Débora Ayeska de Oliveira Santos1 Amanda do Amaral Pires Sobreira¹ Jamylle Correia dos Santos¹ Willma José de Santana2 Caroline Medeiros Machado3
RESUMO
O Pênfigo Vulgar é uma patologia autoimune, sucede em ambos os sexos afetando principalmente pessoas na quarta e na sexta década de vida. Manifesta-se pela produção de anticorpos contra as desmogleínas, acometendo pele e mucosa. O objetivo deste estudo foi verificar o resultado da intervenção dietoterápica no tratamento do Pênfigo Vulgar (PV), sendo este um estudo de caso do tipo descritivo, exploratório, de abordagem qualitativa, na cidade de Juazeiro do Norte. Foi realizado com uma mulher, adulta, diagnosticada com PV onde foi realizado duas avaliações, uma anterior a intervenção dietoterápica e outra após, afim de analisar seu efeito. A paciente apresentou diminuição de 5,8Kg de peso e 10,5 cm de cintura, influenciando diretamente no seu IMC que passou de 35,13 Kg/m² (obesidade grau III) para 32,97Kg/m² (obesidade grau II), sem perda significativa de massa muscular nesse processo de emagrecimento e diminuição dos sintomas decorrentes do PV. Com a intervenção dietoterápica foi percebido que alimentação tem influência direta, positiva e negativa sobre o Pênfigo Vulgar, como também no tratamento e prevenção de comorbidades associadas. O que faz necessária a presença de profissionais multidisciplinares capacitados para tratar pessoas com PV, em especial a inclusão do nutricionista. Ressalta-se a importância de mais estudos envolvendo a influência da alimentação no tratamento e desenvolvimento do Pênfigo Vulgar.Palavras chaves: Terapia Nutricional. Pênfigo Vulgar. Tratamento.
ABSTRACT
Pemphigus Vulgaris is an autoimmune pathology, which occurs in both sexes, mainly affecting people in the fourth and sixth decades of life. Its manifestation occurs by the production of antibodies against desmogleins, affecting skin and mucosa. The objective of this study was to assess the result of a dietary intervention in the treatment of Pemphigus vulgaris (PV), consisting of a descriptive, exploratory and qualitative study in the city of Juazeiro do Norte, with an adult woman diagnosed with PV. Two evaluations were carried out, one prior to the diet-therapy, and the other, after, for the analysis of its effects. The patient presented a decrease in weight of 5.8 kg and 10.5 cm of waist, directly influencing her BMI, which decreased from 35.13 kg/m² obesity grade III to 32.97 kg/m² obesity grade II, without significant loss of muscle mass in the weight loss process and decreased symptoms from PV. The case study with dietary intervention allowed perceiving that food has a direct influence, positive and negative, on Pemphigus vulgaris, as well as there is no treatment and prevention of associated comorbidities. The presence of capable multidisciplinary professionals is necessary to treat patients with PV, especially the inclusion of the dietician. Further studies involving the influence of diet in the treatment and development of Pemphigus vulgaris are of utmost importance.Key words: Nutrition Therapy. Pemphigus. Treatment.
1 Discente da Faculdade de Juazeiro do Norte, Juazeiro do Norte, Ceará, Brasil. Contato correspondente: deboraayeska@gmail.com 2 Docente da Faculdade de Juazeiro do Norte, Juazeiro do Norte, Ceará, Brasil e Dra. em Ciências Biológicas pela UFPE.
