Original Article
DEVELOPM ENT AND EVALUATION OF EVIDENCE BASED
PRE-OPERATIVE PATI EN T EDUCATION BOOKLET IN LU M BAR
DISCECTOM Y
M anish Nagpal *
1, M eena M akhija
2, Abha Sachdev
3.
1Objective: The object ive of t his st udy w as t o cont r ibut e t ow ards f urt her underst anding of t he preoperat ive educat ional requirem ent of pat ient s by developing and evaluat ing suitable evidence based pat ient educat ion booklet in lum bar discect omy.
Summary of background data: The prim ary surgical int ervent ion for lum bar radiculopat hy is lum bar discect omy but it s result rem ains var iable. Pat ient educat ion has been found beneficial in various surgeries and result ed in enhanced out com e of t he surgery w it h respect t o pain, disabilit y and qualit y of life.
M et hodology: It consist s of 5 St eps. 1) Lit erat ure review, inform al int erview and quest ionnaire filled by 3 surgeons, 5 physiot herapist s and 5 pat ient s w ere used t o det erm ine t he dom ains of t he educat ion booklet . 2) Lit erat ure review t o develop t he cont ent for t he dom ains of t he booklet and for m ulat e a rough draf t of t he booklet . 3) M odificat ion in t he booklet as recom m ended by surgeons and t herapist s t o develop t he final booklet . 4) Evaluat ion of t he booklet on readabilit y ease by Flesch reading ease and by Suitabilit y assessm ent of M at er ial quest ionnaire filled by surgeons and t herapist s. 5) Pilot st udy on pat ient s t o take t heir view s regarding t he booklet developed.
Results: The dom ains det erm ined in st ep 1 w ere: Anat omy, understanding t he m echanism of pain, about t he surgery, com plicat ions associat ed w it h surgery and role of physiot herapy. The cont ent w as developed and m odified in st ep 2 and 3. In st ep 4 Flesch reading score is 70.5 and suitabilit y assessm ent of m at erial quest ionnaire score- 77.3%. In st ep 5 pat ient s rat ed t he booklet easy t o read and understand.
Conclusion: The developed pat ient educat ion booklet cam e out t o be fairly easy t o read according t o flesch reading ease and of superior qualit y according t o suitabilit y assessm ent of m at er ial quest ionnaire and hence should be m ade a part of pat ient educat ion.
KEYW ORDS:Lum bar discect omy; Pre operat ive pat ient educat ion booklet ; Flesch reading ease and suitabilit y assessm ent of m at erial quest ionnaire.
Quick Response code
Access this Article online
International Journal of Physiotherapy and Research
ISSN 2321- 1822
w w w.ijmhr.org/ ijpr.html
Received: 02-01-2014 Accepted: 17-01-2014
Published: 11-02-2014
ABSTRACT
INTRODUCTION
Address for correspondence: M anish Nagpal, B-3/178 janak puri New Delhi- 110058, India.
Email: Email: drmanish_pt @yahoo.in
Peer Review : 03-01-2014
*1 M PT (M usculoskeletal)
2 M PT (M usculoskeletal)
3 M PT (M usculoskletal)
Low back pain is t he m ost w idely repor t ed m usculoskelet al disorder in t he w orld w hich affect s funct ion and disabilit y t o a great extent1.
LBP can manifest it self in various clinical ways w h ich can var y f r o m a back p ai n t o
radiculopat hy2. Lumbar surgery for disc prolapse
is w ell established and common, but t he result s
remain variable4, w ith the success rate of lumbar
disc surgery varies bet ween 60-90% as compared t o m o r e t h an 80% i n st ud i es w h er e po st
operat ive rehabilitat ion has been provided3, 4, 6,
7. The primary surgical intervent ion for lumbar
radiculopat hy is lum bar microdiscect omy and
endoscopic discect omy4. Pre operat ive pat ient
veri-DISCECTOM Y.
ous surgeries and lead t o effect ssuch as de-creased post-operat ive medicat ion for pain, bet-ter know ledge or less cognit ive errors, reduct ion in anxiet y, better performance of exercise, bet-ter adherence t o rehabilitat ion inst ruct ions and higher self-esteem8, 10, 12. Pat ient educat ion can
be delivered by various met hods11, out of w hich
booklet s have been advocated as it is a simple, cost effect ive, and popular met hod of providing healt h-related informat ion t o pat ient s, and has been show n t o be feasible and effect ive in low back pain4, 13. It also enhances understanding,
retent ion, and applicat ion of t he informat ion14.
