Analysis of the Resources of
the ABC Program for the
2013/2014 crop year
(Until April)
Summary
Introduction...4
Main conclusions of the study... 6
1 Brief history of the ABC Program... 7
2 ABC Program Analysis for the 2013/14 crop year ... 7
2.1 ABC Program Resource Distribution for the 2013/14 crop year ... 9
2.1.1 Regional distribution of contracts and contracted value ... 10
2.1.2 Distribution of resources and contracts approved according to investment purpose ... 14
2.1.3 Distribution of resources according to transfer agent and source... 15
2.1.4 Comparison to previous crop years ... 17
Project
ABC Observatory
Support
Climate and Land Use Alliance (CLUA)
Organization responsible for the project
Fundação Getulio Vargas (FGV)
Agribusiness Center (GV Agro), School of Economy of São Paulo (EESP)
GV Agro Coordinator
Robert Rodrigues
Project Coordination
Angelo Costa Gurgel Cecília Fagan Costa
Organization responsible for the project
Centro de Estudos em Sustentabilidade da Fundação Getulio Vargas GVces)
Project Coordinator
Aron Belinky Mario Monzoni
Project Technical Team
Annelise Vendramini
Introduction
The main goal of the ABC Plan is to bring about the transition of conventional agriculture to a production model that minimizes the GHG emissions in Brazil. For this purpose, the ABC Program has been adopted, as it aims at providing conditions for farmers to carry through the necessary investments for incorporating technological alternatives of low carbon emission in the productive process. In this context, the ABC Observatory wants to engage different sectors of Brazilian society in this transition by monitoring the ABC Plan and Program's actions and also developing technical studies to support and facilitate discussion and dialogue with society and the government.
During the first year of activity, the ABC Observatory published three studies that were launched in the presence of important decision-makers involved in the ABC Plan and Program. The studies were the following:
1. Study 1 - Low Carbon Emission Agriculture: The Evolution of a New Paradigm. 2. Study 2 - The Governance of the ABC Plan.
3. Study 3 - Low Carbon Emission Agriculture: Financing the Transition.
This is the first in a series of four reports comprising the activities of the second year of work of the ABC Observatory. These reports aim to quantitatively and qualitatively analyze the ABC Program's performance – the financing of low-carbon agriculture in Brazil. This activity also contributes to increase transparency in the availability of information to society, sorting the data regarding the crop year, the transfer agent, the source of financing used, the location (state, city and region) and the purpose of investment.
In addition, during the second year of the Observatory, the information published in the reports will be available in a system of open-access data, at www.observatorioabc.com.br. This system will allow the user to manage – generating graphs and tables – data of disbursements of the ABC Program according to investment purposes, state and region, source of resources, transfer agent and crop year, since the beginning of the program (2010/11 crop year) up to the current crop year.
Desenvolvimento Econômico e Social (BNDES) by means of an agreement signed with the ABC Observatory [01] 123
In the next section, a brief summary of the path of the ABC Program line of credit and its main results in different crop years is presented. In the following one, a detailed analysis of the disbursed sum until April of the 2013/14 crop year is carried out. Lastly, we present closing remarks on the current results of the ABC Program.
1 Previously, in the 2011/12 and 2012/13 crops, data for analyses of the ABC Program proceeded from various sources: Banco do Brasil (BB), BNDES and Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Food Supply of Brazil (MAPA).
2
Circular letter n. 3,620 of December 21, 2012, available at:
http://www.bcb.gov.br/pre/normativos/circ/2012/pdf/circ_3620_v1_O.pdf
Main conclusions of this study
• Despite breaking the record for available funds, with BRL 4.5 billion, the ABC Program stagnated in 2013/14. The disbursements, that had reached 83% of the total in 2012/13 and were rapidly increasing in the previous crop years, reached only 53% in April 30, 2014, two months from the end of the crop year. In absolute value, BRL 2.364 billion were invested in program actions, against BRL 2.993 billion in 2012/13. This indicates that the crop year may end with a decrease in financing emission mitigation in agriculture.
