Extracting natural dyes from wool—an evaluation of extraction methods
Texto
Imagem

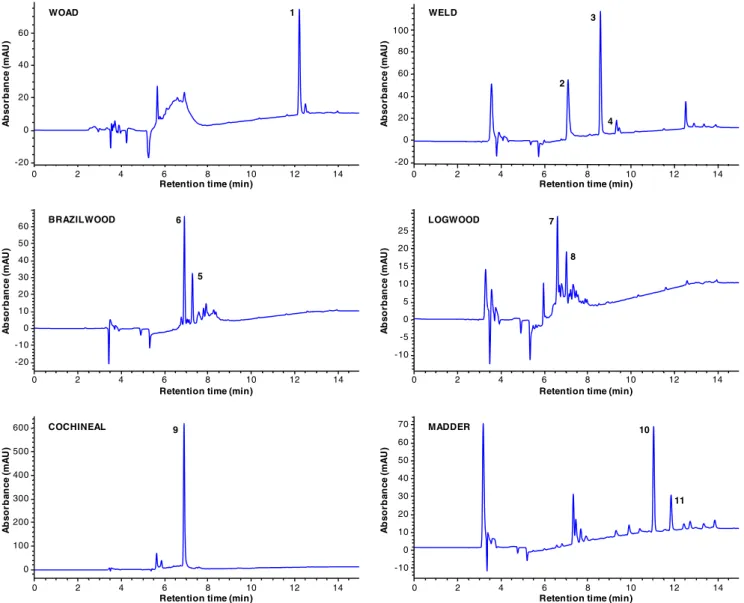
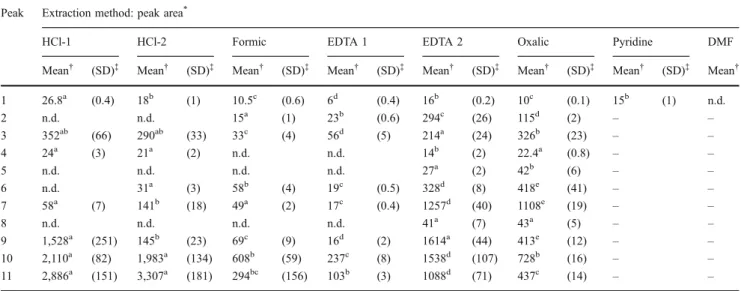

Documentos relacionados
In recent years, some new extraction methods have been employed for the extraction of natural products from herbals, including ultrasound- assisted extraction (Zhang et
The effects of aminooxyacetic acid, benzyladenine, and 1-methylcyclopropene treatments on the post-production flower quality of potted carnation plants ( Dianthus caryophyllus
The objective of this study was to extract collagen from chicken feet, determining optimal extraction conditions according to acetic acid concentration, pepsin content and time
The aim of this study was to extract pectin from the guava pulp during 7 days of ripening by two methods (ethanol and EDTA extraction) and suggest modifications in the methods
The objective of this study was to extract collagen from chicken feet, determining optimal extraction conditions according to acetic acid concentration, pepsin content and time
Results for the analysis of solutions prepared by microwave-assisted nitric acid digestion of these samples were compared to those obtained by formic acid extraction so as
Thus, considering these factors, this study was conducted to compare in vitro the decalcifying effect of 1% citric acid, 1% EDTA, 1% EGTA, 1% CDTA and saline solution (control)
Abstract: This in vitro study evaluated (1) the dissolution of bovine pulp tissue in solutions consisting of varying NaOCl concentrations and com- bined with EDTA; and (2) the
