Annals of “Dunarea de Jos” University of Galati Fascicle I. Economics and Applied Informatics
Years XXII – no3/2016
ISSN-L 1584-0409 ISSN-Online 2344-441X
www.eia.feaa.ugal.ro
Impact of Contemporary Crisis on the European Union's
and United States of America’s Economies
Mihaela NECULITA
A R T I C L E I N F O A B S T R A C T
Article history:
Accepted November Available online December
JEL Classification
F , F , F
Keywords:
Trade, )ntegration, Globalization, Global economy, Economic crises
Globalization is a complex set of processes with the purpose of achieving an international integration at economic, military, political, socio-cultural and security level, aiming to equalize the standards of living and develop on a global scale. Just because of globalization, the effects of a global crisis can propagate extremely fast at planetary level, and countries must find the resources to cope with the shocks that may arise. The contemporary phenomenon of globalization, which has widened the global area of economies, sectors and firms confrontation, has laid an emphasis on their competitiveness importance for their favorable position in the international competition. )n the same time, has obliged to take proper and concerted measures to stimulate the determining factors of action and to take better advantage of their effects. The purpose of the paper is to determine whether an increase in integration could reduce the disparities between countries. The States and regions need significant financial help to solve various problems and achieve their potential of growth.
© EA). All rights reserved.
1. Introduction
At the end of , global economy was taking its first steps towards the deepest crisis in the post-war period. Originally triggered in the form of a financial crisis and subsequently deepened by a generalized economic recession, the present crisis is distinguished through its global nature, all the world regions being maked by the economic slowdown, or even by production contractions, as well as by the unprecedented decline in the international trade. Global size of the crisis highlights the high degree of interconnection existing among the financial and goods markets which has contributed, in turn, to spreading the negative effects of the global financial crisis on the actual economy.
The last decade emphasized crystal clearly both facets of globalization. For most part of the period, the proceedings in terms of efficiency, steady prices and sustainable economic growth were due especially to a decrease in the economic distance and closer interdependence of markets. Nevertheless, the same forces served for extending and amplifying the financial and economic turbulences, proving that the global economy benefits are associated with risks, but also with opportunities. Over the last years, global economy has become multipolar, the economic power being distributed among many countries and regions, where risk and volatility go together with the opportunities for economic growth and development.
2. Methodology
The use of models in economic fields is influenced by a great variety of local, national and international decisions. Only parts of these are registered in the statistic data. )n order to reach the objective of this paper we focused on data regarding economic indicators. This paper aims to develop an objective analysis of the current state of globalization and regionalization using data and statistics provided by international statistics institutions.
3. Global integration versus regional integration
Globalization, marked by the progresses in information technology and communications, by a deeper economic opening and an increase in the geographical scope of multinational companiese, causes markets to be extensively integrated and interdependent. (owever, at the same time, a more marked integration of the markets means that economic and financial shocks are transmitted over the national boards to a speed much higher than in the past, no country in the world being immune to the global interdependencies. The European Union EU has been severely affected by the disturbances of the international financial market and the deep recession in the global economy. The extent of adverse incidents of crisis on the EU'strade and investment
flows mirrors the close commercial and financial relations existing among the Member States' economies, on the one hand, and among the EU and rest of the world, on the other hand Daianu .
The effects of the longest and deepest economic recession from the EU history – as described by the European Commission in its economic forecast from the autumn of – have taken the shape of an unprecedented decline of transborder transactions carried out at intra-EU and extra-EU level.
years have passed since the outbreak of financial crisis and a worrying situation in Europe still exists. )n the U.S.A. it seems that the non-conventional policies of the US central bank have begun to come to fruition and an economic revival is also seen in an unemployment rate decreased below . % at the end of
, from over % in the first years of crisis.
Table . Unemployment rate–EU and USA –
-EU . . . .
USA . . . .
Source: https://data.oecd.org/unemp/unemployment-rate.htm
Europe is being in a major deadlock, with a deep crisis of the EURO zone and facing very slow economic growth, even a quasi - stagnation Summers, Unemployment rate in the European Union/ EU is on the average considerably higher than in the USA and is generating conflicts.