• The possible reasons of the low level of adhesion of producers to the ABC Program continue being the interest rate of 5% a year – that have become less attractive than other lines of credit, such as PRONAMP (Programa Nacional de Apoio ao Médio Produtor Rural - National Program of Support to the Medium Scale Farmer), that had a decrease of interest rate reaching 4,5% - and the high level of requirements for attaining credit, as the ABC demands the producer to present a geo-referenced project of the property and soil analysis.
• As in previous years, ABC financing continues concentrated in the Southeastern states – that hold 40% of the contracts – and in the states of the Midwest that have fewer contracts, but with a higher average value per contract, which makes the region the biggest destination of the ABC money in the current crop year (almost BRL 885 million, against BRL 801 million of the Southeast).
• The North and Northeast regions, although being priority to the ABC actions due to the vast extension of degraded pastures and to the relatively low efficiency of agriculture, continue being the ones that less sign contracts and receive financings from the ABC. The two regions jointly had only 21% of contracts and received BRL 450.1 million, in 2013/14 (until April) - little more than half of what the Midwest region received alone.
•
As previously diagnosed in 2013 by the ABC Observatory, such low participation of the North and Northeast in contracts and disbursements of the ABC Program are due to land issues, lack of technical support and commitment of the producers in the North region to the lines of credit of the Constitutional Fund of Financing of the North - Fundo Constitucional de Financiamento do Norte (FNO) and of the Northeast producers to the National Program of Strengthening of Family Agriculture - Programa Nacional de Fortalecimento da Agricultura Familiar (Pronaf).•
There was also no progress in the commissioning of the Multi-Institutional Virtual Laboratory on Climate Change and Agriculture, an institution in charge of analyzing carbon to affirm whether or not the ABC mitigation goals are being met.•
However, there is good news in the governance of the program: Banco Central (Central Bank) started to closely monitor the rural credit agents by developing, in 2013, a computerized operation control system, SICOR. In 2014, the system became available on the Internet, increasing the transparency of agriculture credit application, which includes the ABC Program.•
More good news is that two important states for the consecution of the ABC mitigation strategythrough a significant expansion of agriculture - left the group of states that less receive financing from the program and are now in the group that receive between 1% and 2% of the total.
1 Brief history of the ABC Program
The Sectoral Plan of Mitigation and Adaptation to Climate Change in order to consolidate an Economy of Low Carbon Emissions in Agriculture (ABC Plan) integrates the commitments made by Brazil under the National Policy on Climate Change (Law No. 12,187/2009 and Decree No. 7,390/2010) to mitigate its emissions of greenhouse gases (GHG). The ABC Program, established by the BACEN – Banco Central (Central Bank) Resolution nº 3,896 of August 17, 2010, is a line of credit that allows rural producers to conform to the ABC Plan guidelines.
For the 2010/11 crop year, BRL 2 billion were provided for investments in techniques that increase efficiency in crops, with a positive balance between sequestration and carbon emissions. And, also, there was the guarantee of financing to farmers and cooperatives, with a financing limit of BRL 1 million per beneficiary. The credit would be financed with an interest rate of 5.5% pa and a term of twelve years repayment.
For the 2011/12 crop year, BRL 3.15 billion were allocated to the ABC Program with financings from Banco do Brasil and BNDES. This showed the willingness of the Federal Government to evidence the line of credit and place the program in the center of the national agricultural production strategy. This motivation advanced to the following crops. The 2012/13 crop year had an increase of BRL 3.4 billion and the 2013/14 crop year had an increase of BRL 4.5 billion. Moreover, in these periods, there was a reduction in the interest rate of the line to 5% per year, reflecting the Government's effort to stimulate demand - which does not yet reach the entire allocated amount.
The 2013/14 crop year will be analyzed with more details below.
2 Analysis of the ABC Program for the 2013/14 crop year
In the 2013/14 crop year, BRL 136 billion were allocated to rural credit, representing an increase of approximately 15% compared to the previous crop year. Of this amount, BRL 97.6 billion were allocated to the financing of costing and marketing, and the remaining BRL 38.4 billion for investments. BRL 4.5 billion were allocated to the ABC Program, with an interest rate of 5% per year, maximum payment term of fifteen years and a grace period of six years for the 2013/14 crop year.4
Table 1 shows the efficiency of financing application when comparing the total programmed and executed by the two most important banks in the ABC Program scenario: Banco do Brasil (BB) and BNDES. In the 2013/14 crop year, 93.7% of the total financing for the execution of the ABC Program came from BB and 6.3% from BNDES. Due to greater participation of the BB in disbursements in the previous crops, it was established that this bank would have greater amount of financing.
