AES BI OFLUX
Ad va n ce s in En vir on m e n t a l Scie n ce s -
I n t e r n a t ion a l Jou r n a l of t h e Bioflu x Socie t y
Or ga n ic pr oduct s: con sum pt ion h a bit s a nd
pe r ce pt ion s
1
Dacinia- Crina Pet rescu,
2I oan G. Oroian,
2Marian Proorocu,
2Tania
Mihă
iescu,
2Laura Paulet t e,
2Dan Vârban
1
Babes- Boly ai Univ ersit y, Facult y of Business, Cluj - Napoca, Rom ania;
2 Univ ersit y of Agricult ural Sciences and Vet erinary Medicine, Cluj - Napoca, Rom ania. Corresponding aut hor: D. - C. Pet rescu, crina. pet rescu@t bs. ubbcluj . ro
Abst r a ct. The obj ect ive of t he r esear ch was t o det er m ine consum pt ion habit s and per cept ions on ecological food pr oduct s. The m ain r esult s ar e: 85% of t he r espondent s per ceive t he dom inant char act er ist ic or ganic food “ healt hy” ; m or e t han half of t he r espondent s ( 60% ) st at es t o have no or lit t le t r ust in sellers claim s about a pr oduct being eco in t he absence of or ganic label; half of t he r espondent s declar e t hey spent less t han 50 lei ( 0- 11.11 Eur o) on or ganic food and 40% of t he r espondent s declar e t hey spent bet ween 51- 200 lei ( 11. 1 2- 44 . 44. Eur o) on or ganic food; alm ost 20 % of t he sam ple bought or ganic cer eals, fr uit s, veget ables and dair y and alm ost 10% b ought biscuit s, m eat , oil dur ing t he last year ; 80% of t he r espondent s ar e willing t o pay for 1 lit er of or ganic m ilk up t o 44% m or e com p ar ed t o super m ar ket pr ice and 80% m or e com par ed t o sm all far m er s’ pr ice.
Ke y W or ds: or ganic food consum pt ion, dom inant char act er ist ic, t r ust , expendit ur e, pur chased bio food cat egor ies, willingness t o pay.
Re zu m a t. Obiectivul cercetării a fost de a determina obiceiurile de consum și percepțiile consum at or ilor pr ivind pr odusele alim ent ar e ecologice. Principalele r ezult at e sunt : 85% dint r e r espondenți percep produsele alimentare organice ca având dr ept caracteristice dominantă "sănătos";
mai mult de jumătate dintre respondenți (60%) afirmă că nu au încr eder e deloc sau puțin în vânzătorii car e susține despre un produs că este ecologic, în absența et ichet ei ecologice; jumătate dintre r espondenți declară că au chelt uit m ai p uțin de 50 de lei (0- 11. 11 eur o) pe pr oduse alim ent ar e ecologice și 40% dintre respondenți declară că a cheltuit între 51- 200 de lei ( 11. 1 2- 44. 44 eur o) pe pr oduse alim ent ar e ecologice; apr oape 2 0% din eșantion a cumpărat cereale ecologice, fr uct e, legum e
și lactate și aproape 10% au cumpărat biscuiți, carne, ulei pe parcursul ultimului an; 80% dint r e r espondenți sunt dispuși să plătească pent r u 1 lit r u de lapt e ecologic cu până la 44% mai mult față de pr et ul de super m ar ket și până la 80% m ai m ult față de pr ețul micilor fermieri.
Cu v in t e ch e ie: consum de alim ent e ecologice, caracteristică dominantă, încredere, cheltuieli, alim ent e bio cumpărate, dispoziție de a plăti.
I n t r odu ct ion. Agricult ure has an im port ant share in Rom anian econom y and organic agricult ure has an raising t rend during t he last decade ( Pet rescu et al 2010; Pet rescu-Mag & Pet rescu 2010) . The int erest in organic agricult ure is visible bot h from producers and from consum ers side and is reflect ed by increasing v alues of: num ber of cert ified operat ors, product ion v alue, area of cult iv at ed land, spending per person, organic share of t ot al food m ark et et c, as reflect ed in Table 1.
