TANIA SANTOS GIANI
EFEITOS DE UM EXTRATO AQUOSO DE BUZHONG YI QI WAN (Fórmula Magistral Chinesa) NA MARCAÇÃO DE CONSTITUINTES SANGUÍNEOS COM
TECNÉCIO-99m, NA MORFOLOGIA E NA FRAGILIDADE OSMÓTICA DE HEMÁCIAS DE RATOS
Wistar
Tese apresentada à Universidade Federal do
Rio Grande do Norte, para obtenção do título
de Doutor em Ciências da Saúde pelo
Programa de pós-graduação em Ciências da
Saúde.
Orientador: Mario Bernardo Filho
Co-orientador: Aldo da Cunha Medeiros
Natal / RN
UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DO RIO GRANDE DO NORTE
CENTRO DE CIÊNCIAS DA SAÚDE
PROGRAMA DE PÓS-GRADUAÇÃO EM CIÊNCIAS DA SAÚDE
Professor Doutor Aldo da Cunha Medeiros
TANIA SANTOS GIANI
EFEITOS DE UM EXTRATO AQUOSO DE BUZHONG YI QI WAN (Fórmula Magistral Chinesa) NA MARCAÇÃO DE CONSTITUINTES SANGUÍNEOS COM
TECNÉCIO-99m, NA MORFOLOGIA E NA FRAGILIDADE OSMÓTICA DE HEMÁCIAS DE RATOS
Wistar
PRESIDENTE DA BANCA: Prof.Dr. Mario Bernardo Filho.
BANCA EXAMINADORA
Prof. Dr. Mario Bernardo Filho – Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro
Prof ª. Drª. Adriana Augusto de Resende – Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte
Prof. Dr. Adenilson de Souza da Fonseca – Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro
Prof ª. Drª. Lúcia Maria da Cunha Galvão – Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte
Prof ª. Drª. Eulália Maria Chaves Maia – Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte
DEDICATÓRIA
In memoriam dedico este título aos meus pais Célia dos Santos Giani e Walmor Giani que me ensinaram a ter persistência, paciência e determinação, com o foco
humanitário sempre ao alcance dos sonhos.
In vivo dedico esta vitória aos meus filhos Daniel Giani e Alexandre Giani que me ensinaram a tolerância, a compreensão e a cumplicidade, mantendo o foco de nossas
vidas e de nossos sonhos.
E a todo aquele capaz de sonhar... planejar... construir... porém, sem jamais perder a
ternura.
AGRADECIMENTOS
Aos amigos... que nos dão todas as chances.
Aos inimigos... que nos dão o exemplo de como não ser e a força de vencer.
Aos colegas de laboratório...pelos exemplos.
Aos colaboradores na pesquisa...Doutor Adenilson de Souza da Fonseca; Dr. Mário Pereira dos Santos; Doutor Severo de Paoli; Doutor Giuseppe Antonio Presta; Doutor Sebastião David dos Santos-Filho; e Dra. Adalgisa Ieda Maiworm.
Ao meu seleto grupo de trabalho... a minha gratidão pelas horas absoluta e absurdamente inadequadas nos fins-de-semana, diurnas e noturnas, em cima do computador e nas bancadas do laboratório, muitas vezes com fome, sono e vertigens...
Ao orientador...Professor Doutor Mario Bernardo Filho, pela enorme capacidade de suportar as minhas desorientações.
Especiais...
Ao Professor Doutor Aldo da Cunha Medeiros e ao Professor Doutor José Brandão Neto, pelo sempre carinhoso recebimento em Natal e pela atenção constante com nossas necessidades. Minha profunda gratidão.
À Doutora Lúcia de Fátima Amorim por toda a ajuda dada aos contatos com a Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte e a hospitalidade carinhosa de seu recebimento em Natal.
LISTA DE ABREVIAÇÕES, SIGLAS E SÍMBOLOS
MTC Medicina Tradicional Chinesa
99mTc Tecnécio-99m
99Mo Molibdênio-99
NaCl Cloreto de sódio (Solução salina a 0,9%)
BYQW Buzhong Yi Qi Wan
C Hemácias
P Plasma
FS-C Fração solúvel da célula
FI-C Fração insolúvel da célula
FS-P Fração solúvel do plasma
FI-P Fração insolúvel do plasma
ATI% Percentagem de radioatividade
ANOVA Análise de variância
Bq Bequerel (unidade de atividade de amostra radioativa no Sistema
Internacional, sendo 1Bq≅1 deseintegração/segundo).
MBq Megabequerel
BC Blood cell
SF-BC cell soluble fraction
IF-BC cell insoluble fraction
FS-P plasma soluble fraction
IF-P plasma insoluble fraction
RBC red blood cell
µl microlitro
DO densidade ótica
rpm rotações por minuto
SnCl2 cloreto estanoso
Sn+2 íon estanoso
TCA áciodo tricloroacético
99mTcO4- íon pertecnetato
Na99mTcO
4 pertecnetato de sódio
UI Unidade Internacional
IPEN Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares de São Paulo
SUMÁRIO
Lista de abreviações ...………...………. vii
Sumario ix
Resumo……… x
1.Introdução... 01
2.Revisão de literatura... 03
3.Indexação de artigos... 06
4.Comentários, críticas e conclusões... 26
5.Referências... 28
6.Apêndices... 31
RESUMO
A pesquisa em Ciências da Saúde, assim como as avaliações clínicas têm sido
favorecidas pelo uso de isótopos radioativos, sendo que o tecnécio-99m (99mTc) tem
sido o mais utilizado para obtenção de radiobiocomplexos com finalidade de
diagnóstico. Diversas drogas naturais ou sintéticas são capazes de interferir na
marcação de estruturas sanguíneas com 99mTc, assim como na biodistribuição de
outros radiobiocomplexos. Os procedimentos relacionados com a medicina tradicional
chinesa também vêm ganhando destaque em todo o mundo. O objetivo deste estudo
foi investigar o efeito da possibilidade de alterações pelo extrato de Buzhong Yi Qi Wan
(fórmula magistral chinesa) nos constituintes do sangue marcados com 99mTc, (i) na
marcação de hemácias e proteínas plasmáticas, (ii) na morfologia, e (iii) na fragilidade
osmótica de hemácias de ratos Wistar. Foi observado, diminuição significativa (p<0,05) na marcação dos constituites sanguíneos com 99mTc, não alteração da morfologia das
hemácias e modificação da curva de fragilidade das hemácias (p<0,05). Esses efeitos
poderiam estar associados com determinadas propriedades de compostos químicos
presentes no extrato Buzhong Yi Qi Wan. O estudo tem caráter multidisciplinar com a
participação das seguintes áreas do conhecimento: Radiobiologia, Botânica, Fitoterapia
e Hematologia.
Palavras-chave: plantas medicinais; medicina chinesa; tecnécio-99m; eritrócitos;
1. INTRODUÇÃO
As aplicações dos radioisótopos em medicina nuclear podem ser como
fontes de radiação e como traçadores. No primeiro caso, o material biológico recebe
apenas as radiações emitidas pelo radionuclídeos usados; no segundo, o próprio
radioisótopo é incorporado no meio biológico que se deseja estudar (1). Sem o uso e a
disponibilidade dos traçadores radioativos (radiofármacos ou radiobiocomplexos), seria
menor e mais complexa a aquisição de informações relativas a um grande número de
processos bioquímicos e fisiológicos (2,3).
Atualmente, muitos estudos e práticas têm sido possíveis devido à
aplicação dos radiobiocomplexos, como os marcados com tecnécio-99m (99mTc).
Dentre esses, são encontradas hemácias e proteínas plasmáticas marcadas com esse
radionuclídeo (4). Tem sido descrito, que diversos produtos naturais ou sintéticos são
capazes de interferir na marcação das referidas estruturas celulares e de proteínas
plasmáticas (5, 6).
