International Journal of Advanced Biotechnology and Research (IJBR) ISSN 0976-2612, Online ISSN 2278–599X, Vol-7, Special Issue3-April, 2016, pp1873-1878 http://www.bipublication.com
Research Article
The investigation of the organizational health relationship with the
citizenship behavior and organizational commitment in East-Azerbaijan
high schools during 2013-2014
1
Khalegh Ebadipour and 2Asadolah Khadivi*
1
Department of Educational Management, Tabriz branch, Islamic Azad University, Tabriz, Iran
2
Phd, Faculty member of Farhangian University, Tabriz, Iran Corresponding author: Khadivia@gmail.com
ABSTRACT:
The main purpose of the present study was to determine the relationship between the organizational health of the high schools and citizenship behavior with teachers' organizational commitment. The used methodology of the study was an applied type of study purposefully and it was also a descriptive correlation method in terms of the application. The statistical population of the study included the whole high school teachers of East Azerbaijan Province during 2013-2014 educational years. The number of the statistical population was estimated about 384 people using Cochran formula. The cluster sampling method was also applied in order to take up the volume of the sample. Three standard questionnaires of the organizational health, organizational commitment and citizenship behavior were also applied to gather the related data in this study.T-test, separation correlation coefficient and Pearson correlation coefficient were used to analyze the research hypotheses. The results of the study showed that there is a significant positive correlation between the schools' organizational health with the organizational commitment and teachers' organizational commitment with 0.51 and 0.39; respectively in 0.01 significant level statistically. The whole dimensions of the organizational health have positive significant correlation with the citizenship behavior and organizational commitment.
Key words: organizational health, organizational commitment, organizational and citizenship behavior
INTRODUCTION:
Based on the recent literature of the different fields of the human kind activity, the education is the most crucial and sophisticated activities of the mankind that has been taken place since the dawn of the history to the modern humanistic community. The whole ideal targets and philosophical purposes of the educational affairs are subjected to the school operational level and a teacher is considered as one of the main three elements of the education in this pavement. Hence, the knowledge, attitude and ability of teacher play key role in the quality of educational affairs and children of a community potentially.
In Islamic educational affairs, the behavior and morality of a teacher is roughly paid attention.
In Iranian culture, the most sophisticated establishment of a teacher is rooted from his or her behavior and moral issues than the science and knowledge. If these teachers do not have the excellent commitment behavior, they will get mitigated to a usual coach and this is not suitable with the nature of the educational and teaching affairs in this regard. The organizations are rooted from the interaction of the humanistic and material-based resources. For making objectivity of the organizations' dimensions, these material resources can be simulated
towards the humanistic resources and
framework can influence on the school health and on the other hand, the school is considered as the body of the same organization influencing on the physical, mental, social, emotional and moral health of the same teacher potentially.
The organizational commitment and
organizational citizenship behavior are combined with the nature of the teacher occupational issues and the effective teachers are those ones that should have the above mentioned features in this pavement.
The increase of these features can raise the efficacy of teachers but the decrease of the same features may lead to the mitigation of their position regarding to the educational affairs. The dimensions of the organizational commitment and organizational behavior indicate the humanistic excellence behaviors being existed in the teaching occupation necessarily. The same feature can be rooted from the personal character and teacher teaching method since childhood to the maturity times. The main influential part of the process is subjected to the organizational factors influencing on teachers' behavior. The management and organizational
leadership, culture and organizational
atmosphere and finally the organizational health are subjected to those factors that balance the organizational commitment and teachers' citizenship behavior. Sheldon (1971, cited of Amirpour, 2009) has defined the organizational commitment as an attitude or orientation towards an organization relating the personal identity with the same organization. One of the most important variables of the related study is subjected to the organizational citizenship behavior.