A booklet developed for pat ient educat ion is m ore helpful if evaluat ed w it h m ost suit able measures available such as; readabilit y ease (via Flesch reading ease, Flesch Kinaid reading score), quest ionnaires (such as Suitabilit y Assessment of M aterial, bernier inst ruct ion scale), quiz and checklist about t he content of t he educat ion
material have been used in various st udies5, 8, 9,
15. It is also important t o obtain feedback from
t he target audience on t heir preferences for t he design and delivery of w rit t en inform at ion15.
Pilot st udies are done for evaluat ion of t he pa-t ienpa-t educapa-t ion booklepa-t by papa-t ienpa-t s, in w hich t here comment s regarding t he material provided are taken3, 9. In t his st udy, a pre-operat ive
evi-dence based pat ient educat ion booklet w ill be developed and evaluated by surgeons, physio-t herapisphysio-t and by paphysio-t ienphysio-t undergoing lum bar discect omy.
M ethods and Results:
STEP 1- Det er m in at io n of d om ai ns o f t h e evidence based pre-operat ive pat ient education booklet for lumbar discect omy on t he basis of l it er at u r e r evi ew, i n fo r m al i nt er vi ew an d quest ionnaire on pat ient educat ion.
STEP 2- To develop t he content of t he evidence based pre-operat ive pat ient educat ion booklet according t o t he domains found in step 1 and it s compilat ion to form a rough draft of t he booklet .
STEP 3- M odificat ion of t he rough draft of t he booklet by spine surgeons and physiotherapist s. STEP 4- Evaluat ion of t he evidence based pre-operat ive pat ient educat ion booklet for lumbar discect omy by surgeons and physiot herapist s u si n g Fl esch read in g ease an d Su i t ab i li t y assessment of material quest ionnaire.
STEP 5- Pilot st udy on pat ient s for evaluat ion of t h e evi den ce based pr e-o per at i ve pat ient educat ion booklet for lumbar discect my.
Sample populat ion
Inclusion Criteria: Spine surgeons w ho performs discect om y w it h a m inim um of 5 year s of experience. Physiot herapist s regist ered w it h Delhi council of physiot herapy and occupat ional t herapy or are a member of Indian associat ion of physiot herapist s and involved in t reat ing lumbar discect omy pat ient s for at least a period of 2 years. Pat ient s w it h age 20-65 years, d i agn o sed of r ad i cul o p at hy d u e t o di sc herniat ion, nerve root irrit at ion, cyst and/ or foram inal st enosis and under w ent m inim al invasive discect omy i.e. endoscopic discect omy or microdiscect omy. Pat ient w ho attended t heir first rout ine post operat ive consultat ion w ith t he surgeon in t he first post surgical mont h.
Exclusion cr it er ia: Absence of co nsent f or
participation. Patients not fluent in English /
requires assistance, have undergone previous spinal surgery or is undergoing revision surgery. Pat ient s w ho are diagnosed w it h condit ions w hich include neurological disorders (e.g., st r o ke, d em en t i a, sei zu r es), un co nt r o ll ed cardiovascular disease, evidence of spinal cord co m p r essi o n, u nco n t r o l l ed hyp er t en sio n , infect ion, severe respirat ory disease, pregnancy, rheum at ic j oint disease, peripheral vascular disease w it h sensory loss at t he foot or any condit ion t he subject ident ifies t hat might limit part icipat ion in physical act ivit y.
t heir part icipat ion in t he st udy.
Informal interview : The aim of t his interview was t o find out t he areas w hich according t o t hem must be included in t he pre operat ive pat ient education booklet. It consist s of few open ended quest ions t hat w ere formulated after literat ure review described earlier regarding t he domains o f t h e p at ien t ed u cat i o n b o ok l et an d i n discussion w it h t he research guide. It t ook around 15-20 minutes during t he interview.