Uma vez que o uso de medicamentos a base de produtos naturais por
seres humanos vem crescendo, torna-se necessária a tentativa de melhor
compreensão dos efeitos biológicos destes produtos. Assim, estudos dos constituintes
do sangue in vitro e in vivo com modelos animais e radiofármacos, interagindo com plantas medicinais, drogas naturais ou sintéticas, torna-se um modelo atrativo para
estudos. Nosso modelo utiliza sangue de ratos Wistar para análise destes efeitos. O medicamento da medicina tradicional Chinesa (MTC) denominado Buzhong YiQi Wan (BYQW) foi objeto de escolha para estes estudos, sendo utilizado em forma de extrato
aquoso (100%=12,8mg/mL em NaCl 0,9%) em várias concentrações (100%; 50%;
Avaliamos e analisamos o efeito das várias concentrações do extrato:
(i) na marcação de hemácias e proteínas plasmáticas e celulares com 99mTc, na
forma de pertecnetato; (ii) na morfologia das hemácias; e (iii) na fragilidade osmótica de
hemácias de ratos Wistar.
Experimentos realizados com sangue in vitro apresentaram resultados que, estatisticamente analisados com significância (p<0,05), demonstram alterações
devido à interações de compostos do medicamento BYQW com o processo de
radiomarcação com 99mTc, além de hemolisar eritrócitos.
Na literatura existente nas principais bases de dados científicos, não
foram encontradas informações à respeito, sendo portanto, inéditos seus resultados.
Outros estudos in vivo estão sendo desenvolvidos, bem como estudos com as plantas constituintes do medicamento, para vermos as possíveis ações isoladas.
O desenvolvimento da Tese de Doutorado, ao longo destes dois anos e
meio, permitiu-me desenvolver a capacidade de trabalho em equipe, além de adquirir
conhecimentos na radiofarmácia experimental e na Medicina Nuclear (através dos
seminários internos realizados e dos Congressos freqüentados). Estes conhecimentos
serão úteis para as ações em projetos futuros, junto aos grupos de pesquisa da
Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro e/ou Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do
Norte, ou em qualquer outro grupo de trabalho.
2. REVISÃO DE LITERATURA
Ervas e produtos naturais, os mais variados, vêm sendo usados pela
medicina popular há milênios sem o conhecimento exato de seus efeitos nas interações
de seus biocomplexos (7,8,9). Desta forma, as interações medicamentosas podem
acarretar resultados inesperados em exames complementares utilizados para
diagnóstico clínico (10).
O conceito de erva medicinal é definido como uma planta ou parte dela,
utilizada em processos de cura pela medicina, como óleos aromáticos, como
sabonetes, em fragrâncias, ou em especiarias. Uma erva pode ser uma folha, uma flor,
um broto, uma raiz, um fruto, ou qualquer outra parte da planta. Datam do início das
civilizações e várias culturas de várias etnias acumularam grande conhecimento sobre
seus usos (9). Este conhecimento foi passado de geração em geração, constituindo as
bases da medicina popular e da farmacologia. Atualmente o uso da medicina popular
vem crescendo em maior proporção sobre o uso da medicina ortodoxa (2,9).
A prática da medicina tradicional Chinesa (MTC) data de mais de 6000
anos, ganhando estruturação farmacológica como “fórmulas magistrais”. A MTC reúne
em seus tratamentos as substâncias oriundas dos reinos: mineral, vegetal e animal, e
outras drogas mais modernas (11,12). Vários profissionais da área de saúde que
aplicam ervas e outros compostos em seus procedimentos, pesquisam resultados que
possam melhor orientar estas práticas (6,13).
O mecanismo de ação do BYQW (fórmula magistral) ainda não é
totalmente esclarecido. Encontra-se na literatura, de forma precária, estudos sobre o
Buzhong Yi Qi Tang (com ginseng associado) ou Hochu-ekki-to (denominação japonesa) citados nas bases de dados científicos (13). Em nossas busca nestes sites
BYQW na biodistribuição dos radiobiocomplexos empregados na Medicina Nuclear e,
tampouco, seus efeitos na radiomarcação de constituintes sangüíneos quer no nível
morfológico ou em fragilidade osmótica (14,15). Assim, o interesse em realizar este
trabalho. Como a interação medicamentosa é um dos possíveis problemas enfrentados
pela Medicina Nuclear, uma das intenções é apresentar sugestões que possibilitem um
maior entendimento de possíveis efeitos em procedimentos de radiodiagnóstico,
embora os resultados in vitro obtidos nesse projeto sejam com sangue de ratos Wistar (3,4,14).
Segundo alguns pesquisadores de efeitos relacionados aos compostos
de ervas, tais como: Tu et al. (1994), que apresentam resultados em estudos de miastenia gravis utilizando a administração de ervas medicinais a base de Astragalus (16); Kuroiwa et al. (2004), que apresentam a formula Hochu-ekki-to (Buzhong YiQi
Tang – TJ-41) como uma das que aumentam a imunidade em pessoas idosas (17); Yamaoka et al. (2001), que apresentam o uso do TJ-41 em pacientes com Listeria
monocitogênica de repetição (18); também, Yamaoka et al.(1998) estudaram os efeitos do TJ-41 em semelhantes estudos imunológicos por infecções orais pela Listeria
monocitogênica, com a melhora de seu controle (19); Du et al. (1993), investigaram a ação do TJ-41 em hepatite tipo B; os estudos feitos por Tang e Wu (1994), sobre os
efeitos da interação do TRH (hormônio tirotropina) e o TJ-41, demonstraram ação
esplênica e hipotalâmica em atividades de apoptose das células, em ratos estressados
(20); Tu et al. (1994), em análises sobre os efeitos em Miasthenia gravis e baseados nas deficiências esplênicas (Pi – baço/pâncreas), viram que as saponinas de
Como o estudo do BYQW vem buscar o entendimento dos efeitos de
biocomplexos na marcação de elementos constituintes do sangue com 99mTc, na
morfologia de hemácias verificando se sofrem alterações em membrana plasmática e
na sua fragilidade osmótica, as hipóteses consideradas foram:
Hipótese substantiva: existem efeitos do extrato aquoso de Buzhong Yi Qi Wan (fórmula magistral Chinesa) na marcação de elementos sanguíneos com tecnécio-99m,
na morfologia e na fragilidade osmótica de hemácias em ratos Wistar.
Hipótese nula: não existem efeitos do extrato aquoso de Buzhong Yi Qi Wan (fórmula magistral Chinesa) na marcação de elementos sanguíneos com tecnécio-99m, na
morfologia e na fragilidade osmótica de hemácias em ratos Wistar.
A pesquisa foi realizada no Laboratório de Radiofarmácia
Experimental do Departamento de Biofísica e Biometria, nos Departamentos de
Histologia e Embriologia e de Anatomia Humana da Universidade do Estado do Rio de
Janeiro, com convênio firmado entre a Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro e a
Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte. As experiências tiveram a orientação do
Professor Doutor Mario Bernardo Filho e a co-orientação do Professor Doutor Aldo da
3. INDEXAÇÃO DE ARTIGOS. 3.1. No prelo:
ȱŗDZȱȃȱȱȱȄȱȮȱŘŖŖŝǯȱ
Assessment of effects of a formula used in the traditional chinese medicine
(Buzhong Yi Qi Wan) on the morphologic and osmotic fragility of red blood
cells.
Tania S. Giani1,2,4*, Severo de Paoli1,2,4, Giuseppe A. Presta1,2, Adalgisa I. Maiworm1,2, Sebastião D. Santos-Filho1,2, Adenilson S. Fonseca2 and Mario Bernardo-Filho1,2,3.
1
Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, Centro de Ciências da Saúde, Pós-graduação em Ciências
da Saúde, Avenida General Gustavo Cordeiro de Farias, s/n, 59010180, Natal, RN, Brasil,
2
Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro, Instituto de Biologia Roberto Alcântara Gomes,
Departamento de Biofísica e Biometria, Laboratório de Radiofarmácia Experimental, Avenida 28 de
Setembro, 87, 20551030, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brasil,
3
Instituto Nacional do Câncer, Serviço de medicina Nuclear, Praça da Cruz Vermelha 23, 4° andar,
20230130, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brasil,
4
Universidade Estácio de Sá, Centro de Ciências da Saúde, Faculdade de Farmácia e Fisioterapia, Rua do
Bispo 83, 20261063, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brasil.
