J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eISSN- 2278-4802, pISSN- 2278-4748/ Vol. 3/ Issue 27/July 07, 2014 Page 7459
PREDICTIVE VALUE OF CREATINE KINASE AND LACTATE
DEHYDROGENASE IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF PERINATAL ASPHYXIA
Shylaja C. G1, Murali B. H2HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
Shylaja C. G, Murali B. H. Predictive Value of Creatine Kinase and Lactate Dehydrogenase in the Diagnosis of Perinatal Asphyxia. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences 2014; Vol. 3, Issue 27, July 07;
Page: 7459-7464, DOI: 10.14260/jemds/2014/2919
ABSTRACT: INTRODUCTION: Birth asphyxia contributes significantly to neonatal morbidity and mortality. Without perinatal details it becomes difficult to establish a diagnosis of perinatal asphyxia based on purely clinical grounds. This study was conducted in neonates with non-specific signs to ascertain whether common enzyme assays would help in distinguishing asphyxiated neonates from non-asphyxiated neonates. OBJECTIVES: To evaluate the diagnostic utility of a set of laboratory tests in the retrospective diagnosis of birth asphyxia. To study the association of laboratory markers of cardiac injury with the severity of perinatal asphyxia. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A study was conducted on 50 asphyxiated neonates comprising the cases and 50 non-asphyxiated neonates comprising the controls, meeting the inclusion and exclusion criteria born in Kempegowda institute of medical sciences, Bangalore from January 2010 to June 2011. In all subjects, serum CK-MB at 8 hours and 24 hours and serum LDH were performed. A serum CK-MB value >92.6 U/L at 8 hours, >60 U/L at 24 hours and LDH value >580 U/L at 72 hours was taken as the cut-off level. The sensitivity, specificity, Positive predictive value (PPV), Negative predictive value (NPV) was calculated for both CK-MB and LDH. RESULTS: The cut-off CK-MB value of >92.6 U/L at 8 hours has 82% sensitivity with a specificity of 80%. CK-MB has a positive predictive value of 80.34% with a negative predictive value of 81.63%.The cut-off CK-MB value of >60 U/L at 24 hours has 58.33% sensitivity with a specificity of 95.83%. CK-MB has a positive predictive value of 93.33% with a negative predictive value of 69.70%.The cut-off LDH value of >580 U/L at 72 hours has 100% sensitivity with a specificity of 88%. LDH has a positive predictive value of 89.29% with a negative predictive value of 100%.
CONCLUSION: Estimation of CK-MB at 8 hours and 24 hours of life and LDH at 72 hours of life can help distinguish an asphyxiated from a non-asphyxiated neonate in correlation with history and clinical features in the neonate. The diagnostic performance of LDH is better than CK-MB.
KEYWORDS: Perinatal asphyxia, Creatine kinase muscle-brain fraction (CK-MB), Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), neonate.
INTRODUCTION: Perinatal asphyxia is an insult to fetus or newborn which may be due to lack of
oxygen and/or lack of perfusion to vital organs of the body. Birth asphyxia is defined by WHO as the failure to initiate and sustain breathing at birth .1It is a common neonatal problem and contributes
significantly to neonatal morbidity and mortality. The incidence of perinatal asphyxia globally has been reported as 1% to 1.5%. In India, however the incidence is more compared to the world and was reported to be 9% by a study conducted by NNPD in the year 2000.2
Mortality attributable to perinatal asphyxia in India is between 250, 000 to 350, 000 each year. Death due to perinatal asphyxia usually occurs within the first three days of life. In addition antepartum and intrapartum asphyxia contributes to 3, 00, 000 to 4, 00, 000 stillbirths.3In India only
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eISSN- 2278-4802, pISSN- 2278-4748/ Vol. 3/ Issue 27/July 07, 2014 Page 7460 personnel attended only 42% of total births.4Perinatal asphyxia may affect all major body systems
and many of these complications are potentially fatal. In perinatal asphyxia, renal, neurologic, cardiac and lung dysfunction occurs in 50%, 28%, 25% and 23% cases respectively.5
Perinatal asphyxia presents as multiorgan injury and the asphyxiated babies could manifest with seizures, renal failure, encephalopathy, respiratory distress, feeding intolerance and cyanosis. These signs and symptoms could also manifest as single system disorder or occur in combination. However, establishment of correct diagnosis is important for immediate management and long term prognosis. The study was aimed to evaluate the diagnostic utility of a set of laboratory tests in the retrospective diagnosis of birth asphyxia.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The study was a prospective study conducted on 50 asphyxiated cases and 50 non-asphyxiated controls admitted in neonatal intensive care unit at Kempegowda Institute of medical sciences hospital from January 2010 to June 2011. Fifty cases were studied with documented birth asphyxia.
The case group included 50 neonates who were delivered at ≥ weeks of gestation, birth
weight of ≥ 5 grams and their delivery attended by a pediatrician who made an accurate
assessment of the presence of asphyxia.
The control group included 5 sick neonates who were delivered at ≥ weeks of gestation, birth weight of ≥ 5 grams and their delivery attended by a pediatrician, without birth asphyxia. Neonates who became symptomatic within 6 hours of birth with one or more of the following non-specific signs of sickness- tachypnea, chest retraction, grunting, lethargy, poor feeding, hypotonia, irritability, central cyanosis, etc. without perinatal asphyxia were among the controls.
Neonates with clinically evident major congenital malformations, preterm babies less than 33 weeks (birth weight less than 1250 grams), neonates born to mothers who had received tramadol, pethidine, magnesium sulphate within 4 hours prior to delivery were excluded from the study. Neonatal details including gestational age, birth weight and Apgar score (1, 5 and 10 minutes) were collected.
Both cases and controls were tested for Serum CK-MB at 8 hours and 24 hours, Serum LDH at 72 hours was tested as well.
Clotted blood was collected at 8 hours and 24 hours and Serum CK-MB was analyzed by immunoassay technique. A value of more than 92.6 U/L at 8 hours and 60 U/L at24 hours were taken as high.6
Clotted blood was analyzed for Serum LDH by immunoassay tests. The normal reference value of LDH in neonates and infants is 170-580 U/L.A value above 580 U/L was taken as high.7
The baseline characteristics, clinical signs and results of investigations were described by descriptive statistics. Sensitivity, specificity and predictive values of the tests were calculated. ROC curves were generated for the laboratory tests. Areas under the curve were compared to determine the most appropriate laboratory test.8
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eISSN- 2278-4802, pISSN- 2278-4748/ Vol. 3/ Issue 27/July 07, 2014 Page 7461 Among the 50 neonates in case group, 20(40%) neonates weighed less than 2.5 kgs, 24(48%) weighed between 2.5-3.0 kgs and 6(12%) weighed between 3-3.5 kgs. Among the control group of 50 neonates, 29(58%) neonates weighed 2.5 kgs, 15(30%) weighed between 2.5-3.0 kgs and 6(12%) weighed between 3-3.5 kgs. Birth weight distribution is statistically similar with P=0.151.
All the neonates in the case group had birth asphyxia and all of them required some form of active resuscitation. Out of the 50 cases, 38 cases required bag and mask ventilation, 24 cases required bag and tube ventilation and 4 required chest compression.
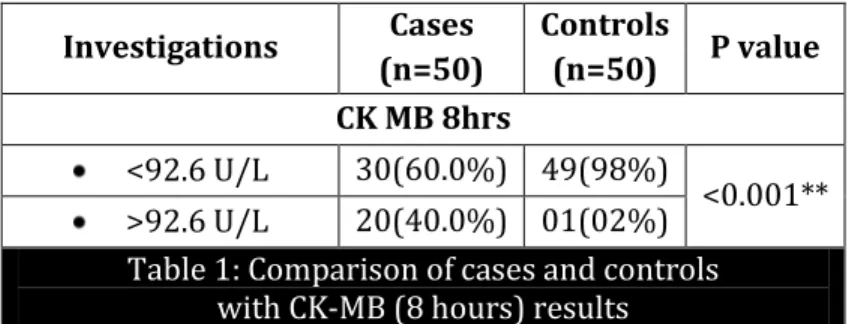
Investigations Cases (n=50)
Controls
(n=50) P value CK MB 8hrs
<92.6 U/L 30(60.0%) 49(98%)
<0.001** >92.6 U/L 20(40.0%) 01(02%)
Table 1: Comparison of cases and controls with CK-MB (8 hours) results
Among the 50 neonates in the case group, 20(40%) had CK-MB levels (8 hours) more than 92.6 U/L. Among the 50 controls, 1(2%) had CK-MB levels (8 hours) more than 92.6 U/L. The number of neonates with elevated CK-MB levels at 8 hours is significantly more in cases when compared to controls with p value of <0.001.
