r e v b r a s r e u m a t o l . 2015;55(3):313–316
w w w . r e u m a t o l o g i a . c o m . b r
REVISTA
BRASILEIRA
DE
REUMATOLOGIA
Case
report
Achilles
tendon
xanthoma
imaging
on
ultrasound
and
magnetic
resonance
imaging
Eloy
de
Ávila
Fernandes
a,
Eduardo
Henrique
Sena
Santos
a,∗,
Tatiana
Cardoso
de
Mello
Tucunduva
a,
Antonio
J.L.
Ferrari
b,
Artur
da
Rocha
Correa
Fernandes
baDepartmentofImagingDiagnosis,UniversidadeFederaldeSãoPaulo,SãoPaulo,SP,Brazil
bDepartmentoofMedicine,UniversidadeFederaldeSãoPaulo,SãoPaulo,SP,Brazil
a
r
t
i
c
l
e
i
n
f
o
Articlehistory:
Received24September2013 Accepted11December2013 Availableonline13May2015
Keywords:
Xanthoma Achillestendon Ultrasound
Magneticresonanceimaging
a
b
s
t
r
a
c
t
TheAchillestendonxanthomaisararediseaseandhasahighassociationwithprimary hyperlipidemia.Anearlydiagnosisisessentialtostarttreatmentandchangethedisease course.Imagingexamscanenhancediagnosis.Thisstudyreportsthecaseofa60-year-old manhavingpainlessnodulesonhiselbowsandAchillestendonswithouttypicalgoutcrisis, followedinthemicrocrystallinediseaseclinicofUnifespfordiagnosticworkup.Laboratory testsobtainedshoweddyslipidemia.Theultrasound(US)showedadiffuseAchilles ten-donthickeningwithhypoechoicareas.Magneticresonanceimaging(MRI)showedadiffuse tendonthickeningwithintermediatesignalareas,andareticulatepatternwithin.Imaging studiesshowedrelevantaspectstodiagnoseaxanthoma,thushelpinginthedifferential diagnosis.
©2014ElsevierEditoraLtda.Allrightsreserved.
Aspectos
de
imagem
do
xantoma
do
tendão
calcâneo
na
ultrassonografia
e
ressonância
magnética
Palavras-chave:
Xantoma Tendãocalcâneo Ultrassonografia Ressonânciamagnética
r
e
s
u
m
o
Oxantomanotendãocalcâneoéumadoenc¸araraetemumaaltaassociac¸ãocom hiper-lipidemiaprimária.Odiagnósticoprecoceéfundamentalparaoiníciodotratamentoe paraalterarocursodadoenc¸a.Osexamesdeimagempodemauxiliarnessediagnóstico. Esteestudorelataocasodeumhomemde60anosapresentandonódulosindoloresnos cotovelosetendõescalcâneos,semcrisestípicasdegota,acompanhadonoambulatório de doenc¸asmicrocristalinas daUnifespparaesclarecimentodiagnóstico.Ostestes lab-oratoriaissolicitadosapresentavamdislipidemia.Ultrassom(US)mostrouespessamento difusodostendõescalcâneoscomáreashipoecoicas.Ressonânciamagnética(RM)mostrou
∗ Correspondingauthor.
E-mail:eduardosena1@yahoo.com.br(E.H.S.Santos). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rbre.2013.12.003
314
rev bras reumatol.2015;55(3):313–316espessamentodifusodostendões,comáreasdesinalintermediárioepadrãoreticuladono interior.Osexamesdeimagemmostraramaspectosrelevantesnodiagnósticodexantoma, auxiliandonodiagnósticodiferencial.
©2014ElsevierEditoraLtda.Todososdireitosreservados.
Introduction
Xanthomasarenonneoplasticlesionscharacterizedbyalocal concentration of lipid-laden macrophages, giant cells, and otherinflammatorycells inresponsetocholesterol deposi-tionintissues.Theyarerelativelycommon,withmostofthem occurringontheskin,especiallyontheeyelids.1Thelesions
are most frequently seen on tendons and synovium and theyusuallyinvolvetheextensortendonsofthehands,both Achilles tendons, and patellar ligaments.1,2 They typically
occuratthethirddecadewithafemale4:3ratiopredominance overmales.2
TheAchillestendonxanthoma isarare disease3 and is
highlyassociatedwiththeprimaryhyperlipidemia.Theearly diagnosisisessentialsothatthetreatmentisstartedandit canchangethediseasecoursebeforethedevelopmentofan advancedcoronarydisease.
Imagingdiagnosismightbeearlierthanclinicaldiagnosis, thusitisclinicallyimportanttorecognizeimaging character-istics,especiallyultrasoundandmagneticresonanceaspects ofxanthomas.
Case
report
A male patient aged 60 with pain nodules on the elbows and Achilles tendons with no typicalgout crisis has been followed in the microcrystalline disease clinic, Depart-ment ofRheumatology, Universidade Federalde São Paulo (Unifesp). A suspected chronic tophaceous gout with an atypical presentationwasconsideredbecause ofthe nodu-lations. Laboratory tests obtained were as follows: total serumcholesterol(268mg/dL)andcholesterolfractions(HDL: 43mg/dL; LDL: 192mg/dL), triglycerides (166mg/dL) and uric acid (5.6mg/dL). He underwent ankle ultrasound (US) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the diagnostic workup.