Abstract
Buzhong Yi Qi Wan (BYQW) is a combination of some medicinal herbs widely used in traditional chinese medicine to treat blood, spleen and stomach disorders. Morphometric analysis and osmotic fragility assay have been used to evaluate changes on membrane integrity of red blood cells. The aim of this work was to evaluate the effect of an aqueous BYQW extract on the morphology and osmotic fragility of red blood cells. Blood samples were treated with BYQW extract, quantitative/qualitative morphological analysis and osmotic fragility assay were carried out against control groups treated with saline. The data obtained indicated no modification on morphology but osmotic fragility assay suggested a significant (p<0.05) increasing of hemolytic in red blood cells isolated from blood treated with aqueous BYQW extract. In conclusion, the aqueous BYQW extract could affect the membrane integrity decreasing the osmotic resistance but without altering the shape of red blood cells.
Análise de efeitos da formula usada na medicina tradicional chinesa (
Buzhong
Yi Qi Wan
) na morfologia e fragilidade osmótica de células vermelhas do
sangue.
Resumo
Buzhong Yi Qi Wan (BYQW) é a combinação de várias ervas medicinais usadas na medicina tradicional chinesa para tratar desequilíbrios no sangue, baço/pâncreas e estômago. A análise morfológica e a fragilidade osmótica têm sido usadas para avaliar a integridade da membrana plasmática de hemácias. O objetivo deste trabalho foi avaliar os efeitos de um extrato aquoso de BYQW na morfologia e na fragilidade osmótica de células vermelhas do sangue. Amostras de sangue foram tratadas com o extrato aquoso de BYQW, analisadas a morfologia qualitativa/quantitativamente e a fragilidade osmótica avaliada em relação ao grupo controle tratado com salina. Os dados obtidos não apresentaram modificações significativas (p<0,5) na morfologia das hemácias, mas sugerem efeito hemolítico em sangue tratado com BYQW. Concluindo, o extrato aquoso de BYQW pode afetar a integridade da membrana diminuindo a resistência osmótica mas não alterando a forma da membrana das células vermelhas do sangue
Unitermos: Buzhong Yi Qi Wan, morfologia, fragilidade osmótica, hemácias.
Introdução.
Buzhong Yi Qi Wan (BYQW) is a mixture of some medicinal herbs widely used in Traditional
Chinese Medicine to treat blood (circulation), spleen (immunology) and stomach disorders, as peristalsis
and digestive process (Wang et all., 2002). This chinese formula is composed by herbs: Radix Astragali
(27.8%), Radix codonopsis (8.3%), Radix glycyrrhizae (14%), Rhizoma atractylodis macrocephalae
(8.3%), Radix angelicae sinensis (8.3%), Rhizoma cimicifugae (8.3%), Radix bupleuri (8.3%),
Pericarpium citri reticulatae (8.3%), Rizhoma zingiberis recens (2.8%) and Fructus jujubae (5.6%),
popularly known as (Tu et all., 1994, Seki et all., 2005).
Results have demonstrated that the beneficial effects of BYQW in miasthenia gravis as
anti-inflammatory action (Tu et al, 1994). Another study showed that BYQW is efficient to treat hepatitis-B
and cancer (Ji et al, 1989). Du et al (1993) showed that BYQW has marked effects on hepatic DNA, RNA
and protein synthesis. It was considered that the mechanism of anti-hepatitis effects could be related to
improving the defense function of organism as a whole. Kuroiwa et al (2004) obtained an increased
immunological response against K562 target cells in old patients submitted to BYQW treatment.
Morphometric analysis has been used to evaluate morphological changes induced in different
cellular systems as: (i) chronic ocular hypertensive effects on thickness of retinal nerve fiber layer and
optic disc structure (Shimazawa et al, 2006), (ii) relationship between miocardiac infarction-related artery
stenosis and capillary density (Prech et al, 2006) and (iii) effects of sexual hormones on mammal gland
(Pompei et al, 2005). Red blood cells have been proposed as a prototypical cellular system regarding drug
mediated plasma membrane effects (Li et al, 1999). Different techniques have demonstrated that
therapeutic drugs can modify the structure and morphology of these cells (Nwafor and Coakley, 1986;
Scheiman and Elta, 1990; Li et al, 1999; Shacter and Weitzman, 2002; Suwalsky et al, 2003; Hubner et al,
2005; Santos et al, 2005; Zhang et al, 2005). The morphometric analysis (area, shape and volume
measurements) has been used to evaluate the alterations induced by natural products and synthetic drugs
on membrane of red blood cells (Oliveira et al, 2002; Moreno et al, 2004).
The osmotic fragility assay can be used to verify the membrane integrity of red blood cells treated
with drugs (Cinara et al, 2006; Spengler et al, 2007). The “osmotic fragility curve” reflects the structural
and geometrical changes on red blood cells due to osmotic treatment. A hemolytic result from a structural
disturbance of these cells and in their cytoskeleton was caused by high distribution of the partition
coefficient in the membrane (Cavalcanti et al, 2003; Didelon et al, 2000).
As in humans the use of BYQW extract and several of its effects are not well understood yet, the
aim of this work was to evaluate the effect of an aqueous extract of BYQW on the morphology and
osmotic fragility of red blood cells.
Material and Methods
Animals
Preparation of BYQW extract
A commercial Buzhong Yi Qi Wan (Gansu Medicines & Health Products Import & Export Corporation, validity November 2008) was used in the assays. As indicated by this manufacturer, lyophilized Buzhong was used to prepare this dried powder. In the preparation of the extract, 128 mg of the material was put in a tube with 10 ml of saline solution (NaCl 0.9%) that was gently shaken. This suspension was centrifuged in a clinical centrifuge (3000 rpm, 5 min) and the supernatant was considered to be 12.8 mg/ml. Dilutions of this solution were performed with 0.9%NaCl solution to obtain diluted solutions.
Spectrophotometric measurements
Immediately after the preparation, the optic densities of aliquots of BYQW extract were measured in a spectrophotometer (Analyzer 800M, Analyzer, Brazil) to obtain the absorbance spectrum and the value at 480 nm was 0.33±0.07. This procedure was carried out as the preparation standard of the extract used in the experimental assays.
Blood colleted
Blood samples (pool) of Wistar rats were prepared after colleted by heparinized cardiac
extraction for fine needle, with thiopental anesthesia (40mg/kg), without death of animals.
Morphology evaluation
Morphology preparations were carried out with blood samples in vitro treated with BYQW extract at different concentrations during 60 min at room temperature, or with saline solution as control group. Blood smears were prepared, dried, fixed and staining by May-Grünwald-Giemsa method. After that, the images of the red blood cells were acquired (Optronics, USA) from blood smears to qualitative morphology analysis under optical microscopy (x1000, Olympus, BX model, Japan). To morphometric analysis of red blood cells, the perimeter/area ratio was obtained from images by specific program (Image ProPlus Software, media Cybernetics, USA). Five fields per each slide were analyzed (x1000).
Osmotic fragility assay
density of each supernatant was compared with that corresponding to 100% lysis (NaCl 0.12%). The supernatant of the tube with NaCl 0.9% was considered the standard tube for the procedure. After, the hemolytic percentage, “fragility curves” were drawn by plotting the percentage of hemolytic (% hemolytic) for each tube (relative to 100% hemolytic tube) and the corresponding NaCl concentrations. According to Cavalcanti et al (2003), three intervals were determinate: interval I (from 0.12 to 0.36%), interval II (from 0.36 to 0.60%), and interval III (from 0.60 to 0.9%) according the curve tendency.
The means and standard deviations of each interval were determinate and the statistical analysis was performed.
Statistical analysis
The data were presented as media ± standard deviation of perimeter/area ratio and
hemolytic percentage. To perimeter/area ratio, the comparison between treated and control
groups were performed by one-way ANOVA, followed by the Turkey-Kramer Multiple
Comparisons Test. To hemolytic percentage, paired t-test was used to compare the intervals I, II
and III between treated and control groups. A significance level at p<0.05 was adopted. InStat
Graphpad software was used to perform statistical analysis (GraphPad InStat version 3.01 for
Windows 95/NT, GraphPad Software, San Diego, USA).
Results.
The figures 1 and 2 represent the photomicrographs of samples of whole blood treated
with saline (control) and treated BYQW extract at the highest concentration used (12.8 mg/ml).
The comparison between these figures indicates that the extract was not capable to induce
alterations on morphology of red blood cells.