4
Livestock Agricultural Plan 2013/14, available at:
Table 1. Effective programming and application of ABC Program funds in the 2010/11, 2011/12, 2012/13 and 2013/14 crop years until April, 2014 (in BRL millions) *
Program 2010/11 2011/12 2012/13 2013/14
Programmed Applied Programmed Applied Programmed Applied Programmed Applied ABC 2,000.00 418.50 3,150.00 1,526.10 3,400.00 2,993.10 4,500.00 2,364.33 BNDES 304.90 2,300.00 310.00 1,900.00 370.30 500.00 148.08 BB 113.60 850.00 1,216.10 1,500.00 2,622.80 4,000.00 2,216.26 * Adapted from the SPA/MAPA March report and SICOR data, until April, 2014
The causes of greater participation of BB in total financing allocated to the ABC Program have already been detailed in 2013 in Study 3 of the ABC Observatory (Low Carbon Agriculture: Financing the Transition). In general, this is due mainly to the use of their own resources from Poupança Rural - Rural Savings; from a financial agent training program (in partnership with the National Confederation of Agriculture and Livestock of Brazil), with the support booklet that guides agents on ABC Plan financing; and further training of the main actors involved in the credit decision process (financial agents, cooperatives etc.) in each state.
Table 2. Volume of resources and credit limit for investment programs in the 2013/14 crop year
(1) Limit for afforestation: BRL 3 million per beneficiary (2) Limit for collective credit: BRL 2.4 million
2.1 Distribution of ABC Program resources in the 2013/14 crop year
This section provides an overview of the implementation of the ABC program in the 2013/14 crop year. Data from the BNDES, the Secretariat for Agricultural Policy of the Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Food Supply (SPA/MAPA) and Banco Central - Central Bank- (SICOR) were consulted and used. Banco do Brasil did not provide the ABC program disbursement data, which was inferred, indirectly, by SICOR.
2.1.1 Regional distribution of contracts and of the contracted value
In this crop year (until April 2014), 9,625 contracts for the ABC Program were signed, with total disbursements of BRL 2,364,339,691.52 and average value of contracts of BRL 245,645.68 (table 3). Among the implemented projects, 3,666 are in the Southeast region, especially in the states of Minas Gerais and São Paulo; 2,405, in the Midwest region, with 1,150 only in Goiás; 1,524, in the South region, especially in Rio Grande do Sul and Paraná; 1,273, in the North region, with 682 only in Tocantins; and 757 in the Northeast region, with 460 contracts approved only in Bahia.
The distribution of the ABC Program contracts, in 2013/14, follows the same logic as the previous crop years, with concentration in the Southeast of the country which represents almost 40% of all projects approved in the 2013/14 crop year (until April 2014), while the North and Northeast regions together account for only 21% of the total (table 3). The Midwest region, second in total number of contracts, presented an average value per contract of BRL 367,900.00 - the highest national average - indicating a high concentration of resources in the states of Mato Grosso do Sul, Mato Grosso and Goiás; while the South region, third in total contracts, presented the lowest national average, with an average contract value of BRL 149,300.00.