Figure . Unemployment rate EU and SUA–
-Source: https://data.oecd.org/unemp/unemployment-rate.htm
These conflicts are felt among net donor countries and net receiving countries of European funds; they are felt heavily in the Eurozone, among creditor countries and debtor countries. )n the E. U. the public debt growing on the average by over % of the GDP, in an effort to salvage the banks, combines with very large private debts, which have accumulated.
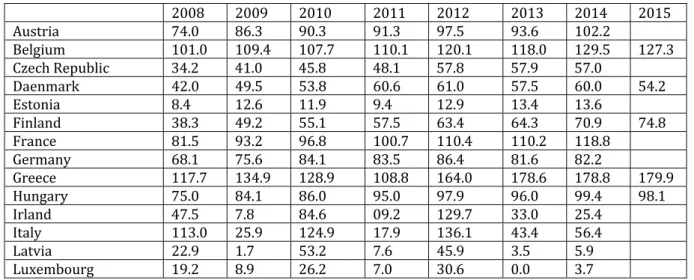
Table . Public debts - EU and USA –
-Austria . . . .
Belgium . . . .
Czech Republic . . . .
Daenmark . . . .
Estonia . . . .
Finland . . . .
France . . . .
Germany . . . .
Greece . . . .
(ungary . . . .
)rland . . . .
)taly . . . .
Latvia . . . .
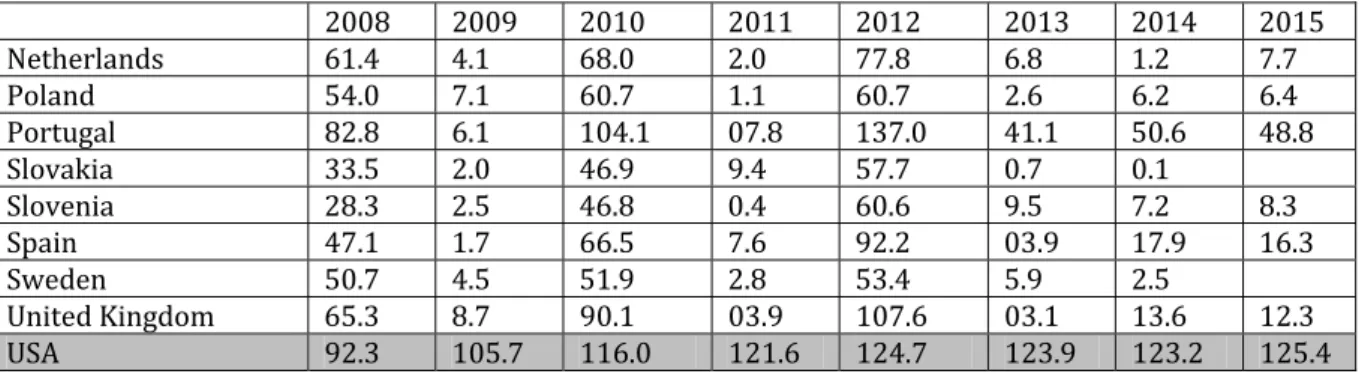
Netherlands . . . .
Poland . . . .
Portugal . . . .
Slovakia . . . .
Slovenia . . . .
Spain . . . .
Sweden . . . .
United Kingdom . . . .
USA . . . .
Source: https://data.oecd.org/gga/general-government-debt.htm
To the rather complicated economic situation is added the geopolitical crisis caused by the annexation of Crimea by Russia and the situation in Ukraine. For the first time, the European Union has realized the importance of continental security arrangements which would protect the European borders. The chaos created by the extremist groups attacks, are other tests for the European countries
The financial and economic crisis overlapped with the crisis of social insurance system welfare state , which, in turn, is caused by the demographic evolutions and the decrease in the competitively of many European economies. The fact that in the EU, Eurozone records external balance surpluses of the current account is a deceitful indication, since Germany is an essential contributor to this result, to which some Nordic countries are added. As a matter of fact, the EU although is one of the richest regions of the global area, is fragmented in respect of economic performance. (ence the high threat to the Union, against the background of slow growth perspective and the deepening of economic and social disparities. This is explained through the fact that Eurozone is not a federal entity that possesses the absorption means of asymmetric shocks. We have to take into account the unemployment rate of more than % from Spain and Greece which among young people reaches % and the average of around . % at the end of in the EU .