To confirm the absence of effects on morphology of red blood cells by extract BYQW the
morphometric evaluations were carried out. The data of perimeter/area ratio are showed in figure
3 and indicate that no modifications on this morphometric parameter confirming the qualitative
Osmotic fragility was used as another technique to study the effects of BYQW on
membrane integrity. Our data suggest that the treatment with BYQW extract could induce
significantly (p<0.05) the hemolytic at higher concentration used and therefore to increase
osmotic fragility of red blood cells when compared to control group (Figure 4). The comparison
of the means of hemolytic between blood treated with BYQW extract and control was significant
(p<0.05) to the interval II and III (Figure 5).
Discussion
BYQW is a traditional magistral formula composed by different herbs that has been used
long time in the Traditional Chinese Medicine due to its importance to health of human beings
and several authors have reported biological effects associated with this formula (Du et al, 1993;
Tu et al, 1994; Kuroiwa et al, 2004). The action mechanism related with the extract of BYQW is
not fully understood (Cordeiro et al, 2005). The use of different assays could permit to evaluate
and to obtain more information about the possible action mechanisms of this secular formula.
Different techniques have been used to evaluate the effects of the interaction between
drugs and plasma membrane (Li et al. 1999, Pompei et al. 2005). Qualitative and quantitative
morphological analysis have permitted to verify the effects of natural products on membrane of
red blood cells (Oliveira et al. 2002, Oliveira et al. 2003). The morphological analysis of blood
smears suggested no alteration on shape red blood cells from blood treated with BYQW extract
in quantitative and qualitative assays (Figures 1, 2 and 3). However, the data obtained from
osmotic fragility experimental study have indicated that BYQW extract could alter the
membrane integrity at NaCl concentrations near to physiologic level (0.9%). The data from
morphological analysis could be useful to understand the use do this magistral formula to treat
several disorders (Kiyohara et al., 2006, Shinozuka et al. 2007, Yamaya et al. 2007, Onogi et al.
2006, Tajima et al., 2006, Kanehara et al. 2006). Furthermore, considering the concepts of the
(Wang et al, 2002), due to these applications could be associated with the direct production of
blood or related with the transformation action of the food by the spleen to aid in the production
of blood (Maciocia, 2007). These uses in circulatory, immunology and digestive systems have
been studied by various occidental and oriental researches. By the way, the distribution
mechanism of energy and compounds food, as well as the blood circulations, probably can be
alters by BYQW. The major compound of BYQW is the radix Astragalus (radiech) wealthy in
saponins and flavonoids, which promote tissue repairs (Du et al., 1993), anothers health effects.
The result obtained by osmotic fragility assay is in according with the antibacterial effects
(Yamaoka et al. 1998, Yamaoka et al. 2001, Yan et al. 2002) suggesting that BYQW could act
on bacteria cells modifying their membrane integrity.
In conclusion, probably substances present in aqueous BYQW extract could affect the
membrane integrity decreasing the osmotic resistance but without altering the shape of red blood
cells indicating that osmotic fragility assay could be more sensitive than the morphology analysis
to evaluate effects of BYQW extract on membrane integrity of red blood cells.
ȱ
This research was supported by Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de
Janeiro (FAPERJ), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (UERJ).
References
- Cavalcanti TC, Gregorini CC, Guimarães F, Rettori O, Vieira-Matos NA 2003. Changes in red blood cell osmotic fragility induced by total plasma and plasma fractions obtained from rats bearing progressive and regressive variants of the Walker 256 tumor. Braz J Med Biol Res. 36, 887-895.
- Cinara L, Bollini A, Gayol Mdel C, Hernandez GN 2006. In vitro effect of insulin on rats erythrocytes rheological behaviour. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 35, 367-373.
- Cordeiro CHG, Chung MC, do Sacramento LVS 2005. Drug interactions between herbs and medicines: Hypericum perforatum and Piper methysticum. Braz. J. Pharmacog. 15(3):272-277.
- Didelon J, Mazeron P, Muller S, Stoltz JF 2000. Osmotic fragility of the erythrocyte membrane: characterization by modeling of the transmittance curve as a function of the NaCl concentration. Biorheol. 37, 409-416.
- Hubner Y, Hoettges KF, Kass GE, Ogin SL, Hughes MP (2005), Parallel measurements of drug actions on Erythrocytes by dielectrophoresis, using a three-dimensional electrode design. IEE Proc. Nanobiotechnol 152, 150-154.
- Ji YB, Jiang WX, Zhang XJ 1989. Effects of buzhong yiqi decoction on the anticancer activity and toxicity induced by cyclophosphamide. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 14, 48-51
- Junqueira L, Carneiro C 2004. Histologia básica. Rio de Janeiro: Guanabara Koogan.
- Kanehara M, Ogirima T, Tano K, Maenaka T, Ishida T, Zhang B, Li G, Wang X, Guo Y 2006. Effects of Chinese herbal medicine based on hachimi-jio-gan on osteopenia in rats. J Tradit Chin Med 26, 72-77.
- Kiyohara H, Nagai T, Munakata K, Nonaka K, Hanawa T, Kim SJ, Yamada H 2006. Stimulating effect of Japanese herbal (kampo) medicine, hochuekkito on upper respiratory mucosal immune system. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 3, 459-467.
- Kuroiwa A, Liou S, Yan H, Eshita A, Naitoh S, Nagayama A 2004. Effect of a traditional Japanese herbal medicine, hochu-ekki-to (Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi Tang), on immunity in elderly persons. Int J Immunopharmac 4 ,:317-324.
- Li A, Seipelt H, Muller C, Shi Y, Artmann M 1999. Effects of salicylic acid derivatives on red blood cell membranes. Pharmacol. Toxicol 85, 206-211.
- Maciocia G 2007. Fundamentos da medicina chinesa. São Paulo: Roca.
- Moreno SRF, Carvalho JJ, Nascimento ALR, Freitas RS, Diré GF, Lima EA, Lima-Filho GL, Rocha EK, Bernardo-Filho M 2004. Biodistribution of sodium pertechnetate and light microscopy of organs isolated from the rats: study of the effects of a Ginkgo biloba extract. Pakistan J Nut 3, 64-67.
- Nwafor A, Coakley WT 1986. Charge-independent effects of drugs on erythrocyte morphology. Biochem. Pharmacol 35, 953-957.
- Oliveira JF, Avila AS, Braga ACS, Oliveira MBN, Boasquevisque EM, Jales RL, Cardoso VN, Bernardo-Filho M 2002. Effect of extract of medicinal plants on the labeling of blood elements with technetium-99m and on the morphology of red blood cells: I – a study with Paullinia cupana. Fitoterapia 73, 305-312.
- Oliveira JF, Santos-Filho SD, Catanho MTJA, Srivastava SC, Lima-Filho GL, Bernardo Filho M 2003. Effect of extract of medicinal plants on the labeling of blood elements with technetium-99m and on the morphology of red blood cells (RBC): Toxicological actions of roast coffee beans (Coffea arabica). Indian J Nucl Med 18, 52-56. - Onogi K, Niwa K, Tang L, Yun W, Mori H, Tamaya T 2006. Inhibitory effects of Hochu-ekki-to on endometrial carcinogenesis induced by N-methyl-N-nitrosourea and 17beta-estradiol in mice. Oncol Rep 16,1343-1348.
- Pompei LM, Carvalho FM, Ortiz SC, Motta MC, Cruz RJ, Melo NR 2005. Morphometric evaluation of effects of two sex steroids on mammary gland of female rats. Maturitas 5, 370-379.
- Prech M, Grajek S, Marszalek A, Lesiak M, Jemielity M, Araszkiewicz A, Mularek-Kubzdelat T, Cieslinski A 2006. Chronic infarct-related artery occlusion is associated with a reduction in capillary density. Effects on infarct healing. Eur J Heart Fail 8, 373-380.
- Santos NC, Martins-Silva J, Saldanha C 2005. Gramicidin D and dithiothreitol effects on erythrocyte exovesiculation. Cell Biochem. Biophys 43, 419-430.
- Scheiman JM, Elta GH 1990. Gastroduodenal mucosal damage with salsalate versus aspirin: results of experimental models and endoscopic studies in humans. Sem Arthritis Rheumatism 20, 121-127.