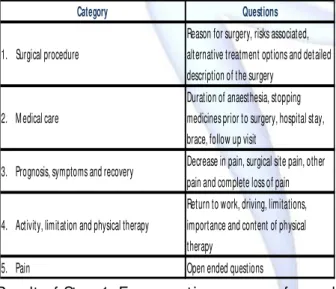
Quest ionnaire on pat ient educat ion material: It was developed and proved as a valid t ool in a st udy on pat ient educat ion in spine surgery by Louw A. The quest ionnaire was requested from t he aut hor and permission t o use t he same in
t he present st udy was taken. The quest ionnaire
was organized int o t hree sect ions: Sect ion one – Dem ograp hi c in fo r m at i on , Sect i on t w o : inst ruct ions on complet ing t he quest ionnaire; and Sect ion t hree consist ing of a ser ies of quest ions regarding educat ional needs, divided int o five categories (Table 1). A 10cm linear scale was used t o rate t he importance of a quest ion being answ ered by t hem , ranging from “ not important ” t o “ very important ”. Fift h category was on pain and had few open ended quest ions w hich w ere described in result s.
Table 1: Cat egories of sect ion 3 in quest ionnaire.
Category Questions
1. Surgical procedure
Reason for surgery, risks associated, alternative treatment options and detailed description of the surgery
2. Medical care
Duration of anaesthesia, stopping medicines prior to surgery, hospital stay, brace, follow up visit
3. Prognosis, symptoms and recovery Decrease in pain, surgical site pain, other pain and complete loss of pain
4. Activity, limitation and physical therapy
Return to work, driving, limitations, importance and content of physical therapy
5. Pain Open ended questions
Result of Step 1: Few quest ions w ere reframed in quest ionnaire and inform al int erview on request of surgeons. Table 2 and 3 show s t he result of literat ure review and informal interview resp ect i vel y. Graph 1 sh ow s t he r esul t of category 1-4 of t he quest ionnaire used in step 1 w hereas t able 4 show s t he result of t he 5t h
category of t he quest ionnaire.
Table 2: Dom ains obt ained from lit erat ure review and t heir frequency.
Dom ain Frequency
Anat om y 4
Surgical procedure 5
Reason for surgery 6
Risk and com plicat io ns 5
Frequent ly asked quest ions 2
Act ivit y lim it at ion/ exercises/ prot ect ion of back/ Ret urn t o w ork/ Pain m anagem ent
13
W hen t o seek m edical help 2
Out co m e 1
Im plant s 1
M edical care 2
Ho spit al st ay 2
Table 3: Inform at ion regarding dom ains t hat w ere highlight ed during inform al int erview.
Group Domains highlighted after the informal interview
Pre operat ive functional stat us
Inform ation about t he surgery
Post operative physiot herapy
Risk/ complications associat ed w it h the surgery
Psychological aspects
Outcome of the surgery
Goal of the surgery
Surgical procedure
Risk about surgery
Post ure educat ion
Post operative rehabilit ation
Activity modification
Pre operat ive functional stat us
Transfer education
Outcome of the surgery
Surgical procedure
Outcome of the surgery
Post operative rehabilit ation
Activity modification
Pain management aft er surgery Spine surgeons
Physiot herapists
Patient s
Table 4: Inform at ion obtained from 5t h sect ion of t he
quest ionnaire used in st ep 1.
10-15 % patients have pain at their 1st
follow up ranging from 2-3 on VAS scale where 0 is rated as no pain and 10 is rated for excruciating pain.
All of them think that patient will benefit from patient education and they will be interested in their prognosis after surgery. 2 out of 3 surgeons says that patient expect pain post operatively.
M edicines, ice pack and rest are measures adopted by patients for pain relief.
2 out of 3 surgeons wrote that their patients may feel depressed due to pain following surgery.
15-25 % patients have pain at their 1stfollow up ranging from 3-4 on VAS scale where 0 is rated as no pain and 10 is rated for excruciating pain.
All of them think that patient will benefit from patient education and 3 out of 5 believe that patients will be interested in their prognosis after surgery. All physiotherapists says that patient do not expect pain post operatively.
M edicines, ice pack and rest are measures adopted by patients for pain relief.
All physiotherapists believe that patients feel pain at surgical site, which will reduce with time.
4 out of 5 patients were having pain at their follow up visit. They rated their pain 2-3 on VAS.
2 patients were having pain at surgical site whereas 2 were having pain in the leg but of less intensity. They were advised exercises for pain relief.
3 patients expected no pain after surgery and hope that pain will disappear completely. 2 were still afraid that pain might come back.
