THE RELATI ONSHI P BETW EEN DRUGS USE AND RI SK BEHAVI ORS
I N BRAZI LI AN UNI VERSI TY STUDENTS
1Sandr a Cr ist ina Pillon2 Bev er ley O’Br ien3 Ket t y Ar acely Piedr a Ch av ez4
Pillon SC, O’Brien B, Piedra KAC. The relat ionship bet ween drugs use and risk behaviours in brazilian universit y st u den t s. Rev Lat in o- am En fer m agem 2 0 0 5 n ov em br o- dezem br o; 1 3 ( n ú m er o especial) : 1 1 6 9 - 7 6 .
The aim was t o describe relat ionships bet ween gender and drug use as well as risk behaviors t hat m ay be associat ed wit h drug use am ong first - year st udent s at t he Universit y of São Paulo- Ribeirão Pret o. The Yout h Risk Behavior Survey ( YRBS) is an anonym ous survey t hat w as used for t his descript ive correlat ional st udy. I t w as dev eloped by t he Cent er s for Disease Cont r ol and Pr ev ent ion in t he Unit ed St at es. The sam ple ( n= 200) included ( 50% ) m ales and ( 50% ) fem ales. Their ages r anged fr om 18 t o 26 year s. Result s show ed t hat m or e fem ale t han m ale st udent s use alcohol and t obacco, but t hat t he pr obabilit y of heav y consum pt ion is higher am ong m en. Ther e w as a low incidence of illicit dr ug use for bot h gr oups. Male st udent s w er e m or e likely t o dr iv e under t he influence of alcohol t han fem ale st udent s and m or e m en w er e inv olv ed in v iolent behav ior s such as fight s w it h fr iends and police. I n r elat ion t o sex ual behavior , m ale st udent s w er e likely t o have m or e par t ner s and less pr ot ect ion w hile under influence of alcohol. I t w as concluded t hat gender is associat ed w it h r ecr eat ional dr ug use, specifically t obacco and alcohol, as w ell as ot her r isk behav ior s in univ er sit y st udent s.
DESCRI PTORS: st udent s; r isk fact or s; st r eet dr ugs
LA RELACI ÓN ENTRE EL USO DE DROGAS Y COMPORTAMI ENTOS DE
RI ESGO ENTRE ESTUDI ANTES BRASI LEÑOS
El uso de sust ancias psicoact iv as ent r e est udiant es ha sido m uy inv est igado en las últ im as décadas con obj et o de for t alecer cam pañas pr ev ent iv as de dr ogas. La finalidad de est e est udio es descr ibir la r elación ex ist en t e en t r e el u so d e d r og as y com p or t am ien t os d e r iesg o en t r e los u n iv er sit ar ios d el p r im er añ o d e pr egr ado de la Univ er sidad de São Paulo- Ribeir ão Pr et o, Br asil. El Yout h Risk Behav ior Sur v ey ( YRBS) es un cu est ion ar io an ón im o q u e f u e u t ilizad o p ar a la r ecop ilación d e d at os. La m u est r a f u e com p u est a p or 2 0 0 ( 100% ) alum nos del prim er año. El 50% de est os eran hom bres y el 50% m uj eres, con edad de 18 a 26 años. Los result ados m ost raron la presencia del uso recreat ivo de sust ancias psicoact ivas. Las m uj eres beben dent ro de los lím it es de baj o riesgo, m ient ras los hom bres t ienen consum o m ás pesado. Para el uso de drogas ilícit as, los r esu lt ados f u er on en m en or pr opor ción par a am bos sex os. Los h om br es dir igen m ás baj o el ef ect o del alcoh ol q u e las m u j er es y se in v olu cr an m ás en p eleas con am ig os y con p olicía en com p ar ación con las m u j er es. En r elación a los com p or t am ien t os sex u ales, los r esu lt ad os ap u n t an q u e los h om b r es t am b ién m ant uv ier on m ay or núm er o de r elaciones, con un núm er o m ay or de par ej as, con poca pr ot ección y baj o el efect o del alcohol. Est e est udio dem uest r a que el géner o es asociado al uso r ecr eat iv o de dr oga, bien com o ot r os com por t am ient os de r iesgo ent r e est udiant es univ er sit ar ios.
DESCRI PTORES: est udiant es; fact or es de r iesgos, dr ogas ilícit as
A RELAÇÃO ENTRE O USO DE DROGAS E COMPORTAMENTOS DE
RI SCO ENTRE UNI VERSI TÁRI OS BRASI LEI ROS
O obj et iv o desse ar t igo é descr ev er a r elação ex ist ent e ent r e o uso de dr ogas e com por t am ent os de r isco ent r e univer sit ár ios do pr im eir o ano de gr aduação da Univer sidade de São Paulo- Ribeir ão Pr et o. O Yout h Risk Behavior Survey ( YRBS) é um quest ionário anônim o que foi ut ilizado para a colet a de dados. A am ost ra foi com post a por 200 ( 100% ) alunos de prim eiro ano. Dest es, ( 50% ) eram hom ens e ( 50% ) m ulheres, com idade ent r e 18 e 26 anos. Os r esult ados m ost r ar am a pr esença do uso r ecr eacional de subst âncias psicoat ivas, com as m ulheres bebendo dent ro dos lim it es de baixo risco e os hom ens m ais pesadam ent e. Para o uso de drogas ilícit as, os result ados foram em m enor proporção para am bos os sexos. Os hom ens dirigem m ais sob efeit o do álcool que as m ulher es e est iver am m ais envolvidos em br igas com am igos e polícia do que as m ulher es. Em r elação aos com por t am ent os sex uais, os hom ens t iv er am r elações em m aior núm er o, com um núm er o m aior de par ceir as e com m enor pr ot eção e sob efeit o de álcool. Est e est udo conclui que o gêner o est á associado com o uso recreacional de drogas, bem com o out ros com port am ent os de riscos ent re est udant es universit ários.
