeolit es appear t o be relat ed t o t heir ion exchange capacit y t hat affect s t issue absorpt ion, as w ell t he t ransfer of NH4+, Pb2 +, Cd2 +, Cu2 +, Cs+ and ot her cat ions in anim als body ( Pond 1995) .
Not iceable result s w ere seen at anim als in decreasing t he num ber of cases of gast ric ulcer, pneum onia, heart dilat ion and in ov erall m ort alit y ( Mum pt on & Fishm an 1977) .
When t he cow s diet cont ains aflat oxin, it s am ount in m ilk is reduced w het her in t he anim als diet clinopt ilolit e is added. Also, t est s hav e show n t hat in cases of diarrhea and drug int oxicat ion t he presence of clinopt ilolit e in diet is beneficial ( Rodriguez- Fuent es et al 1997; Lam et al 1998; Riv era- Garza et al 2000) .
The benefit s of nat ural zeolit es for healt h are ( Hecht 2010) :
Det oxificat ion by rem oving t he pollut ant s and st opping t he free radicals;
Dev eloping t he im m une sy st em ;
Cont rolling t he m ineral m et abolism , blood circulat ion, nerv ous sy st em and digest ion;
I m prov ing t he skin aspect by inhibit ion of t he aging process;
Generat e ant i- bact erial, ant i- viral, ant i- fungal effect s;
Assure posit iv e effect on sleep and reduce st ress;
Reduce t he effect of drug, m edicines, alchool and caffeine.
I n case of endot ox icosis of hum an and anim al organism s, t he m echanism s of det oxificat ion by nat ural zeolit es act by adsorpt ion t he endot ox ins and ex ogenous t ox ins in t he m acropores and m esopores of nat ural zeolit es ( Hect 2010) .
The w ork m ade by Russian researchers using a nat ural zeolit e from Kholinsk oe deposit ( Russia) hav e conduct ed t o sev eral conclusions regarding t he im port ant role of nat ural zeolit e use in different m ecial affect ions. The obt ained dat a from ex perim ent al w ork on rat s, hav e show n t hat t he preparat e cont aining t he zeolit e from abov e m ent ioned deposit , has t he capacit y t o reduce t he lev el of endogenic int oxicat ion in relat ion t o at ropine, am it ript yline, digi- t oxin and organophosphorus com pounds. This zeolit e underw ent in viv o t est s, is effect iv e in relat ion t o alcaloids ( at ropine) , barbit urat es ( et ham inal- sodium ) , t ricyclic ant i- depressant s ( am it ript yline) , in case of poisoning wit h arsenic, t oxic m et als ( copper, barium , lead) . I t also allow s effect ive reduct ion of endogenic int oxicat ion lev el in case of radiat ion dam age, and as ent erosorbent t o t he st andard t herapy course cont ribut es t o t he im prov em ent of funct ional condit ion of m ain barrier and det oxicat ing organs and sy st em s, correct ion of basic pat hogenic m echanism s of t ox icit y in indust rial poisons ( Nov osy olov a 2010) .
As w ell, ot her Russian researchers show t hat nat ural zeolit e can be an ex cellent ent erosorbent , w hich can be used in int est inal form of ant hrax , and possibly wit h sept icem ia ( I bragim ov a 2010) .
The ex perim ent s m ade on calv es in order t o observ e t he influence of clinopt ilolit e on resorpt ion of colost rum s im m unoglobulin, haem at ology param et ers and enzy m e act ivit ies in blood serum ( AST, ALD and LDH) , body w eight and daily w eight gains of calves in first t hree m ont hs of life hav e show n t hat increases t he resorpt ion rat e of colost rum im m unoglobulin G in t he digest iv e t ract of calv es, evidenced by t heir significant ly higher concent rat ion in blood serum and causes no significant funct ional or m orphological changes in t he t issue of parenchy m at ous organs and m uscles.
Pav elic et al ( 2001) report ed t hat clinopt ilolit e has been successfully used as v accine adj uv ant and for diarrhea t reat m ent for anim als. Ot her dat a published by t hem , indicat e t he role of nat ural zeolit es as pot ent ial adj uv ant in ant icancer t herapy according t o his research m ade on m ice and dogs w hich present ed t um ors. The clinopt ilolit e applicat ion has im prov ed t he ov erall healt h st at e and dim inished t um or size of t he anim als.