Table 3. Regional distribution of ABC Program disbursements in the 2013/14 crop year (until April 30, 2014)
Region Nº of contracts Disbursements Average contract value
Southeast 3,666 BRL 801,646,772.08 BRL 218,670.70
MG 1,953 BRL 421,895,930.98 BRL 216,024.54
SP 1,437 BRL 337,530,816.07 BRL 234.885.75
ES 175 BRL 30,568,802.79 BRL 174,678.87
RJ 101 BRL 11,651,222.24 BRL 115,358.64
Midwest 2,405 BRL 884,945,003.48 BRL 367,960.50
GO 1,150 BRL 348,667,938.98 BRL 303,189.51
MS 686 BRL 325,966,274.29 BRL 475,169.50
MT 566 BRL 209,954,658.83 BRL 370,944.63
DF 3 BRL 356,131.38 BRL 108,710.46
South 1,524 BRL 227,601,086.20 BRL 149,344.54
RS 659 BRL 105,810,374.84 BRL 160,562. 03
PR 608 BRL 99,169,135.78 BRL 163,107.13
SC 257 BRL 22,621,575.58 BRL 88,021.69
North 1,273 BRL 241,421,294.82 BRL 189,647.52
TO 682 BRL 135,220,435.31 BRL 198,270.43
PA 295 BRL 63,570,474.28 BRL 215,493.13
RO 136 BRL 25,641,270.24 BRL 188,538.75
AC 134 BRL 11,902,654.09 BRL 88,825.78
AM 9 BRL 1,519,423.41 BRL 168,824.82
Northeast 757 BRL 208,725,534.94 BRL 275,727.26
BA 460 BRL 143,161,604.93 BRL 311,220.88
MA 242 BRL 46,067,624.17 BRL 190,362.08
PI 47 BRL 18,663,730.84 BRL 397,100.66
PE 7 BRL 646,680.00 BRL 92,382.86
CE 1 BRL 185,895.00 BRL 185,895.00
Total 9,625 BRL 2,364,339,691.52 BRL 245,645.68
Source: SICOR
The distribution of the number of contracts approved per municipality in the 2013/14 crop year (until April 2014) can be visualized in figure 1. It shows high concentration of approved contracts in municipalities in the West of Goiás, Minas Gerais, Bahia and Mato Grosso, as well as in northern Mato Grosso do Sul. The states of the North and Northeast regions present very low participation, and no contracts in Amazonas, Alagoas, Rio Grande do Norte, Sergipe or Paraíba.
Source: Numbers based on data from SICOR
The regional distribution of the contracted value in the 2013/14 crop year (until April, 2014) can be visualized in figure 2. In the east of Mato Grosso do Sul, two municipalities are pointed out: Água Clara, with BRL 40 million in contracts, and Ribas do Rio Prado, with BRL 80 million. The West of Minas Gerais, Bahia, Goiás and Midwest of Mato Grosso presented high concentration of disbursements with a total of contracts ranging from BRL 5 million to BRL 21 million. Once again, the low participation of the states of the North and Northeast regions in total disbursements of the ABC Program is evident.
One of the reasons for that would be that producers from these regions are committed to other sources of financing for agricultural practices, such as Constitutional Funds of the North and Northeast (Fundos Constitucionais do Norte e Nordeste) and the line of credit from Pronaf.
Figure 2. Space distribution of disbursements for the ABC Program in the 2013/14 crop year (until April, 2014)
Source: Numbers based on data from SICOR
mainly in the North and Northeast regions that present great extension of degraded pastures5. Great part of the disbursements were allocated to municipalities of the Midwest region, with the highest number of cattle in the country (34.4% of the total) and with considerable areas of degraded pastures in some of the municipalities that received disbursements.
Minas Gerais, Goiás, São Paulo and Mato Grosso do Sul took the lead with 17.80%, 14.75%, 14.28% and 13.79%, respectively. The states of the North and Northeast, mainly Ceará, Pernambuco, Amazonas, Roraima, and Distrito Federal (Federal District), had the lowest participation in this crop year until April 2014 (figure 3). The situation is similar regarding approved contracts: Minas Gerais, São Paulo, Goiás and Mato Grosso do Sul presented more participation, in descending order; and Ceará, Pernambuco, Amazonas, Roraima and Distrito Federal (Federal District), less participation (figure 4).