This is a new concept that has been applied in
the literature of the management and
organization recently. In the organizational situation, this concept has a positive and suitable conceptualization (cited of Amirpour, 2009). The organizational citizenship behavior is consisted of complex structures. The related factors are related to the personal traits and other factors are related to the organizational and managerial factors. Padsakov et al (2000) have defined more than 30 types of behaviors regarding to the organizational citizenship that
the most famous cases are as following: Altruism, peace, fairness, polite, task and citizenship approaches. These behaviors have been recognized as the Extra Role Behavior (Din and Graham, 1995). Also, in the recent studies, there have been established many various structures such as the organizational self motivation, social organizational behavior and situational function for representing the same organizational citizenship behavior (Padsakov et al, 2000). This concept has been rooted from the same idea of Ketz and Kann (1968, cited of Organ et al, 2006). In addition, the effectiveness of the citizenship behavior on the organizational data has been confirmed practically.
Loyalty and commitment dimensions:
In a healthy organizational atmosphere, there has been established a high trust atmosphere between people working there. The whole staffs and employers are waiting to come up to work making their suitable feeling towards their occupational issues. In the same organizational setting, there is no found any non-moral cases in this case. The whole staffs tend to worthwhile and value the hidden part of the morality affairs potentially (cited of Jahed, 2005). As it mentioned, it is observed that the loyalty and commitment dimensions have correlation with the morality dimensions of the citizenship behavior.
potentially. Indeed, the organizational health plays a key role regarding to the physical, mental, privacy, possession and ability and value of wisdom, expert and personality of people in one hand, and on the other hand it influences on the behavior effectiveness of every system efficiently. The theoretical basics and experimental observations have shown that there is a considerable interaction and overlap between the variables of the organizational
health, organizational commitment and
citizenship behavior. In other words, a healthy organization can lead to the moral and behavioral health of its own staffs.
In contrast, the human resources can also recover the organizational health of a job place potentially. Macintosh et al (2007) pointed to the fact that the personal health and organizational health are always complex together. They defined the phenomenon of the health as following: the health is a complete status of people regarding to the physical, social, mental and social welfare and the lack of illness does not relate to the related process. Kit Davis considers a healthy organization as a place where people feel their own beneficent into an organization. They tend to carry out their own tasks potentially making internal comfort and relaxation. Many staffs are seeking their own
occupational success into their own
responsibilities trying to achieve occupational progression in this pavement. They like to be paid attention potentially; they also like to be valued morally and personally.
They try to get confident of their own problems to be solved (cited of Azkhishi, 2009). Many researchers have reported the relationship between the organizational health and the organizational commitment and citizenship behavior together (Fattahi, 2007; Organ and Ryan 1995; Hacket and Lapiri 2004; O'Riley and Gotmann 1986; Gatham et al 2006; Chia and Tesaiee 2007; Suiee et al 1994; Nier 2002; Orgeon and Nier 1983; Williams and Anderson 1991; Patel 2002). Although the organizational health is very worthwhile for the whole organizations, but the importance of the organizational health regarding to schools should be paid attention doubly. Due to the
outlet of the schools as the main valuable human resources is very influential and effective element than other organizations, it can be concluded that the school organizational health is the most fundamental background for the social organizations.
The commitment teachers having suitable citizenship behavior can lead to develop the valuable behaviors between the whole students. Based on the above mentioned statements the main aim of the present study is to investigate the status of the organizational health of the province high schools' and the degree of the organizational commitment and teachers' citizenship behavior trying to evaluate the relationship of the schools' health established in
East Azerbaijan Province with the
organizational commitment and citizenship behavior. It should be mentioned that the main aim of the study is to reply the questions of the study: how is the status of the province organizational health? How is the citizenship
behavior and teachers' organizational
commitment? Is there any relationship between the schools' organizational health and the organizational citizenship behavior and the teachers' organizational commitment? Nasiri et al (2011) concluded that there is a significant positive relationship between the whole organizational health dimensions and the organizational commitment. The organizational cohesion is the most effective predictive element and the second element is subjected to the staffs'
organizational commitment and their
temperament (Nasiri et al, 2011). Ferdowsi (2012) reported that the organizational commitment is considered as the most sophisticated predicting and estimating factor of the organizational health. Semsar et al (2011) concluded that the justice and interactive justice have significant positive relationship with the citizenship behaviors towards the organizations. Majidi (2010) reported that there is a significant relationship between the emotional intelligence and schools' organizational health established in MARAGHEH City.