RELATO DE CASO
INTERVENÇÃO DIETOTERÁPICA NO TRATAMENTO
DE PÊNFIGO VULGAR: RELATO DE CASO
DIETOTERAPIC INTERVENTION IN PEMPHIGUS
VULGARIS TREATMENT: CASE REPORT
INTRODUÇÃO
Pemphigus vulgaris (PV) is an autoimmune disease in which patients produce antibodies against the proteins found mainly in the neck region, and, later, expressed in the mucous membranes and the skin. The mild and moderate initial manifestations occur in the entire length of the buccal mucosa, especially the jugal mucosa and palate. Then, there is the appearance of bubbles (these may have serous, purulent or bloody content) or vesicles that rupture and cause pain, loss of liquids, resulting in an electrolyte imbalance, forming ulcers and irregular edges, and can also present desquamated gingivitis.1
The aggressions caused by the pathology have a direct relationship with the patient's nutritional state in a negative way. Advanced oral lesions interfere in the feeding since it causes pain and burning; the same can also affect the conjunctive, nose, pharynx, larynx, esophagus, labial, vaginal, urethral, cervical and anal mucosas.2
Many dermatological diseases are chronic and have no definitive cure; however, dietary reformulation, through supplementation and exclusion, is an extremely popular treatment modality for patients with dermatologic conditions. The nutrition thus presents benefits and damages according to specific dietary interventions adopted by the individual.3
Nutritional therapy is relevant in cases of malnutrition when the oral route is the most affected by PV, or therapy of corticosteroids is used, which, in long term, may trigger osteoporosis, recommending supplementation of vitamin D and calcium.4
Therapy with corticosteroids associated with the use of other medications seeks to promote health by treating the pathology and the problems arising from other drugs used. This medicine may cause diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, changes in mood and ulceration in the gastrointestinal tract, among others.5
The increasing number of cases of Pemphigus Vulgaris, and in view of the importance of diet therapy of many diseases, including autoimmune diseases, shows the importance of nutrition therapy in patients with PV, adjusting their diet not only to the specific pathology, but to symptoms they may develop due to medications used for their therapy.
METHODOLOGY
This is a descriptive-type, exploratory case study, with qualitative approach, which was submitted to the Research Ethics Committee of the College of Juazeiro do Norte (FJN), carried out by means of approval as record of opinion 2.244.739.
The research occurred in the city of Juazeiro do Norte, Ceará, where, firstly, there was the exposure of the research and, after agreeing to participate, the signing of the Informed Consent Form (ICF) and the Post-Informed Consent Form was collected.
Then, initial data collection occurred through a semi-structured questionnaire with personal data, food frequency, analysis of exams, habits and anthropometric assessment (height, weight, body mass index (BMI), arm circumference (AC), waist circumference (WC) and hip circumference (HC)), with assessment of results. The anthropometric assessments were classified according to WHO and Duarte.6,7
Based on the patient’s information and its interpretation, there was a nutritional intervention with the elaboration of a food plan for positive developments in the condition of bearer of PV and her nutritional needs.
After 45 days of nutritional intervention, there was the reassessment, with a new evaluation of her anthropometric measurements, as well as other notorious physical aspects, evaluation of the proposed diet, analysis of difficulties or complaints reported, showing an improvement of symptoms of Pemphigus Vulgaris and comparison of the available data of laboratory examinations before and after implementing the diet.
DESCRIPTION OF THE CASE AND RESULTS
The subject of the study is a 29-year-old woman, of initials A.P.A., whose symptoms began in December 2014, and the Pemphigus Vulgaris diagnosis occurred in May 2015. Since January 2015, she had been already using corticosteroids without even having the diagnosis of the disease; after confirming the pathology, she started the treatment with the use of specific medications.
The established diet offered 2094 kcal/day (24.63 kcal/kg), 25% of proteins (1.5 g of protein/kg of adjusted weight), 45% carbohydrates, and 30% of lipids, in order to reduce weight, anthropometric measures, risk of morbidities associated to overweight, in addition to treating the disease and the effects caused by the medication. She also received instructions on increasing antioxidant food as fruits, emphasizing the exclusion of foods such as: garlic, onions, cherries, blackberries, black pepper, red wine, tea, coffee, because they have a direct influence on the development of the disease.8
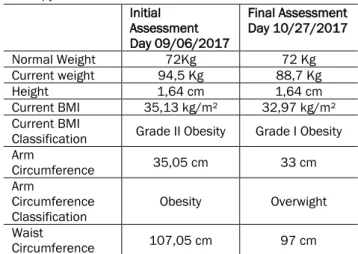
In the first assessment, the patient presented weight (94,5Kg decreasing to 88.7 (BMI for overweight) at reassessment; height (1.64 m), with Body Mass Index (BMI) indicating a grade II obesity (BMI=35.13 kg/m²) initially, high WC (107.5cm) and 97 cm after, HP (122 cm) going to 116.5, AC indicating obesity (35.05 cm), subsequently 33cm (overweight) and waist-hip ratio (WHR) (0.88 cm), decreasing to 0.83, indicating, in both assessments, high risk for cardiovascular diseases (Table 01).