DESCRI TORES: est udant es; fat or es de r isco; dr ogas ilícit as
1
The opinions expressed in t his art icle are t he sole responsabilit y of t he aut hors and do not in any way represent t he posit ion of t he organizat ion t hey work at or it s adm inist rat ion; 2 Facult y Mem ber, Universit y of São Paulo at Ribeirão Pret o College of Nursing, WHO Collaborat ing Cent re for Nursing Research Developm ent , Brazil, e- m ail: pillon@eerp.usp.br; 3 PhD Nursing Facult y at t he Universit y of Albert a, Canada; 4 RN, MSc, Nursing Facult y, Universit y of Guayaquil, Ecuador
I NTRODUCTI ON
S
ubst ances m isuse am ong st udent s has beeninvest igat ed for a long t im e, wit h t he aim of specifically
ident ifying and st udying int ervent ions t hat will m inim ize
d r u g u s e i n t h i s g r o u p( 1 ). I n f o r m a t i o n o n t h e
r e l a t i o n s h i p b e t w e e n r i s k b e h a v i o r a n d u s e o f
su bst an ces in sch ool en v ir on m en t s is n ecessar y f or
t he developm ent of effect ive prevent ive program s and
t o pr om ot e en v ir on m en t t h at ar e fr ee of dr u gs an d
t he violence generat ed by t hem . The m at uring of t his
idea com es u p w it h t h e gr ow in g r ecogn it ion on t h e
researchers’ part of t he high prevalence of t he healt h
pr oblem s an d at t en den t r isk s t o societ y associat ed
wit h drug use by adolescent s and young adult s. Many
o f st u d i e s w h e r e t h i s t o p i c ca n b e e x p l o r e d a r e
conduct ed in schools/ univ er sit ies as t hey ar e places
t h a t p r e s e n t e a s y a c c e s s t o a l a r g e n u m b e r o f
indiv iduals and w her e t hese people ar e consider ed a
t ar get populat ion for pr ev ent iv e cam paigns( 2).
Th e u se o f r ecr eat i o n al d r u g s am o n g t h i s
p o p u l a t i o n i s w o r r i so m e . Un i v e r si t y st u d e n t s a r e
con sid er ed on e of t h e sp ecial g r ou p s f or scien t if ic
i n v e st i g a t i o n i n t h e co u n t r y, m a i n l y d u e t o t h e i r
im port ance for t he fut ure developm ent of our societ y
in an incr easingly com plex w or ld( 3).
St u d ies of t h e p r ed om in an ce of t h e u se of
drugs am ong st udent s are frequent ly done in Brazilian
universit ies and m ainly in t he St at e of São Paulo, for
t he planning of pr ev ent iv e cam paigns and t o infor m
u n iv er sit y p olicy in r elat ion t o d r u g u se. Sin ce t h e
1980’s Br azil is t he Lat in- Am er ican count r y t hat has
g en er at ed t h e m ost d at a on ad d ict ion , as w ell as
st andards of drug and alcohol consum pt ion in specific
populat ions( 4), including j unior school and high school
st udent s( 5- 7), universit y st udent s( 3) and undergraduat e
st udent s of m edicine( 3- 4).
Th e u se of alcoh ol by dif f er en t popu lat ion s
h as been r eceiv in g special con sider at ion du e t o t h e
incr eased av ailabilit y and low cost of alcohol as w ell
as t h e social per m issibilit y of it s u se an d t h e m or e
uninhibit ed em ot ions of t hose who use it . St udies m ake
it ev ident t hat alcohol is t he subst ance t hat is m ost
associat ed w it h specific r isk s( 8) due t o it s effect s on
t he behav ior( 9).
Th e d i r ect a n d v er y co m m o n r el a t i o n sh i p
bet ween alcohol and aggression is t hrough int oxicat ion
or consum pt ion of t oo m uch alcohol. The aggr ession
is ex plained by lack of fear due t o t he t r anquilizing
a c t i o n i f a l c o h o l a n d a n i n c r e a s e t h e o f f e n s i v e
percept ion, which can be one of t he causes of a higher
def en siv e aggr ession . How ev er, t h is can ser v e as a
t r igger t o dem on st r at e act s of aggr ession for t h ose
who really have t he inclinat ion in relat ion t o violence
a n d t h a t f i n d t h e m s e l v e s i n s i t u a t i o n s o f
“ aggressiveness”( 10). For exam ple t here are alt erat ions
i n t h e c o g n i t i v e f u n c t i o n s , t h u s d e c r e a s i n g t h e
in div idu al’s capacit y t o plan act ion s in r espon se t o
m enacing sit uat ions ( i.e., act ing w it hout t hink ing) .
Va r i o u s a t t e m p t s t o f o r m u l a t e a
com prehensive t heory of t he relat ionship bet ween t he
u se o f p sy ch o - a ct i v e su b st a n ce s, a n d a sso ci a t e d
v i o l e n t a n d / o r a g g r e ssi v e b e h a v i o u r s h a v e b e e n
g e n e r a t e d . To u n d e r s t a n d t h i s r e l a t i o n s h i p , t h e
aut hor( 8) revised previous research based on concept s
of biological, psy ch o- ph ar m acological, psy ch ological
and psy chiat r ic m odels as w ell as social and cult ur al
per spect iv es in an at t em pt t o dev elop and pr esent a
m odel of t his r elat ionship t hat w ould be r elev ant for
adolescent s and y oung adult s in Lat in Am er ica. Most
in v est igat or s n ot e t h at t h e m ost im por t an t ar ea of
agr eem ent fr om t hese differ ent per spect iv es is t h at
i n t o x i cat i o n h as a si g n i f i can t i m p act o n co g n i t i v e
abilit ies an d f u n ct ion in g. Th e n at u r e of t h is im pact
v ar ies accor ding t o t he int ox icat ing subst ance used,
but it is m oderat e in t he cont ext in which t he behavior
occu r s.
Fo r i n s t a n c e , t h e c u l t u r a l a n d s o c i a l
si g n i f i ca n ce, h o w t h e p er so n f u n ct i o n s u n d er t h e
influence of t he psycho- act ive subst ances, t he im pact
of int oxicat ion on t he j udgm ent , t he abilit y t o perceive
social sit uat ions ar e ext r em ely im por t ant fact or s t hat
det erm ine w het her t he int oxicat ing sit uat ion in w hich
drug use is present will result in violence. The presence
or escalat ion of v iolen ce is also in f lu en ced b y t h e
int ox icat ed indiv idual’s abilit y t o focus on shor t t er m
r esult s and desir es.
Through an invest igat ion of t he lit erat ure and
p r act i cal ex p er i en ce, i t i s d eem ed t h at u n i v er si t y
st udent s are a vulnerable group when exposed t o t he
p r esen ce an d u se of p sy ch oact iv e su b st an ces. Th e
use of t hese subst ances are associat ed wit h developing
r esu lt beh av ior s w h ich m ot iv at ed u s t o dev elop t h e
cur r ent st udy.