- Shimazawa M, Taniguchi T, Sasaoka M, Hara H 2006. Nerve fiber layer measurement using scanning laser polarimetry with fixed corneal compensator in normal cynomolgus monkey eyes. Ophthalmic Res 38,1-7.
- Shinozuka N, Tatsumi K, Nakamura A, Terada J, Kuriyama T 2007. The traditional herbal medicine Hochuekkito improves systemic inflammation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Am Geriatr Soc 55, 313-314.
- Spengler MI, Leroux MB, Svetaz MJ, Contesti JF, Parente FM, Bertoluzzo SM 2007. Nifedipine effect on red cell rheological properties in patients with systemic scleroderma. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 36,105-110.
- Suwalsky M, Hernandez PL, Villena F, Sotomayor CP 2003. The anticancer drug cytarabine does not interact with the human erythrocyte membrane. Z Naturforschung 58, 885-890.
- Tajima S, Bando M, Yamasawa H, Ohno S, Moriyama H, Takada T, Suzuki E, Gejyo F, Sugiyama Y 2006. Preventive effect of Hochu-ekki-to on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in BALB/c mice. Lung 184,
318-323.
- Tu LH, Huang DR, Zhang RQ, Shen Q, Yu YY, Hong YF, Li GH 1994. Regulatory action of Astragalus saponins
and Buzhong yiqi compound on synthesis of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antibody in vitro for myasthenia gravis.
Chin Med J 107, 300-303.
- Wang ZT, Wang SR, Zhao MJ 2002. Comparative study on effect of recipe for activating blood circulation and replenishing Qi on left ventricular remodeling in rats with left heart failure after myocardial infarction. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 22, 376-378.
- Yamaoka Y, Kawakita T, Kishihara K, Nomoto K 1998. Effect of a traditional Chinese medicine, Bu-zhong-yi-qi-tang on the protection against an oral infection with Listeria monocytogenes. Immunopharmacology 39, 215-223. - Yamaoka Y, Kawakita T, Nomoto K 2001. Protective effect of a traditional Japanese medicine Hochu-ekki-to (Chinese name: Bu-zhong-yi-qi-tang), on the susceptibility against Listeria monocytogenes in infant mice. Int Immunopharmacol 1, 1669-1677.
- Yamaya M, Sasaki T, Yasuda H, Inoue D, Suzuki T, Asada M, Yoshida M, Seki T, Iwasaki K, Nishimura H, Nakayama K 2007. Hochu-ekki-to inhibits rhinovirus infection in human tracheal epithelial cells. Br J Pharmacol 150, 702-710.
- Yan X, Kita M, Minami M, Yamamoto T, Kuriyama H, Ohno T, Iwakura Y, Imanishi J 2002. Antibacterial effect of Kampo herbal formulation Hochu-ekki-to (Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang) on Helicobacter pylori infection in mice.
Microbiol Immunol 46, 475-482.
FIGURES
Figure 1 – ∅ control (2µm) Figure 2 – ∅ treated (2µm)
2µµµµm 2µµµµm FIGURE 1: Photomicrography of blood
smears from blood samples in vitro treated
with NaCl 0.9% solution (control group). Blood smears were stained with May-Grünwald-Giemsa method. The morphology
of red blood cells was evaluated under optical microscopy (x 1000) after image
capture.
FIGURE 2: Photomicrography of blood smears from blood samples in vitro treated (100%) with BYQW extract. Samples of whole blood from
Wistar rats were treated with BYQW extract (1.28 mg/ml) during 60 minutes. Blood smears were prepared, dried, fixed and staining by May-Grünwald-Giemsa method. The morphology of
red blood cells was evaluated under optical microscopy (x 1000) after image capture.
Figure 3
FIGURE 3: Effects of BYQW extract on the perimeter/area ratio of red blood cells from blood in vitro. Samples of whole blood from Wistar rats were treated with BYQW extract at different concentrations during 60 minutes. Blood smears were prepared, dried, fixed and staining by May-Grünwald-Giemsa method. The morphology of red blood cells was evaluated under optical microscopy (x 1000) after the capture of images in five fields for each smear and five smears for each BYQW extract concentration. After that, morphometric measurements (perimeter and area) were carried out and perimeter/area calculated.
0 0,1 0,2 0,3 0,4 0,5 0,6 0,7 0,8 0,9
0.00 0.08 0.16 0.32 0.64 1.28
P er im et er /A re a ra ti o
m
Figure 4 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
0.12 0.24 0.36 0.48 0.60 0.72 0.90 NaCl (g/dl) H e m o l y s i s ( % )
I II III
Dacie & Lewis (2001) – hemolisys ll and lll
FIGURE 4: Osmotic fragility of blood samples treated or not treated with BYQW extract) or with sodium chloride solution (0.9% NaCl), as control, during 60 minutes at room temperature. Aliquots of blood (100
µl) were gently mixed with NaCl at different concentrations. After 30 minutes (room temperature) and centrifugation (1500 rpm, 15 min), the supernatants were isolated and the optical densities (OD) were determined in a spectrophotometer at 480 nm. The optical density of each .supernatant was compared with that corresponding to 100% lysis (NaCl 0.12%). The supernatant at NaCl 0.9% was considered the standard to the procedure. The hemolytic percentage were calculated and “fragility curves” were drawn
plotting the percentage of hemolytic (% hemolytic) for each NaCl concentration (relative to 100% hemolytic tube). (●) controle, (■) treated with BYWQ extract.
Figure 5
Dacie & Lewis (2001) – hemolisys II and III.
FIGURE 5: Means of hemolytic grade of the blood samples treated or not treated with BYQW extract. Three intervals were determinate: interval I (from 0.12 to 0.24%), interval II (from 0.24 to 0.48%), and interval III (from 0.48 to 0.9%) according the curve tendency. The means and standard deviations of each interval were determined and the statistical analysis performed. (□) control bars, (■) treated bars with BYQW extract were statistically compared. (*) p<0.05.
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
I II III
Interval
M
ean of
H
em
o
ly
si
s (
%
)
*
Artigo 2: “Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology” – 2007.
An extract of a formula used in the traditional Chinese
medicine (
Buzhong Yi Qi Wan
) alters the labeling of blood
constituents with technetium-99m
∗Tania Santos Giani1,2,4, Severo de Paoli1,2,4, Giuseppe Antonio Presta1,2,5, Adalgisa Ieda Maiworm1,2, Sebastião David Santos-Filho1,2 and Mário Bernardo-Filho, M1,2,3.
1. Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, Centro de Ciências da Saúde, Pós-graduação em Ciências da Saúde, Natal, RN, Brasil;
2. Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro, Instituto de Biologia Roberto Alcântara Gomes, Departamento de Biofísica e Biometria, Laboratório de Radiofarmácia Experimental, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brasil;
3. Instituto Nacional do Câncer, Serviço de medicina Nuclear, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brasil.
4. Universidade Estácio de Sá, Centro de Ciências da Saúde, Faculdade de Farmácia e Fisioterapia, Rio de janeiro, RJ. Brasil;
5. Universidade Federal do Estado do Rio de Janeiro/UNIRIO, Instituto Biomédico, Departamento de Fisiologia Humana, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brasil.
Corresponding author:
∗Tania Santos Giani
Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro
Instituto de Biologia Roberto Alcantara Gomes
Departamento de Biofísica e Biometria
Laboratório de Radiofarmácia Experimental
E-mail: bernardo@uerj.br
20551-030, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil
An extract of a formula used in the traditional Chinese
medicine (
Buzhong Yi Qi Wan
) alters the labeling of blood
constituents with technetium-99m
∗Tania Santos Giani1,2,4, Severo de Paoli1,2,4, Giuseppe Antonio Presta1,2,5, Adalgisa Ieda Maiworm1,2, Sebastião David Santos-Filho1,2 and Mário Bernardo-Filho, M1,2,3.
1. Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, Centro de Ciências da Saúde, Pós-graduação em Ciências da Saúde, Natal, RN, Brasil;
2. Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro, Instituto de Biologia Roberto Alcântara Gomes, Departamento de Biofísica e Biometria, Laboratório de Radiofarmácia Experimental, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brasil;
3. Instituto Nacional do Câncer, Serviço de medicina Nuclear, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brasil.