Only 2 patients received education prior to surgery but no one was satisfied with the education given.
Patients Spine Surgeons
Physiotherapists
DISCECTOM Y.
hence w as excluded. Whereas surgical proce-d ur e w as i nclu proce-deproce-d bu t i nf or m at io n ab ou t alternat ive t reat ment was also excluded as t he bo ok let w as sp ecif ic t o d iscect om y. Af t er review ing all t he result s infor m at ion st at ed im port ant in 3rd category w as included under
“ Outcome of surgery”. Category 4 was included under t he domain “ role of physical t herapy ”. M ore informat ion was also obtained regarding domains of pat ient educat ion material but due t o lack of t heir im port ance or relevance t hey w ere exclu ded by t he resear ch er and t he research guide. The follow ing domains w ere included in t he booklet and w ere approved by su rgeo ns and t her api st s: 1) An at o m y 2) Understanding t he mechanism of pain 3) About t he surgery 4) Complicat ions associated w ith the surgery 5) Role of physiot herapy.
Step 2- A narrat ive review was done t o develop t he content for t he dom ains. Standard books w ere referred for anat omy and understanding t he m echanism of pain. About t he surger y, com plicat ions and out com e of surgery w ere developed after review ing few art icles w here as no detailed descript ion was available regarding t he im m ediat e physiot herapy prot ocol aft er discect omy t herefore informat ion from various art icles was used t o decide on t he dosage and descr ipt ion of exercises. Technical m edical t erminologies used in research art icles w ere m ade easy by t he r esear ch er an d n o n copyrighted images w ere used at appropriate places in t he booklet . Images for t he exercises w ere developed by a graphic designer and w ere used in t he booklet . A rough draft of t he booklet was t hus developed.
Step 3- 3 spine surgeons and 5 physiot herapist s w ere asked t o read t he booklet and suggest any modificat ion regarding t he content and language of t he booklet t hat are relevant and w it hin t he aim of t he st udy. M odificat ions w ere regarding making t he language easy, labeling t he diagram for easy understanding of pat ient s. M ost of t he req uest ed t o d elet e one im age d escr i b ing d i scect o m y t o be chan ged as i t co u l d b e misleading. Cont roversy was present regarding inclusion of nerve st retching exercise and lift ing of driving restrict ions which w ere done after
suit-able references w ere found16. Few addit ions
w ere also recommended like precaut ions during
exercises, ankle toe movement s, deep breat hing exercise and sitt ing on inclined chair rat her t han st raight back chair, t hese w ere also included after suitable evidence w ere found17, 18, 19, 20.
Step 4- Evaluat ion was done on readabilit y ease by using Flesch reading ease on readabi lit y st at ist ics of M icrosoft office w ord 2003. The readabilit y ease came out t o be 70.5 w hich rated t he booklet as fairly easy t o read. The suitabilit y assessment of material quest ionnaire was filled by surgeons and physiot herapist s after reading t he inst ruct ions t o use it . The quest ionnaire had 22 q u est i o ns w hi ch w er e d i vi d ed i n t o 6 categories: Content , literacy demand, graphics, layout and t ypography, learning st imulat ion and m ot i vat i o n an d cu lt u r al app r o pr i at en ess. According t o t his quest ionnaire t he booklet score obt ained w as 77.3% w hich rat ed it of superior qualit y.
Step 5- Pilot st udy on 5 pat ient s was done t o get t heir com m ent s regarding t he booklet developed. The quest ionnaire had t w o part s:
(1) 11 forced-choice quest ions;
(2) Open quest ions about t he most important messages t hey t ook from t he booklet and t heir overall rat ing of t he booklet on a scale from 1t o10.
The quest ionnaire was used by A.H. M cgregor in his study on pat ient education material. A copy of t he quest ionnaire and permission t o use it in t he present st udy was taken.
•
All t he pat ient s believed t hat t he book wasint erest ing, w it h clear inform at ion, enough pract ical t ips and easy t o follow. They also ment ioned t hat t hey w ill look back t he booklet from t ime to t ime, to check w hat t o do; the book w ill help people as t hey learned som e new helpful t hings and t hey w ill also recommend this book t o a friend or family member.
•
4 out of 5 pat ient s marked t hat t he book waseasy t o read, is of t he right lengt h and t hey believe m ost of w hat is said in t he booklet . Average pat ient rat ing for t he booklet came out t o be 9 out of 10.