Ou r f o cu s i s st u d en t s’ w h o w er e r ecen t l y
adm it t ed t o universit y as during t his t im e t he cult ural
act iv it ies ar e u su ally celebr at ed w it h par t ies an d in
t he m aj orit y of t he t im es alcohol is present . This m ay
t h e f ir st t im e t h at m an y of t h e y ou n g people h av e
h a v e h a d e x p e r i e n c e w i t h t h e u s e o f o t h e r
psy ch oact iv e su bst an ces. Th er ef or e t h e sit u at ion of
beginning univ er sit y, w hich oft en includes separat ion
fr om t he fam ily and m ak ing new fr iends is par t of a
new phase in t he dev elopm ent of an indiv idual t hat
can put t hem in a great er risk for t he use of illicit or
p sy ch o a ct i v e su b st a n ce s. Pe e r p r e ssu r e a n d t h e
acquisit ion of independence m ay cr eat e an incr eased
p o t e n t i a l f o r s u c h b e h a v i o r s . I n s u m m a r y, t h e
en v ir on m en t is fav or able t o ex per im en t w it h dr u gs,
w hich could w ell lead t o becom ing inv olv ed in ot her
unex pect ed behav ior s ( e. g., dr unk en dr iv ing, sex ual
pr act ice w it hout pr ot ect ion) .
Th e a i m o f t h i s st u d y i s t o d e scr i b e t h e
p r ed om in an ce of t h e u se of dr u g s am on g st u den t s
s o o n a f t e r t h e y a r r i v e a t u n i v e r s i t y ; t o f u r t h e r
underst and, t o underst and which subst ances are used
and t o descr ibe t he r elat ionship bet w een t he use of
dr ugs, associat ed r isk behav ior s and t he gender.
METHODOLOGY
This is a descript ive quant it at ive st udy which
i s p a r t o f t h e CI CA D / OEA Pr o j e c t , w i t h t h e
par t icipat ion of 1 3 Lat in Am er ican cou n t r ies. Th ese
count r ies ar e w or k ing t oget her t o fur t her infor m and
pr epar e nur se r esear cher s t o addr ess t he pr oblem of
dr ug use in t heir count r ies.
The dat a were collect ed am ong t he freshm en
or fir st y ear univ er sit y st udent s at t he Univ er sit y de
São Paulo- Cam pus Ribeir ão Pr et o. A non- pr obabilit y
sam p le w as r ecr u it ed in t h at all p ar t icip an t s w er e
v olu n t eer s.
The Yout h Risk Behav ior Sur v ey ( YRBS) is a
q u est ion n air e t h at can b e u sed in an on y m ou s an d
v olu n t ar y su r v ey s. I t w as dev eloped by t h e Cen t er
for Disease Cont rol ( CDC) and Prevent ion in t he Unit ed
St a t e s( 1 1 ) t o m o n i t o r t h e p r e v a l e n c e o f s p e c i f i c
behav ior s am ong y oung people, such as engaging in
r isk , including t he use of psy choact iv e. Ev en t hough
t he quest ionnair e is in t he public dom ain, a r equest
t o use and adapt t he quest ionnaire for it s use in Brazil
w as m ad e t o t h e CDC. Th is or g an izat ion ap p r ov ed
r eq u est .
The original YRBS quest ionnaire m onit ors six
behav ior al cat egor ies: a) behav ior s w it hout int ent ion
t hat cont ribut e t o vandalism and violence, b) t he use
of alcohol, c) t he use of t obacco and ot her drugs, d)
sexual behaviors, e) physical act ivit y, and f ) diet . The
cat egor ies ph y sical act iv it y an d diet w er e ex clu ded
si n ce t h ey a r e n o t r el ev a n t t o t h i s i n v est i g a t i o n .
Ca t e g o r i e s r e l a t e d t o t h e u s e o f s u b s t a n c e s ,
per cept ion of r isk ( av ailabilit y of dr ugs, r isk s t o t he
use of drugs) , and t he percept ion in relat ion t o violence
a n d a g g r e s s i v e b e h a v i o r s ( v i o l e n c e , r e b e l l i o u s
ag g r ession , an t i- social b eh av ior ) w er e ad ap t ed f or
t his st udy.
Pr ior t o beginning t he st udy, per m ission was
ask ed of t he dir ect or s of t he facult ies inv olv ed. This
led t o a clar if icat ion of st u d y aim s. Also, p r ior t o
begin n in g dat a collect ion , for m al appr ov al fr om t h e
Et hics Com m it t ee for Resear ch of FMRP.USP and t he
Un iv er sit y of Alber t a w as obt ain ed. Th e an aly sis of
t he dat a w as done using a st at ist ical pr ogram , i. e.,
St at ist ical Pr ogram for t he Social Sciences; v. 1 1 for
Win dow s ( SPSS) .
RESULTS
The quest ionnaire was dist ribut ed t o t he first
y ear st u d en t s in t h e ar eas of b iolog y, scien ce an d
ar t s ( n = 2 0 0 ) Th is n on pr obabilit y sam ple con sist ed
o f 2 0 p e r ce n t o f t h e st u d e n t p o p u l a t i o n f o r t h e
par t icipat ing facult ies. Am ong t hese 100 ( 50% ) w er e
fem ale and 100 ( 50% ) w er e m ale. The av er age age
w as 19 y ear s old ( SD 2) w it h a m inim um age of 18
and a m axim um age of 27. The m aj orit y of st udent s
w er e single ( n= 197 or 98% ) and Cat holic N= 110 or
5 5 % ) . A m aj or it y also liv ed w it h t h eir par en t s ( n =
6 9 , 3 4 . 5 % ) ane w er e fr om a fam ily of four people.
Ninet y - t hr ee ( 4 6 . 5 % ) had nev er liv ed in m or e t han
on e r esiden ce.
We found t hat t he psycho- act iv e subst ances
used by t he fam ily w er e 7 5 ( 3 7 . 5 % ) of t he fat her s
use alcohol and 25 ( 12. 5% ) of t he m ot her s sm ok e.
The use of psychoact ive subst ances wit hin t he past 6
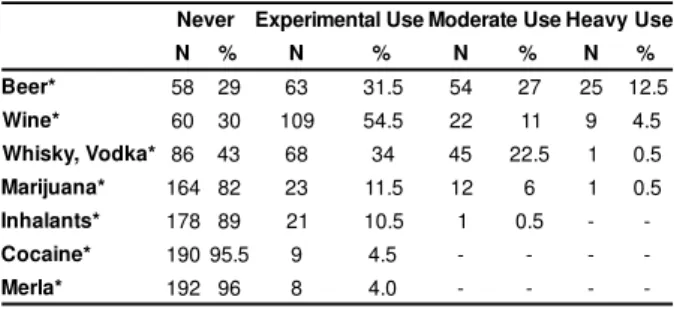
m ont hs for t his sam ple is present ed in Table 1.
Table 1 - Frequency of st andard use of psycho- act ive
subst ances wit hin t he last 6 m ont hs ( n= 200)
r e v e
N ExperimentalUseModerateUseHeavyUse
N % N % N % N %
* r e e
B 58 29 63 31.5 54 27 25 12.5
* e n i
W 60 30 109 54.5 22 11 9 4.5
* a k d o V , y k s i h
W 86 43 68 34 45 22.5 1 0.5
* a n a u j i r a
M 164 82 23 11.5 12 6 1 0.5
* s t n a l a h n
I 178 89 21 10.5 1 0.5 -
-* e n i a c o
C 19095.5 9 4.5 - - -
-* a l r e
-I n t his sam ple, m ale st udent s report ed m ore
int ense use in t he t hree cat egories ( i.e., experim ent al, m oderat e and heavy use) t han did t he fem ale st udent s.