4. Universidade Estácio de Sá, Centro de Ciências da Saúde, Faculdade de Farmácia e Fisioterapia, Rio de janeiro, RJ. Brasil;
5. Universidade Federal do Estado do Rio de Janeiro/UNIRIO, Instituto Biomédico, Departamento de Fisiologia Humana, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brasil.
ABSTRACT
Buzhong Yi Qi Wan (Buzhong) is a medicinal herbs widely used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat systems digest and circulation. Red blood cell (RBC) and plasma proteins labeled with technetium-99m (99mTc) are used in nuclear medicine. The aim of this work was to investigate
the effects of an aqueous Buzhong extract on the labeling of blood constituents with 99mTc.
Heparinized blood (Wistar rats) was incubated in vitro with different Buzhong extract
concentrations and 99mTc-labeling was performed. Plasma (P) and blood cells (BC) were
separated and soluble (SF-P/SF-BC) and insoluble (IF-P/IF-BC) fractions were isolated. The radioactivity on blood constituents was determined and the percentage of incorporated
radioactivity (%ATI) was calculated. Buzhong extract at the highest concentrations used (6.4 and
12.8mg/ml), altered significantly (p<0.05) the %ATI in blood constituents. Substances present in
the Buzhong extract could alter the cell membrane and plasma and/or generation of free radicals that have oxidant properties.
KEYWORDS: Technetium-99m, Red blood cell, Oxidant agent, Radiobiocomplex, Plasma
INTRODUCTION
Ethnobotany and ethnopharmacology have the focus on the systematic exploration of medicinal herbs among folk medicines (Rauh et al., 2007). Buzhong Yi Qi Wan (Buzhong) is a mixture of some medicinal herbs widely used in Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat the digestive system and circular blood disorders (Maciocia, 1996, Carvalho, 2002).
The Buzhong formula is compound by Radix Astragalus (27.8%), Radix codonopsis (8.3%),
Radix glycyrrhizae (14%), Rhizoma atractylodis macrocephalae (8.3%), Radix angelicae sinensis (8.3%), Rhizoma cimicifugae (8.3%), Radix bupleuri (8.3%), Pericarpium citri reticulatae (8.3%), Rizhoma zingiberis recens (2.8%) and Fructus jujubae (5.6%). (Tu et al.,
1994, Kuroiwa et al., 2004, Seki et al., 2005).
This formula has been subject of many studies on chronotherapy against cancer, on immunity in the elderly, on natural killer cell activity and endocrine in stressed mice, chronic hepatitis B and on myasthenia gravis (Ji et al., 1989, Du et al., 1993, Tang et al., 1994, Kuroiwa et al., 2004, Seki et al., 2005). In Traditional Chinese Medicine, Buzhong has been widely used also as middle Jiao tonic and chi stimulator (vital energy), to harmonize blood energy (Xue) and increase the physically strength of the spleen and stomach (Zang-Fu) (Wang et al., 2002).
Tu et al. (1994) analyzed the effects of Buzhong to treat myasthenia gravis suggesting an anti-inflammatory action.
Combined methods at molecular and cellular levels can help to elucidate the mechanisms and effects of these natural products.
An experimental model based in the labeling of blood constituents with a radionuclide has been used to assess some properties of the medicinal herbs (Moreno et al., 2002, Oliveira et al., 2003, Santos-Filho et al., 2004, Santos-Filho et al., 2005, Abreu et al., 2006b).
Classically, blood constituents are labeled with 99mTc and used as radiopharmaceuticals to obtain diagnostic images in nuclear medicine by single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) (Harbert, 1996, Saha, 2004, Bernardo-Filho et al., 2005).
The labeled process with 99mTc, as sodium pertechnetate, depends on a reducing agent and stannous ion (Sn+2) is usually used for this purpose (Harbert et al., 1996, Saha, 2004). When whole blood is employed on the labeling of blood constituents with 99mTc, radioactivity is mainly found on red blood cells (Bernardo-Filho et al., 1990).
As human beings can use the Buzhong and several effects about this natural product are not well understood yet, the aim of this work was to evaluate the effect of a Buzhong aqueous extract on the labeling of blood constituents with 99mTc.
ȱ
Instrument Company, mod C5002, USA). After that, the percentual of incorporated radioactivity (% ATI) was calculated as described previously (Bernardo-Filho et al, 1986).
Spectrophotometric measurements
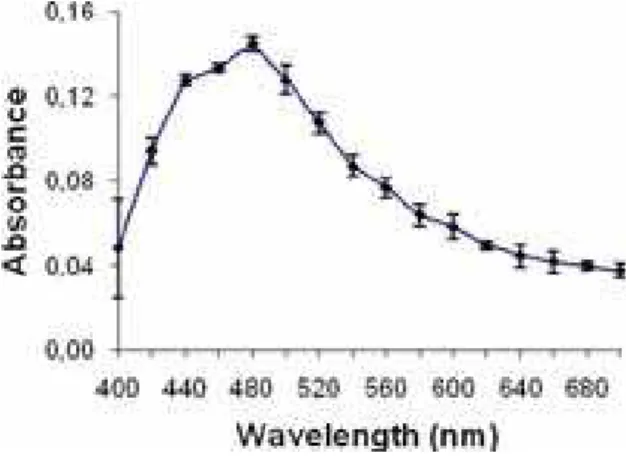
A spectrophotometric analysis (Analyser, 800M, São Paulo, Brazil) of the extract was carried out. The absorbance at 480nm (figure 1) was considered the marker of the quality control of this extract. All extracts used in the experiments, showed the optical density of 1.45±0.01 OD.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis involved one-way ANOVA, followed by the Turkey-Kramer Multiple Comparisons Test, with the significance level being P<0.05. InStat Graphpad software was used to
RESULTS
Figure 1 shows the absorption spectrum of the Buzhong extract used in the experiments. The pattern of the absorption spectra presents the highest measure of the optical density
(1.45±0.01) at 480 nm. This parameter has permitted to control the conditions to prepare the extracts and has been used as a marker.
Figure 1: Absorbance spectrum of Buzhong
extract.
Table 1 shows the distribution of the radioactivity in the cellular and plasma compartments from whole blood treated with different concentrations of Buzhong extract. A significant (p<0.05) decrease in radioactivity distribution by the BC was found in presence of
Buzhong extract.
Table 1 – Effect of Buzhong extract on the distribution of radioactivity between cellular and plasma compartments
Buzhong
extract (mg/ml)
Blood Cells Plasma
0.0 97.87±1.45 2.13±1.45 0.8 96.36±1.05 3.64±1.05 1.6 95.06±0.41 4.94±0.41 3.2(*) 92.42±1.02 7.58±1.45 6.4(*) 83.88±0.42 16.12±0.42 12.8(*) 70.57±0.46 29.43±0.46
Blood samples (n=25) were incubated with Buzhong extract. As controls, blood samples (n=5) incubated with saline solution (0.9%
NaCl). Then, labeling of blood constituents was performed. The radioactivity in plasma and cellular compartments were counted and the percentages of incorporated radioactivity (%ATI) were calculated. (*) p<0.05 when compared with controls.
the Buzhong extract. There was a significant (p<0.05) decrease in radioactivity fixation by the IF-BC in presence of Buzhong extract.
Table 2 – Effect of Buzhong extract on the fixation of 99mTc on the insoluble and soluble fractions of blood cells
Buzhong
extract (mg/ml)
IF-BC SF-BC
0.0 91.27 ± 1.36 8.73 ± 1.36 0.8 86.41 ± 0.79 13.59 ± 0.79 1.6(*) 83.34 ± 1.56 16.66 ± 1.56 3.2(*) 80.54 ± 1.07 19.46 ± 1.07 6.4(*) 77.60 ± 0.78 22.40 ± 0.78 12.8(*) 72.28 ± 1.34 27.72 ± 1.34
Blood samples (n=25) were incubated with Buzhong extract. As controls, blood samples (n=5) incubated with saline solution (0.9%
NaCl). Then, labeling with 99mTc was performed. Insoluble (IF) and soluble (SF) fractions of blood cells (BC) were isolated, the radioactivity was counted and the percentages of incorporated radioactivity (%ATI) were calculated. (*) p<0.05 when compared with controls.