Figure . Public debts - EU and USA –
-Source: https://data.oecd.org/gga/general-government-debt.htm
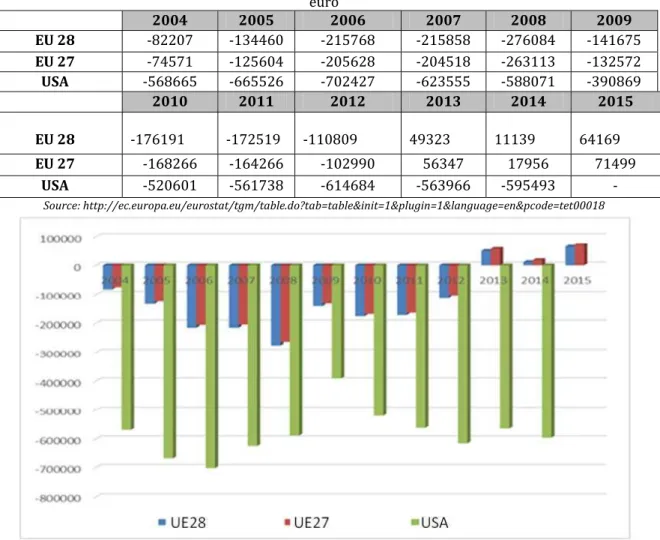
to . in . Following the trade surplus went through a declining trend. Thus, in it was recorded a surplus of only . billion €, and in of just . billion €. For , the surplus was of only . billion € and for , compared to the sharp decrease from , the surplus amounted to . billion .
Table . Balance of the European Union s of trade with the United States of America - million euro
2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009
EU 28 - - -
-EU 27 - - -
-USA - - -
-2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
EU 28 - -
-EU 27 - -
-USA - - -
Source: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/tgm/table.do?tab=table&init=1&plugin=1&language=en&pcode=tet00018
Figure . Balance of the European Union s of trade with the United States of America - million euro
The global trade of goods has increased both in the USA, and in the EU until . )n there has been a drop in the global trade of goods, both of the USA and of the EU. With only one exception, all decreases amounted to over %.
)n terms of value, the total imports of the European Union had an upward movement, from until imports undergoing an increase from . billion € to . billion €. This rise is explained, particularly by the increase in the number of members of the Union. The European Union s total exports had an upward trend between - . Thus, from the amount of . billion Euro recorded in , it has reached around . billion € in . The Union s weight of exports to the USA, in total exports, between - , has increased, in the first stage, followed by a drop for the rest of years. )n this manner, in , the export rate went up by . %. Since the exports have fallen down yearly, from . % in , until , when it has been recorded the most dramatic decline, . % compared to the previous year. )n the decrease was smaller in comparison with , but kept on being significant %. The bilateral trade between the USA and EU arrived at mammoth-values: approximately billion euro for goods and billion for services. per cent of the EU foreign investments are performed in the USA, and per cent of the USA foreign investments are made in the EU s Member States.
The poor results of the European governments and institutions in managing the crisis, delaying the economic recovery, emphasized the skepticism about the European project. The victory of Syriza grouping in Greece, the rise of Podemos movement in Spain, National Front in France, the vehemence of political parties that reject the traditional parties mainstream , show a deterioration in the political process by promoting some classes of politicians who reject the democracy and liberal values.
The crisis has revealed a failure of certain cognitive and operational models. Perhaps the most telling example is the thesis that price stability is equivalent with financial stability, with the complete use of resources. A consequence of these failures is that central banks and governments are forced to resort to unconventional methods in order to cope with the extreme situation represented by the Great Recession as this crisis is named so as to distinguish it from the Great Depression of the last century .
Jaime Caruana, General Director of the Bank for )nternational Settlements B)S , shows that the last decades have been accompanied by a massively deficient allocation of resources corresponding to a large speculative bubble Caruana, .This allocation went in tandem with over indebtedness, which makes inevitable a process of financial disintermediation, with impact on investments and consumption.