Table 1
Ev olut ion of organic agricult ure indicat ors
2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011
No of r egist er ed oper at or s in or ganic
far m ing 3409 3834 4191 3228 3155 1025 3
Ar ea of cult ivat ed land in or ganic
far m ing, cr ops on ar able land ( ha) 4558 5 6508 4 8641 7 1099 68 1479 71 1587 58
Ar ea of cult ivat ed land in or ganic
far m ing, hay cr ops ( ha) 5117 8 5757 5 4598 6 3921 5 3156 7 8945 2
Ar ea of cult ivat ed land in or ganic far m ing, per m anent cr ops or char ds and vineyar ds ( ha)
294 953 1518 1869 3093 4582
Collect ing spont aneous flor a ( ha) 3868 3 5870 3 8124 4 8884 6 7726 2 4708 1
I m por t s ( m ill. Eur o) 2. 28 4. 15 6. 92 8. 31 31. 16 35. 31
Expor t s ( m ill. Eur o) 44. 31 74. 08 89. 31 93. 47 133. 62 177. 93
Dom est ic m ar ket ( est im at ed) ( m ill.
Eur o) 4. 15 4. 15 6. 92 9. 69 11. 77 18. 00
Tot al dom est ic consum pt ion ( I m por t s
+ Dom est ic m ar ket ) ( m ill. Eur o) 6. 44 8. 31 13. 85 18. 00 42. 93 53. 31
Populat ion ( m illion) 21. 5 21. 5 21. 5 21. 5 21. 5 21. 5
Spending per per son ( Eur o) 0. 30 0. 38 0. 64 0. 84 1. 99 2. 48
Or ganic Shar e of Tot al Food Mar ket
( % ) 0. 21 0. 29 0. 33
Sour ce: St oenescu, 2012, p. 2- 3.
M a t e r ial a n d Me t h od. The result s present ed in t his paper w ere obt ained t hrough an inv est igat ion on a 40 person sam ple ( wit h t he ex cept ion of t he last quest ion, t est ed on a 200 person sam ple) , aged ov er 18, urban resident s, from Cluj - Napoca cit y ( Rom ania) , in 2012. The quest ionnaires w ere sent online, self- adm inist ered by t he respondent s and sent back t o t he researcher. The obj ect iv e of t he research w as t o det erm ine consum pt ion habit s and percept ions on ecological food product s. The inv est igat ion t hrough self-adm inist ered quest ionnaire w as preferred because of it s fast im plem ent at ion, low er cost s t han int erviewing, reduced int erview er bias, pot ent ial anony m it y of t he respondent , w hich can lead t o m ore t rut hful or v alid responses, conv enience for t he respondent s on answ ering it ( Eiselen & Uy s, p. 2) . How ev er, due t o t he sm all size of t he sam ple, t he result s have lim it ed represent at iv eness and should be used as pre- t est result s for a broader st udy . The t erm s organic, ecological ( eco) and bio in relat ion t o food are used here as sy nony m s.
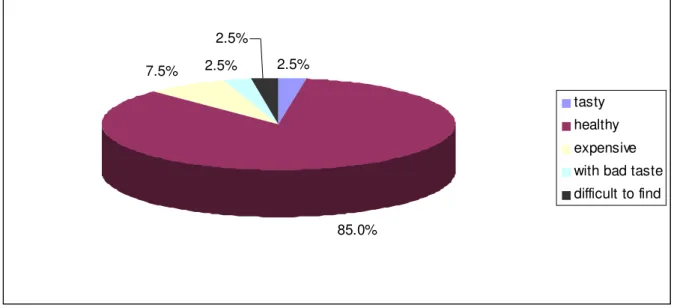
Re su lt s an d D iscussion. The first quest ion aim ed t o det erm ine t he m ain charact erist ics t hat consum ers associat e wit h organic food: “I n y our opinion, w hich of t he follow ing w ords describes best t he organic food: a) t ast y b) healt hy c) ex pensiv e d) w it h bad
t ast e e) difficult t o find?” ( see Figure 1) .
