Vol-7, Special Issue-Number2-April, 2016, pp1232-1244 http://www.bipublication.com
Review Article
A survey of effective factors on improvement of environmental
quality of Tehran book city-Iran
1
Hanieh Sadat Zendehbad and 2Mehdi Sheibani
1
MA of architecture, Azad University of Shiraz branch h.s.z.architect@gmail.com
2
Professor of landscape architecture, Shahid Beheshti University
M-SHEYBANI@CC.SBU.AC.IR
*This paper is based on MA thesis of Hanie Sadat Zendeyad “ Design of book city with the approach of improving environmental quality, Supervisor: Mehdi Sheibani in Azad University of Shiraz
ABSTRACT
Architecture, art, technique of building construction, urban spaces and other outer and inner spaces are used for harmonious fulfillment of functional and aesthetic requirements. Architecture should be distinguished from structural engineering. Based on the concentrated designs in common urban architecture projects, one of the basic studies in the present world is considering the improvement of human-based environmental quality in relevant plan. Master plans as one of the most important managerial tools at region and township in the past decades have encountered the problems inhibiting the achievement of results and goals. Also, the designers and architects of urban projects have not considered environmental space creation despite its requirements with the leisure time of the youth, adolescents and the elderly. Today, urban green space is used as one of the main indicators of sustainable development of qualitative space creation in the border of designed building and it is a criterion to recognize a healthy city. From the view of architecture planning and urban design and architects expert in landscape, development of green space in landscape of site has broader concept than mere vegetation and improvement of surrounding natural environment requires much attention. Hence, the present study is aimed to perform space creation consistent with book reading in study design “Book city” in Iran, Tehran, Shahrak-e Gharb district. For data collection, field-descriptive and library methods are applied. In theoretical method “library researches” by referring to Persian and English resources (different types of journals, theses and related books) and the important relevant websites. Descriptive method includes direct observation and indirect observation and the results showed that there was a positive correlation between liveliness and the components of image ability in citizens and environmental quality with the invitation to the designed building. In addition to the presence of plants, fountains and the appropriate lighting for days and nights, the safety of pedestrians against vehicles in the edges design of a site which is on the corner of an intersection with a heavy traffic; other factors are also very effective such as different land uses in the central yard of a design and the accessibility to the assembling and attractive elements for creating a pleasant and safe situation as well as psychological features like calm and tranquility feelings which are necessary for reading books. This means that the research hypothesis titled “urban green spaces, improving the quality of reading books” is supported. It’s evident that using a gentle slope for the site is helpful in designing the landscape proportional to the construction form.
Key words:Book city design, Environmental quality, Space creation, Urban anthropology, Urban landscape, Urban green space
INTRODUCTION
“The role of nature and organic architecture as innovative strategy of improving environmental quality in space creating and creating urban place and its link in blot and design of library and its effect on the increase of interest of the
need to recreation and leisure among urban dwellers and it is turned into one of the most important items. Leisure time includes the set of activities a person does for rest, recreation or development of personal training or free social participation or creativity if there is no job, family and social commitments. Simply, leisure is the activity being selected for its fulfilling quality in relative freedom (Less Haywood, et al., 2001: 384). Leisure activities include wide range of artistic, cultural, sort, pilgrimage, audio-visual, recreation, social relations, relationship with nature, computer activities and each one requires special grounds (Amestoy, 2008:65).
Recreational activities outside of house are based on participative and collective aspects requiring special space. Here, public spaces play important role in formation of such activities. Urban green spaces are part of urban areas with natural vegetation against stoned areas or buildings (Balram and, Dragicevic, 2005:149). As an important element of urban areas, they play important role in improvement of quality of life of residents and environmental sustainability of cities (Gupta et al,. 2012:325). One of the most important advantages is the tangible health benefits for people as reduction of stress and mental pressure and balancing the temperature of urban environments, absorption of polluted air and oxygen generation and creating opportunity for participation in physical activities (2012:52) ,(Villeneuve et al). Also, these areas are effective as beautiful visual landscape in reduction of noise and eliminating spatial uniformity of cities (Grahn and Stigsdotter, 2010:265).
