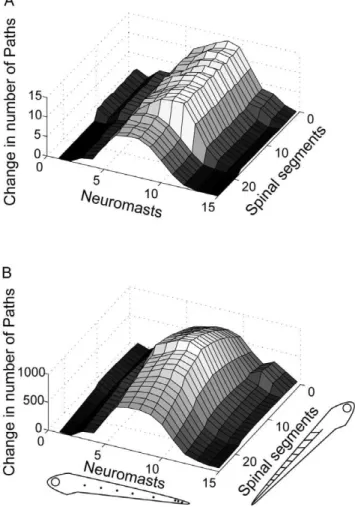
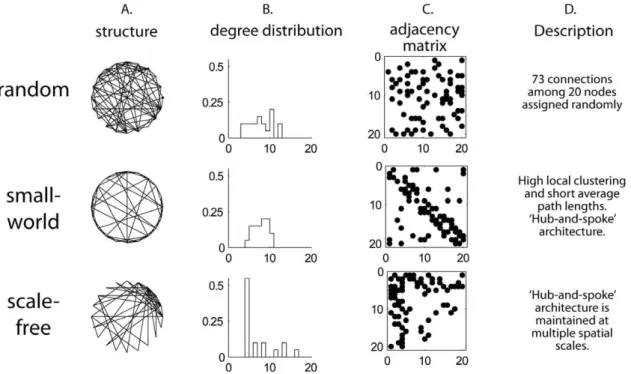
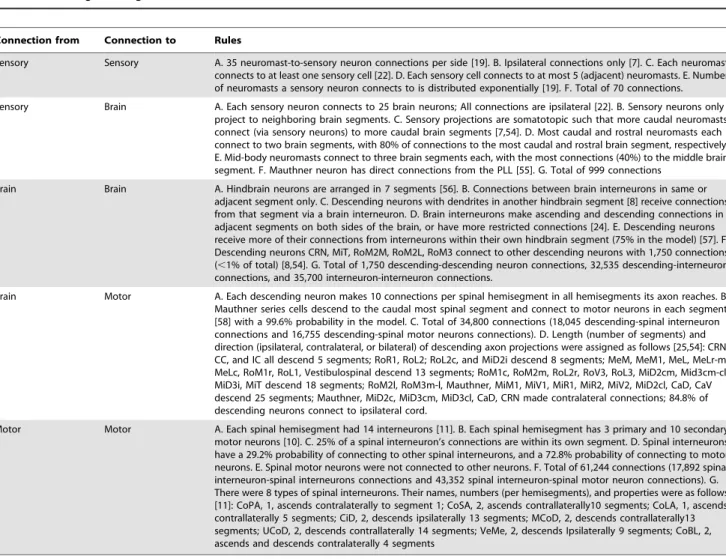
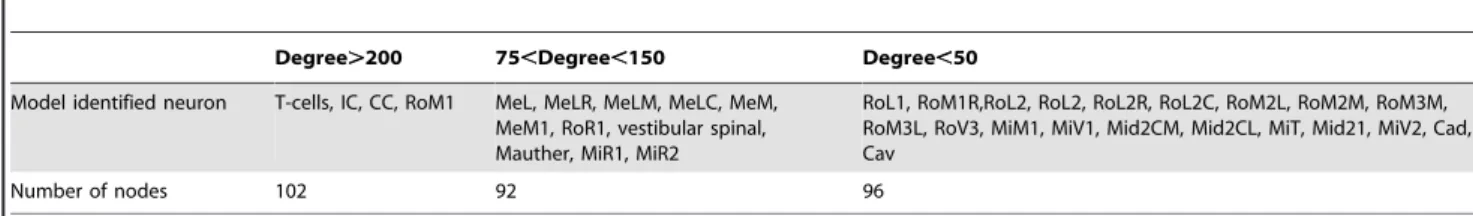
Graph theoretical model of a sensorimotor connectome in zebrafish.
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
The probability of attending school four our group of interest in this region increased by 6.5 percentage points after the expansion of the Bolsa Família program in 2007 and
Na hepatite B, as enzimas hepáticas têm valores menores tanto para quem toma quanto para os que não tomam café comparados ao vírus C, porém os dados foram estatisticamente
Laser capture microdissection (LCM) was used to study miRNA profiles in motor neurons of spinal cord tissue from SOD1 G93A mice, the best characterized model of ALS.. In
Using the data entered, the materials characteristics built in the database system, and the knowledge base on changes in prop- erties due to additional treatment, the
social assistance. The protection of jobs within some enterprises, cooperatives, forms of economical associations, constitute an efficient social policy, totally different from
Regarding hatchling sea turtles, (i) Are the hatching and emergence successes of ‘‘small’’ adult sea turtles lower than in ‘‘large’’ adult sea turtles (O1)?; (ii)
The model equations take into account the synaptic characteristics of the somatodendritic membrane of neurons in a morphofunctional unity of the spinal reflex activity.. This model
Our objectives were to assess the ef- fects of wood burn status, conditioning, and their in- teraction on macroinvertebrate community composi- tion, taxon and functional diversity,