DISCUSSION
Pat ient educat ion program s aim t o im par t know ledge and skills t o individuals so t hat t hey
may be able t o better manage t heir condit ion21.
If pat ient s are educated about t heir condit ion, t h e p r ogn o si s af t er t h e su r ger y an d i t s management is associated w it h higher pat ient
sat isfact ion and better short term outcomes3.
Determinat ion of domain was an important step in t he st udy as it provides t he basic framew ork for t he development of t he pat ient educat ion booklet as here we are t rying t o find out domains and t his step is not act ively used in most st udies available on pat ient educat ion material. It also becomes easier for a reader t o refer content in a booklet by presence of domains. Present st udy i nco r p o rat es l i t er at u re rev iew alo n g w it h informal int erview and quest ionnaire given t o spine surgeons, physiot herapist s and pat ient s t o determine t he domains of t he booklet was not p er fo r m ed so ext ensiv el y in any r esearch review ed during t his step.
In t he 2nd step of t he st udy evidences available
r egar d in g im m edi at e p o st o per at i v e rehabilitat ion and it s dosage w ere limited, best possible effort w as m ade t o for m ulat e t he dosage and descript ion of exercises during t his phase w it h t hese limit ed evidences. How ever more randomized cont rolled t rials are needed t o come t o a conclusive dosage. Post operat ive exercises of t he init ial phase i.e. from 1-3 w eeks w as included in t he booklet , for lat er m ore specific rehabilitat ion patient s w ould be advised t o go t o outpat ient rehabilitation depart ment as t he mot ive of pat ient educat ion material is not t o provide it as a subst it ut ion for physiot herapy. The expert team was alt hough consulted for t he images but no detailed analysis or review of images was done because of lack of t ime.
After modificat ions were done in step 3, t he final booklet was completed by making an att ract ive front cover by t he researcher. The follow ing informat ion was also provided in t he booklet : cont act inform at ion for any suggest ions, t he copyr ight st at em ent , t he out com es of t he surgery may vary, all exercises described is for init ial phase of rehabilitat ion and may not be p er f o r m ed by ever y pat i en t . Fi n al l y acknow ledgem ent and list of cont ent s w as added before t he actually content of t he booklet st art s.
CONCLUSION
The ev id ence b ased p reo perat iv e p at i en t educat ion booklet developed is fairly easy t o read according t o Flesch Reading Ease and is of sup er io r qu al it y acco rd i n g t o su i t ab i li t y assessm en t of m at er i al quest ion naire and t herefore can be given t o pat ient s prior t o discect omy t o prepare t hem for t he surgery.
Limitat ions
1. Psychological issues w ere not addressed in the booklet .
2. Sample size was small due t o t ime limitat ion.
3. Sample populat ion was recruited from only one hospital.
4. Informat ion obtained from t he pain category of the questionnaire used in step 1 was described
Graph 1: Level of im portance rat ed t o each quest ion by surgeons, physiot herapist s and pat ient s.
DISCECTOM Y.
REFERENCES
Conflicts of interest: None
10. Henr ot i n Y., Ced raschi C., Du plan B., Bazin T., Duequesnoy B.: Inform at ion and Low back pain M anagem ent : A syst em at ic Review. Spine 2006: 31(11), 326-334.
11. Fr iedm an A., Cosby R., Boyko S.: Effect ive Teaching St rat egies and M et hods of Deliver y for Pat ient Educat ion. Program in Evidence-Based Care 2009, 20-22.
12. Johansson K, Nuut i la L, V ir t anen H, Kat ajist o J,
Salant erä: Pre-operat ive educat ion for or t hopedic
pat ient s: Syst em at ic review. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2005; 50(2):212-223.
13. Chou R., Qaseem A., Snow V., Casey D., Cross Jr. J., Shekelle P., et al: Diagnosis and Treat m ent of Low Back Pain: A Joint Clinical Pract ice Guideline f rom t h e Am er i can Co l l e ge o f Phy si ci an s an d t h e Am erican Pain Societ y. Ann Int ern M ed 2007; 147: 478-491.