Figure 3. Percentage of each state´s participation in total ABC Program disbursements in the 2013/14 crop year (until April 30, 2014)
Source: Numbers based on data from SICOR
Figure 4. Percentage of each state´s participation in total approved contracts for the ABC Program in the 2013/14 crop year (until April 30, 2014)
5
Source: Numbers based on data from SICOR
The low participation of the North and Northeast regions in the national panorama of ABC contracting is a reflection of the lack of technical support, severe land issues - mainly in the states of the North, the commitment of great part of Northern producers to the FNO (Fundo Constitucional de Financiamento do Norte- Constitucional Fund of Financing of the North) and of the Northeastern producers to Pronaf (Programa Nacional de Fortalecimento da Agricultura Familiar - National Program of Strengthening of Family Agriculture). This reinforces the need of greater participation of the main actors involved in the ABC Plan and Program in the Northeast region, as well as a bigger approach of the Ministry of Agriculture, by means of Embrapa and of the recently established Anater (Agência Nacional de Assistência Técnica e Extensão Rural - National Agency for Technical Assistance and Rural Extension), in relation to the Northeast states to improve technical qualification.
2.1.2 Distribution of the resources and contracts approved for investment purposes
For the analysis of resources and contracts approved by ABC's action in the 2013/14 crop year, only data provided by BNDES was used, representing 6.3% of total disbursements for the program, disaggregated by investment purposes. As previously reported, SICOR does not contemplate subprograms of agricultural lines of credit and, therefore, disaggregated data by investment purposes are not available in that system of BACEN. Until the publication of this report, the ABC Observatory had not received the disaggregated data referring to ABC Program disbursements for the ongoing crop.
afforestation accounted for 6.8%, concentrated, in descending order, in Minas Gerais, Paraná and Rio Grande do Sul; and animal waste treatment for 0.3%, in Santa Catarina and Minas Gerais.
The ABC Environment, that finances practices such as the recovery of degraded areas and permanent preservation areas (that are not part of the ABC Plan scope), represented only 0.1% of total disbursements. Thus, it does not really affect the allocation of ABC Plan resources, which aims to help meet the voluntary goals for reducing greenhouse gases (GHG), announced by the Brazilian government at the Copenhagen Climate Conference, in 2009.
Despite representing the smallest part of the ABC Program sum, the disaggregated data from BNDES reflects the overall trend of the program´s performance. Such performance is similar to the one observed in the previous crop in relation to the regional distribution of ABC Program disbursements, with pasture recovery up to almost 80% of the total. The low adhesion of the North and Northeast regions to the ABC Program techniques occurs once again, as well as some of the causes: lack of technical assistance and severe land issues in the Northern States.
Table 4. Value of disbursements for each investment purpose of the ABC Program in each state by BNDES in the 2013/14 crop year (until April, 2014)
States ABC Environment ABC Forests ABC No-Till Farming ABC Recovery ABC
Waste Treatment Total (BRL)
SP 132,000 363,206 450,000 2,555,870 3,501,076
ES 780,016 309,346 1,089,362
GO 267,135 1,543,634 51,389,824 53,200,593 MG 3,817,551 2,133,160 15,109,102 41,523 21,059,813
PR 2,721,254 1,155,000 3,150.00 7,026,939
RS 1,379,483 8,477,999 4,772,711 14,630,193
PI 3,600,000 3,600,000
SC 1,967,493 272,985 356,480 2,240,478
TO 1,126,174 11,879,353 13,005,527
BA 500,000 500,000
MS 10,180,235 10,180,235
MT 1,275,000 1,275,000
PA 7,679,960 7,679,960
RJ 129,685 129,685
RO 600,000 600,000
Total 132,000 9,460,645 20,453,460 109,804,756 398,003 139,850,861
Source: BNDES
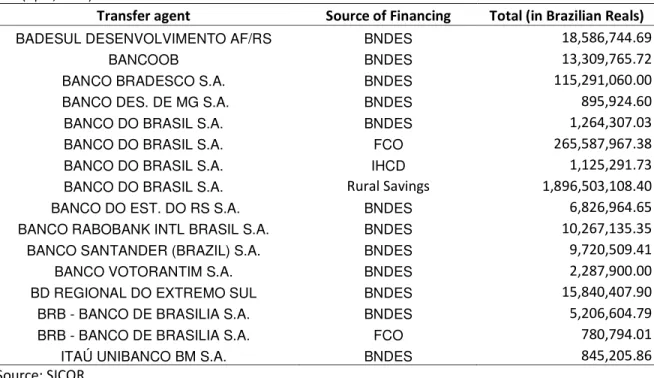
2.1.3 Distribution of the resources by transfer agent and financing source.
Table 5. Transfer agent, source of financing and total disbursements for the ABC Program in the 2013/14 crop year until (April, 2014)
Transfer agent Source of Financing Total (in Brazilian Reals)
BADESUL DESENVOLVIMENTO AF/RS BNDES 18,586,744.69
BANCOOB BNDES 13,309,765.72
BANCO BRADESCO S.A. BNDES 115,291,060.00
BANCO DES. DE MG S.A. BNDES 895,924.60
BANCO DO BRASIL S.A. BNDES 1,264,307.03
BANCO DO BRASIL S.A. FCO 265,587,967.38
BANCO DO BRASIL S.A. IHCD 1,125,291.73
BANCO DO BRASIL S.A. Rural Savings 1,896,503,108.40
BANCO DO EST. DO RS S.A. BNDES 6,826,964.65
BANCO RABOBANK INTL BRASIL S.A. BNDES 10,267,135.35
BANCO SANTANDER (BRAZIL) S.A. BNDES 9,720,509.41
BANCO VOTORANTIM S.A. BNDES 2,287,900.00
BD REGIONAL DO EXTREMO SUL BNDES 15,840,407.90
BRB - BANCO DE BRASILIA S.A. BNDES 5,206,604.79
BRB - BANCO DE BRASILIA S.A. FCO 780,794.01
ITAÚ UNIBANCO BM S.A. BNDES 845,205.86
Source: SICOR
Figure 5 shows the regional distribution of the ABC Program's funding sources for the 2013/14 crop year (until April 2014). As expected, there is a clear dominance of the use of Poupança Rural (Rural Savings) from Banco do Brasil (BB) for ABC Program contracting. However, in the Midwest, FCO6
has greater participation as a source of funds. Although the FCO not having offered as attractive interest rates as the ABC Program's, the process of getting credit through this source is less bureaucratic (there is no need to present a project nor a soil organic matter analysis) and the credit limit is significantly higher than the one offered by the ABC Program.56 7
Resource from BNDES were allocated, mainly, to the South and Southeastern regions and to the state of Goiás.
The North and Northeast regions, once again, had very low participation. The reasons have already been reported in previous ABC Observatory studies as well as throughout this report. A possible alternative would be the inclusion of the ABC lines of financing in the Fundos Constitucionais de Financiamento do Norte e Nordeste - Constitutional Funds of the North and Northeast (FNO and FNE), in the same way as with the FCO. This way, the program would have higher dissemination.
6
The Fundo Constitucional de Financiamento do Centro-Oeste (Constitutional Fund of Financing of the Midwest (FCO) was created by Law n º 7,827 of September 27, 1989, that regulates section 159, subsection I, clause “c”, of the Federal Constitution, with the objective to contribute to the economic and social development of the region, by means of the execution of financing programs for productive sectors.
7
Ceiling of BRL 20 million per borrower with fixed interest rates established between 5 %(mini-producer) - 8.5% (large producer) pa according to the producer, cooperative or association; except for forest operations destined to the regulation and recovery of Legal Reserve degraded areas with 4% pa. Available at:
http://www.sudeco.gov.br/documents/10157/170829/Anexo+08+-+Programa%C3%A7%C3%A3o+do+FCO+para+2014.pdf
8
Figure 5. Regional distribution of the ABC Program's funding source for the 2013/14 crop year (until April, 2014).
Source: Numbers based on data from SICOR
2.1.4 Comparison to previous crop years.
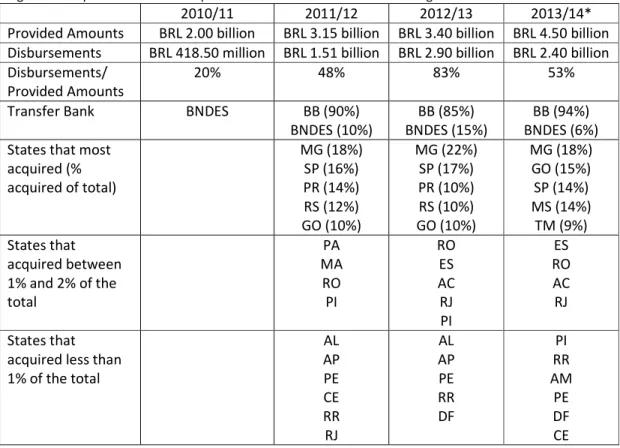
months before the end of the crop year, that goes until the end of June (table 1). Banco do Brasil increased its participation, going from 85% of the financing in 2012/13, to 94% in 2013/14.