2.5%
85.0%
7.5% 2.5%
tasty healthy
expensive with bad taste difficult to find
Figure 1. Dom inant charact erist ic of organic food in consum ers’ m ind.
The dom inant charact erist ic of organic food is “ healt hy ” : 85% of t he respondent s perceiv es it like t his. This is a posit iv e fact because healt h concern is an im port ant fact or det erm ining t he buying decision, and t hus it can st im ulat e bio food consum pt ion. How ev er, 7. 5% sees organic food as prim arily “ ex pensiv e” , w hich is usually a barrier for t he acquisit ion. I t is a correct percept ion because m ost of organic product s are significant ly m ore ex pensiv e t han conv ent ional ones. The first m ent ioned charact erist ic can also be one of t he dom inant fact ors influencing t he buy ing decision. This is w hy , for t he 7. 5% abov e m ent ioned, price m ight m ore im port ant t han healt h concern. The rej ect ion effect of t his percept ion can be dim inished by v arious m eans: changing t he hierarchy of t he charact erist ics in consum ers’ m ind – t ry ing t o put on t he t op t hose t hat st im ulat e consum pt ion, such as long t erm healt h, env ironm ent prot ect ion et c; changing t he qualit y - price rat io ev aluat ion – prom ot ing t he higher price as fair for t he qualit y offered; changing t he ev aluat ion of t he price, m ak ing it seem lower t hrough com parison w it h ot her higher prices or ex penses ( Fest inger & Carlsm it h 1959; Kow ol p. 4) . Consum ers t hat see t he organic food as being first of all “ t ast y ” ( 2. 5% ) hav e higher chances t o acquire it t han t he ot her 2. 5% w ho perceiv e it as being “ wit h bad t ast e” , because t ast e is, nat urally , an im port ant crit erion for in select ing food product s ( Shaw Hughner et al 2007, p. 8) . The 2. 5% w ho put “ difficult t o find” as m ain feat ure of organic food are consum ers t hat , m ost probably, had difficult ies in finding organic food; t his m eans t hat hav e already t ried t o purchased it , didn’t find it or find it wit h a high effort , w hich generat ed an int ense negat iv e ex perience as a result of t he rat io high int erest / need/ desire and high lev el of dissat isfact ion. The dom inat ion of “ healt hy ” at t ribut e revealed by our st udy is congruent wit h t he findings of ot her research. An OECD st udy on 10000 respondent s from 10 OECD count ries ( Aust ralia, Canada, Czech Republic, France, I t aly , Korea, Mexico, t he Net herlands, Norw ay and Sw eden) , in 2008, found t hat organic product s are st ill perceived as healt hier t han conv ent ional ones: alm ost 50% of t he sam ple rank s “ bet t er for healt h‟ attribute first ( Boccalet t i 2009, p. 7) .
30.0%
30.0% 35.0%
5.0% 0.0%
not at all a little average trust high trust absolute trust
Figure 2. Lev el of t rust in seller recom m endat ions in t he absence of organic label.
I n t he case of organic product s, consum ers should be aw are of t he organic label appearance and m eaning and should not rely only on seller’s affirm at ions. False affirm at ions of sellers can dam age t he t rust in qualit y of bio food and ca harm cust om ers t hat need it for it s int rinsic charact erist ics ( due t o healt h reasons, for inst ance) . More t han half of t he respondent s ( 60% ) has no or lit t le t rust in sellers claim s, w hich is a posit iv e fact because t hey are aw are or infer t hat anot her fact , m ore obj ect iv e, m ore reliable, is a bet t er indicat or of t he organic cat egory – a label, a dedicat ed selling place et c. More t han one t hird ( 35% ) has av erage t rust in sellers claim s, w hich can m ean eit her t hey consider sellers quit e reliable inform at ion sources ( professional, concerned w it h consum ers’ w ellbeing, honest et c) or t hey are not v ery concerned w it h t he ecological product s and choose t he m ost conv enient posit ion ( t he av erage one) and do not inv est a lot of effort in finding out w hich is t he correct crit erion for classificat ion or in est ablishing t he reliabilit y of t he sellers. A sm all percent age ( 5% ) has high t rust in sellers claim s, eit her because t hey consider t hem selv es well inform ed about t he sellers and t rust t hem ( t hey m ight liv e in sm all com m unit y w here people k now and t rust each ot her or t hey m ight had previous posit iv e ex periences in relat ion t o t he inform at ion receiv ed from t he sellers) or t hey consider t he feat ure “ bio” a com m on one, about w hich a seller w ould hav e no reason t o lie about .