Koo,
(ence the extent of necessary corrections, severe economic and social costs induced by imbalances. For stimulating investments and encouraging consumption should operate strongly negative interest rates , which is very difficult when inflation is closed to zero, or when there is even a deflation.
The central banks had to take much of the burden of supporting the economy, a entered into a logic of action that can no longer bet on simple rules, apparently inerrable, such as Taylor s rule ; as Olivier Blanchard, the )MF chief economist, said „monetary policy will never be the same , Blanchard, while the economic policy will have to avoid the „ dark corners . Larry Summers believes that there is a trade-off between the efforts of economic revival and financial stability; )f we want to avoid in the future the speculative bubble, it must implements the credit control macro-prudential tools Blanchard, Ostry, .
)n the world of business, crisis shown background problems of the models that ignore systemic risks, emphasized the importance of trust in the relation among companies banks, other financial institutions and customers.
Robert Okun specified the relation between equality and efficiency- the market economy requires differentiation of labor remuneration according to the performance. But there are critical thresholds that can make the economy to function less well, even bad. Blatant inequalities of income and population aging influence the economic growth.
)f the control system has faults in resources allocation and fails to respect economic freedom, laissez-faire proves its limits in avoiding precarious balances. The analyzes of Thomas Piketty , and of certain economists from OCDE şi )MF advocates for public policies that regard income distribution, that combines private sector with the production of public goods generating economic, social and political capital. Too much of the economic activity has come to reflect a competition in which "the winner takes all". Under these circumstances and taking into account zero sum games of the global economy, there is no way to be unconcerned to what is happening to the middle class – on which depends the endurance of a democracy.
As concerns the emerging countries, changing the optics of the )MF in respect of capital markets liberalization shows an alienation from the simplistic approach of another time. The so called Washington Consensus, advocating the fast liberalization of capital markets, favored the occurrence of crises of the balances of payments in the emerging economies. )t is necessary an international regime to alleviate the negative externalities caused by the economic policies of the developed countries.
The cluster of crises may lead to a larger fragmentation, or to spurs of more marked integration. The Bank Union is an institutional spike to a deeper integration, even if is incomplete by lacking a solid financial arrangement and a scheme of collective guarantee for deposits. Those who do not believe in the European project would welcome the Union's further fragmentation and even its disappearance –inclusively by stimulating a secessionist trend.
4. Place the European Union and the United States in the world
The G group of most advanced economies in the world will record in a GDB rise of more than %, thus arriving at the fastest pace of growth recorded following . On the other hand, although the economic growth from the emerging states E will have a trend higher than of the G , this is slower than the trend of the last years. Member of the E economies of Brazil and Russia will shrink, China will slow, while )ndia will have a top performance.
Geopolitics, rather than the economy, will be a priority on the agenda of policy makers. The three major topics of the year are: immigrant s crisis in Europe, response of the international community to the crisis from the Middle East, the referendum about the fate of Great Britain's membership to the European Union.
The interest rates from the USA and Great Britain will rise in . Last year in December, the American Federal Reserve Fed set the tone through the first increase of interest after . )t is expected that Fed will continue to gradually increase interest rates in . Excluding any major unfavorable global shocks, the Bank of England is expected to follow the same line in . Compared to the USA and Great Britain, the Central European Bank, Bank of Japan, the People's Bank of China are expected to maintain a cautious monetary policy in .
The USA will lead the G league from the viewpoint of GDP increase trend. The United States economy will grow, contributing to the increase on the whole in the G economies in . The USA is expected to continue to create an average of approximately . jobs per month, in this way supporting also the consumption increase. Nevertheless, the USA will not have ensured the first position among the fastest growing economies within the G . Great Britain will be the main challenger in this competition, its economic growth being estimated between and , %.
The end of the Eurozone crisis: the Eurozone peripheral economies will have, for the second year consecutively, a faster growth than that of national economies.
