Role of chemokines in promoting instability of coronary atherosclerotic plaques and the underlying molecular mechanism
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
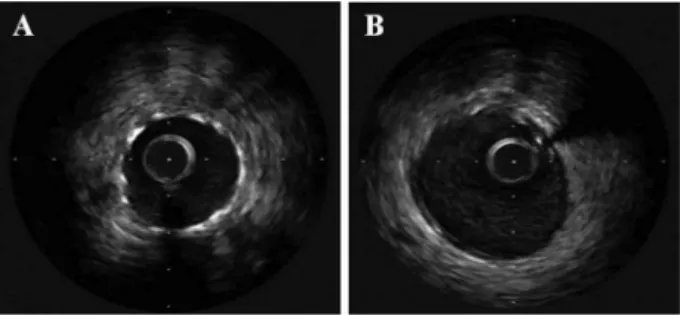
There were 5 types of plaques identified and measured in the 4 major arteries (left main, left anterior descending and diagonals, left circumflex and marginals, and right coronary
We have shown that increasing cadmium exposure is associated with increased burden of subclinical atherosclerotic plaques and that symptomatic carotid plaques contain cadmium in
Thus, to evaluate the presence of DNA of cariogenic and periodontopathogenic bacteria in the mouth and in atherosclerotic plaque samples of the same patients, in addition to
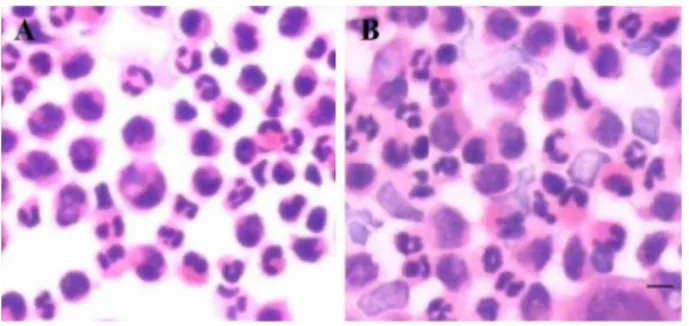
The different forms of presentation of the corneal cal- cium deposits found in the histopathological examination were granules (Figure 1), plaques (Figure 2), and oval formations or
Marcas que estão na própria história da inserção das mulheres no campo literário: as negociações a serem feitas com as editoras que as publicam, as estratégias de difusão de
20 , in a recent study, in which 30 atherosclerotic plaques of the carotid arteries were also analyzed using the PCR technique, did not find any positive results for
The control group was formed by patients that presented atherosclerotic plaques in the carotid arteries and that had not undergone a ischemic event, thus being consid- ered to be
composition of the atherosclerotic plaques in the four major epicardial coronary arteries in acute myocardial infarction and in sudden coronary death. Kragel AH, Reddy SG, Wittes