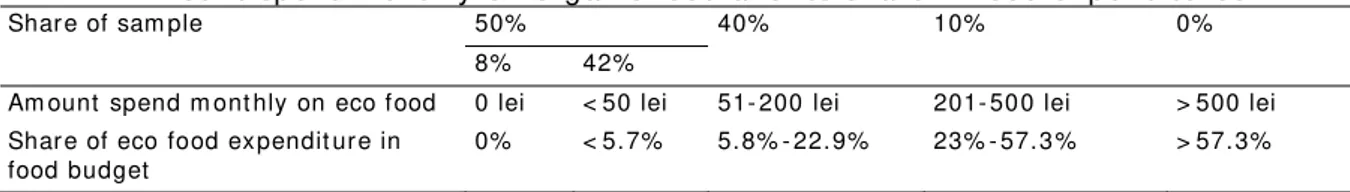
Through t he t hird quest ion w e w ant ed t o discov er how m uch people spend m ont hly on organic food: “ How m uch did y ou spent on organic food in a m ont h, in av erage, during t he last 12 m ont hs: a) 0- 50 lei (0- 11. 11 Euro1) b) 51- 200 lei ( 11.12-44. 44 Euro) c) 201- 500 lei ( 11.12-44. 45- 111. 11 Euro) d) > 500 lei ( > 111. 11 Euro) ” ( see Figure 3, Table 2) .
50.0% 40.0%
0-50 lei (0-11.11 Euro) 51-200 lei (11.12-44.44 Euro) 201-500 lei (44.45-111.11 Euro) > 500 lei (>111.11 Euro)
Figure 3. Am ount spent m ont hly on organic food.
Table 2 Am ount spent m ont hly on organic food and it s share in food ex pendit ures
50% Shar e of sam ple
8% 42%
40% 10% 0%
Am ount spend m ont hly on eco f ood 0 lei < 50 lei 51- 200 lei 201- 50 0 lei > 500 lei Shar e of eco food expendit ur e in
food budget
0% < 5. 7% 5. 8% - 22. 9% 23% - 57. 3 % > 57. 3%
The av erage household food ex pendit ure in t he first sem est er of 2012, in urban areas, in Rom ania w as 671 lei/ m ont h2 ( 149 Euro) . Tak ing int o account t hat Cluj - Napoca has m any superm ark et s and 2 large m alls and t hat t he prices in Cluj - Napoca are higher t han t he count ry av erage, w e est im at e t his figure increased wit h 30% : 872 lei ( 194 Euro). Half of t he respondent s declare t hey spent less t han 50 lei on organic food, w hich w ould be less t han 5. 7% of food ex pendit ures; t he 8% w ho didn’t buy any eco food, according t o quest ion four, are included here. 40% of t he respondent s declare t hey spent bet w een 51-200 lei, w hich w ould be bet w een 5. 8% - 22. 9% of t heir food budget on organic food. 10% of t he respondent s declare t hey spent bet ween 201- 500 lei on organic food, w hich approx im at es 23% - 57. 3% of t heir food budget and nobody declare t o spend m ore t han 500 lei. These figures m ust be underst ood as consum ers’ percept ions on t here ow n ex pendit ures and not as obj ect iv es ex pendit ures. A sim ple com parison bet w een consum ers’ est im at ions and organic food offer in Cluj - Napoca suggest a high gap bet w een t he t w o groups – a m uch low er real lev el of bio food consum pt ion. There is only one specialized shop, a lim it ed shelf space and product range in t he hy perm ark et s and superm ark et s, and m any locat ions such as pharm acies st ores herbal or t radit ional product s t hat sell random ly bio product s ( food, cosm et ics, et c) am ong a m aj orit y of ot her non- bio product s. The over- ev aluat ion m ay be unint ent ional, due t o t he difficult y t o est im at e t he v alue or t o confusions in t he organic concept ( w hich is oft en confused for
2
t radit ional, hom e m ade, sm all farm m ade, sold by sm all farm ers et c) , or int ent ional, deriv ed from t he desire t o im press t he ot hers, t o hide som e fact et c.