Investigations Cases (n=50)
Controls
(n=50) P value CK MB 24hrs
<60 U/L 30(60.0%) 48(96%)
<0.001** >60 U/L 20(40.0%) 02(04%)
Table 2: Comparison of cases and controls with CK-MB (24 hours) results
Among the 50 neonates in the case group, 20(40%) had CK-MB levels (24 hours) more than60 U/L. Among the 50 controls, 2(4%) had CK-MB levels (24 hours) more than 60 U/L. The number of neonates with elevated CK-MB levels at 24 hours is significantly more in cases when compared to controls with p value of <0.001.
Investigations Cases (n=50)
Controls
(n=50) P value LDH
<580U/L 3(6.0%) 45(90%)
<0.001** >580U/L 47(94.0%) 05(10%)
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eISSN- 2278-4802, pISSN- 2278-4748/ Vol. 3/ Issue 27/July 07, 2014 Page 7462 Among the 50 neonates in the case group, 47(94%) had LDH levels more than 580 U/L. Among the 50 controls, 5(10%) had LDH levels more than 580 U/L. The number of neonates with elevated LDH levels is significantly more in cases when compared to controls with P value of <0.001.
Investigations Cases(n=50) Controls(n=50) p value
CK MB 8hrs 138.90±198.94 41.97±21.05 <0.001 CK MB 24hrs 74.95±90.28 26.27±10.03 <0.001 LDH 851.98±345.90 272.38±222.16 <0.001 Table 4: Mean, standard deviation and p values of various investigations
Sensitivity Specificity PPV NPV
CKMB-8 hrs. U/L 82.00 80.00 80.39 81.63 CKMB-24 hrs. U/L 58.33 95.83 93.33 69.70
LDH U/L 100.00 88.00 89.29 100.00
Table 5: Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of some of the laboratory investigations
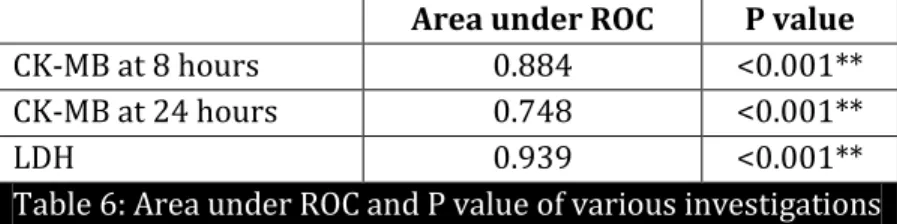
Area under ROC P value
CK-MB at 8 hours 0.884 <0.001** CK-MB at 24 hours 0.748 <0.001**
LDH 0.939 <0.001**
Table 6: Area under ROC and P value of various investigations
We generated ROC (Receiver operator characteristics) curves for CK-MB at 8hours, CK-MB at 24hours and LDH at 72 hours. The LDH had the highest ability to discriminate between cases and controls. The area under the ROC curve was highest for LDH (0.939), followed by CK-MB at 8 hours (0.884) and CK-MB at 24 hours (0.748). ROC of CK-MB at 8 hours was better than 24 hours.
DISCUSSION: Present study was done to ascertain whether CK-MB and LDH can distinguish an asphyxiated from a non-asphyxiated term neonate. These tests are routinely available in most centres and hence a comparative study was done to establish the usefulness of these enzymes in diagnosis of perinatal asphyxia patients.
In the present study, the number of neonates with CK-MB levels >92.6 U/L is significantly more in cases when compared to controls. 40% of the cases in the present study had CK-MB levels >92.6 U/L. This is comparable to Reddy S, et al9 in which 36% of cases had CK-MB levels >92.6 U/L.
In the present study the number of neonates with CK-MB levels at 24 hours was >60 U/L is significantly more in cases when compared to controls. 40% of the cases in the present study had CK-MB levels >60 U/L. This is exactly the same as that of Reddy S et al in which 36% of cases had CK-CK-MB levels >60 U/L.
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eISSN- 2278-4802, pISSN- 2278-4748/ Vol. 3/ Issue 27/July 07, 2014 Page 7463 value and negative predictive value in our study were almost identical with that of their counterparts in the study conducted by Reddy S, et al.
In our study 94% of the cases had LDH levels >580 U/L. This is similar to the study conducted by Karlsson M et al10in which 100% of cases had LDH levels >580U/L. In both the studies, the
number of neonates with LDH levels >580 U/L is significantly more in cases when compared to controls.
In the present study, the sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV of LDH at 72 hours were 100%, 88%, 89.29% and 100%. The Specificity, sensitivity, NPV and PPV are comparable to Reddy S et al and Karlsson M et al.
CONCLUSION: The cut-off CK-MB value of >92.6 U/L at 8 hours has 82% sensitivity with a specificity of 80%. CK-MB has a positive predictive value of 80.39% with a negative predictive value of 81.63% in diagnosing birth asphyxia. The cut-off CK-MB value of >60 U/L at 24 hours has 58.33% sensitivity with a specificity of 95.83%. CK-MB has a positive predictive value of 93.33% with a negative predictive value of 69.70% in diagnosing birth asphyxia.
The cut-off LDH value of >580 U/L at 72 hours has 100% sensitivity with a specificity of 88%. LDH has a positive predictive value of 89.29% with a negative predictive value of 100% in diagnosing birth asphyxia. LDH is having more diagnostic value than CK-MB with more Area under ROC (Receiving operating Characteristic) value when compared to CK-MB at 8 hours and 24 hours (0.939 vs. 0.884 vs. 0.748), but both are excellent tests to differentiate asphyxiated and non-asphyxiated term neonates. CK-MB at 8 hours was better than 24 hours.
The results of the present study could be of utility to pediatricians in referral hospitals, who receive sick neonates, whose birth details are not well recorded.CK-MB and LDH could be used to diagnose asphyxia retrospectively in correlation with history and clinical features in the neonate.
BIBLIOGRAPHY:
1. Agarwal R, Jain A, Deorari AK, Paul VK. Post-resuscitation management of asphyxiated neonates. Indian Journal of Pediatrics February, 2008; 75:175-180.
2. Addock LM, Papile L. Perinatal asphyxia. Chapter no 27C.In: Cloherty JP, Eichenwald EC, Stark AR, editors. Manual of neonatal care. 6th edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, a WoltersKluwar business; 2008: p. 518-528.
3. NNPD network. National Neonatal Perinatal Database–report for the year 2002-2003. NNF NNPD network. New Delhi: 2005.
4. Maternal and reproductive health. In: National family health survey-2, India. International institute of population sciences (Mumbai).1998-99; 13-14.
5. Perlman JM, Tack ED, Martin T, Shackelford G, Amon E. Acute systemic organ injury in term infants after asphyxia. Am J Dis Child 1989; 143: 617-620.
6. Nicholson JF, Perce MA. Reference ranges for laboratory tests and procedures. In: Nelson textbook of pediatrics, 17thedn, Behrman RE, Kliegman RM, Jenson HB. Saunders Co.2004;
2396-427.
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eISSN- 2278-4802, pISSN- 2278-4748/ Vol. 3/ Issue 27/July 07, 2014 Page 7464 9. Sanath Reddy, Sourabh Dutta and Anil Narang. Evaluation of Lactate Dehydrogenase, Creatine
Kinase and Hepatic Enzymes for the Retrospective Diagnosis of Perinatal Asphyxia among Sick Neonates. Indian Pediatrics February 17, 2008; 45: 144-147.
10.Karlsson M, Wiberg-Itzel E, Chakkarapani E, Blennow M, Winbladh B, Thoresen M. Lactate dehydrogenase predicts hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy in new born infants: a preliminary study. Acta Paediatrica August 2010; 99 (8): 1139-1144.
AUTHORS:
1. Shylaja C. G. 2. Murali B. H.
PARTICULARS OF CONTRIBUTORS:
1. Senior Resident, Department of Paediatrics, Kempegowda Institute of Medical Science, Bangalore.
2. Associate Professor, Department of Paediatrics, Kempegowda Institute of Medical Science, Bangalore.
NAME ADDRESS EMAIL ID OF THE CORRESPONDING AUTHOR:
Dr. Shylaja C. G, #31/2, 18th Main,
A. G. S. Layout, Bangalore – 61.
Email: dheemanthap@gmail.com