The results shown in Table 3 indicate the fixation of the radioactivity in the soluble and insoluble fractions of the plasma compartment isolated from blood treated with different concentrations of the Buzhong extract. There is a significant (p<0.05) decrease in the radioactivity fixation in the plasma proteins (IF-P) in presence of Buzhong extract.
Table 3 – Effect of Buzhong extract on the fixation of 99mTc on the insoluble and soluble fractions of plasma
Buzhong
extract (mg/ml)
IF-P SF-P
0. 0 72.57 ± 0.42 27.43 ± 0.42 0.8 68.41 ± 0.93 31.59 ± 0.93 1.6(*) 64.04 ± 0.89 35.96 ± 0.89 3.2(*) 63.16 ± 0.88 36.84 ± 0.88 6.4(*) 61.78 ± 0.84 38.22 ± 0.84 12.8(*) 57.15 ± 0.69 42.85 ± 0.69
DISCUSSION
Traditional Chinese medicine is widely based on experience and is guided by holistic concepts. Theories such as the 'yin-yang' and 'five-element' embrace the view that treatment is targeted at correcting an underlying imbalance (Cheng, 2000). Yin-yang literally means “opposites” and refers to opposing influences and the five-element theory defines that everything is maintained in kinetic balance under the movement of five elements (Maciocia, 1996, Carvalho, 2002). Prescription of herbs is based on these ancestral theories and may comprise a single medicinal herb or more commonly a mixture of medicinal herbs at different amounts.
The findings presented in the Tables 1, 2 e 3 could permit integrating the knowledge of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western medicine. The results indicate that the substances present Buzhong extract could have an effect on the labeling of the blood constituents with
99m
Tc and this fact could be associated, at least, with the property of the Buzhong in the Traditional Chinese Medicine to be “blood harmonized energy (Xue)”.
Buzhong should have an effect on the NK activity, improving to some degree the immunological capacity in elderly people (Kuroiwa et al., 2004). Probably this action could be associated with action in the plasma membrane and could explain the effect of the Buzhong
decreasing the labeling of blood cells compartment (Table 1) vas well as the fixation of radioactivity on blood cells proteins (Table 2).
Data have been reported associated with important actions of Buzhong extracts (Tu et al., 1994, Kuroiwa et al., 2004, Du et al., 1993, Ji et al., 1989). The action mechanism in these phenomena could be associated with the generation of free radicals that have oxidant properties. Considering the free radicals generated due to the treatment with Buzhong, it would be expected the oxidation of the stannous ions and the fixation of 99mTc in the various blood constituents would be decreased. This action could be used to justify the findings presented in the Table 1, 2 and 3.
In conclusion, the data presented in this indicate that substances present in the Buzhong
extract could be associated, at least in part, with its property of “bloods harmonized energy (Xue)”, with its action on the plasma membrane and/or related to the generation of free radicals that have oxidant properties.
ȱ
We are grateful for the biologist Mario Pereira (UERJ) for his technical support and to Mr. Carlos Brown Scavarda (B. A., University of Michigan) for the English language revision. Financial support: CNPq, CAPES and UERJ.
RESUMO
99m
Tc. Amostras de sangue de ratos Wistar foram incubadas com diferentes concentrações do extrato de Buzhong e a marcação de constituintes sangüíneos com 99mTc foi realizado. Plasma e células sangüíneos foram separados, frações solúveis e insolúveis do plasma e das células sangüíneas foram isoladas. A radioatividade nos constituintes sangüíneos foi contada e as porcentagens de radioatividade incorporada (%ATI), determinada. Extrato de Buzhong nas maiores concentrações utilizadas altera significativamente (p<0.05) a %ATI nos constituintes sangüíneos. Substâncias presentes no extrato de Buzhong poderiam alterar a membrana celular e/ou gerar radicais livres, que têm propriedades oxidantes, modificando a marcação dos constituintes sangüíneos com 99mTc.
REFERENCES
Abreu PR, Almeida MC, Bernardo RM, Bernardo LC, Brito LC, Garcia EA, Fonseca AS,Bernardo-Filho M. (2006b) Guava extract (Psidium guajava) alters the labelling of blood constituents with technetium-99m. J.Zhej.Univ. Sci.7:429-435.
Bernardo-Filho M, Nogueira J, Sturm J, Boasquevisque E. (1990). Plasma proteins labelling with 99mTechnetium. Braz. Arch. Bio. and Tech.33:811-817.
Bernardo-Filho M, Santos-Filho SD, Moura EG, Maiworm AI, Orlando MMC, Penas ME, Cardoso VN, Bernardo LC, Brito LC. (2005) Drug interaction with radiopharmaceuticals: a review. Braz. Arch. Bio.Tech. 48:13-27.
Carvalho G.E.F. (2000) Acupuntura e Fitoterapia Chinesa Clássica. Taba Cultura: Rio de Janeiro.Cheng J. Review: drug therapy in Chinese traditional medicine. J. Clin. Pharm. 40: 445-450.
Du FB, Wang RJ, Shao TY. (1993) Clinical and experimental observations of buzhong yiqi decoction in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 13:333-335.
Harbert J.C., Eckelman W.C., Neumann R.D. (1996) Nuclear Medicine Diagnosis and therapy. Thieme Medical Publishers: New York.
Ji YB, Jiang WX, Zhang XJ. (1989) Effects of buzhong yiqi decoction on the anticancer activity and toxicity induced by cyclophosphamide. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 14:48-51
Kuroiwa A, Liou S, Yan H, Eshita A, Naitoh S, Nagayama A. (2004) Effect of a traditional Japanese herbal medicine, hochu-ekki-to (Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi Tang), on immunity in elderly persons. Int. Immunopharmac.4:317-324.
Maciocia G. (1996). Os fundamentos da medicina chinesa. Roca: São Paulo, Brasil.
Moreno S.R.F., Diré, G., Freitas R.S., Farah M.B., Lima-Filho G.L., Rocha E.K., Jales R.L.C., Bernardo-Filho M. (2002) Effect of Ginkgo biloba on the labeling of blood elements with technetium-99m: in vitro study. Rev. Bras. Farm. 12:62-63.
Oliveira, J F, Santos-Filho S.D., Catanho MTJA, Srivastava S C, Lima-Filho V, Bernardo Filho M. (2003) Effect of extract of medicinal plants on the labeling of blood elements with technetium-99m and on the morphology of red blood cells (RBC): Toxicological actions of roast coffee beans (coffea arabica). Ind. J. Nuc. Med. 18:52-56.
Saha GB. (2004) Fundamentals in Nuclear Pharmacy. Springer-Verlag: New York.
Santos-Filho SD and Bernardo-Filho M. (2005) Effect of Hypericum perforatum extract on in vitro labeling of blood elements with technetium-99m and on biodisponibility of sodium pertechnetate in Wistar rats. Act. Cir. Bras. 20:121-125.
Santos-Filho SD, Diré GL, Lima E, Oliveira MN, Bernardo-Filho M. (2004) Effect of Mentha crispa (mint) extract on the labeling of blood elements with technetium-99m: A possible evaluation of free radicals. J. Bio. Sci.4: 266-270.
Seki K, Chisaka M, Eriguchi M, Yanagie H, Hisa T, Osada I, Sairenji T, Otsuka K, Halberg F. (2005) An attempt to integrate Western and Chinese medicine: rationale for applying Chinese medicine as chronotherapy against cancer. Biomed. & Pharmac. 59: S132-S140
Tu LH, Huang DR, Zhang RQ, Shen Q, Yu YY, Hong YF, Li GH. (1994) Regulatory action of Astragalus saponins and buzhong yiqi compound on synthesis of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antibody in vitro for myasthenia gravis. Chin. Med. J.107:300-303.
4. COMENTÁRIOS, CRÍTICAS E CONCLUSÕES.
O estudo do Buzhong Yi Qi Wan veio trazer um melhor entendimento dos efeitos de biocomplexos (fórmulas magistrais) na
radiomarcação de elementos constituintes do sangue, as possíveis alterações
morfológicas e as ações na fragilidade osmótica de hemácias. A utilização
destas informações pode contribuir para uma maior segurança diagnóstica e
terapêutica.
Desta forma, através de experimentos de radiomarcação de
constituintes sanguíneos, de estudos da morfologia da membrana das
hemácias, da fragilidade osmótica de hemácias de ratos Wistar, verificou-se os efeitos produzidos pelo Buzhong Yi Qi Wan.
A droga medicamentosa escolhida para análise é um
biocomplexo de várias ervas, sendo uma mistura muito utilizada na medicina
tradicional Chinesa, para tratar desordens do sistema imunológico, do
circulatório e do digestório (10). Poucos trabalhos com este biocomplexo foram
desenvolvidos e nenhum com este foco sobre os efeitos produzidos nas
interações com o radionuclídeo mais utilizado na Medicina Nuclear – o
tecnécio-99m. Este é o primeiro trabalho que se tem conhecimento publicado
como a morfologia e fragilidade osmótica de hemácias de ratos Wistar, com o extrato aquoso de Buzhong Yi Qi Wan.
Os resultados encontrados apresentam efeitos de alterações na
marcação dos constituintes do sangue nas maiores concentrações do extrato
(3,2; 6,4 e 12,8 mg/ml); não apresentam efeitos estatisticamente significativos
na morfologia de hemácias, e apresentam hemólise de hemácias nas faixas II e
III (Dacie e colaboradores) de concentrações do extrato próximas ao pH do
plasma (NaCl 0,9%). Conclusão, provavelmente as substâncias presentes nos
extratos aquosos de BYQW podem alterar (p<0,05) a marcação de
constituintes do sangue com 99mTc; afetar a integridade da membrana
plasmática de hemácias diminuindo a resistência osmótica, sem alterar a forma
da membrana, demonstrando maior fragilidade na integridade da membrana do
que na sua morfologia.
As hipóteses levantadas no início do projeto apresentam
coerência com os resultados. Assim, a hipótese substantiva foi confirmada no
que se refere aos efeitos dos extratos aquosos de Buzhong Yi Qi Wan de que “existem efeitos na marcação de elementos sanguíneos com tecnécio-99m e
na fragilidade osmótica de hemácias em ratos Wistar.” E a hipótese nula foi confirmada no que se refere aos efeitos dos extratos aquosos de Buzhong Yi
Qi Wan de que “não há alterações morfológicas nas hemácias de sangue de ratos Wistar.”
Nossos estudos continuam, buscando maior entendimento
nestas alterações quanto ao processo de proteção aos agentes redox, ao pH
do meio e a qualquer outra possibilidade existente no extrato ou em suas
seus efeitos moderadores de toxidade das demais plantas, segundo relatos da
Herbasin Chinese Industry (China; 2007) onde o composto é processado,
assim como em outras indústrias fora da China.
5. REFERÊNCIAS
1. Hesslewood S, Leung E. Drug interactions with
radiopharmaceuticals. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine 1994; 21,
348-356.
2. Saha GB. Fundamentals of Nuclear Pharmacy. Springer-Verlag, New
York. 2004.
3. Early PJ, Sodee DB. Principles and Practice of Nuclear Medicine. Mosby,
London. 1995.
4. Hladik III, W.B.; Saha, G.B.; Study, K.T. Essentials of Nuclear Medicine
Science. William and Wilkins, London, 1987.
5. Freitas RS, Moreno SR, Lima-Filho GL, Fonseca AS, Bernardo-Filho M.
Effect of a commercial extract of Paullinia cupana (guarana) on the binding of 99mTc-DMSA on blood constituents: An in vivo study. Applied Radiation and
Isotopes. 2007; 65:528-533.
6. Cordeiro CHG, Chung MC, do Sacramento LVS. Drug interactions
between herbs and medicines: Hypericum perforatum and Piper methysticum.
7. Cheng J. Review: drug therapy in Chinese traditional medicine.
Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 2000; 40: 445-450.
8. Sampson CB. Textbook of radiopharmacy theory and practice. Gordon
and Breach: Amsterdam, 1999.
9. Vilela JD. Mummification and medicine in ancient Egypt. Revista Paulista
de Medicina. 1977. 89: 115-24
10. Rotblatt M, Ziment I. Evidence-Based Herbal Medicine. Hanley &
Belfus: Philadelphia, 2002.
11. Bastos SRC. Shiatsu Tradicional: Fundamentos, Prática e Clínica de
Shiatsuterapia. Rio de Janeiro: Sohaku-in Edições, 2000.Carvalho GEF.
Acupuntura e Fitoterapia Chinesa Clássica. Rio de Janeiro: Taba Cultura,
2002.PubMed. Base de dados: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov; acessos de 2005 a 2007.
14. Bernardo-Filho M, Santos-Filho SD, Moura EG, Maiworm AI, Orlando
MMC, Penas ME, Cardoso VN, Bernardo LC, Brito LC. Drug interaction
with radiopharmaceuticals: a review. Brazilian Archives Biology and
Technology 2005; 48:13-27.
15. Didelon J, Mazeron P, Muller S, Stoltz JF. Osmotic fragility of the
erythrocyte membrane: characterization by modeling of the transmittance curve
as a function of the NaCl concentration. Biorheology. 2000. 37, 409-416.
16. Tu LH, Huang DR, Zhang RQ, Shen Q, Yu YY, Hong YF, Li GH.
Regulatory action of Astragalus saponins and BYQW yiqi compound on
synthesis of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antibody in vitro for myasthenia
gravis. Chinese Medical Journal. 1994; 107:300-303.
immunity in elderly persons. International Immunopharmacology. 2004;
4:317-324.
18. Yamaoka Y, Kawakita T, Nomoto K. Protective effect of a traditional
Japanese medicine Hochu-ekki-to (Chinese name: Bu-zhong-yi-qi-tang), on the susceptibility against Listeria monocytogenes in infant mice. Internal Immunopharmacology. 2001. 1, 1669-1677.
19. Yamaoka Y, Kawakita T, Kishihara K, Nomoto K 1998. Effect of a
traditional Chinese medicine, Bu-zhong-yi-qi-tang on the protection against an oral infection with Listeria monocytogenes. Immunopharmacology 39: 215-223. 20. Tang B, Wu MY. Effect of TRH and BYQW yiqi tang on natural killer cell
activity and endocrine in stress mice. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi
1994; 14:104-105.
21. Shinozuka N, Tatsumi K, Nakamura A, Terada J, Kuriyama T. The
traditional herbal medicine Hochuekkito improves systemic inflammation in
patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Journal of the American
Geriatric Society. 2007. 55: 313-314.
22. Kiyohara H, Nagai T, Munakata K, Nonaka K, Hanawa T, Kim SJ,
Yamada H Stimulating effect of Japanese herbal (kampo) medicine,
hochuekkito on upper respiratory mucosal immune system. Evidence Based
6. APÊNDICES. 6.1. Análise espctrofotométrica do extrato de BYQW.
B) Espectrofotometria ao longo de 120 dias do mesmo extrato de BYQW – 10
de fevereiro, abril e junho de 2007 (0,142; 0,144; e 0,149 0,004 DO com 480
É possível perceber que o espectro de absorção do referido extrato se
manteve ao longo dos experimentos, com absorbância em 480nm.
6.2. Análise de contaminação do extrato.
A análise da contaminação por micróbia dos extratos aquosos (1:10 –
extrato/salina) de BYQW foi realizada através da observação de crescimento
de unidades formadora de colônias (UFC) em placa de Petri (n=4 para cada
experimento), colocadas em estufa a 37°C por 24h. Os extratos não
apresentaram formação de UFC nas placas.
ABSTRACT
Technetium-99m (99mTc) has been used to obtain several radiobiocomplexes
utilized to aid in the diagnosis of diseases. Blood constituents, as red blood
cells (RBC) and plasma proteins, have been labeled with 99mTc. Natural and
synthetic drugs can alter the labeling of these constituents. The aim of this work
was to investigate the possibility of a Buzhong YiQi Wan extract to alter (i) the
labeling of blood constituents with 99mTc, (ii) the RBC morphology, and (iii)
osmotic fragility of RBC withdrawn from Wistar rats. The data showed that the BYQW extract (i) could affect labeling of blood constituintes with 99mTc, (ii)
with properties of the substances present in the aqueous extract of BYQW. This
study has multiple disciplinary aspects in knowledge areas: Radiobiology,
Botanic, Phytotherapy and Haematology.
Keywords: medicinal plants, Chinese medicine, technethium-99m, red blood