The fourt h quest ion t arget ed t he t y pes of organic food acquired: “ What t y pe of organic food did y ou buy during t he last 12 m ont hs: a) none b) biscuit s c) cereals d) fruit s e) v eget ables dairy e) m eat f) oil i) ot her; w hich?. . . ?” ( see Figure 4) .
8.0%
7.0%
16.8%
18.8% 16.8%
18.8%
7.0% 5.0% 2.0% none
biscuits cereals
fruits vegetables dairy meat oil other
Figure 4. Type of organic food purchased.
First places belong t o cereals, fruit s, v eget ables and dairy ( m ent ioned each by less t han 20% of t he sam ple) . Biscuit s, m eat , oil ( m ent ioned each by less t han 10% ) follow, 2% bought ot her product s and 8% any . Cereals are t he m ost widely present bio product in Cluj - Napoca m ark et , but fresh fruit s and v eget ables are v ery hard t o find and only as an ex cept ion are pack ed and labeled wit h eco label. This suggest s t hat , eit her t he respondent s are highly int erest ed in bio fruit s and v eget ables, m onit ored const ant ly t he m ark et and t ook adv ant age of t he rare occasions w hen t hey w ere av ailable or, m ost probably, t hey m ist ak e t he concept of organic for t hose of t radit ional, obt ained in t he count ry side by fam ily or friends, wit h no preserv at iv es or colorings added et c.
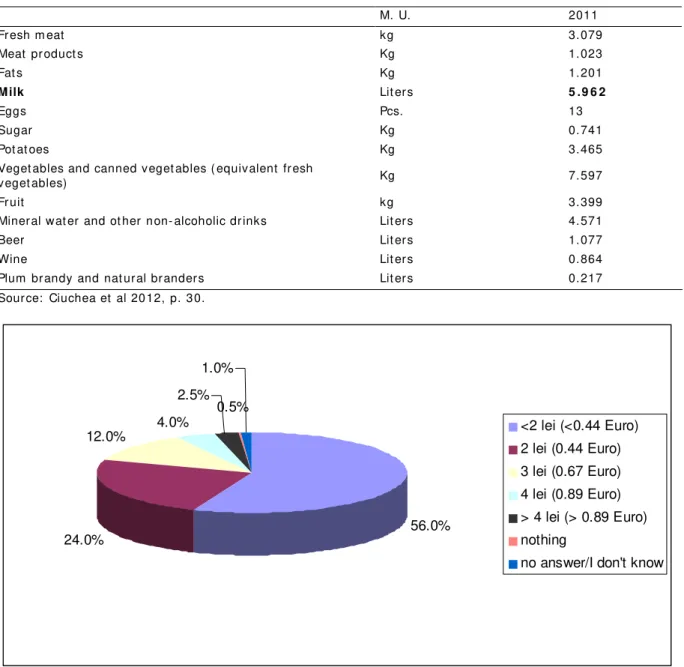
The last quest ion est im at ed t he willingness t o pay m ore for one organic product : m ilk : “ How m uch are y ou willing t o pay m ore for one lit er of organic m ilk com pared t o conv ent ional m ilk : a) < 2 lei ( < 0. 44 Euro) b) 2 lei ( 0. 44 Euro) c) 3 lei ( 0. 67 Euro) d) 4 lei ( 0. 89 Euro) e) > 4 lei ( > 0. 89 Eur o) f ) not hing g) no answ er/ I don't k now?” ( see Figure 5, Table 4) .