One of the effects of modernism thought in the past decades is development of wide streets with the dominance of card and ignoring open collective spaces as these spaces have lost their functional quality as supporting space of social interactions. The shortage of open pedestrian-based spaces and bad quality of existing spaces in present cities have weakened the social interaction among the citizens.Book city of Tehran is a cultural-educational set composed of various sub-spaces including library and book café, galleries, music spaces, green restaurant in
one of the blocks, recreational workshops and educational classes and ateliers, collective and welfare spaces and raps and bicycle and pedestrian path and garden spaces to fulfill the urban requirements of citizens namely the children and the youth and the elderly and its main aim is focusing on urban body. Also, it is based on the approach of improving environmental quality including green space making in one of the townships of Tehran-Shahrak-e Gharb. Considering citizenship welfare and considering happy space in the city namely considering sitting in the pedestrian are the basics of the definition of this complex. 1-Study questions
The present study responds to the following questions:
Improvement of environmental quality and green space creation strategy is effective on good improvement of study design?
Based on the experiences of advanced countries in urban design with emphasis on the role of organic architecture and its effect on study, how can we express the structure of “Book city”? 2-Study method
Qualitative strategy is used in inferential approach. The theoretical items and initial basics of study are collected by library studies. The study method is descriptive. The data collection is document. Finally, the results are inferred based on the above stages.
3-Hypothesis
Green urban spaces improve architecture design of book and book reading.
4-Theoretical basics of study
4-1 The interaction between space and human being
specific location. Indeed, space is a part of environment reality as placed in objectivity class and it has form and performance like other phenomena and it is not only as independent entity from human being and it is in interaction with human being, it has the subjectivity in an image form (Pakzad, 1999). Space is classified into three types: Geographical space, life space and architecture space.
Math space and its size are not dependent upon time but if we consider time factor in space attitude, a new difference is created. The night space has no depth and direction and it has indefinite effect on human being. Day and night space are two ends of a spectrum and their difference is in their lighting type (Grotter, 2011:224). Spaces include wide range of different types of public or private spaces. All parts of urban texture to which the public have access physically from street, square and urban park to the façade of the buildings defining them are public spaces of city (Tibalds, 1992). In definition of different types of space we have:” If some buildings are observed simultaneously, we feel some relations among them and these relations are created only via their middle spaces (Grotter, 2011:227).
Empty space doesn’t mean uniformity or the lack of any absolute perception stimulation and it is felt among the uniform residential buildings on condition that the buildings are located as uniformity is increased and facades are designed and no effective stimulation is created on perception. In this case, human being feeling is full of loneliness or he perceives “emptiness”. The problem of emptiness is one of the reasons by which modern urbanization plans like the plan and vision design of Le Corbusier was failed. The buildings of these cities were independent objects repelling the space and they were in contradiction with traditional idea of a city. Colin rowe compared these two cities as one is a building with empty spaces in an integrated mass and another one is a set of volume in an intact vacuum. By any small thing in an empty space, tension is created. A good example is Zen Japanese stone garden in Ryoan ji temple in Kyoto.There are stones in a rectangle ground with definite distance. The
ground is flat and raked with gravel and is surrounded by three sides by a wall. This yard without these stones is empty and there is a type of balanced contrast by form of stones and relationship between stones and it is comfortable and pretty and creates movement (Grotter, 2011:238). We consider existence space as a stable system of perceptions or “environmental image”. The existence space is a general abstract of similar phenomena, it has objective feature (C.Norberg-Schulz, 1963:28). An object is a system of perception images and despite its movements it has fixed space form and it is separated in the set of causality over time (Jean Piaget, 1955:92). The titles of existence elements include domain and township, center and place, direction, domain, place and node are important centers as created in intersection of paths or concentration of some indices and the observer can go into them (Kevin Lynch, 1960:72). The path is organizing factor for real movement and it presents a symbolic direction making various elements equal and mostly they are associated to bigger integrity. In most cases, the path and area are the same (Norberg-Schulz, 1926:61). Other concepts of space in architectural design include the importance of material, level as spatial elements and spatial organization. Multi-functional space is a convincing answer for modern architects to achieve flexibility.