Pav elic et al ( 2002) also report ed t hat m icronized zeolit es adm inist rat ed in diet of m ice inj ect ed wit h m elanom a cells, significant ly reduced t he num ber of m elanom a m et ast ases and t he ly m phocy t es from ly m ph nodes prov ok ed a not iceable higher allogeneic graft - versus- host react ion t han cells of cont rol m ice. They also refer t o an increased of perit oneal m arcrophages and t heir product ion of superox ide anion. The researchers concluded t hat m icronized zeolit es have ant im et ast at ic and im m unost im ulat ory effect on organism s.
any biological dam age t o hum ans. I t is also a good gast ric alcalinisant and ant i- diarrheic adj uv ant ( Farías et al 2003) .
According t o Vrzgula & Seidel ( 1989) , clinopt ilolit e prov ed his abilit y as sorbent for arsenic, cadm ium , and lead ion from t he rum en and abom asum s j uice. Zeolit e w as found t o sorb 91% of lead and 45% of cadm ium from rum en fluid in 24 hours. The sorpt ion effect iv eness w as ev en higher from abom asum s j uice w here zeolit e sorbed 98% lead in 24 hours.
Nat ural zeolit es, also hav e a benefic role in healing t he derm al affect ions, and also hav e a good role in healing quickly t he inflict ed w ounds, scrapes, surgical lesions and ot her open w ounds ( I zm irov a et al 2002) .
Con clusion s. Nat ural zeolit es due t o t heir rem ark able propert ies as ion ex changers and m olecular siev e, hav e k now n a significant approach in t he last decades especially in nut rit ion and m edicine fields. The result s of t heir usage in feeding anim als have show n a significant ly success in gaining w eight and assuring a bet t er healt h t o t he research subj ect ed anim als.
Researchers hav e got encouraging result s on anim als so t hat t here is a prem ise t o apply t he usage of t hese zeolit es in hum an nut rit ion w it h ex cellent result s.
A v ery im port ant role of nat ural zeolit es w as regist ered in applicat ions against v arious diseases and ot her organism affect ions where t hey got excellent result s ev en in cancer dim inishing effect s. This could represent a hope for hum an m edicine t hat t he usage of nat ural zeolit es could com e in support ing t he incurable diseases healing.
Re fe r en ce s
Ack ley M. W. , Rege U. S. , Sax ena H. , 2003 Applicat ion of nat ural zeolit es in t he purificat ion and separat ion of gases. Microporous and Mesoporous Mat erials
6 1: 25–42.
Cerri G., Langella A. , Pansini M., Cappellet t i P. , 2002 Met hods of det erm ining cat ion ex change capacit ies for clinopt ilolit e rich rock s of t he Logudoro region in Nort hern Sardinia, I t aly. Clay s and Clay Minerals 5 0: 127- 135.
Christ ie T. , Brat hw ait e B. , Thom pson B. , 2002 Mineral Com m odit y Report 23 – Zeolit es, New Zealand Mining Volum e 31 June 2002.
Coom bs D. , Albert i A., Arm brust er T., Art ioli G., Colella C. , Galli E., Grice J. , Liebau F., Mandarino F. , Minat o H. , Nick el E. , Passaglia E., Peacor D. , Quart ieri S. , Rinaldi R. , Ross M. , Sheppard R. , Tillm anns E. , Vezzalini G. , 1998 Am erican Mineralogist Special Feat ure, I MA Zeolit e Report , p. 1- 28.
Çulfaz M., Yağız M., 2004 Ion exchange properties of natural clinopt ilolit e: Lead- Sodium and Cadm ium - Sodium equilibria. Separat ion and Purificat ion Technology
3 7( 2) : 93- 105.
Farías T. , Ruiz- Salv ador A. R. , Riv era A., 2003 I nt eract ion st udies bet w een drugs and a purified nat ural clinopt ilolit e, zeolit e. Microporous and Mesoporous Mat erials 6 1( 1-3) : 117- 125.