This quest ion w as t est ed on a higher sam ple t han t he ot hers – 200 persons ( ov er 18 y ears, urban resident s, from Cluj - Napoca) . We chose t he m ilk because it is largely used by all populat ion cat egories ( children, adult s, aged persons, urban, rural resident s) during all y ear long ( see Table 3) .
Mont hly av erage consum pt ion for t he m ain food product s and bev erages ( per person, in individual households; 2011, est im at ion)
M. U. 2011
Fr esh m eat kg 3. 079
Meat pr oduct s Kg 1. 023
Fat s Kg 1. 201
M ilk Lit er s 5 . 9 6 2
Eggs Pcs. 13
Sugar Kg 0. 741
Pot at oes Kg 3. 465
Veget ables and canned veget ables ( equivalent fr esh
veget ables) Kg 7. 597
Fr uit kg 3. 399
Miner al wat er and ot her n on- alcoholic dr inks Lit er s 4. 571
Beer Lit er s 1. 077
Wine Lit er s 0. 864
Plum br andy and nat ur al br ander s Lit er s 0. 217
Sour ce: Ciuchea et al 20 12, p. 3 0.
56.0% 24.0%
12.0% 4.0%
2.5% 1.0%
0.5%
<2 lei (<0.44 Euro) 2 lei (0.44 Euro) 3 lei (0.67 Euro) 4 lei (0.89 Euro) > 4 lei (> 0.89 Euro) nothing
no answer/I don't know
Figure 5. The am ount cust om ers are willing t o pay m ore for 1 lit er of organic m ilk.
Table 4
Price increase, absolut e and relat iv e, t hat cust om ers are w illing t o pay m ore for 1 lit er of organic m ilk com pared t o superm ark et and m ark et prices
Shar e of sam ple 56% 24% 12% 4% 2. 5% 0. 5% 1%
Absolut e incr ease < 2 lei ( < 0. 44 Eur o)
2 lei ( 0. 44 Eur o)
3 lei ( 0. 67 Eur o)
4 lei ( 0. 89 Eur o)
> 4 lei ( >
0. 89 Eur o) not hing
no answer / I don't know Relat ive incr ease:
pr ice incr ease com par ed t o super m ar ket pr ice
< 44.44 % 44.44 % 66.67% 88.89% > 88. 89 % 0% -
Relat ive incr ease: pr ice incr ease com par ed t o m ar ket pr ice
Con clusion s. The dom inant charact erist ic of organic food in consum ers’ m ind, revealed by t he m aj orit y ( 85% ) of t he respondent s, is “ healt hy ”. This is a posit ive prem ise, on w hich a st rong at t it ude in fav or of organic food consum pt ion can be built and enhanced. More t han half of t he respondent s ( 60% ) st at es t o hav e no or lit t le t rust in sellers claim s about a pr oduct being eco in t he absence of organic label, w hich is a good sit uat ion, but im prov able: m ore consum ers should be educat ed t o k now t he m eaning of eco-cert ificat ion, t he appearance and significance of t he eco- label and t o require it s presence on t he pr oduct as a guarant ee of being an ecological product . Half of t he respondent s declare t hey spent less t han 50 lei ( 0- 11.11 Eur o) on organic food ( equiv alent of less t han 5. 7% of food ex pendit ures; t he 8% w ho didn’t buy any eco food, according t o quest ion four, are included here) and 40% of t he respondent s declare t hey spent bet w een 51- 200 lei ( 11. 12- 44. 44 Euro; equiv alent of 5. 8% - 22. 9% of t heir food budget ) on organic food. These percent ages are high because t he quest ionnaires w ere sent online, self adm inist ered, t he t opic of t he research st im ulat ed m ore t he int erest of organic food consum ers t han of non- consum er s and so, t he sam ple cont ains m ore consum ers t hat t he univ erse populat ion. At t he sam e t im e, t he m oney cust om ers perceiv e t hem selves as spending on organic foods are higher t he t han count ry av erage – 2. 48 Eur o/ pers. in 2011 ( St oenescu 2012, p. 3) . The m ost frequent ly present bio food cat egories in consum ers’ purchases are, according t o consum ers’ opinions, cereals, fruit s, v eget ables and dairy . These result s m ust be read as consum ers’ percept ions on t heir ow n shopping and not as real bio food consum pt ion. Willingness t o pay for 1 lit er of organic m ilk up t o 44% m ore com pared t o superm ark et price and 80% m ore com pared t o sm all farm ers’ price by m ost of respondent s ( 80% ) indicat es high int erest in t his t y pe of product . These findings are encouraging in t he sense of dev eloping posit iv e at t it udes t ow ards and increasing t he consum pt ion of organic food.