14. Lee T., Yeh Y., Liu C., Chen P. et al: Developm ent and evaluat ion of a pat ient -or ient ed educat ion syst em for diabet es m anagem ent . Int ernat ional journal of m edical inform at ics 2007: 76; 655–663. 15. Eam es S., M cKenna K., Worrall L., Read S.: The Suitability of Writt en Educat ion M aterials for Stroke Survivors and Their Carers. Top St roke Rehabil 2003; 10(3): 70–83.
1 6. Scr i m sh aw V. B. , M ah e r C. G. : Ran d o m i zed Cont rolled Trial of Neural M obi lizat ion Aft er Spinal Surgery. Spine 2001: 26 (24); 2647-2652.
17. W ilke H.J., Neef P., Caim i M ., Hoogland T., Claes L. E.: New In V ivo M easurem ent s of Pressures in t he Int er ver t ebral Disc in Daily Life. Spine 1999; 24: 755–762.
18. Rosenquist R. W., Rosenberg J.: Post operat ive Pain Guidelines. Reg Anest h Pain M ed 2003; 28: 279-288.
19. Agnelli G. Prevent ion of Venous Throm boem bolism in Surgical Pat ient s.Circulat ion2004; 110: IV-4-IV-12.
20. Kw on OY, Jung DY, Kim Y, Cho SH and Yi CH: Effect s of ankle exercise com bined w it h deep breat hing on blood f low velocit y in t he fem oral vein. Aust ralian Jour nalofPhysiot herapy2003; 49: 253–258. 21. Osbor ne R., Buchbinder R., Acker m an I.: Can a
disease-specific educat ion program augm ent self-m anageself-m ent ski lls and iself-m prove Healt h-Relat ed Qu al i t y o f Li f e i n p eo p l e w i t h h i p o r k n e e ost eoar t hr it is? BM C M uscul oskelet al Disor ders
2006,7:90-10. 1. Kulig K, Beneck GJ, Selkow it z DM , Flanagan S.P.,
Popper t E. M ., Yam ada K. A. et al; An int ensive, progressive exercise program reduces disabilit y and im proves funct ional perform ance in pat ient s af t er single-level lum bar m icrodiskect omy. Phys Ther 2009; 89:1145–1157.
2. Ost elo RWJG, de Vet HCW, Wadell G, Kerckhoffs M R, Lefflers P, Tulder M .; Rehabilitat ion follow ing
lum bar disc surgery. Spine 2009; 34(17):1839-1848. 3. Louw A, Louw Q, Crous L; Preoperat ive educat ion for lum bar surgery for radiculopat hy. SA Journal of physiot herapy 2009; 65 (2): 3-8.
4. Gulat i Y.: Lum bar m icrodiscect omy. Apollo m edicine 2004; 1: 29-32.
5. M cGregor A. H., Burt on A.K., Sell P., G. Waddell: The developm ent of an evidence based pat ient booklet for patient s undergoing lum bar discect omy and uninst r um ent ed decom pressio n. European Spinal Journal 2007; 16:339-346.
6. Gr ev i t M . P., M cl ar en A., Sh ackl ef o r d I. M ., M u l h o l l an d R. C.: Au t o m at ed p er cu t an e o u s discect omy: An outcom e st udy. J Bone Joint Surg [Br ] l995; 77-B: 626-9.
7. Taha M ., Faead h M .H.: Funct ional Recovery for
Pat i en t s w i t h Lu m b ar - Sacr al Di sc Pr o l ap se Undergoing Lam inot omy & Diskect omy. Eur J Sci Res 2010, 45, 22-36.
8. M cClune T., Burt on A. K., Waddell G.: Evaluat ion of an evidence based pat ient educat ional booklet for m anagem ent of w hiplash associat ed disorders. Em erg M ed J 2003; 20: 514–517.
9. Spiegel B., Talley J., Shekelle P., Agarw al N., Snyder B., Bolus R. et al: Developm ent and Validat ion of a Novel Pat ient Ed ucat ional Bo oklet t o Enhance Colonoscopy Preparat ion. Am J Gast roenterol 2011; 106: 875–883.
How to cite this article
:
M anish Nagpal, M eena M akhij a, Abha Sachdev.DEVELOPM ENT AND EVALUATION OF EVIDENCE BASED PRE-OPERATIVE PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET IN LUM BAR DISCECTOM Y. Int J Physiot her Res 2014;2(1):359-64. in result s but was not analyzed for determinat ion
of domains.
Acknow ledgements