The Greek crisis might light up again, but will not contaminate the entire block. Thus, it is foreseen that to mark at least beginning of the end of financial crisis in the enlarged Eurozone. Most imbalances in the peripheral economies being under control, and the structural reforms in progress, the Eurozone GDP is expected to increase in by about . % – the fastest growth rate after .
The exit of Great Britain from the European Union Brexit will push the EU from the second place to third place in the rating of the largest economies by GDP and Purchasing Power Parity PPP . Brexit changes the ranking of global leaders: the EU from the nd place . trillion dollars by GDP and PPP — goes to the
rd . trillion dollars . After China . trillion dollars and USA . trillion dollars .
5. Conclusions
To believe only in the force of moral values and of the open society for the purpose of stimulating states and economies is an utopia in the current global situation. )n the world economic competition, Germany might have a great say. The positive alternative is a strengthening of the integration processes, that would make the Union stronger, more robust, more durable. )n order to obtain a new image of the Europe it is necessary to adjust the Eurozone rules and principles that should not perpetuate the situation of mutual distrust.
A bolder approach of the challenges in the Eurozone, through significant investments a changed Juncker Plan, that should include more new public funds, together with those gathered from private sector , CEB efforts to fight deflation, national structural reforms, and, last but not least, an institutional reorganization, would provide a perspective of economic recovery. The social State should be reformed and it takes tenacity to change an European state of mind.
We agree that financial reforms need to continue and anti-trust legislation has to be also enforced in the financial industry. )t should be re-entered a Glass-Steagal type legislation to separate banking from trading retail, speculative transactions , and bank capitalization should be consolidated, Pagan, should be avoided abuses on the market, it should be changed a deeply flawed institutional culture; as Mark Carney, the head of Bank of England and president of the Financial Stability Board, „ we have not only rotten apples, but even the crate in which they are kept is not right . Carney, )n vain are introduced tighter rules for liquidity and capitalization if the institutional culture remains the same. Larosiere and Liikanen Reports in Europe, Turner, Vickers and Tyrie in Great Britain, show the right direction, but it takes more considering the size of certain banking groups. The capital markets that needs to develop in Europe should also be better regulated. Democracy is not predetermined; it needs to be permanently cared for, though what its citizens and institutions are doing.
Could Europe benefit from a new industrial revolution? Asia is becoming more and more efficient in the field of invention and innovation. Europe should review its social systems, education, to create jobs for young people, to fight against social and economic exclusion. The jobs problem will be increasingly higher under the pressure of certain innovations and globalization.
An agreement with the USA for free trade and investments Transatlantic Trade and )nvestment Partnership , may be of help, especially if it is built and implemented to the benefit of society on the whole, not of the big business circles. Such an agreement might have a geopolitical importance in a world multipolar and with severe tensions.
References
1. Daianu Daniel, „Limits of Openness”, in Which way goes capitalism, CEU Press, 2009
2. Summers Larry, „Reflections on the ‘New Secular Stagnation Hypothesis’”, in Teulings Coen and Richard Baldwin, Secular stagnation:
facts, causes and cures, a VoxeBook, 2014
3. Caruana Jaime, „Stepping out of the shadow of the crisis: three transitions for the world economy”, speech at the BIS General Assembley,
Basel, 29 June, 2014
4. Koo Richard, „The World in balance-sheet effect recession: causes, cure and policies”, Real World Economics Review, Issue No.58, 2011
6. Okun Robert, Equality and Efficiency: The Big Trade-off, Washington DC, Brookings, 1975
7. Piketty Thomas, Capital in the Twenty-first century, Cambridge (Mass), Harvard University Press, 2014
8. Blanchard Olivier, Ostry Jonathan, „The multilateral approach to capital controls”, VoxEU, 2012
9. Daianu Daniel, „Limits of Openness”, in Which way goes capitalism, CEU Press, 2009
10. Pagan Ugo et.al., „Is Europe overbanked?”, Reports of the Advisory Scientific Committee, No.4, ESRB, June, 2014
11. Carney Mark, „Speech at the Monetary Authority of Singapore”, 17 November, 2014
12. *** EUROSTAT
13. *** https://data.oecd.org/unemp/unemployment-rate.htm