Ack n ow le dge m e n t s. Part of t his paper w as elaborat ed w it hin t he Rom anian Nat ional Program m e ( PN I I ) Capacit ies, Module I I I - Bilat eral Cooperat ions Rom ania- Wallonia, Cont ract no. 590/ 13. 09/ 2012” , proj ect t it le: I dent ificat ion of t he opport unit ies for prom ot ion and dev elopm ent of organic agricult ure in Wallonia and Nort h- West of Rom ania for t he sust ainable dev elopm ent of rural space ( “ La présent e publicat ion a ét é rendu possible grâce à l’Accord qui lie Wallonie- Brux elles et la Roum anie” ) .
Re fe r en ce s
Barbir J. , Prat s Ferret M., 2011 Assessm ent of t he agricult ural and dom est ic w at er usage by t he w om en of N’Ham bit a village, Sofala prov ince, Mozam bique. St udia Univ ersit at is Vasile Goldis Seria St iint ele Viet ii 21( 2) : 409- 416.
Boccalet t i S., 2009 Organic food consum pt ion: result s and policy im plicat ions. Av ailable at : ht t p: / / w w w . oecd. org/ env / consum pt ioninnov at ionandt heenv ironm ent / 43039314. pdf [ ret riev ed on January 2013] .
Ciuchea A., Badea D., Pisică S., et al, 2012 Rom ania in Figures 2012, The Nat ional I nst it ut e of St at ist ics, Voineagu V. (coord. of publication), Stănică C. N. et al ( cords. of edit ion) , Badea D. ( ed. ) , Vaida- Munt ean G. et al ( coords. ) ht t p: / / w w w .insse. ro/ cm s/ files/ publicat ii/ Rom ania% 20in% 20figures_2012. pdf
[ ret riev ed on January 2013] .
Daily Business – Resursa online de afaceri: ht t p: / / cursv alut ar. daily business. ro/ curs-v alut ar- 1- august - 2011 [ ret riecurs-v ed on January 2013] .
Eiselen R. J., Uy s T. , Quest ionnaire Design. Av ailable online at : ht t p: / / w w w . uj . ac. za/ EN/ Research/ St at k on/ Docum ent s/ St at k on% 20Quest ionaire% 2 0Design. pdf adapt ed from Eiselen R. , Uy s T., Pot giet er N. , 2005. Analy sing surv ey dat a using SPSS13: A w ork book . Univ ersit y of Johannesburg. [ ret riev ed on January 2013] .
organic food consum ers? A com pilat ion and rev iew of w hy people purchase organic food. Journal of Consum er Behav iour 6: 1–17. doi: 10. 1002/ cb. 210.
Kow ol A. , The t heory of cognit iv e dissonance. Av ailable online at : ht t p: / / adam k ow ol.info/ w ork s/ Fest inger. pdf [ ret riev ed on January 2013]
Neagu O. , 2012 Com m unicat ion in t he ecological m ark et ing. St udia Univ ersit at is Vasile Goldis Seria St iint ele Viet ii 22( 4) : 587- 595.
Ogunniy i L. T. , Sanusi W. A. , Ezekiel A. A. , 2011 Det erm inant s of rural household w illingness t o pay for safe w at er in Kw ara St at e, Nigeria. AACL Bioflux 4( 5) : 660-669.
Pele G., Ardelean A., Turcus V. , 2008 The ecological foot print : a t ool t o be used in sust ainable dev elopm ent decisionm aking process at regional scale in Rom ania. St udia Universit at is Vasile Goldis Seria St iint ele Viet ii 18: 265- 267.