Table 01: Data of weight and anthropometric assessment of the patient in both evaluations, before and after the diet therapy. Initial Assessment Day 09/06/2017 Final Assessment Day 10/27/2017 Normal Weight 72Kg 72 Kg Current weight 94,5 Kg 88,7 Kg Height 1,64 cm 1,64 cm Current BMI 35,13 kg/m² 32,97 kg/m² Current BMI
Classification Grade II Obesity Grade I Obesity Arm
Circumference 35,05 cm 33 cm
Arm
Circumference
Classification Obesity Overwight
Waist
Hip
Circumference 122 cm 116,5 cm
WCR 0,88 cm 0,83 cm
WCR Classification
Very high risk for cardiovascular
diseases
Very high risk for cardiovascular
diseases
In the evaluation of the InBody Bioimpedance, her results improved, with values on the body composition with weight reduction preserving the skeletal muscle mass and reducing fat mass (Graph 01).
In the biochemical data before and after the follow-up to the food plan, the majority was within the normal range, with a slight increase in the hematocrit, which was below recommended levels, but evolved to a minimum acceptable level. The hemoglobin concentration in the initial examination was according to the reference, but, in the second, it was a little below the recommended levels, alerting to a possible anemia, the value of red cell distribution width (RDW) was above the acceptable, thus indicating anisocytosis. The typical lymphocytes presented an increase in the second moment, indicating an increase in defense of the body against something, such as infection. The levels of total cholesterol reduced 24 mg/dl, outside the limit and turning to the desirable level, HDL cholesterol decreased, however, remained in the desirable, vitamin D reduced, but remained within the normal range (Table 2).
In the assessments in relation to gastrointestinal symptoms, the patient presented no allergies or food intolerances, denied any alteration and reported feeling nausea due to the high daily amount of medicines. She had no difficulty chewing, however reported discomfort caused by lesions in the oral cavity resulting from her pathology.
The patient used contraceptive Yasmin, omeprazole, azathioprine, prednisone, a complex of vitamin D and calcium (2 times a day, after lunch and dinner). The medications used remained the same, but, in the period of implementation of the
food plan, there was the simultaneous weaning of a drug, prednisone, where the patient had an evolution reaching the lowest dose, which went from 20mg to 15mg, and then to 10 mg and subsequently the 7,5Mg where there was a rebound effect that was characterized by the appearance of lesions of Pemphigus vulgaris in various sites.
DISCUSSÃO
By analyzing her food routine, the research subject had relevant changes in her habits, such as greater consumption of antioxidants, which was very important, since she demonstrated the need to improve the level of antioxidants.8 A study showed that 43 patients newly diagnosed with PV presented activities of antioxidant enzymes significantly higher and lower total antioxidant capacity.
In this study, the patient underwent restrictions in the diet of foods (garlic, onions, cherries, blackberries, black pepper, red wine, tea, coffee) beneficial in the PV therapy according to Ruocco; however, this article showed no improvement of symptoms.9 In the case studied by Czerninsky, citrus fruits and tomatoes, hard, spicy foods and alcohol were avoided.10
Graph 01: InBody Exam
Weight - Kg
Skeletal Muscle Mass
-Kg
Body Fat Mass - Kg Fat Percentage % BMI - Kg/m² Waist-Hip Ratio Level of Viceral Fat 08.01.2017 94,6 27,9 44,4 47 35,2 1,03 23 11.01.2017 89,3 27,7 39,3 44 33,2 1,01 20 0 20 40 60 80 100
InBody Exam
08.01.2017 11.01.2017Regarding the nutritional status, Palheta states that the increased body weight is a risk factor for diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, dyslipidemia, among other comorbidities.11 Moraes corroborates by stating that obesity is classified as a chronic disease, equated by environmental and genetic factors, pro-inflammatory precursors in adipocytes, whose main targets are the cardiovascular system and the metabolic system.12 Thus, the healthy weight loss seen in the patient of this study improves the prevention of these diseases, since she is likely to develop it due to the chronic use of corticosteroids. Another important point was the evolution of the obesity range from grade II obesity to grade I obesity.