The frequency of every using psychoact ive subst ance for m ales and fem ales in t his sam ple is pr esent ed in
Table 2.
Ta b l e 2 - Fr e q u e n cy o f e v e r u si n g p sy ch o a ct i v e subst ances for m ale and fem ale st udent s ( n= 200)
e l a
M Female Total
N % N % N %
, r e e b f o n a c 1 ( l o h o c l a f o e s o d e n O * ) a ç a h c a c f o l m 0 4 , e n i w f o s s a l g
1 92 53 81 47 173 86.5
d e k o m s s t e r r a g i C
* 86 66 44 34 130 65
* e t t e r a g i c e l o h w
A 67 75 22 25 89 44.5
* a n a u j i r a
M 48 84 9 16 57 28.5
e n i c i d e m ( g u r d l a g e l l i f o d n i k e m o S * . ) n o i t p i r c s e r p s ' r o t c o d a t u o h t i
w 39 36 14 39 53 26.5
* ) f f u n S r o w e h C ( o c a b a t s s e l e k o m
S 26 86 4 14 30 15
, l o s o r e a , e u l g , e n i l o s a g ( s t n a l a h n I * ) t n i a
p 21 72 8 28 29 14.5
* e n i m a t e h p m A / e n i m a t e h p m a t e
M 17 85 3 1.5 20 10
* ) k c a r c ( e n i a c o
C 8 4 3 1.5 11 5.5
) e t o y e p , s d i c a ( D S
L 8 4 3 1.5 11 5.5
) A M D M ( y s a t c x
E 8 4 3 1.5 11 5.5
a l r e
M 2 1 0 0 2 1
Significant differences am ong t he class for p.< 0.005
Dif f er en ces w er e n ot ed bet w een m ales an d
fem ales but it m ust be not ed t hat while t his sam ple is
large, it is a not necessarily represent at ive of t he t his
par t icular st udent at populat ion.
I n relat ion t o t he age when alcohol was used
for t he first t im e, t he average age was of 13 ( SD = 2
y ear s) w it h a r ange of 10 t o18 y ear s of age, When
a sk e d a b o u t e x p e r i m e n t a l u se o f d r u g s ( e x ce p t
alcoh ol) t h e av er age w as of 1 6 ( SD = 1 . 6 4 y ear s)
w i t h a r an g e o f 1 0 t o 1 8 y ear s o l d . Th ese r esu l t s
indicat e t hat som e st udent s experim ent ed wit h or used
bot h alchol and dr ugs pr ior t o ent er ing univ er sit y.
Of t he m ale st udent s, 36 ( 18% ) report ed t hat
t h ey dr ov e 7 or m or e t im es u n der t h e in f lu en ce of
alcoh ol. Of t h e f em ale st u d en t s, 1 4 ( 7 % ) r ep or t ed
t h at t h ey d r ov e w h ile in t ox icat ed on at least on ce
occasion .
I n t his sam ple, 150 ( 75% ) st udent s report ed
b e i n g i n a st a t e o f d r u n k e n n e ss o n a t l e a st o n e
occasion . Of t h e m ales, 6 6 ( 3 3 % ) r ep or t ed b ein g
drunk on 7 or m ore occasions, whereas, of t he fem ales,
2 4 ( 1 3 . 5 % ) r ep o r t ed b ei n g d r u n k o n ce o r t w i ce.
Am ong t he m ales 55 ( 27.5% ) report ed t he experience
of “ bein g h igh or in t ox icat ed by t h e u se of dr u gs”,
an d 4 7 ( 2 3 . 5 % ) bein g dr u n k in t h e u n iv er sit y. Th e
m ale st udent s in t his sam ple were m ore likely t o report
int ox icat ion t han w er e t he fem ales.
When evaluat ing t he use of subst ances in t he
l a st 3 0 d a y s, w e f o u n d t h a t 3 5 ( 1 7 . 5 % ) sm o k ed
cigaret t es from 1 t o 19 days, and t hat 24 ( 68.6% ) of
t hese w er e m ale st udent s. As for t he use of alcohol
1 7 5 , ( 7 5 % ) had at least one dr ink and t his include
100 ( 100% ) of t he m ale st udent s. Of t he 100 m ales,
30 ( 30% ) had or current ly used m arij uana. The m ale
s t u d e n t s r e p o r t e d m o r e f r e q u e n t u s e o f t h e s e
subst ances t han did t he fem ale st udent s.
I n t h e 3 0 d a y s p r i o r t o c o m p l e t i n g t h e
quest ionnaire, 5( 2.5% ) of st udent s report ed t hat t hey
h ad u sed in h alan t s on at least on e occasion . On e
st u den t ( 0 . 5 % ) r epor t ed u se of cocain e an d 8 ( 4 % )
t h e u se o f LSD . Th e r ep o r t ed u se a cr o ss g en d er
appear ed t o be equiv alent .
Wh en ask ed abou t t h e u se of psy ch oact iv e
su b st an ces d u r in g t h e p ast m on t h w h ile at t en d in g
univ er sit hy, 11( 5.5% ) of t he m ale st udent s r epor t ed
sm ok in g ( m ar ij u an a?) f or at least 1 t o 2 day s an d
21( 10.5% ) had at least one dose of alcohol. The sam e
n u m b er r ep or t ed t h at t h ey h ad sm ok ed m ar ij u an a
ov er t he sam e t im e per iond.
Of t h e m ale st u d en t s, 5 3 ( 2 6 . 5 % ) r ep or t ed
t hat t hey enj oyed alcoholic drinks enough t o becom e
a bit h igh , w h ile of t h e fem ale st u den t s 3 7 ( 1 8 . 5 % )
r epor t ed t hat t hey did not dr ink at all. Am ong t hose
w h o did dr in k 3 0 ( 1 5 % ) r epor t ed t h at t h ey lik ed t o
have one or t wo sips, a drinking habit wit hin t he lim it s
consider ed of low r isk .
I n r e f e r e n c e t o d r i n k i n g a n d d r i v i n g ,
95( 47.5% ) r epor t ed t hat t hey dr ov e on at least one
occasion u n d er t h e in f lu en ce of alcoh ol. Of t h ese,
21( 10.5% ) fem ale st udent s report ed t hat t hey did t his
once or t wice, whereas 36( 18% ) of t he m ale st udent s
report ed t hat t hey did t his 7 or m ore t im es.
Wh en ask ed ab ou t t h eir p er cep t ion of t h e
dam aging use of subst ances we found t hat 39( 19.5% )
m a l e s t u d e n t s c o n s i d e r t h e o c c a s i o n a l u s e o f
cigar et t es t o be ex t r em ely har m ful, w hile 45( 22.5% )
f e m a l e s t u d e n t s c o n s i d e r t h i s h a r m f u l . Fo r t h e
o cca si o n a l u se o f a l co h o l , o f t h e m a l e st u d e n t s
30( 15% ) r epor t ed t hat t hey consider ed t his har m ful
an d of t h e f em ale st u d en t s 4 0 ( 2 0 % ) con sid er t h is
harm ful. As t o t heir percept ion about t he harm in using
m ar ij u an a, b ot h t h e sex es 5 8 ( 2 9 % ) con sid er t h is
p r act ice ex t r em ely h ar m f u l. For am p h et am in e an d
ecst asy use, bot h genders unanim ously report ed t hat
t hek y consider ed t his pr act ice ex t r em ely har m ful.
We also f ou n d t h at 6 8 ( 3 4 % ) of t h e f em ale
w r o n g a n d 6 6 ( 3 3 % ) r e p o r t e d t h a t t h e u s e o f
m ar ij u an a w as v er y w r on g . Few er f em ale st u d en t s
i.e., 36( 18% ) report ed t hat t he use of alcoholic drink
w as not t ot ally w r ong.
Mo r e f e m a l e st u d e n t s r e p o r t e d t h a t t h e y
p er cei v ed a h i g h er r i sk f o r sm o k i n g o n e o r m o r e
p ack et s of cig ar et t es p er d ay ( 8 0 ; 4 0 % ) , sm ok in g
m a r i j u a n a o n c e o r t w i c e ( 4 6 ; 2 3 % ) , s m o k i n g
m ar ij u an a occasion ally ( 5 9 ; 2 9 . 5 % ) an d con su m in g
a l co h o l i c d r i n k s ( 6 8 ; 3 4 % ) t h a n d i d m a l e m a l e
st u den t s.
Bot h m ale and fem ale st udent s considered it
v er y easy t o obt ain cigar et t es and alcoholic dr ink s.
I n t h is sam ple, 7 2 ( 1 4 4 % ) of t h e st u den t s
report ed t hat it is possible t o obt ain drugs at part ies
or ev en t s ou t sid e t h e u n iv er sit y an d 1 3 1 ( 6 5 . 5 % )
report ed t hat it was possible t o find t hese subst ances
w it h in t h e u n iv er sit y, t h r ou gh con t act s w it h f r ien ds
( n= 119; 59.5% ) and drug dealers ( n= 91; 46% ) . The
r eason s t h at st u d en t s r ep or t ed f or u sin g alcoh olic
dr in k s w as t o h av e f u n ( n = 4 8 ; 7 4 % ) , escape f r om
t h e i r p r o b l e m s ( n = 1 1 8 ; 5 9 % ) a n d b e ca u se t h e i r
fr iends use t hem ( n= 108; 54% ) .
The st udent s est im at ed t hat on average 22%
( SD 14% ) of t he st udent s in t heir course sm oke less
t h an on ce a m on t h . Th e r an ge w as 1 0 t o 6 0 % . I n
r elat ion t o est im at ing t he num ber of t he classm at es
t h at h av e t r ied m ar ij u an a, st u d en t s r ep or t ed t h at
about 35% ( SD 23% ) of t he st udent s in t heir course
had t ried it . The range in t heir est im at es was from 10
t o 8 0 % . W h e n a sk e d a b o u a t t h e i r p e r ce p t i o n o f
punishm ent for t he use of subst ances in t he universit y,
95 ( 47.5% ) of t he st udent s replied t hat it is possible
for a st udent t o be suspended, expulsed or t ransferred
if t h ey w er e cau g h t u sin g or p ossessin g alcoh ol of
ot her dr ugs in t he univ er sit y. As t o t he possibilit y of
f in din g h elp f or t h e pr oblem s r elat ed t o t h e u se of
subst ances, we found t hat 99 ( 49.5% ) of t he st udent s
found t hat it is possible for a st udent t o find help in
t he univ er sit y.
The st udent s r epor t ed aggr essiv e or v iolent
b eh av iou r s t h at t h ey ex p er ien ced at t h e u n iv er sit y
over t he past 12 m ont hs. Of 200, 61 ( 30.5% ) st udent s
report ed t hat t hey were vict im s of m ockery ( bullying)
due t o t heir physical appearance or t he way t he spoke
an d w er e af r aid of bein g ph y sically h it . For t y - eigh t
( 24% ) report ed t hat t hey were vict im s of gossips and
39 ( 19.5% ) report ed t hat t hey were vict im s of lies on
4 or m or e occasions.
I n reference t o sexual act ivit y, 128 ( 64% ) of
t he st udent s report ed t hat t hey have or had had sexual
r elat ionships. Of t hese, 87 ( 68% ) w er e m ales.
I n d escr ib in g sex u al b eh av ior r ep or t ed b y
bot h m ales and fem ales, we found t hat 55 ( 27.5% ) of
t h e f e m a l e s t u d e n t s h a d n e v e r h a d a s e x u a l
r e l a t i o n sh i p . Of t h e m a l e st u d e n t s, 3 5 ( 1 7 . 5 % )
r epor t ed t h at t h ey h av e h ad m or e t h an on e sex u al
part ner and 20( 10% ) report ed t hat t hey used alcohol
or d r u g b ef or e en g ag in g in sex u al act iv it y. Of t h e
st udent s, 66 ( 33% ) report ed t hat t hey used condom s
and 43 ( 65% ) of t hese r esponses w er e fr om m ales.
I n relat ion t o t he problem s caused by t he use
of subst ance, 56 ( 28% ) of t he st udent s for got w hat
had happened or passed out follow ing t he ingest ion
of alcohol. Am ong t he st udent s t hat had used alcohol,
5 6 ( 2 8 % ) r ep or t ed t h at t h ey n ev er h ad p r ob lem s.
When using m ar ij uana, 9 r epor t ed t hat t he had had
ot her pr oblem s. The pr oblem s r elat ed t o t he use of
alcohol were m ore num erous t han t hose report ed due
t o t h e u se of m ar ij u an a. Male st u den t s w er e m or e
lik ely t o r epor t pr oblem s w it h subst ance abuse.
I n r ef er en ce t o h o n est y i n an sw er i n g t h e
quest ions, we found t hat t he m aj orit y of t he st udent s,
1 4 1 ( 7 0 . 5 % ) r esp on d ed t h at t h ey w er e h on est in
replying t o all t he quest ions. Of t hese, 92 were fem ale
st u den t s.
DI SCUSSI ON
The associat ion bet ween t he use of drugs and
t h e p r e se n ce o f r i sk b e h a v i o r s a m o n g f r e sh m e n
st udent s in a public Brazilian universit y was evaluat ed.
The use of drugs in t his populat ion is dist urbing. This
st udy was prelim inary and t he int ent was t o describe
d r u g u s i n g , r e l a t e d b e h a v i o u r s a n d p o s s i b l e
predisposing fact ors in bot h m ale and fem ale st udent s.
Th e v o l u n t e e r sa m p l e f o r t h i s st u d y w a s
com p osed of y ou n g st u d en t s in t h eir f ir st y ear of
univ er sit y. The m aj or it y consider ed t hem selv es t o be
a m em ber of a religious denom inat ion, lived wit h t heir
p ar en t s an d h ad m o v ed h o u se v er y l i t t l e i n t h ei r
for m at iv e y ear s. These char act er ist ics ar e consider ed
t o b e p r o t e c t i v e f a c t o r s a g a i n s t t h e u s e o f
psy choact iv e subst ances, alt hough t he use of dr ugs,
such as alcohol and cigar et t e m ay be pr esent in t he
fam ily unit ( i.e., fat her, m ot her, brot her or sist er) . This
can also favor t he use of t hese subst ances. Dat a are
sim ilar t o t hose found in ot her Brazilian universit ies( 4).
sam p l e f o r t h i s st u d y b u t p ar t i ci p an t s i n cl u d ed a
subst ant ial proport ion ( i.e., about 20% ) of t he eligible populat ion. There did not appear t o be great difference
in how m ale and fem ale st udent s in t his st udy used dr ugs or in how t hey dealt w it h t heir ow n or ot her s
a g g r e ssi o n o r v i o l e n ce . Fo r t h e m a j o r i t y o f t h e v ar iables, m ales r epor t ed m or e use of v ar ious t y pes
o f l i c i t a n d i l l i c i t p s y c h o - a c t i v e s u b s t a n c e s , consum pt ion st andar d ( fr equent and “ heav y ” use) .
Alcohol w as t he psy choact iv e subst ance t hat w as r epor t ed t o be m ost used by t he st udent s, w it h
8 6 per cen t r epor t in g som e u se in t h eir lifet im e, 7 1
percent report ing som e use in t he last 6 m ont hs, and 78.6% report ing som e use w it hin t he last few days.
I n t he last 30 days in t he universit y 46.5% of t he sam ple had used a psychoact ive subst ance which
i s co n si st en t w i t h f i n d i n g s i n p r ev i o u s st u d i es o f st udent s in Brazil( 3,12).
Th e u se of on e dr in k of alcoh ol am on g t h e m aj or it y of t h e st u d en t s is in con son an ce w it h an
Am er ican st udy t hat show s t hat m or e t han half t he st u d en t s u sed alcoh ol ex cessiv ely an d 4 0 % of t h e
st udent s report ed t hat on at least one occasion in t he last 2 w eeks t hey w er e int oxicat ed( 13).
Th e r eason s t h at t h e st u den t s r epor t ed f or
“ w hy y oung people use alcoholic dr ink s” ar e t o hav e f u n an d t o escape t h eir pr oblem s. Th e r eason t h at
t h e st u d e n t s g a v e f o r w h y t h e y l i k e t o u se t h e subst ances w as t o becom e “ high” or “ dr unk .
Ex per im ent al r esear cher s hav e r epor t ed t hat m any of t he behavioural changes are not only due t o
t he phar m acological use of alcohol, but also t hr ough
t he beliefs of t he t hose who use it( 14). The relat ionship bet ween alcohol and use of higher risk behaviors are
not only relat ed t o t he consequences of drinking, but a l so t o w h a t p e o p l e b e l i e v e i n d i f f e r e n t cu l t u r a l
cont ext s, i.e. drinkers can have different expect at ions w hen ex per iencing t he effect s of alcohol.
More m ale st udent s report ed t hat t hey drove w h ile d r u n k t h an d id t h e f em ale st u d en t s. Dr iv in g
u n d er t h e in f lu en ce of alcoh ol is on e of t h e m ost com m on h igh r isk fact or s am on g y ou n g people an d
h as b een r elat ed t o in cr eased f at alit y r at es in t h is
age gr ou p.
To b a cco u se w a s a l so r e p o r t e d b y st u d y
p ar t icip an t s. Th er e w as a p er cep t ion t h at u se w as h a r m f u l , a l t h o u g h t h e p r e v a l e n c e w a s s t i l l
con sid er ab le. Th e n u m b er of d ay s p er m on t h t h at st udent s sm oked was low ( t he m aj orit y was bet ween
1 and 2 days) which would suggest t hat use was not habit ual. For t he use of cigaret t es 65 percent report ed
t hat t hey had sm oked at least once in t heir life; 44.5
per cen t r epor t ed t h at t h ey h ad sm ok ed on at least on e occasion in t h e last 6 m on t h s; 1 7 . 5 p er cean t
r epor t ed t hat t hey had sm ok ed at least once in t he last few days ( 17.5% ) ; and 14 percent report ed t hat
t h ey h ad sm ok ed in t h e last 3 0 d ay s w h ile at t h e univer sit y. Such r esult s indicat e t hat t he st udent s of
t h i s sa m p l e h a v e sm o k ed m o r e f r eq u en t l y i n l i f e com pared t o report ed in anot her Brazilian st udy ( 12) .
Com par in g w it h an ot h er r elev an t st u dy( 1 5 ) in v olv in g t he st udent s fr om t he USP Cam pus of São Paulo, it
was report ed t hat t he prevalence of t obacco use was
50.5 percent in t he st udent ’s lifet im e and 20.16 percent in t he last few days. The age of report ed experim ent al
use of alcohol and dr ugs ( i.e., 13 & 16 r espect ively ) was very young so not associat ed wit h universit y life.
I n t h is st u d y w e f ou n d t h at m ale st u d en t s w er e m or e lik ely t o r ep or t t h at t h ed u sed alcoh ol,
i n h a l a n t s , a n a b o l i c s u b s t a n c e s , c r a c k , c o c a i n e , h allu cin og en s an d m ar ij u an a. Th e f em ale st u d en t s
were m ore likely t o report t hat t hey used t ranquilizers, am ph et am in es an d opiat es. Th e dif f er en t iat ion w as
v ery lit t le in t his st udy, as t he drug use t hat was m ost f r e q u e n t l y r e p o r t e d w a s a l c o h o l , t o b a c c o a n d
m ar ij u an a.
Th e t h i r d t y p e o f d r u g m o st u sed a m o n g st u den t s w as m ar ij u an a. Th is dr u g is con sider ed t o
b e t h e i l l i ci t d r u g m ost u sed am on g t een ag er s of dev eloped count r ies and t he fr equency of m ar ij uana
use cont inues t o incr ease. A possible ex planat ion for t his is t he percept ion t hat m arij uana is a “ light drug”,
wit hout m any consequences t o t he individual’s healt h,
in cont rast t o ot her illicit drugs( 8).
Th e u se an d abu se of alcoh ol est ablish es a
sig n if ican t p r ob lem am on g st u d en t s in t h e v ar iou s cam pu ses. Resear ch er r elat e t h at appr ox im at ely 9 0
p er cen t of t h e st u d en t s u se alcoh ol an d 2 5 t o 5 0 percent use it “ heavily”( 13). St udent s t hat drink heavily
a r e m o r e l i k e l y t o e n g a g e i n h i g h r i sk p h y si ca l , e m o t i o n a l , a n d se x u a l b e h a v i o u r s w i t h n e g a t i v e
consequences such as being in accident s, inj ur ed at school and im pair ed sex ual healt h.
The m aj orit y of t he st udent s t hink it possible
t o o b t a i n d r u g s a t p a r t i e s o r e v e n t s o u t o f t h e u n i v er si t y ( 7 2 % ) w i t h i n t h e u n i v er si t y ( 6 5 % ) , o r
t hrough friends ( 59.5% ) . The use of drugs and ot her high r isk behav ior s at t he cam puses can be st r ongly
r elat ed , alt h ou g h m an y y ou n g p eop le w h o ar e n ot u n iv er sit y st u den t s r epor t t h at t h ey u se of alcoh ol.
t he pr obabilit y of using t hese subst ances. Ther e ar e various reasons and purposes for drinking, which have been shown t o be influent ial in m aking a decision about
w h et h er or n ot t o u se of alcoh ol. Th e p u r p oses of drinking are oft ennot relat ed t o heavy drinking but t o
social d r in k in g w h ich is p r esen t am on g t h e y ou n g p eop le.
N o t a l l t h e u n d e r g r a d u a t e co u r se s o f f e r in f or m at ion w it h r esp ect t o t h e u se of d r u g s. I t is n e c e s s a r y t o d i s c u s s t h e n e c e s s i t y o f i n c l u d i n g
in f or m at ion ab ou t t h e u se of illicit d r u g w it h in t h e univ er sit y cur r iculum . Less t han half of t he st udent s
report ed t hat t hey t hought it possible for a st udent t o be suspended, expulsed or t ransferred if caught using or p ossessin g alcoh ol or ot h er d r u g s at u n iv er sit y.
Th is f in d in g can b e r elat ed t o t h e lack of sp ecif ic p o l i ci e s a b o u t t h e u se o f d r u g s o n t h e ca m p u s. Re se a r ch e r s i n d i ca t e t h a t t h e g e n d e r ca n b e a n
indicat or of violence report ed in schools. Men probably get involved m ore in violent incident s relat ed and t hese
are usually m ore t hreat ening or dam aging t han t hose in w hich w om en becom e inv olv ed.
I n s t u d i e s a b o u t y o u n g p e o p l e w h o u s e p sy ch oact iv e su b st an ces an d en g ag e in ag g r essiv e b e h a v i o r, t h e r e h a s b e e n a n e m p h a s i s p h y s i c a l
v iolence( 8). How ev er, t hese behav ior s ar e only som e of t he aggressive responses t o int erpersonal conflict s.
Dur ing an ar gum ent , for inst ance, y oung people can engage in aggressiveness such as pushing and hit t ing as a r esponse t o feelings of host ilit y These answ er s
do not cont ribut e t o solving t he problem or resolving in t er per son al con flict s.
Th e u se of p sy ch o- act iv e su b st an ces lead s t o a h igh er pr obabilit y of en gagin g in ot h er h igh er r isk behav ior s such as not using condom s or hav ing
m o r e s e x u a l p a r t n e r s . On e o f t h e f a c t o r s t h a t cont ribut e t o t he risk of acquiring sexually t ransm it t ed
diseases is t he behavior relat ed t o t he use of alcohol an d psy ch oact iv e dr u gs pr ior t o en gagin g in sex u al act iv it y. Ev en p eop le w h o d o n ot in j ect d r u g s b u t
con su m e t h em in an ot h er w ay can b e in f ect ed b y m e a n s o f se x u a l r e l a t i o n sh i p s w i t h o u t co n d o m s.
Var iou s st u d ies h av e sh ow n t h at p eop le u n d er t h e ef f ect of alcoh ol f r eq u en t ly g et in v olv ed in sex u al act iv it iy w it hout pr ot ect ion.
CONCLUSI ON
Alt hough t his st udy has been done wit h a
non-r epnon-r esent at iv e sam ple it w as possible t o ident ify t he
c h a r a c t e r i s t i c s o f t h e f r e s h m e n u n d e r g r a d u a t e st u d en t s at t h is u n iv er sit y. I t was also p ossib le t o
ident ify t he st andard use of drugs wit hin and out side of t he univ er sit y env ir onm ent and t o ev aluat e som e of t he high risk behaviors for bot h m ales and fem ales.
Th e r elat ion sh ip b et w een t h e u se of p sy ch o- act iv e su b st a n ce s a n d v i o l e n ce i s m u l t i d i m e n si o n a l a n d
condit ioned by social fact or s.
We id en t if ied t h e p r esen ce of r ecr eat ion al dr u g u se am on g t h e st u den t s. Alcoh ol con t in u es t o
be t he drug which is m ost frequent ly used by st udent s, followed by t obacco and m arij uana. The m ale st udent s
m o s t o f t e n r e p o r t e d h i g h e r c o n s u m p t i o n a n d frequency in psychoact ive drug use and also use of a g r eat er v ar iet y of su b st an ces t h an d id t h e f em ale
st u d en t s. Th e f em ale st u d en t s w er e m or e lik ely t o r ep or t lig h t u se alcoh ol w it h in t h e lim it s of social
d r in k in g , w h ile t h eir m ale cou n t er p ar t s w er e m or e lik ely t o r epor t t hat t hey dr ank t o get dr unk or high and also as a form of escapism . The “ heavy- drinking”
ep i so d es ar e a p h en o m en o n am o n g st u d en t s an d st udent s t hat drink excessively were at increased risk
for a v ar iet y of consequences.
Th e m a l e s t u d e n t s r e p o r t e d h i g h e r fr equencies of sex ual act iv it ies, w it h m or e par t ner s,
while t he fem ale st udent s who had used psychoact ive su b st an ces w er e m or e lik ely t o r ep or t en g ag in g in
sexual act ivit y wit h less prot ect ion. The universit y can b e a v u l n e r a b l e e n v i r o n m e n t b e c a u s e o f t h e a v a i l a b i l i t y a n d u se o f p sy ch o - a ct i v e su b st a n ces,
alt h ou g h m an y st u d en t h ad u sed t h ese su b st an ce ex per im ent ally pr ior t o at t ending univer sit y.
Findings from t his st udy can be used t o design a st u dy w it h a lar ger an d r epr esen t at iv e sam ple of universit y st udent s. This fact can be a way t o discuss
t h e i n ser t i o n o f t h e d r u g t h em at i c i n t h e v ar i o u s co u r ses o f f er ed a t t h e USP Ca m p u s, b esi d es t h e
planning of policies for t he prevent ion in t he universit y con t ex t .
ACKNOW LEDGEMENTS
We ar e grat eful t o t he I nt er- Am er ican Dr ug A b u s e Co n t r o l Co m m i s s i o n / CI CA D , t h e OA S
Sch olaish ip Pr ogr am , t h e Gov er n m en t of Japan , all Facult y of t he Univ er sit y of Alber t a/ Canada, and t he
e l e v e n r e p r e s e n t a t i v e s f r o m t h e s e v e n La t i n -A m e r i c a n c o u n t r i e s t h a t p a r t i c i p i t e d i n t h e “ I I nt er nat ional Resear ch Pr ogr am ”, im plem ent ed at t he
REFERENCES
1. Lange, JE, Clapp JD, Turrisi R, Reavy RL, Jaccard J, Johnson MB, et al. College Binge Drinking: What I s I t ? Who Does I t ? Alcoh olism : Clin Ex p Res 2 0 0 2 ; 2 6 ( 5 ) : 7 2 3 - 3 0 .
2. Bot vin GJ, Bot vin EM. Ruchlin H. School- based approaches t o d r u g ab u se p r ev en t ion : ev id en ce f or ef f ect iv en ess an d suggest ions for det er m ining cost - effect iv eness. I n: Nat ional I n st i t u t e o n D r u g Ab u se. Co st - b en ef i t / co st - ef f ect i v en ess r e s e a r c h o f d r u g a b u s e p r e v e n t i o n : i m p l i c a t i o n s f o r pr ogram m ing and policy. Washingt on; Gov t Pr int Off.; 1998. ( NI DA Resear ch Monogr. n. 1 7 6 . ) .
3 . An d r ad e AG, Qu eir oz S, Villab oim RCM, César F, Alv es MCGP, Bassit AZ, et al. Uso de álcool e dr ogas ent r e alunos d e g r ad u ação d a Un iv er sid ad e d e São Pau lo ( 1 9 9 6 ) . Rev ABP- APAL 1 9 9 7 ; ( 1 9 ) : 5 3 - 9 .
4 . Ker r - Cor r êa F, An drade, AG, Bassit , AZ, Boccu t o, NMVF. Uso de álcool e por est udant es de m edicina da UNESP. Rev Br as Psiq u iat r ia 1 9 9 9 ; 2 1 ( 2 ) : 9 5 - 1 0 0 .
5 . Car lin i- Cot r in B, Car lin i EA, Silv a ARF, Bar b osa MTS. O uso de drogas psicot rópicas por est udant es de 1º . e 2º . graus da rede est adual, em dez capit ais brasileiras, 1987. I n: Cent ro de Docum ent ação do Minist ério da Saúde. Brasília ( DF) : MS; 1 9 8 9 . n . 9 - 8 4 . ( Sér i e C: Est u d o s e Pr o j et o s Co n su m o d e dr ogas psicot r ópicas n o Br asil em 1 9 8 7 ) .
6 . Gal d u r ó z JCF, D ’Al m ei d a V, Car v al h o V, Car l i n i EA. 3 . Levant am ent o sobre uso de drogas ent re est udant es de 1o. e 2 o . g r au s em 1 0 cap i t ai s b r asi l ei r as ( 1 9 9 3 ) . São Pau l o : CEBRI D/ Escola Pau list a d e Med icin a ( UNI FESP) ; 1 9 9 4 . 7. Scivolet t o S, Tsuj i RK, Car m it a HNA, Queir óz S, Andrade, A G. Ga t t a z W F. Re l a ç ã o e n t r e c o n s u m o d e d r o g a s e com port am ent o sexual de est udant es de 2º grau de São Paulo. Rev Br as Psiq u iat r ia 1 9 9 9 ; 2 1 ( 2 ) : 8 7 - 9 4 .
8. Fagan J. I nt oxicacao and agression in drugs and crim e. I n Crim e and Just ice: a review of reserch. Chicago: Univ Chicago Pr e ss; 1 9 9 0 .
9. Lav ine R. Psy chophar m acological t r eat m ent of aggr ession a n d v i o l e n c e i n t h e s u b s t a n c e u s i n g p o p u l a t i o n . J Psy ch o act i v e Dr u g s 1 9 9 7 ; 2 9 ( 4 ) : 3 2 1 - 9 .
10. Feldm an M. Cr im inal behav ior : a psy chological analy sis. London: Wiley ; 1 9 7 7 .
11. Yout h v iolence in t he Unit ed St at es. Cent er for Disease Cont r ol and Pr ev ent ion. [ ser ial online] 2000 [ cit ed 2004 Set 3 ] ; ( 1 ) : [ 2 4 s c r e e n s ] . A v a i l a b l e f r o m : U RL: h t t p : / / w w w . cd c. g ov / n cip c/ f act sh eet s/ y v f act s. h t m
12. Ker r - Cor r êa F, Dalben I , Tr inca L, Sim ão MO, Mat t os PF, Cerqueira ATAR, Mendes AA. I Levant am ent o do uso de álcool e d r o g a s p o r e s t u d a n t e s d a U N ES P. S ã o Pa u l o ( S P) : Pu b l i ca çã o VUNESP 1 4 ; 2 0 0 1 .
13. Wechsler H, Dow dall GW, Maenner G, Gledhill- Hoyt J, Lee H. Ch an ges in bin ge dr in k in g an d r elat ed pr oblem s am on g Am er ican colleg e st u d en t s b et w een 1 9 9 3 an d 1 9 9 7 . J Am Coll Healt h 1 9 9 8 ; 4 7 : 5 7 - 6 8 .
14. Marlat t GA, Baer JS, Kivlahan DR, Dim eff LA, Larim er ME, Quigley LA, et al. Scr eening and br ief int er v ent ion for highrisk college st udent drinkers: Result s from a t w o year follow u p assessm en t . J Con su lt i Clin Psy ch ol 1 9 9 8 ; 6 6 ( 4 ) : 6 0 4 -1 5 .
15. St em pliuk VA. Uso de drogas ent re alunos da Universidade de São Pau lo: 1 9 9 6 v er su s 2 0 0 1 . [ Tese] . São Pau lo ( SP) : Facu ld ad e d e Med icin a/ USP; 2 0 0 4 .