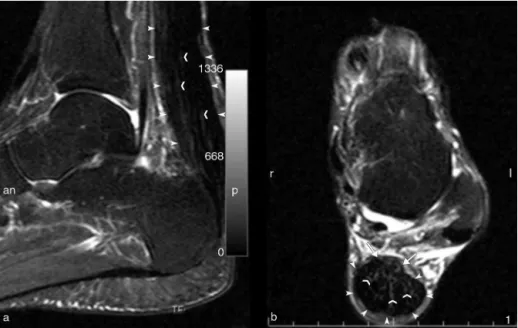
TheUS(Fig.1)showedadiffusethickeningoftheAchilles tendonswithhypoechoicareasandothersmallhyperechoic confluences.MRI(Fig.2)showedadiffusethickeningof ten-donswithintermediatesignalareasandareticularpattern within.
Thepatientunderwentaresectionbiopsyofelbowlesions.
Discussion
TheAchilles tendon xanthoma is a rare condition of con-cern to orthopedic surgeons when planning surgeries for cosmetic deformities. The numbers of lesions, cholesterol levels,age,andgenderarecorrelated.4Itisimportantin
Inter-nalMedicineand inDermatologybecause ofalinkwith a
specificchangeinthelipid metabolism,thefamilial hyper-cholesterolemia. Thefamilial hypercholesterolemia has an autosomaldominantinheritanceandischaracterizedbyan elevated LDL-cholesterol, tendonxanthomas, and coronary disease. Although xanthomas have been described in the absenceoffamilialhypercholesterolemia,thiscanbethefirst diseasemanifestation.5
Despite thexanthoma isusuallyknown asasofttissue lesion,itcanrarelybefoundinbone.6Thevariabilityofcell
compositionleadstoadiscussiononwhethertheseskeletal systemlesionsaretrulytumorsornot.Histologicalfindings similartoxanthomascanbeseeninneoplasticand nonneo-plastic bone lesions.Xanthomatous changes may occur in lesionssuchasfibrousdysplasia,giant-celltumor, aneurys-maticbonecyst,nonossifyingfibroma,fibrouscorticaldefect, benignandmalignantfibroushistiocytoma,Erdheim-Chester disease,xanthogranulomatousosteomyelitis,andrenal car-cinoma metastasis. Xanthomas, therefore, can develop a conditionunrelatedtohyperlipidemia.7
Clinical manifestations of Achilles tendon xanthomas depend on the lesion sizes. The smaller lesions are often asymptomatic.Thelargerlesionsareclinicallyapparentand manifestascosmeticallydisfiguringmasseswhichcanimpair ambulationandcauselocalpainorirritatingskinsymptoms.7
Radiography,US,and MRIcanbeusedpreviouslytothe emergence of clinical manifestations. On X-rays, tendon xanthomas areshowneitherasanabnormaltendon thick-eningor softtissuenoncalcifiedmasseswithanonspecific appearance.7,8
US and MRI are effective techniques in assessing and detectingAchillestendonxanthomas.RMtendonxanthoma imagingmaypresent morphologicalorsignalchanges.The ventralmarginoftheAchillestendonisnormallyflator con-cave,butitmayhaveaconvexappearanceinaxialimaging whenaxanthomaispresent.7
MRIcharacteristicsoftendonsaffectedbyxanthomasshow eitheradiffusereticulatepattern9orfocalareaswithahigh
signalonT1andT2,withthislatteraspectoccurringwhen triglycerides are predominantly deposited.5 In the current
case,adiffusereticulatepatternwasobserved.Thispattern maybeexplainedbythepatient’slipidprofile–predominantly LDLfractiondyslipidemiaandtriglyceridelevelscloseto nor-malrange.
Althoughsmallareas withhigh signal,especiallyonT2, canbefoundintendonxanthomas,theyarepredominantly characterizedbyatendonenlargementonMRIwhichis indis-tinguishable from thatseen in tendondiseases with other etiologies,thuslimitingtheclinicaluseofMRIintendon xan-thomaworkup.5
rev bras reumatol.2015;55(3):313–316
315
Figure1–1a)Achillestendonultrasoundextendedinthelongitudinalplane(P=proximal;D=distal)and1b)cross-sectional plane(D=right;E=left)showingmarkeddiffuseandconcentricthickeningoftheAchillestendon(arrowheadsmarkthe tendonexternalmargins)predominatinginmiddle-anddistalsectionswithadiffuseheterogeneity,withconfluent hypoechoicareas(openarrows)andthinhyperechoicfociwithinthetendonbeingobserved,whichcausealossofthe fibrillarpatternoftendons.Arrowsdelineatecalcaneuscorticalbone,(*)demonstratesKagerfatpadand(sc)isthe subcutaneoustissue.Nohyperechoicmassesareseeninthetendondespitetheextensorinvolvementofthetendon.
a fibrillar pattern. The histological correlation shows that fibrillarechoesarisefromtheinterfacebetweenendotendon septa.10Achillestendonxanthomashavebeendescribed as
hypoechoicnoduleswithinthetendonorhavingadiffusely heterogeneouspattern.9
Inthecurrentcase,theUSstudywascrucialto differenti-atetheintratendinousxanthomafrompyrophosphatecrystal deposition,gout,andtendondisease.