In the 2011/12 and 2012/13 crop years, the main borrowers were Minas Gerais, São Paulo, Paraná, Rio Grande Do Sul and Goiás. In the 2013/14 crop year, all the states of the Midwest became part of the group of the five largest borrowers of ABC resources, while the states of the South no longer belong to that group. This shows that the program has received more adhesion from the Midwest than from the South, despite the decrease in the total of funding.
The states of the North and Northeast, Rio de Janeiro, Espirito Santo and Distrito Federal each had less than 2% of participation. Pará, that has great area of degraded pastures, no longer belongs to the group of states with less expression in acquisition of financings of the program from 2012/13, as well as the state of Maranhão, that has had strong agriculture expansion in recent years.
Figure 1 Comparison between crops of selected indicators of the ABC Program
2010/11 2011/12 2012/13 2013/14*
Provided Amounts BRL 2.00 billion BRL 3.15 billion BRL 3.40 billion BRL 4.50 billion Disbursements BRL 418.50 million BRL 1.51 billion BRL 2.90 billion BRL 2.40 billion Disbursements/
Provided Amounts
20% 48% 83% 53%
Transfer Bank BNDES BB (90%)
BNDES (10%)
BB (85%) BNDES (15%)
BB (94%) BNDES (6%) States that most
acquired (% acquired of total)
MG (18%) SP (16%) PR (14%) RS (12%) GO (10%) MG (22%) SP (17%) PR (10%) RS (10%) GO (10%) MG (18%) GO (15%) SP (14%) MS (14%) TM (9%) States that acquired between 1% and 2% of the total PA MA RO PI RO ES AC RJ PI ES RO AC RJ States that
acquired less than 1% of the total
AL AP PE CE RR RJ AL AP PE RR DF PI RR AM PE DF CE * Until April 30, 2014 - Crop year ends on June 30.
Source: Numbers based on data from SICOR and SPA/MAPA
3 Conclusion
some essential factors for the program to be totally successful, in terms of disbursements and the ultimate goal of reducing GHG in the atmosphere.
Regarding the ABC Program governance, a remarkable advance was the engagement of BACEN in the process of monitoring resources provided by the line's financial transfer agents, by SICOR, that, from April of 2014, also began providing the SICOR-Web system, in which the user can consult information and values of contracts referring to the agricultural credit in the country, contributing to more transparency8. SICOR gathers information from all financial operations of rural credit, including the ABC Program, and the partnership between BACEN and the ABC Observatory is an important milestone for society as to the availability and legitimacy of the data. BNDES also contributed to the transparency of the ABC Program by providing the ABC Observatory its disaggregated data for investment purposes, which are not contemplated by SICOR, allowing a broader analysis of the results.
While the monitoring of the financial resources advances, the tracking of the balance of mitigated and/or captured carbon by productive techniques financed by the ABC Program is still pending. There was no practical action to put the Multi-institutional Virtual Lab on Climate Change and Agriculture in operation, and it is still necessary to create special lines of credit for the acquisition of equipment for carbon analyses in the soil including the details required by the ABC Plan. Only with that structure can the assessment to whether their goals and objectives are being achieved take place.
As seen in the analysis of the 2013/14 crop year throughout this report, the demand for financing is less than expected compared to previous periods. If the interest rate is still the main attraction for producers to access the resources and modify their production models, it needs to be more attractive than other investment lines available, taking into account the costs of transaction involved in resource acquisition in the ABC program.
Resource distribution is concentrated in the Midsouth, although the North and Northeast regions are also a priority, mainly for actions of recovery of pastures, as these regions present extensive degraded areas. To balance credit distribution, it is important to strengthen the qualification process of rural extension workers, producers and financial analysts in order to stimulate demand and to evidence the systemic aspects linked to the projects.