(2009) showed thatthere is a significant positive relationship between the variables of the organizational justice and citizenship behavior and the staffs' occupational satisfaction. Pateel (2002) in a study regarding to the investigation of the relationship between the organizational health and organizational commitment in the industrial staffs reported that there is a significant positive relationship between the organizational health and organizational commitment.
METHODS AND MATERIALS:
The used methodology of the study was an applied type of study purposefully and it was also a descriptive correlation method in terms of the application. The statistical population of the study included the whole high school teachers of East Azerbaijan Province during 2013-2014 educational years. The number of these students is about 9300 people. The number of the statistical population was estimated about 384 people using Cochran formula.
The cluster sampling method was also applied in order to take up the volume of the sample. After receiving the teachers' statistics, they have been categorized based on the educational ministry statement using the educational expert to analyze the next data in this regard. After the determination of the main clusters, two to four areas are taken up as the main sample of the study using a simple accidental sampling method. Finally, the percent of the minor clusters have been selected due to the volume of the study based on every district and school. Data collection tool:
There have been established three main and standard questionnaires to gather the related data as following:
Organizational health inventory:
Huwi and Tartar (1997) school organizational health is applied in order to measure the organizational health. This tool is designed for measuring the high school organizational health (Ohi-S) and has been translated by Alaghehband in 2008.
This tool has 44 options in seven dimensions of the organizational health: organizational cohesion, manager penetration, consideration,
structuralism, resource support, temperament and scientific emphasis. This questionnaire has been designed in four degrees LIKERT based.
Organizational citizenship behavior inventory:
This questionnaire has been established for the elements of the organizational citizenship behavior by Oregon in 1988 measuring the organizational citizenship behavior. Also, the elements of OCB have been represented by Fareh et al (1997) for the Chinese cultural affairs. This tool has been designed based on four LIKERT having 27 questions with the elements of the virtue, personal mutual
cohesion, and fair, preservation of
organizational resources, polite, social culprits and altruism.
Organizational commitment inventory:
Mayer and Allen (1987) questionnaire is used for measuring the organizational commitment. This questionnaire has 25 questions being designed in four LIKERT based. It has been also consisted of three subscales of emotional
commitment, continuous commitment and
normative commitment. The reliability of the related questionnaire is measured 0.74 using Cronbach alpha method representing high reliability of the questionnaire fairly.
Reliability and validity of the research tool:
Reliability:
Based on the standard application of the related questionnaires, the former studies (Amirpour 2009, Khishi 2009, Vahedi 2002 and Majidi 2010) have been also applied in this pavement. Hence, there is no need to investigate the reliability of these tools again.
Validity:
The results of Cronbach alpha showed that three related tools have acceptable validity and reliability in this regard. The obtained alpha coefficient for three questionnaires is given in the following table.
Data analysis method:
RESULTS:
Table 1: summary of Pearson correlation coefficient test regarding to the first hypothesis
First variable Second variable Correlation
coefficient Sig level
Determination
coefficient Result of test
School organizational health Organizational
citizenship behavior 0.51 0.01 0.26 Significant
School organizational health Teachers' organizational
commitment 0.39 0.01 0.15 significant
The above mentioned data shows that the correlation coefficient between the schools' organizational health and teachers' organizational citizenship is 0.51 and it is established in 0.01 significant levels statistically. Hence, it can be concluded that there is a positive significant relationship between the schools' organizational health and teachers' organizational citizenship behavior.
The determination coefficient is 0.26 showing that about 26 percent of the teachers' organizational citizenship behavior variance is being represented by the schools' organizational health and their studying place.
The above mentioned data shows that the correlation coefficient between the schools' organizational health and teachers' organizational citizenship is 0.39 and it is established in 0.01 significant levels statistically. Hence, it can be concluded that there is a positive significant relationship between the schools' organizational health and teachers' organizational citizenship behavior. The determination coefficient is 0.15 showing that about 15 percent of the teachers' organizational citizenship behavior variance is being represented by the schools' organizational health and their studying place.
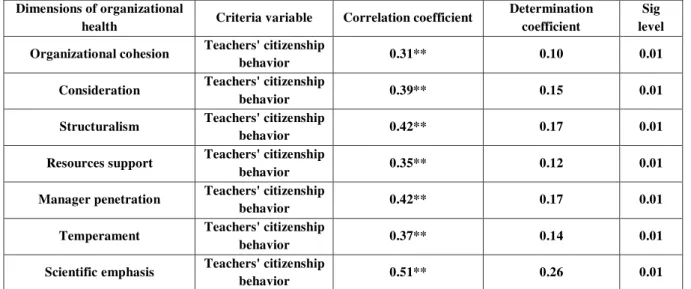
Table 2: correlation matrix of organizational health with teachers' organizational citizenship behavior
Dimensions of organizational
health Criteria variable Correlation coefficient
Determination coefficient
Sig level
Organizational cohesion Teachers' citizenship
behavior 0.31** 0.10 0.01
Consideration Teachers' citizenship
behavior 0.39** 0.15 0.01
Structuralism Teachers' citizenship
behavior 0.42** 0.17 0.01
Resources support Teachers' citizenship
behavior 0.35** 0.12 0.01
Manager penetration Teachers' citizenship
behavior 0.42** 0.17 0.01
Temperament Teachers' citizenship
behavior 0.37** 0.14 0.01
Scientific emphasis Teachers' citizenship
behavior 0.51** 0.26 0.01
The above mentioned data shows the correlation coefficient of the schools' organizational health and the teachers' organizational citizenship behavior. Based on the same data, the whole dimensions of the organizational health have positive correlation with the teachers' organizational citizenship behavior. The correlation coefficients of the organizational cohesion, considerations, structuralism, resources support, manager penetration, temperament and scientific emphasis are 0.31, 0.39, 0.42, 0.35, 0.42, 0.37 and 0.51, respectively.
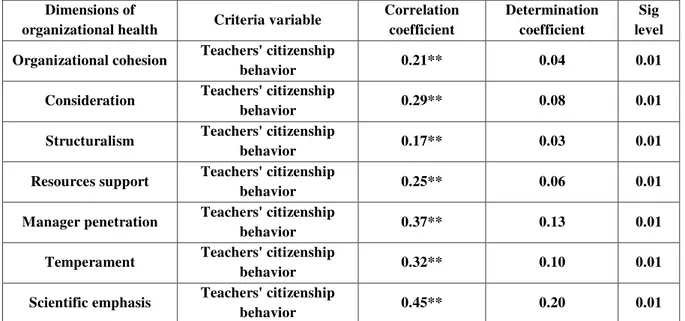
Table 3: correlation matrix of the organizational health with teachers' organizational commitment Dimensions of
organizational health Criteria variable
Correlation coefficient
Determination coefficient
Sig level
Organizational cohesion Teachers' citizenship
behavior 0.21** 0.04 0.01
Consideration Teachers' citizenship
behavior 0.29** 0.08 0.01
Structuralism Teachers' citizenship
behavior 0.17** 0.03 0.01
Resources support Teachers' citizenship
behavior 0.25** 0.06 0.01
Manager penetration Teachers' citizenship
behavior 0.37** 0.13 0.01
Temperament Teachers' citizenship
behavior 0.32** 0.10 0.01
Scientific emphasis Teachers' citizenship
behavior 0.45** 0.20 0.01
The above mentioned data shows the correlation coefficient of the schools' organizational health and the teachers' organizational citizenship behavior. Based on the same data, the whole dimensions of the organizational health have positive correlation with the teachers' organizational citizenship behavior. The correlation coefficients of the organizational cohesion, considerations, structuralism, resources support, manager penetration, temperament and scientific emphasis are 0.21, 0.29, 0.17, 0.25, 0.37, 0.32 and 0.45, respectively. They are wholly significant statistically. The highest correlation coefficient is subjected to the scientific emphasis with the organizational citizenship behavior about 0.45 and the lowest correlation coefficient is related
to the organizational cohesion and
organizational citizenship behavior about 0.17. The determination coefficients show that about 4% of the teachers' organizational citizenship behavior variance can be seen and about 8% for considerations, 3% for structuralism, 6% for resources support, 13% for the manager penetration, 10% for the temperament and 20% for the scientific emphasis have been represented potentially.
DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION:
The general process of the obtained results and data analysis showed that there is a positive significant relationship between the variables of the organizational health and the organizational
commitment and teachers' citizenship behavior of East Azerbaijan Province. The obtained results of the main hypothesis showed that the correlation coefficient between variables of the
organizational health, organizational
commitment is 0.39 and 0.26 that both are established in 0.01 significant levels. Hence, it seems that the variable of the teachers' organizational citizenship can lead to balance the correlation between the variables of the schools' organizational health and teachers' organizational commitment so that the related data of the separation correlation coefficient shows that the correlation coefficient between both mentioned variables has been reduced from 0.39 to 0.26. Also the determination coefficient of the citizenship behavior without control is 0.15 and with control 0.07. Thus it can be concluded that the without control variable is 15% and the control variable is 7% of the teachers' organizational commitment of East Azerbaijan Province.
can be represented by the same teachers. The obtained results of the third hypothesis showed thatthe whole dimensions of the organizational health have positive significant correlation with the teachers' organizational citizenship behavior. The correlation coefficients and its dimensions of organizational cohesion, consideration, structuralism, resources support, manager penetration, temperament and scientific emphasis with the teachers' organizational citizenship behavior are 0.31, 0.39, 0.42, 0.35, 0.42, 0.37 and 0.51, respectively. They are wholly significant statistically.
The obtained results of the third hypothesis showed that the whole dimensions of the organizational health have positive significant correlation with the teachers' organizational
citizenship behavior. The correlation
coefficients and its dimensions of organizational cohesion, consideration, structuralism, resources support, manager penetration, temperament and scientific emphasis with the teachers' organizational citizenship behavior are 0.21, 0.29, 0.17, 0.25, 0.37, and 0.45, respectively. They are wholly significant statistically.
The obtained results of the present study are coincident with the results of EntezarNazari's study. Based on EntezarNazari's study regarding to the relations of the above mentioned variables, it seems that the schools' organizational health is a fundamental background for teachers' different behaviors and their reduction or balance. The theoretical basics of the study show that there is a considerable
interaction and overlap between the
organizational health variables and
organizational commitment. In other words, a healthy organization can lead to the healthy morality and behavior of staffs and the human resources can also recover the self behavior and job occupational location. Macintosh et al (2007) pointed to the phenomenon of the personal health and organizational health that they are related together.
They defined the phenomenon of the health as following: the health is a complete status of people regarding to the physical, social, mental and social welfare and the lack of illness does not relate to the related process. Kit Davis
considers a healthy organization as a place where people feel their own beneficent into an organization. They tend to carry out their own tasks potentially making internal comfort and relaxation. Many staffs are seeking their own
occupational success into their own
responsibilities trying to achieve occupational progression in this pavement. They like to be paid attention potentially; they also like to be valued morally and personally. They try to get confident of their own problems to be solved (cited of Azkhishi, 2009). According to Lyden and Clingel viewpoints, the relationship of the organizational health with the variables of the organizational commitment and citizenship behavior is clarified. According to Lyden and Clingel people want to stay and survive into their own occupational situation efficiently. The staffs of the healthy organizations are those staffs that they will have more commitment with higher temperament making open channels successfully along with others (cited of Jahed, 2005). Loyalty and commitment dimensions: In a healthy organizational atmosphere, there has been established a high trust atmosphere between people working there. The whole staffs and employers are waiting to come up to work making their suitable feeling towards their occupational issues. In the same organizational setting, there is no found any non-moral cases in this case. The whole staffs tend to worthwhile and value the hidden part of the morality affairs potentially (cited of Jahed, 2005). As it mentioned, it is observed that the loyalty and commitment dimensions have correlation with the morality dimensions of the citizenship behavior. According to Lyden and Clingel
viewpoints, the relationship of the
the organization and management and there have been represented many various elements for the health of these organizations in the framework of the models and patterns by the related experts. The healthy organization is a place where people are very interested in working in their own situations potentially. Indeed, the organizational health plays a key role regarding to the physical, mental, privacy, possession and ability and value of wisdom, expert and personality of people in one hand, and on the other hand it influences on the behavior effectiveness of every system efficiently. The theoretical basics and experimental observations have shown that there is a considerable interaction and overlap between the variables of the organizational
health, organizational commitment and
citizenship behavior.
Andaroudi (2002) in his study showed that there is a significant relationship between the organizational health in the whole dimensions of the organizational health and the organizational commitment. Ferdowsi (2012) in his study titling the relationship between the personality traits and organizational commitment with the organizational health among the youth sport organization of Khouzestan Province has reported that the organizational commitment is a predictive and determinant variable for the organizational health. Nasiri et al (2011) in his study concluded that there is a significant positive relationship between the whole dimensions of the organizational health and organizational commitment. The obtained results of the regression analysis showed that the organizational health is able to represent the staffs' commitment about 55.6%. The most effective predictive element is subjected to the organizational cohesion and the second element is related to the organizational commitment and temperament of the staffs (Nasiri et al, 2011). Shakerinia (2011) concluded thatthere is a
significant relationship between the
organizational support and organizational citizenship behavior of Rasht City Hospital Nurses. Shams (2012) in his study reported that there is a significant relationship between the organizational health and organizational
citizenship behavior. The correlation coefficient of these variables is 0.84 as significant statistically. Also the correlation coefficient between the organizational health with task or duty, respect, altruism, fair and citizenship excellence is 0.71, 0.46, 0.67, 0.61 and 0.63 (Shams, 2012). Suiee et al (1994) investigated the relationship of the teachers' perception from the school health viewpoint and their teachers' persona traits. Based on the results of the present study, the status of the school organizational health can predict the teachers' organizational commitment. There have been established five dimensions of the scientific emphasis, consideration, organizational cohesion, and temperament and manager penetration from the seven dimensions of the organizational health as the predictive cases in this pavement.Three dimensions have higher power of predicting the organizational commitment (Suiee et al, 1994). Nier (2002) in a study titling the school health and its relationship with teachers' commitment found out that the school health is the main sophisticated factor and teachers in the healthy schools can show their best organizational commitment. Williams and Anderson (1991) in their study reported that the occupational satisfaction including two emotional and cognitive variables can influence on the organizational commitment having positive correlation with the organizational citizenship behavior. Pateel (2002) in a study regarding to the investigation of the relationship between the organizational health and organizational commitment reported that there is a positive
significant relationship between the
organizational health and organizational commitment.
REFERENCES:
1. Amirpour Maryam (2009): the investigation of the relationship between the occupational satisfaction and organizational commitment of MARAGHEH City guidance school teachers, a thesis for MA, Uremia University 2. AndaroudiRazieh (2002): the investigation of
the relationship between the organizational
commitment in Tehran girls guidance school, a thesis for MA, university of Tehran
3. Iranzadeh Suleiman and AsadiNazel (2009): the investigation of the relationship between the citizenship behavior and organizational justice with the occupational satisfaction of Ardebil research center, research-scientific article, seasonal magazine of Management, 3rd year, no: 10, pp: 43-75
4. JahedHusseinali (2005): organizational health, Tadbir Monthly magazine, no: 159, pp: 16-29
5. Davis Kit and New Storm John (1994): organizational behavior at job, translated by
Mohammad Ali Toosi, governmental
management training center
6. Shams Lida (2012): the relationship between
the organizational health and the
organizational citizenship behavior in Tehran medical sciences faculty hospitals, magazine of health message, Tehran medical sciences college, no: 6, pp: 412-422
7. ShakeriniaIraj (2011): the relationship of the moral setting and organizational support on the organizational citizenship behavior
among Rasht governmental hospitals,
seasonal magazine of hospital, archive, SID 8. Abbaszadeh 1990: Mir Mohammad: teaching
occupation and occupational satisfaction
9. Alaghehband Ali (1997): training
management, Tehran: NashrRavan
Publication
10.Alaghehband Ali (1999): school
organizational health, seasonal magazine of management in education, no: 21, spring
11.Ferdowsi Mohammad Hassan
MarashianFatemeh and Talebpour Mehdi (2012): the relationship of the personality traits and organizational commitment with the organizational health in the staffs of the youth sport organization of Khouzestan Province, seasonal magazine of sport sciences, no: 15, pp: 173-188
12.Majidi Mohsen (2010): the investigation of the emotional intelligence of managers and school organizational health, a thesis for MA, Islamic Azad University of Bonab
13.Mayer John. P. and Allen N.G (1996):
organizational commitment and its
relationship with abandoning the job location, translated by Saroughi, seasonal magazine of management, no: 21
14.Nasiri Amir Ashkan, Ali Mohammadzadeh, Khalil, RaieesiPouran and JaafariMehrnoush (2011): the relationship of the organizational culture and Azad University staffs' commitment, seasonal magazine of the treatment and health organization, 3rd year, no: 1-2, pp: 49-57
15.Houwi Win, Cook MisckelSisil J (1997): theory, research and practice, translated by Mir Mohammad Abbaszadeh, 2nd printing, Uremia: Uremia University Publication 16..Alper ,Ertürk, (2007) "Increasing
organizational citizenship behaviors of Turkish academicians: Mediating role of trust in supervisor on the relationship
between organizational justice and
citizenship behaviors", Journal of Managerial Psychology, Vol. 22 Iss: 3, pp.257 - 270 17..Blanchard, K.(1999), The Heart of a
leader,Honor books.