Hecht K., 2010 Clinopt ilolit e- Zeolit e and Mont m orillonit e Minerals Rich in Sio2: What Are They ? What Can They Achiev e? Why Are They so I m port ant f or Hum an Healt h?, Applicat ion of nat ural zeolit es in m edicine and cosm et ology – ZEOMEDCOS. SWB, Bak u- London, 2010, pg. 7- 45.
Hugon O. , Sauv an M. , Benech P. , Pij olat C. , Lefebv re F., 2000 Sensors Act uat ors B: Chem . , 67, p. 235.
I bragim ov a S. M., 2010 The Researching Result s Of Adsorpt ion Op- Port unit ies Of Nat ural Zeolit es For The Bacillus Ant hracis, Applicat ion of nat ural zeolit es in m edicine and cosm et ology – ZEOMEDCOS. SWB, Bak u- London, 2010, pg. 81- 85.
I zm irov a N., et al. , 2002 Diagnost ics, Prophy lact ics and Healing by Clinopt ilolit e Zeolit e, Zeolit e ’02, 6t h I nt ernat ional Conference, Occurrence, Propert ies and Ut ilisat ion of Nat ural Zeolit e, P. Misaelides ( Ed. ) , pg. 150 – 151;
zeolit es. Sesk ok hoziaj st rennay a biologiy a. Seriy a Biologiy a Zhiv ot nyk h ( Russian Federat ion) 2: 77- 81.
Lam A. , Sierra L. R. , Roj as G. , Riv era A., Rodriquez- Fuent es G. , Mont ero L. A. , 1998 Theoret ical st udy of t he phy sical adsorpt ion of aspirin on nat ural clinoptilolit e. Microporous and Mesoporous Mat erials 2 3( 5- 6) : 247- 252.
Loughbrough R. , 1993 Minerals for Anim al Feed, in a St able Mark et . I ndust rial Minerals, March 1993, pg. 19 –33.
Mier M. V. , Callej as R. L. , Gehr R. , Cisneros B. E. , Alv arez P. J. J., 2001 Heav y m et al rem ov al wit h Mexican clinopt ilolit e: m ult i- com ponent ionic ex change. Wat er Research 3 5( 2) : 373–378.
Mum pt on F. A. , Fishm an P. H., 1977 The applicat ion of nat ural zeolit es in anim al science and aquacult ure. J Anim Sci 4 5: 1188- 1203.
Mum pt on F. A., 1983 The Role of Nat ural Zeolit es in Agricult ure Zeo - Agricult ure use of Nat ural Zeolit es in Agricult ure ( ed. Wilson. 6 Paundand F. A. Mum pt on) , p. 3- 27. Mum pt on F. A., 1999 La roca m agica: Uses of nat ural zeolit es in agricult ure and indust ry .
Proceedings of Nat ional Academ y Sciences, USA 9 6: 3436- 3470.
Nicula M. , Banat ean- Dunea I . , Gergen I . , Harm anescu M. , Sim iz E. , Pat ruica S., Polen T. , Marcu A. , Lunca M. , Szucs S. , 2010 Effect of nat ural zeolit e on reducing t issue bioaccum ulat ion and cadm ium ant agonism relat ed t o som e m ineral m icro- and m acronut rient s in Prussian carp (Carassius gibelio) . AACL Bioflux 3( 3) : 171- 179. Nik ashina V. A., Galkina N. K. , Kom arov a I . V. , Anfilov B. G. , Argin M. A. , 1995 I n: D. W.
Ming, F. A. Mupht on ( Eds. ) , Nat ural Zeolit es 93: Occurrence, Propert ies, Use, Brock port , NY, 1995, p. 289.
Nov osy olov a T. I . , 2010 Pre- Clinical And Clinical St udies of “ Lit ovit ” Biologically Act iv e Food Supplem ent ( BAFS) , Applicat ion of nat ural zeolit es in m edicine and cosm et ology – ZEOMEDCOS. SWB, Bak u- London, 2010, pg. 58- 71.
Pabalan R. T. , Bert et t i F. P. , 2001 Cat ion ex change capacit y of nat ural zeolit es. I n: Nat ural zeolit es: occurrence, propert ies, applicat ions. Review s in Mineralogy and Geochem ist ry v . 45, David Bish and Doug Ming ( Eds) Mineralogical Societ y of Am erica, p. 453- 518.
Pansini M., 1996 Nat ural zeolit es as cat ion ex changers for env ironm ent prot ect ion. Miner Deposit a 3 1: 563–575.
Pav elic K. , Colic M. , et al. , 2001 Nat ural zeolit e clinopt ilolit e: new adj uv ant in ant icancer t herapy . J Mol Med ( Springer- Verlag) 7 8: 708- 720.
Pav elic K., Colic V., et al., 2002 I m m unost im ulat ory effect of nat ural clinopt ilolit e as a possible m echanism of it s ant im et ast at ic abilit y . J Cancer Res Clin Oncol ( Springer- Verlag) 1 2 8: 37- 44.
Pond W. G. , 1995 Zeolit e in anim al nut rit ion and healt h: A rev iew. I n: Nat ur al Zeolit e '93: Occurrence, Propert ies, Use. D. W. Ming and F. A. Mum pt on ( eds. ) , I nt Com m Nat Zeolit e, Brock pot New York, p. 449- 457.
Riv era- Garza M. , Olguín M. T. , García- Sosa I . , Alcánt ara D. , Rodríguez- Fuent es G. , 2000 Silv er support ed on nat ural Mexican zeolit e as an ant ibact erial m at erial. Microporous and Mesoporous Mat erials 3 9: 431–444.
Rodriguez- Fuent es G. , Ruiz- Salv ador A. R. , Mir M., Picazo O. , Quint ana G. , Delgado M. , 1998 Therm al and cat ion influence on I R v ibrat ions of m odified nat ural clinopt ilolit e. Microporous and Mesoporous Mat erials 2 0: 269- 281.
Sm ical I . , 2011 Sorpt ion k inet ics of Pb2 +, Cu2 + and Zn2 + ions by nat ural zeolit es from Maram ures Count y ( nort hern Rom ania) : pot ent ial applicat ion in w ast ew at er reuse. AACL Bioflux 4( 4) : 481- 489.
Sm ical I . , Mihaly - Cozm ut a L. , Cost in D. , 2010a Research concerning t he influence of sev eral fact ors on Pb2 +, Cu2 + and Zn2 + ions adsorpt ion by nat ural zeolit e t uff from
Maramureş count y , Nort hern Rom ania. AES Bioflux 2( 2) : 171- 180.
Sm ical I . , Mihaly - Cozm ut a L., Cost in D., 2010b Use of nat ural zeolit es from Maram ures count y ( Rom ania) in rem ov al of Cu2 +, Pb2 +, Zn2 + ions from indust rial w ast ew at ers. AES Bioflux 2( 2) : 181- 188.
Volesk y B., 2003 Sorpt ion and biosorpt ion. BV Sorbex , I nc. , Mont real, Canada, I SBN 0-9732983- 0- 8, 316 p, p. 103.
Vrzgula L. , Seidel H. , 1989 Sorpt ion charact erist ics of nat ural zeolit e ( Clinopt ilolit e) in biological m at erial in vit ro. Vet Med ( Praha) 3 4( 9) : 537- 544.
Woinarski A. Z., Snape I . , St ev ens G. W. , St ark S. C. , 2003 The effect s of cold t em perat ure on copper ion ex change by nat ure zeolit e for use in a perm eable react iv e barrier in Ant arct ica. Cold Regions Science and Technology 3 7: 159- 168.
Received: 02 Oct ober 201 0. Accept ed: 18 Decem ber 2010. Pu blished online: 08 July 20 11. Aut hor :
I r ina Sm ical, Facult y of Environmental Science, Babeş- Bolyai Univer sit y of Cluj - Napoca, 30 Fânt ânele St r eet , Cluj - Napoca Cit y, Cluj Count y, Rom ânia, ir inadan20 03@yahoo. com
New adr ess: I r ina Sm ical, Envir onm ent al Pr ot ect ion Agency of Mar am ur es Count y, Rom ania, loc. Baia Mar e, st r. I za, nr. 1A, judeţul Maramureş, ir inadan200 3@yahoo. com
How t o cit e t his ar t icle: