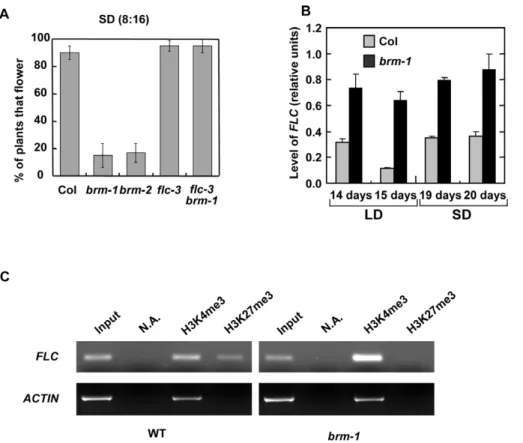
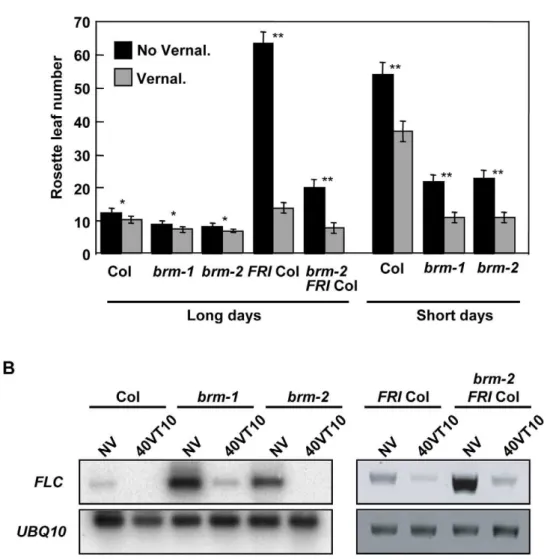
Brahma is required for proper expression of the floral repressor FLC in Arabidopsis.
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
In this context, the present work provides results regarding better reaction conditions for the coal mining waste composed of pyrite in N 2 and CO 2 atmospheres, aiming to
Figure 2 – Diurnal-integrated CO 2 assimilation (Ai, in a), transpiration (Ei, in b) and water use efficiency (WUEi, in c) of tomato plants subjected to variation of substrate
Taken together, these data suggest that the reduction in TfR1 expression and increased ferritin expression in Irp2 2 / 2 mice could lead to reduced iron uptake and increased
Both in tobacco and Arabidopsis transgenic plants, GUS transcript levels were higher for the pSiM24 binary vector than for the pKYLX-based expression vector pKCaMV35 (Figure
Taken together, these considerations prompted us to investigate the existence of a cross-talk between FHC and FTH1P3 transcript levels by modulating the endogenous FHC expression in
Consistent with the data observed in PBMCs, IHC data showed trends of reduced expression of HDAC4 (Figure 4A) and increased expression of TSP1 (Figure 4B) in obese compared to
Taken together, the results suggested a direct effect of palmitoyl-Ova in the increased expression of CD86, CD80 and CD11b in the peritoneal cavity adherent
albicans in the vaginal mucosa, both in colonization processes and in infections, but a differential expression of these genes is observed when comparing the transcript levels