The different tendon impairment patterns by tophi in chronictophusgouton aultrasoundstudy includesodium monourato crystal deposits, translatedashyperechoic dot-tedfociorintratendongoutytophi,whichareheterogeneous hyperechoicnodulationswithbrightdotssometimeshaving calcifications within. Ill-defined nodules, multiple grouped nodules and the presence of an anechoic halo are also described as characteristics oftophi.11 Thetophus can be
locatedinvolvingthetendonhavingnorelationshipwiththe tendon,atthetendoninsertion,compressingitorwithinthe tendon,12thusbeingeasilydetectedonultrasound.
AsanextendeddiffuseimpairmentoftheAchillestendon wasobservedinthecurrentcaseandnogroupedtophiwere observedashyperechoicovoidmasseswithinthetendonor calcifiedareas,thediagnosisoftophusinAchillestendonswas ruledoutbytheultrasound.
In calcium pyrophosphate disease, crystal depositionin tendons is typically linear and extended, thus an acous-ticshadowmightbegenerated.13 Thisappearancewasnot
observedinthestudyeither.Thediffusethickeningpattern associatedwithhyperechoicareasobservedinAchilles ten-donssupportedtheultrasounddiagnosisofxanthoma.14
Anearly diagnosis ofxanthoma isessential sothat the treatment can be initiated and the disease course can be
316
rev bras reumatol.2015;55(3):313–316modifiedpriortothedevelopmentofanadvancedcoronary disease. Imaging studies showed relevant aspects in xan-thomadiagnosis,thusaidinginthedifferentialdiagnosis.The USwasshowntobemorehelpfulandspecifictocharacterize thiscondition.
Conflicts
of
interest
Theauthorsdeclarenoconflictsofinterest.
r
e
f
e
r
e
n
c
e
s
1. FairKP.Xanthomas.Emedicine[online].
http://www.emedicine.com/derm/topic461.htm.Updated January15,2008.
2. FaheyJJ,StarkHH,DonovanWF,DrennanDB.Xanthomaof theAchillestendon.JBoneJointSurgAm.1973;55:211–1197. 3. Carranza-BencanoA,Fernandez-CentenoM,Leal-CerroA,
Duque-JimenoV,Gomez-ArroyoJA,Zurita-GutierrezM. XanthomasoftheAchillestendon:reportofabilateralcase andreviewoftheliterature.FootAnkleInt.1999;20:314–6. 4. MuranoS,ShinomiyaM,ShiraiK,SaitoY,YoshidaS.
Characteristicfeaturesoflong-livingpatientswithfamilial hypercholesterolemiainJapan.JAmGeriatrSoc.
1993;41:253–7.
5. LiemMS,GeversLeuvenJA,BloemJL,SchipperJ.Magnetic resonanceimagingofAchillestendonxanthomasinfamilial hypercholesterolemia.SkeletalRadiol.1992;21:453–7.
6.BertoniF,UnniK,McleodRA,SimFH.Xanthomaofbone.Am JClinPathol.1988;90:377–84.
7.NarvaezJA,NarvaezJ,OrtegaR,AguileraC,SanchezA,Audia E.Painfulheel:MRimagingfindings.RadioGraphics. 2000;20:333–52.
8.MathiesonJR,ConnellDG,CooperbeiPL,Lloyd-SmithDR. SonographyoftheAchillestendonandadjacentbursae.AJR. 1988;151:127.
9.DussaultRG,KaplanPA,RoedererG.MRimagingofAchilles tendoninpatientswithfamilialhyperlipidemia:comparison withplainfilms,physicalexamination,andpatientswith traumatictendonlesions.AJRAmJRoentgenol.
1995;164:403–7.
10.MatinoliC,DerchiLE,PastorinoC,BertolonoM,SilvestriE. AnalysisofechotextureoftendonswithUS.Radiology. 1993;186:839–43.
11.FernandesEA,SandimGB,MitraudSAV,KubotaES,Ferrari AJL,FernandesARC.Ultrasoundfeaturesoftophiinchronic tophaceousgout.SkeletalRadiol.2011;40:309–15.
12.FernandesEA,SandimGB,MitraudSAV,KubotaES,Ferrari AJL,FernandesARC.Sonographicdescriptionandclassificatio oftendinousinvolvementemrelationtotophiinchronic tophaceousgout.InsightsImaging.2010;1:143–8.
13.GrassiW,MeenaghG,PascualE,FilippucciE.Crystalclear” sonographicassessmentofgoutandcalciumpyrophosphate depositiondisease.SeminArthritisRheum.2006;36: 197–202.
14.BudeRO,AdlerRS,BassettDR.DiagnosisofAchillestendon xanthomainpatientswithheterozygousfamilial