Pet rescu D. C. , 2008 Env ironm ent orient ed behav ior. A case st udy on cust om ers of a w at er com pany . AACL Bioflux 1( 1) : 85- 98.
Pet rescu D. C., 2013 Consum ers’ percept ions on urban w at er services and connect ion t o sust ainable behavior. AACL Bioflux 6( 2) : 105- 110.
Pet rescu D. C. , Pet rescu- Mag R. M., Surd V. , 2010 Rom ania’s Agricult ure - Trends and Challenges. AAB Bioflux 2( 2) : 151- 174.
Pet rescu- Mag R. M. , Pet rescu D. C., 2010 Organic agricult ure as com ponent of sust ainable dev elopm ent . Rom ania’s case. AAB Bioflux 2( 2) : 121- 132.
St oenescu I . , 2012 Organic Mark et Ov erview – Rom ania, GAI N Report Num ber: RO1225. [ ret riev ed on January 2013] Av ailable online at : ht t p: / / gain. fas. usda. gov / Recent % 20GAI N% 20Publicat ions/ Organic% 20Mark et % 20 Ov erv iew % 20- % 20Rom ania_Bucharest _Rom ania_11- 8- 2012. pdf
The Nat ional I nst it ut e of St at ist ics ( a) , 2012 Pr ess release No. 155 of July 5, 2012. Household incom e and ex pendit ure in Quart er I 2012, av ailable at ht t p: / / w w w .insse. ro/ cm s/ files/ st at ist ici/ com unicat e/ abf/ ABF_I _e12. pdf [ ret riev ed on January 2013] .
The Nat ional I nst it ut e of St at ist ics ( b), 2012 Press release No. 239 of Oct ober 5, 2012. Household incom e and ex pendit ure in Quart er I I 2012. The st at ist ical surv ey of t he fam ily budget s ( ABF) . Docum ent av ailable online at : ht t p: / / w w w .insse. ro/ cm s/ files/ st at ist ici/ com unicat e/ abf/ ABF_I I _e12. pdf [ ret riev ed on January 2013] .
Received: 16 Decem ber 2012. Accept ed: 16 Januar y 2 013. Pu blished online: 17 Januar y 201 3. Aut hor s:
Dacinia- Cr ina Pet r escu, Babes- Bolyai Univer sit y, Facult y of Business, St r . Hor ea no. 7, Cluj - Napoca 400 174, Rom ania, Eur opean Union; e- m ail: cr ina. pet r escu@t bs. ubbcluj .r o
I oan Or oian, Univer sit y of Agr icult ur al Sciences and Vet er inar y Medicine Cluj - Napoca, Cluj - Napoca 40 037 2, 3- 5
Calea Mănăştur Street, Cluj, Romania, European Union; e- m ail: ior oian@usam vcluj . r o
Mar ian Pr oor ocu, Univer sit y of Agr icult ur al Sciences and Vet er inar y Medicine Cluj - Napoca, Cluj - Napoca 4 003 72, 3-5 Calea Mănăştur Street, Cluj, Romania, European Union.
Tania Mihăiescu, Univer sit y of Agr icult ur al Sciences and Vet er inar y Medicine Cluj - Napoca, Cluj - Napoca 4 003 72, 3-5 Calea Mănăştur Street, Cluj, Romania, European Union.
Laur a Paulet t e, Univer sit y of Agr icult ur al Sciences and Vet er inar y Medicine Cluj - Napoca, Cluj - Napoca 400 372, 3-5 Calea Mănăştur Street, Cluj, Romania, European Union
Dan Vâr ban, Univer sit y of Agr icult ur al Sciences and Vet er inar y Medicine Cluj - Napoca, Cluj - Napoca 40 037 2, 3- 5
Calea Mănăştur Street, Cluj, Romania, European Union.
This is an open- access ar t icle dist r ibut ed under t he t er m s of t he Cr eat ive Com m ons At t r ibut ion License, which per m it s unr est r ict ed use, dist r ibut ion and r epr oduct ion in any m edium , pr ovided t he or iginal aut hor and sour ce ar e cr edit ed.
How t o cit e t his ar t icle: