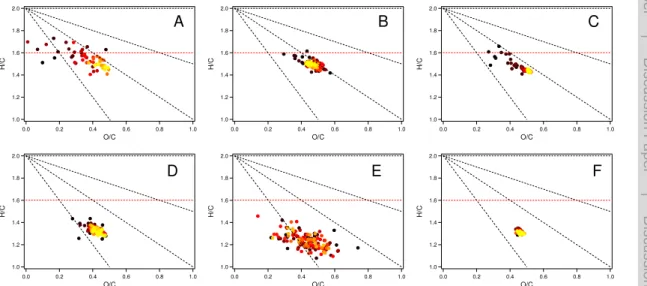
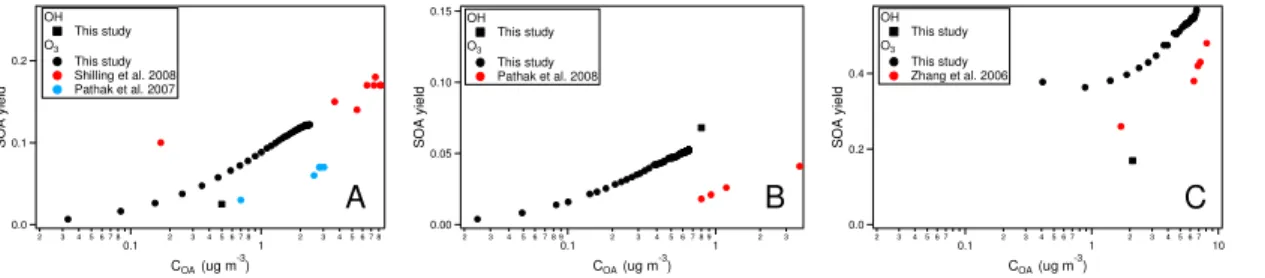
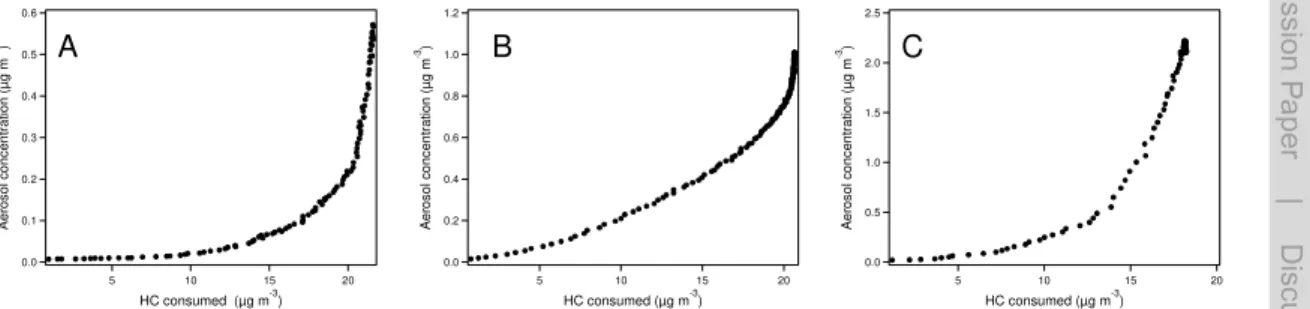
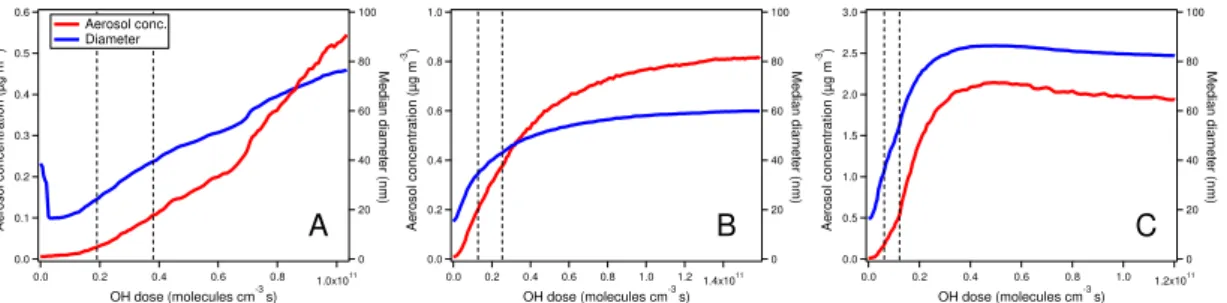
Secondary Organic Aerosol (SOA) formation from hydroxyl radical oxidation and ozonolysis of monoterpenes
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
growth rates over homogeneous surfaces at the field scale and could, for example, be used to derive aerosol growth rates due to biogenic secondary organic aerosol forma- tion in
The volatile and hygroscopic properties of ammonium sulphate seeded and un-seeded secondary organic aerosol (SOA) derived from the photo-oxidation of atmospherically
algorithm organic derived radicals are involved in activation and growth and link the formation rate of smallest aerosol particles with OH during daytime and NO 3 during
The OA mass yields are greatly different for α-pinene and the xylenes (m-xylene and p-xylene), but the fractions of m/z 43 and m/z 44 to the total OA mass concentration, f 43 and f 44
The experimental data obtained for the particle number concentration are pre- sented together with the simulated profile of 2,5-DHF (from the known initial concentrations and
Time traces of aerosol volume as a result of SOA growth from OH oxidation of α -pinene followed by injection of ammo- nium sulfate seed (black) or ammonium sulfate and sulfuric
Time series of wall-loss-corrected aerosol mass (right axis) and VOC consumed by each oxidant (left axis) for α -pinene and β - pinene at 0 (“O 3 -only”), low, and medium NO
We report first results obtained from chamber produced secondary organic aerosol (SOA) from ozonolysis of isoprenoids and from ambient aerosol as measured during the