4-2 City and urban space infrastructures “City is a cultural-physical complex based on the needs, activities and behaviors of residents. Based on their individual or group needs, people start their activities and present their special behavior model. City and its different spaces are used for these events (Pakzad, 2005). Live city is the one in which conscious expression of space in its highest architectural expression is vital (Daneshpour cited in Baken, 1997:15). From the view of urban anthropology,perception of space manifests itself in its different organizing and based on any culture and subculture, it can be different. Any type of organizing has a type of order and this order can be based on symbolic religious, political, economic and social beliefs and space division can not be occurred without any order. Today, buildings are designed with “intelligent body” to create an image. In some countries (e.g. Singapore), lighting of buildings is considered to increase liveliness of spaces at night. Entering such factors in city from the view of some experts is urban design as it creates changes in city (John Leng, 1938:192).
4-2-1 Time city
At urban times, we are encountered with time density or peak times and it is creating more functional intersections in a special point. For example, in big cities at special times with traffic, energy consumption on power or water distribution is increased and this shows time density. Such densities lead to the standardization of urban behaviors of residents can increase economic and social costs and urban time management attempts to reduce such densities or manage them to reduce their social costs (Fakuhi, 2004:261).
4-2-2 Culture city
City is social organizing in space to consider it as permanent producer of culture. If we consider culture as the set of behavioral and mental phenomena of each society giving identity to the society, the society attempts to reproduce via mechanisms by its transfer from one generation to another. Thus, city is the best ground for “culture construction” process. Urban elites at first rank and public subcultures are inclined to
emphasize on their cultural personality (Fakuhi, 2004:286).
4-2-3 City of expression
In definition of city of expression we should refer to the urban aesthetics. Thus, we can say urban aesthetics is a relationship between dynamic city and city as alive creature. The urban text is re-written and its meaning and symbols are increased and it can be interpreted any time.
Street: One of the examples of axial space is urban expression.
“Street is one of the urban spaces dating back to the cities and it is encountered with many things (Naser Fakuhi, 2004:314).
4-2-4 Economy city
In common law, city is an economic entity as it has a great wealth. The relationship between city and surrounding has a relationship to absorb wealth. Wealth distribution in city is dependent mostly on social labor division. We can find a full relationship between economic dimension of urban life and active applied spaces. As it was said in space, space includes wide range as applied spaces (labor, housing, leisure time and damages of inefficiency of its management, transportation and market, landscape) are the most important concepts in economy dimension of human-based urban studies.
4-3 Urban and cultural landscape and sustainable environment
In common scientific definition, urban landscape is the quality in the relationship between audience and city body. One of the physical urban components of producing such quality is public spaces and streets playing important role in audience perception. Some of the reasons of such feature is quality and quantity of social events occurred in them. Cultural landscape was emerged in the early 20th century in environmental studies. At first, this term was the production of interaction between human and nature.
between building and environment, we should consider human view about environment or generally to nature. The basis of building is manipulation of nature. This manipulation is close relationship with human thought about nature. In most eastern cultures, there is a close relationship between human and nature and this relationship is observed today. Human being considers himself a part of nature and it is in multiple relationship with it. This close relationship gives life continuance to human being and nature (Grotter, 2011:148).
The goal of sustainable landscapes is optimization of culture, controlling cyber space, normal environmental ethics and new criterion of equality law for all residents.
The researches on human being behavior in leisure activities show escape of people of cities to achieve nature. Environment with natural qualities is the best tranquilizer and there is no substitute for it. Regarding research on urban design, we can say most urban designs are based on urban landscape or in this regard. For example, we can refer to the effect of Versay palace on Paris and generalizing its model to most cities as Chicago, Sainfrasnsisco and Saint Louise. Urban landscape plan as one of the basic issues of master plan of current cities has a good position (Sirus Sabri, 2003:22).
4-4 Theoretical concepts of design in space creation
Key concepts in this regard refer to elements as urban squares, intersection as an important point, semi-close space, blockers, bottom, street lighting, and advertising in outside, integrating trees with building, level change and water.
Image1-Urban Planning Japan, The university of Tokyo, Fabrication Lab
Source: www.Arch daily.com<
Image 2. The Australian Garden, Taylor Cullity Lethlean
Source: www.Arch daily.com<
Based on what was said about the generalities about space creation and its principles in urban design, in different architectural use, they are used and its necessity in different examples of architectural projects and in this study, libraries need spatial reading as silence and comfort in libraries and book experts and authors hare unified elements. The library of Korean women University with open design and its green ceiling of hard urban body is a successful example in creating architectural spacecreation and considering city landscape as inviting with two wings and its central yard.
Image 3:Woman University, Seoul, South Korea, Dominique Perrault Architecture
Source: www.archdaily.com
5-Introduction of study area
With its geographical situation and locating in a low-pressure area compared to high-pressure areas of the north and North West is in major movements. Tehran city is located in eastern
longitude 51 and northern
latitude 35 . Based on the first
formal census in 1956, this city with 1560934
people is the most populated city in Iran. Based on the latest census in 2011, Tehran population is 8154051 (Tehran Municipality site, www.tehran.ir).
District 2 as the study site is located in Shahrak-e Gharb township and is onShahrak-e of thShahrak-e dShahrak-evShahrak-elopShahrak-ed regions in middle and northern area of Tehran city.
6-The results analysis and design results
Chart 1-The components of the relationship between liveliness and image ability (based on the paper of Bazovandi Farshad, 2014. The research of city landscape, First period)
Chart 2- The model of stages of personality design for urban cultural landscape (based on paper of Zandi Marjane, 2014, landscape NO. 28, cited in Buckle).
Table 1- The effective components of subjective and objective landscape on entrance inviting (based on Mozafaripour, Najme, 2014. The researches of city landscape, NO. 1).
Objective components Subjective components
Cleanliness Comfort
Pretty façade Spirituality
Using green space Originality
Consistency with wall Recalling
Consistency or variety to the surrounding façade Meaningful
Lighting Liveliness
Landscape charact er
evaluat ion Det ermine
change and
separat ion
point in
cult ural urban
landscape Invest igat ion of
int egrat ion of
layers of landscape in
different t ime
periods Explain t he
source of cit y
format ion Nat ural
Cult ural
Aest het ics
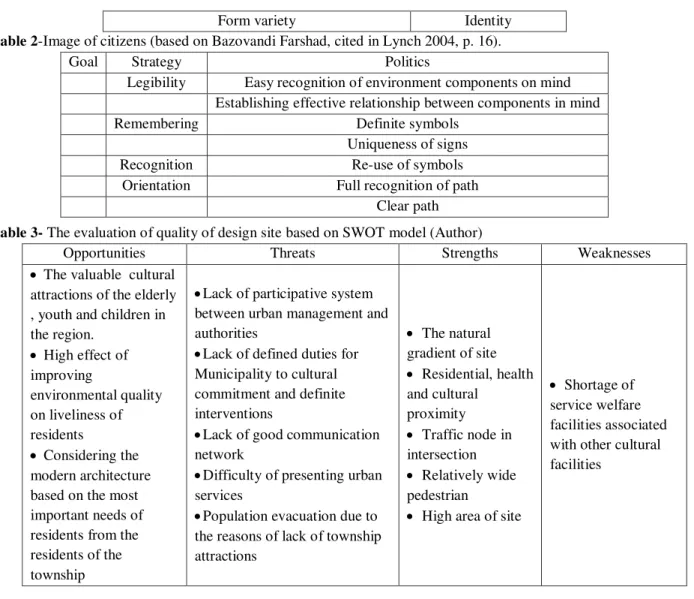
Form variety Identity Table 2-Image of citizens (based on Bazovandi Farshad, cited in Lynch 2004, p. 16).
Goal Strategy Politics
Legibility Easy recognition of environment components on mind Establishing effective relationship between components in mind
Remembering Definite symbols
Uniqueness of signs
Recognition Re-use of symbols
Orientation Full recognition of path Clear path
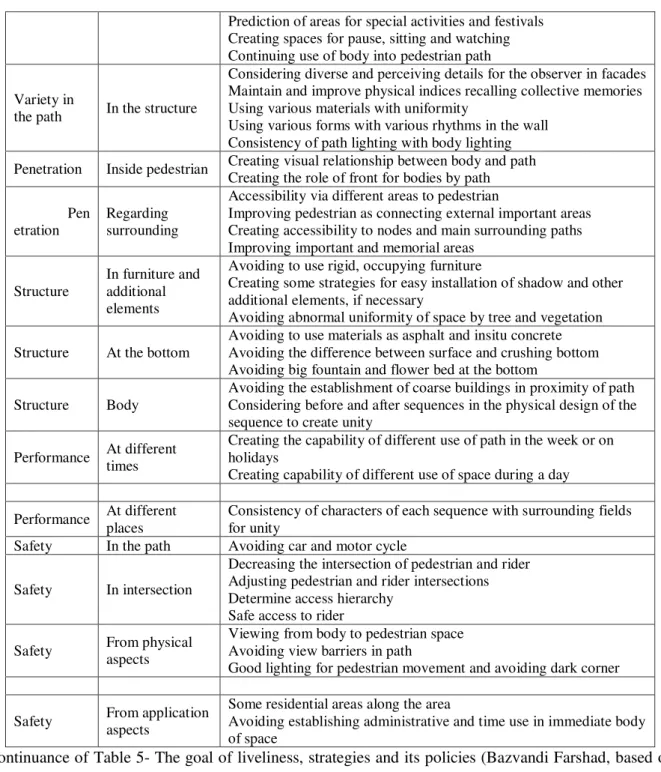
Table 3- The evaluation of quality of design site based on SWOT model (Author)
Opportunities Threats Strengths Weaknesses
The valuable cultural attractions of the elderly , youth and children in the region.
High effect of improving
environmental quality on liveliness of residents
Considering the modern architecture based on the most important needs of residents from the residents of the township
Lack of participative system between urban management and authorities
Lack of defined duties for Municipality to cultural commitment and definite interventions
Lack of good communication network
Difficulty of presenting urban services
Population evacuation due to the reasons of lack of township attractions
The natural gradient of site
Residential, health and cultural
proximity
Traffic node in intersection
Relatively wide pedestrian
High area of site
Shortage of service welfare facilities associated with other cultural facilities
Table 4- The analysis of site landscape and the designed street (Author)
Criterion Index Explanation Score
Identity Natural features Limited topography in site (it has slope). Tree and water Average Continuance at
time
Traffic node. Recreational point, artistic gathering and
thought center Strong
Scheduling Architecture
style Modern architecture design, slope landscape design Average Memory Cultural, artistic, exhibit, health points Weak
Relationship Integrity and fluidity
Borderless influence of street into public spaces and easy
movement-access Strong
Mixture of
activities Cultural, recreational, commercial, health Strong
Table 5- The goal of liveliness and strategies and its policies (Bazovandi Farshad, based on Pakzad, 2005, 287).
Goal Strategy Policy
Dividing various use
Variety in use as absorbing different social Groups.
Avoiding the establishment of use in the body creating passive areas. Prediction of service use including the continuance of presence of citizen in pedestrian.
Establish leisure use Variety in
the path In activities
Prediction of areas for special activities and festivals Creating spaces for pause, sitting and watching Continuing use of body into pedestrian path
Variety in
the path In the structure
Considering diverse and perceiving details for the observer in facades Maintain and improve physical indices recalling collective memories Using various materials with uniformity
Using various forms with various rhythms in the wall Consistency of path lighting with body lighting
Penetration Inside pedestrian Creating visual relationship between body and path Creating the role of front for bodies by path
Pen etration
Regarding surrounding
Accessibility via different areas to pedestrian
Improving pedestrian as connecting external important areas Creating accessibility to nodes and main surrounding paths Improving important and memorial areas
Structure
In furniture and additional elements
Avoiding to use rigid, occupying furniture
Creating some strategies for easy installation of shadow and other additional elements, if necessary
Avoiding abnormal uniformity of space by tree and vegetation
Structure At the bottom
Avoiding to use materials as asphalt and insitu concrete Avoiding the difference between surface and crushing bottom Avoiding big fountain and flower bed at the bottom
Structure Body
Avoiding the establishment of coarse buildings in proximity of path Considering before and after sequences in the physical design of the sequence to create unity
Performance At different times
Creating the capability of different use of path in the week or on holidays
Creating capability of different use of space during a day
Performance At different places
Consistency of characters of each sequence with surrounding fields for unity
Safety In the path Avoiding car and motor cycle
Safety In intersection
Decreasing the intersection of pedestrian and rider Adjusting pedestrian and rider intersections Determine access hierarchy
Safe access to rider
Safety From physical aspects
Viewing from body to pedestrian space Avoiding view barriers in path
Good lighting for pedestrian movement and avoiding dark corner
Safety From application aspects
Some residential areas along the area
Avoiding establishing administrative and time use in immediate body of space
Continuance of Table 5- The goal of liveliness, strategies and its policies (Bazvandi Farshad, based on Pakzad, 2005, 287).
Table 6-Final formulation of physical plan based on studies (Author)
External examples Space use Total space Sub-space Area
Library Meeting rom Maker space Music space Event hall Child area Automated self Check out Performance Art Video art Gallery Sculpture space Painting space Cultural Library Study hall Cafee book Amphitheater Book critic hall Galleries Arrangement gallery Performance art Video room Study room Gathering space Temporary workshop Music space Meeting space Reading hall Book reference Close shelf Open shelf Librarian counter
Individual space of reading book
Collective space of reading book
Drawing space Open
Emphiteater Book cafee Roof of the book Roof garden Readers garden
Library cafee Institute of children’s book
Various library activities Lively public library Auditorium
Media boulevard Public child area Seat community meeting Read relax Rejuvenate Self-check Automated service With internet Computer Mixed used Internal space Children space Book garden Audience hall
Cash additional hall Child gallery Adult gallery
Collective space of child game Collective workshop of child Child maintenance room Parents rest room Open music room Music close room Video projector room Scene of performance Music hall
Make up room Cloth changing room Instrument store Teria kitchen
Teria food warehouse Visitors instrument keeping
Main entrance WC Parking Observatory Restaurant Culverts Elevator Escalator Road rail Ramp Rest room Shopping Store Rest room Green square service Entrance WC Utilities Parking Warehouse Safety
Lift, escalator, ramp and rails
Supply stores Restaurant
Resting and prayer rooms
Female WC Male WC Chief WC Employees WC Disabled WC Information room Guard room Lost room
Safety and equipment room Children maintenance room Child changing room Mother rest room Store warehouse Exhibit window Female prayer room Male prayer room Electrical utilities room Mechanical utilities room Reservoir room Ateliero Studio Work shop Laboratory Training room Class room Internet room Educational Ateliero Master class Work shop Workshops Laboratories Design ateliero Painting Ateliero Graphic Ateliero Lecturers Ateliero Lecturers resting room Workshop warehouse Equipment warehouse Conference room Video room Internet room
Office Administrative Management and subordinate
Hanieh Sadat Zendehbad, et al. 1242
In Tehran metropolis and its north west population texture, the complex site is formed in Shahrak-e Gharb the intersection of two main streets of Ponak Bakhtari and Farahzadi based on Iranian gardens introversion with the difference that in modern plan despite Koshak in which yard includes the garden, the building is around the yard. The building form is with unified cubic image around the linear and sloped circuit with attractive structure with communicative formal of the complex as a gateway for inviting. Here, in four sides, the building guides the visitors with ramp device and it passes from blocks with different height and flexible form and various spaces. In design of this project, public, semi-public and private areas are considered with the aim of creating various qualities for people namely the elderly, children and the youth: it is ranging from directing urban activities beside main street to resting, pause places and central yard in building formed based on initial form and concept for open gathering as theater, music and sale cultural stores. In this yard, some trees are planted and their shadow is beside foundation and cafees are used for attractive places and short pause. Also, close amphitheater exit in block A is leading to central yard. Restaurant and cafee with roof garden are designed on the ceiling of block C as leveled with upper part of complex site. Considering natural topography of site and using it are of great importance in improving green space and design of landscape in idea creation leading to the complex plan. Flexible façade based on plans shows the project performance. To have natural light for book reading, the glasses are transparent and wide. There are four blocks with varied height code around polymer core with special supporting structure. In this complex, maintaining volume integrity is of great importance. In volume composition, the entrance is much emphasized based on network lines of urban design as linking four blocks and brining the urban body into the building.
We should suggest visual attraction to general volume and the best natural light orientation is of great importance for us. Although neighboring residential texture had the mean floors, to avoid noise pollution, improvement of landscape , this was done with denting and rotation of angle to south west and horizontal and oblique directions were combined.
By volumes with pure, mild geometry, there was an interaction between volumes and a balanced volume was designed.
Hanieh Sadat Zendehbad, et al. 1243
Image 5- Design of central urban core strip and entrance bridge in Rino software (Author)
Image 6-Diagram of zoning the performances (Author)
Hanieh Sadat Zendehbad, et al. 1244
Image 8-3-D modeling of volume in 3D MAX software (author).
7-CONCLUSION
Based on the studies of the author and its collection with the case study and previous studies of present research, the results analysis emphasizes on the space creation in urban environment and its constructive role in social interactions. The spaces without environmental quality escape from society and in human daily encountering, resorting to any space creation idea improving citizenship interaction is a good acceptor in local community. Residential proximities have great importance in different proximities as the residents are using different daily communications and due to the importance of leisure of the resident mostly female adults, elderly and children, special models are required and it affects functional proximity of the project. Human being requires collective interaction and this is the main aim of the author of research. Any township for the comfort of residents in efficient human interaction can achieve stability.
Regarding the study and analysis of results, the author believes that improving environmental quality and various space creation are the principles of all purposeful executive plans and in cultural use, urban human-based activities, there
are some places requiring science, culture and reading (libraries). Depending upon the type of perception, this expectation is dependent upon objective components as good form, variety of structure and its surrounding wall in landscape and landscape design and subjective components as intimacy, originality, liveliness, mobility and identity and silence. Entrance inviting, lighting in attraction of place at day and night, form variety, form consistency in landscape are effective on environmental improvement with emphasis on green space and good urban landscape.
Design strategies by urban view components
- Improving entrance space performance by installing bridge (ramp) of structure with the approach of improving urban internal passing and easy orientation
- Improving the quality of entrance landscape with the attitude of creating visual attraction
- Improving identity with the approach of central yard based on Iranian garden concept
- Improving physical attractions and fluidity of visual elements
Hanieh Sadat Zendehbad, et al. 1245
- Improving accepting of children and the youth with the approach of creating new, open and fluid spaces
- Special importance to the elderly and disabled *-For idea creation, the paper of Farshad
Bazovandi and Marjane Zandi are used.
REFERENCES
1. Biken, Edmond, 1997, The Designs of Cities, Farzaneh Taheri, The Center of Studies and Researches of urban planning and architecture in Iran
2. Pakzad, Jahanshah, 1998, The Theatrical Principles and Urban Design, Shahidi Publications, Tehran
3. Pakzad, Jahanshah, 2005, A Guide to the Design of Urban Spaces, Ministry of House 4. Tibadelz, Francis, 1992, The Citizen-oriented
urban planning, Mohammad Ahmadi Nejad, Isfahan
5. Fakouhi, Naser, 2004, Urban Anthropology, T Publication, Tehran
6. Kwin, Linch, 1972, The Appearance of a City, Dr. Manucher Mazini, Tehran University Publications, Tehran
7. Groter, York Kourt, 2011, Aesthetics in Architecture, Jahanshah, Pakzad, Beheshti Publications
8. Leng, John, 1938, Translation by Hossein Bahraini, Tehran University
9. Norenberg, Shoultes, Christian, 1926, Existence, Space, Architecture, Dr. Vida Borazjani, Parham Naghsh, Page 21
10.Hiyoud, Less, 2001, Leisure Time, Mohamad Ehsani, Omid Danesh Publications, Tehran 11.Sabri, Sirous, 2003, Urban View of
Architecture of Iran, Number 12 and 13, Pages 22-25
12.Arnheim, Rudolf, 1978, Kunst und sehen, Berlin
13.Balram and Dragicevi, 2005, Urban Ecology, Kevin j. gaston, Sheffield, pp.149
14.Grahn and Stigsdetter, 2010, Forests- Trees and Human Health, K NILsson etal, Springer, New York, pp.265
15.Gupta et al, 2012, The Hand book of Mites of Economic Plants, Alexandra Lainsburg, Oxford, Uk,
16.K. Lynch, the Image of the city, 1960, p.72 17.Norberg- Schultz, 1963, Christian: Meaning in
wetern architecture, Lon- don, pp.28
18.Piaget, jean, 1955, The Developmental psy chology of jean Piaget, Florencel. Goodenough, New
19.york, pp.92
20.Venturi, Robert, 1978, Komplexitat und Widerspruch in der Architektur, Braunschweig, p.50
21.Villeneuve et al, 2012, Engineering Geology for Society and Territory, Gioogio Lollino et al, pp.52