18..Cholowski, C. and Chan, L.(1992), Diagnostic reasoning among second year nursing students” J AdvNurs, Vol.17,No.2. 19..Chang,H.T., chi,M.W, &Miao,M.C.(2007).
Testing the relationship between three component organizational / occupational
commitment and organizational
occupational turnover intention using a none-recursive model, jounal of vocational behavior,2,320-335.
20..Dieter,N.(1999),“From demand to desire: What do we offer when we offer group analytic training” Journal of Group analytic Psychotherapy, Vol.32,No.2,pp.(99-109). 21..Donelson, F.(1999), “Group dynamics” third
edition, InteractionsThomposon publishing Co.
22..Dyne .Linn .van &Graham Jill
&dienesh.Richard(1995)” Organizational
citizenship behanior :construct
redefinition,measurement and validation “Academy of Management Journal,vol 37 N,4.pp765-802.
Occupational and Organizational psychology, 80:665691.
24..Haber,J(1997), “ Comprehesive psychiatric nursing” 5th Ed, Mosby.
25..Herzberg, F(1974). Motivation- Hygiene Profiles. Organizational Dynamics 3(2) 18-29.
26..Hood , Christopher(1998). The art of the state : Culture, rhetoric, and public management. Oxford: Clarendon Press. 27..Hoy,W.K.,Tarter,C.J.,&kottkamp,R.B.(2000
).open schools/helthysckools:Measurement organizational climate.E-book has been republished by Arlington writers,LTD. 28.. Jolia,l(1992), “Psychatric and mental healt
nursing”.
29.. Julie A Lynden &Willam, Klingle.(2000),
“Supervising Organizational
Health”Supervision Journal, 2000, pp:3-5 30.. Kaplan , R Norton. (1992)" The Balanced
Scorecard – Measurement that drive
performance ,Harvard Business review, January February.
31..Lepnurm, R, Dobson.Backman,
A.&Keegan,D.(2006) Factors planning career satisfaction among psychiatrists and
surgeons in Canda.Canda Journal of
Psychiatry: Vol.51 ,pp.43-50
32..Landy ,F.J &Conte,J.M .(2007). Work in the 21stcentury : An introunction to industrial And organizational psychology , (2nd.). Maladen MA : Blackwell Publishing.
33..LiviaMarkozy and Katherine Xin(,2004),the virtues of omission in organizational citizenship behavior,university of California ,pp.28-30.
34.. MacIntosh ,Robert, Donland MacLean and Harry, Burn, (2007), Health in Organization: Towards a Process- Based View, Journal of Management studies44:2 March pp:206-219. 35.. Meyer.J.P. and N.J Allen . (1991) Athree
components conceptualization of
organizational commitment . Journal of Applied psychology .
36..Mexer .J.P and Allen , N, (1984) " Three-Components of Organizational commitment " ,Human Resource management Review.
37..Nir,adam,(2002).School health and its Relation to teacher commitment ,Joural of planning and changing, 1-2,106-126.
38..Organ, D. W .Podsakoff, P.M. & Mackenzie, S.B.(2006). Organizational citizenship behanior : Its true nature , antesedents and consequences.Beverly Hills, CA:Sage.
39..Organ, D. ,Ryan,K.(1995):”A meta-analytic review of attitudinal and dispositional predictors of Organizational citizenship behanior”.personel psychology ,48(4),775-802.
40..Organ, D.W &Konovsky ,M , .(1989):” Cognitive versus affective determinants of Organizational citizenship behanior”. Journal of applied psychology ,74:,157-164.
41.. Organ D. W., & Near J. (1983). Organizational citizenship behavior: Its nature and antecedents. Journal of Applied Psychology, 68(4), 653-663.
42..Organ, D. W. (1988). Organizational Citizenship behavior: The good soldier
syndrome. Lexington, MA: Lexington
Books.
43..Organ, D. W. (1997). Organizational citizenship behavior: It’s construct cleanup time. Human Performance, 10(2), 85-97.
44..Organ, D. W., Podsakoff, P. M.,
&MacKenzie S. P. (2006). Organizational citizenship behavior: Its nature, antecedents,
and consequences. London: Sage
Publications.
45..Pateel.C.(2002).Examination of
organizational health and organizational commitment among industrial employees .journal heals train vol,4:180-195.
46..Podsakoff, N. P., Blume, B. D., Whiting, S. W., &Podsakoff, P. M. (2009). Individual- and organizational-level consequences of organizational citizenship behaviors: A meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology, 94(1), 122-141.
behaviors. The Leadership Quarterly, 1(2), 107-142.
48..Podsakoff, N. P., Whiting, S. W., Podsakoff, P. M., & Mishra, P. (2010). Effects of organizational citizenship behaviors on
selection decisions in employment
interviews. Journal of Applied Psychology. Advance online publication.
49.. Podsakoff , E & Mackenzie, J; Paine J.&Bachrach ,D. (2000): Organizational citizenship behaniorAcritical review of the theoretical and imprical literature and sugestions for future research . Journal of Managememnt , 26: 513-563.
50..Polanyi, H. (2004) .Healthy organizational practices. A multi – stakeholder Conference. May 11-13, 2004, March 2004.
51..Quinn ,F,(1995),“The principles and practice of nurse education” London: Chapman& Hall Co.
52..Rabi S. Bhagat, Pamela K. Steverson and Games C. Segovis, (2007), Internationl and Cultural Variation in Employee Assistance Programmes: Implication for Managerial Health and Effectiveness, Journal of Management studies 44:2 March, pp: 222 – 240.
53..Sadler, P. (1998), Designing Organizations, Third Edition, Kogan Page.
54..Spector ,P&Fox,S.(2010).Theorizing abute the deviant citizen. Human Resource Management Review,20:132-143.
55..Thomas,A: Grugle, M.(1994), “Group therapy” Journal of Psychiatry, Vol.14, No.5,.pp.(56-60).
56..Tsui,K,T.,&Cheng,Y.S (1999), School
organizational health and teacher
commitment:Acontingency study with multi-level Analyses.EducationalReserch and Education ,3,429-268.
57..Tsui,K,T,Leung.T.W.,
Cheng,Y.S.,mok,H.T.,&Ho,W.S. (1994). The relationship of teacher organizational
commitment to their perceived
organizational health and personal
characteristics in primary schools.Journal of primary Education.4,27-41.
58..Todd, S. Y., & Kent, A. (2006). Direct and indirect effects of task characteristics on
organizational citizenship behavior. North American Journal of Psychology, 8(2), 253-268.
59..Wagoner, R. &Matcalfe , S.&Olaore, I. (2005). Fisical reality and academic quality : part – time faculty and the challenge to organizational culture at community college , community collegeon. Journal of Research and Practice the University of Arizona. USA, 29;25-44.
60..Warschauer, M. (2000). The changing global economy and the future of English teaching. TESOL Quarterly, 34, 511–535.
61..Wayne , K.&Feldman,J
(1987),Organziational health: the concept and the measure. Journal of Research and Development in Education. No. 4,p.30. 62..Weihrich& Koontz, (1993), Management: A
Global perspective, Tenth Edition, Mcgraw Hill.
63..Williams,L.J,Anderson,S.E(1991)’job
satisfiction and Orgnanizational
Commitment as predictor of Organizational
Citizenship Behavior’ Journal of