Analyzing the patient’s laboratory exams, in the beginning, the estimated average glucose and total cholesterol were elevated, which may be due to her treatment and excess weight. Risso, in a case report, also noted the presence of diabetes in a 59-year-old woman, who, even after the PV treatment, remained with this pathology.13
The laboratory exams also showed a slight decrease in the value of vitamin D, remaining in the normal classification. Sousa states that vitamin D acts in the innate and acquired
immune system; autoimmune diseases relate to the presence of a condition of hypovitaminosis.14 The same act in the activation, regulation and differentiation of cells such as lymphocytes, also participating in other processes in different cells. Therefore, the increase of typical lymphocytes, in the study patient, may relate to the decreased levels of vitamin D in her body.
Leukopenia results from the presence of antagonistic antibodies of white blood cells, especially lymphocytes. Neutropenia may also be present, which is normally associated with the use of immunosuppressive drugs, although it may also be due to an autoimmune mechanism.15 According to this thesis, it is possible to interpret the increase of typical lymphocytes simultaneously with the low segmented neutrophils, since the patient in this study uses immunosuppressant drug.
CONCLUSION
The study showed that food influences positively and negatively Pemphigus Vulgaris, and the treatment and prevention of associated comorbidities. The lack of professionals with specific knowledge about the pathology, Table 2: Laboratory exams performed before and after the patient’s nutritional follow-up.
Initial Assessment Day 08/02/2017 Final Assessment Day 11/01/2017 Reference Value ERITROGRAM
Blood cells 4.07 millions/mm³ 4.09 millions/mm³ 3,90 a 5,30 cel/mm³
Hemoglobin 12,40 g/dL 11,90 gdL 12,00 a 16,00 cel/mm³ Hematocrit 35,70 % 37,00 % 36,00 a 48,00 cel/mm³ M.C.V. 87,90 fL 90,40 Fl 80,00 a 100,00 cel/mm³ M.C.H. 30,60 pg 29,10 pg 26,00 a 34,00 cel/mm³ M.C.H.C. 34,80 g/dL 32,20 g/ dL 31 a 36 cel/mm³ RDW 16,20 % 16,60 % 10,00 a 15,00 cel/mm³ LEUCOGRAM
Leukocyte-Global 10400 cel/mm³ 10300 cel/mm³ 4500 a 11000 cel/mm³
Neutrophils 6354 cel/mm³ 5624 cel/mm³ 1570 a 7700 cel/mm³
Segmented 6354 cel/mm³ 5624 cel/mm³ 1570 a 770000 cel/mm³
Eosinophils 83 cel/mm³ 196 cel/mm³ 90 a 550 cel/mm³
Basophils 52 cel/mm³ 82 cel/mm³ 00 a 330 cel/mm³
Typical Lymphocytes 3307 cel/mm³ 3883 cel/mm³ 900 a 3850 cel/mm³
Monocytes 603 cel/mm³ 515 cel/mm³ 72 a 1100 cel/mm³
THROBOCYTES AMOUNT
Thrombocytes 335 mil/mm ³ 384 mil/mm³ 150 a 450 mil/mm ³
Glycosylated hemoglobin
(HbA1C) 5,5 % 5,4 % Normal: 5,7 %
Glicemia média estimada 111,15 mg/dL 108,28 mg/ dL
TOTAL CHOLESTEROL AND FRACTIONS
Total cholesterol 201,00 mg/ dL 177,00 mgdL Desejável: < 200 mg/ dL
HDL Cholesterol 77,00 mg/ dL 61,00 mg/dL Desejável: > 60 mg/ dL
Triglycerides 98,00 mg/ dL 114,00 mg/dL Normal: < 150 mg/ dL
including dieticians, is notorious. The monitoring of a dietician is necessary to assist in the treatment, thus improving the symptoms of the disease. However, it is important to emphasize the importance of further studies involving the influence of foods in the treatment and development of Pemphigus Vulgaris.
REFERENCES
1 - Melo EL. Pênfigo Vulgar com Acometimento de Mucosa Bucal e pele: Relato de Caso. Monografia (Odontologia), 28 p.— Universidade estadual da Paraíba-UEPB. 2015. Acessodo em: 05 de maio de 2017, Disponível em: <
http://dspace.bc.uepb.edu.br/jspui/bitstream/123456789/1
1049/1/PDF%20-%20Elo%C3%ADza%20Leonardo%20de%20Melo.pdf> 2 - Cunha PR, Barraviera SRCS. Dermatoses bolhosas auto-imunes. In: Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia. [S.l.: s.n.], 2009. p. 111 – 122. DOI: Acesso em: 05 de maio de 2017, Disponível em:
http://dspace.bc.uepb.edu.br/jspui/bitstream/123456789/1
1049/1/PDF%20-%20Elo%C3%ADza%20Leonardo%20de%20Melo.pdf 3 - Lakdawala N. The role of nutrition in dermatologic diseases: facts and controversies. Clinics in Dermatology, 2013;31(6):667 – 700. DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.05.004 4 - Hertl M, Jedlickova H, Karpati S, Marinovic B, Uzun S, Yayli S, et al. Pemphigus. S2 Guideline for diagnosis and treatment – guided by the European Dermatology Forum (EDF) in cooperation with the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV). European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 2014;10(1111):406 – 414. DOI:
10.1111/jdv.12772. Epub 2014 Oct 22.
5 - Ferreira VYN. et al. Eficácia do uso de corticosteroide sistêmico no tratamento do pênfigo vulgar oral. Arquivos de Ciências da Saúde, 2016;23(3):10 – 13. DOI:
10.17696/2318-3691.23.3.2016.215
6 - World Health Organization. Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a World Health Organization Consultation. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2000. p. 256. WHO Obesity Technical Report Series, n. 284. 7 - Duarte ACG. Avaliação Nutricional: Aspectos Clínicos. 1. Ed. São Paulo. Atheneu, 2007.
8 - Javanbakht MH. Avaliação da atividade enzimática antioxidante e capacidade antioxidante em pacientes com pênfigo vulgaris recentemente diagnosticado. Dermatologia clínica e experimental.2015;3(40):313-317. DOI:
10.1111/ced.12489.
9 - Ruocco V, Ruocco E, Lo SA, Brunetti G, Guerrera LP, Wolf R. et al. Pemphigus: Etiology, pathogenesis, and inducing or triggering factors: Facts and controversies. Clinics in Dermatology, 2013;31:374 – 381. DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.01.004 10 - Czerninski R, Zadik Y, Kartin-Gabbay T, Zini A, Touger-Decker R. Czerninski R. Dietary alterations in patients with oral vesiculoulcerative diseases. Oral surgery, oral medicine, oral pathology and oral radiology, 2014;117(3):319-323.
11 - Palheta RCA, Costa LV, Brigida ES, Dias JS, Nogueira AC, Figueira MS. Avaliação da perda de peso e comorbidades em pacientes submetidos à cirurgia bariátrica em uma clínica particular em Belém-Pa. Revista Brasileira de Obesidade, Nutrição e Emagrecimento, São Paulo, 2017;11(65):281-289. 12 - Moraes VCS. Identificação do risco de cardiopatia através do estudo combinado de circunferências corporais. Acta Biomedica Brasiliensia. 2016;7(1). DOI:10.18571/acbm.096. 13 - Risso M, Villalpando KN, Pinho MN, Pallotta FR. Pênfigo vulgar: relato de caso clínico. Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia. Porto Alegre, 2011;59(3):515-520.
14 - Sousa SM. A vitamina D e o seu papel na prevenção de doenças. 2016. 57 p. Monografia (Mestrado Integrado em Ciências Farmacêuticas) — Universidade Fernando Pessoa Faculdade de Ciências da Saúde. Acesso em: 05 de maio de 2017, Disponível em:
<https://bdigital.ufp.pt/bitstream/10284/5829/1/PPG_297 06.pdf>
15 - Hilbig C, Martinez JV, Martinez JE. Necrose de medula óssea em paciente portadora de lúpus eritematoso sistêmico. Revista da Faculdade de Ciências Médicas de Sorocaba, 2016;4(18):187-192. DOI: