w w w . r b o . o r g . b r
Original
Article
Functional
evaluation
of
patients
with
injury
of
the
distal
insertion
of
the
biceps
brachii
muscle
treated
surgically
夽
,
夽夽
Alberto
Naoki
Miyazaki,
Marcelo
Fregoneze,
Pedro
Doneux
Santos,
Luciana
Andrade
da
Silva
∗,
Guilherme
do
Val
Sella,
Denis
Cabral
Duarte,
Sergio
Luiz
Checchia
DepartmentofOrthopedicsandTraumatology,SchoolofMedicalSciences,SantaCasadeSãoPaulo,SãoPaulo,SP,Brazil
a
r
t
i
c
l
e
i
n
f
o
Articlehistory:
Received11January2013 Accepted20May2013 Availableonline27March2014
Keywords:
Elbow/surgery Elbow/injuries Treatmentoutcome
a
b
s
t
r
a
c
t
Objective:tofunctionallyevaluatepatientswithinjuryofthedistalinsertionofthebiceps brachiimusclethatwastreatedsurgically.
Methods:betweenApril2002andJune2011,15elbowsof14patientsunderwentsurgical treatmentperformedbytheShoulderandElbowSurgeryGroup,DepartmentofOrthopedics andTraumatology,SchoolofMedicalSciences,SantaCasadeSãoPaulo.Theminimum follow-upwassixmonths,withameanof28months.Thepatients’agesrangedfrom28to 62years,withameanageof40years.Allthepatientsweremaleandthedominantarmwas affectedin64.2%.Theclinicalevaluationontheresultswasconductedusingthecriteria oftheAmericanMedicalAssociation(AMA),asmodifiedbyBruce,withevaluationofthe jointrangeofmotion(flexion–extensionandpronosupination),thepresenceofpainand thepatient’sdegreeofsatisfaction.
Results:fromtheAMAcriteria,asmodifiedbyBruce,weobtained100%satisfactoryresults, ofwhich85.7%wereconsideredtobeexcellentand14.3%good.Weobservedthatwhen distal injuriesofthebicepsbrachiimuscleaffected youngandactivepatients,surgical treatmentwasagoodoption.
©2014SociedadeBrasileiradeOrtopediaeTraumatologia.PublishedbyElsevierEditora Ltda.Allrightsreserved.
Avaliac¸ão
funcional
dos
pacientes
com
lesão
da
inserc¸ão
distal
do
músculo
bíceps
braquial
tratados
cirurgicamente
Palavras-chave:
Cotovelo/cirurgia
r
e
s
u
m
o
Objetivo:avaliar funcionalmenteospacientes comlesão da inserc¸ãodistaldo músculo bícepsbraquialtratadoscirurgicamente.
夽Pleasecitethisarticleas:MiyazakiAN,FregonezeM,SantosPD,SilvaLA,ValSellaG,DuarteDC,ChecchiaSL.Avaliac¸ãofuncionaldos
pacientescomlesãodainserc¸ãodistaldomúsculobícepsbraquialtratadoscirurgicamente.RevBrasOrtop.2014;49:129–133.
夽夽WorkperformedintheShoulderandElbowGroup,DepartmentofOrthopedicsandTraumatology,SchoolofMedicalSciences,Santa
CasadeSãoPaulo,FernandinhoSimonsenWing,SãoPaulo,SP,Brazil.
∗ Correspondingauthor.
E-mail:ombro@ombro.med.br,lucalu@terra.com.br(L.A.daSilva).
2255-4971/$–seefrontmatter©2014SociedadeBrasileiradeOrtopediaeTraumatologia.PublishedbyElsevierEditoraLtda.Allrightsreserved.
Cotovelo/lesões Resultadodetratamento
Métodos: entreabrilde2002ejunhode2011,15cotovelosde14pacientesforam submeti-dosatratamentocirúrgicopeloGrupodeCirurgiadeOmbroeCotovelodoDepartamento de OrtopediaeTraumatologiada Faculdadede CiênciasMédicasdaSanta CasadeSão Paulo.Oseguimentomínimofoideseismeses,commédiade28.Aidadevarioude28 a62anos,commédiade40.Todosospacienteseramdosexomasculinoeomembro dom-inantefoiacometidoem64,2%.Aavaliac¸ãoclínicadosresultadosfoifeitapeloscritérios daAmericanMedicalAssociation(AMA),modificadosporBruce,pelograudeamplitude articular(flexoextensãoepronossupinac¸ão),pelapresenc¸adedorepelograudesatisfac¸ão dopaciente.
Resultados: peloscritériosda AMA,modificadospor Bruce,obtivemos100%de resulta-dossatisfatórios,85,7%consideradosexcelentese14,3%bons.Observamosquequandoas lesõesdistaisdomúsculobícepsbraquiaisacometempacientesjovenseativos,otratamento cirúrgicoéumaboaopc¸ão.
©2014SociedadeBrasileiradeOrtopediaeTraumatologia.PublicadoporElsevier EditoraLtda.Todososdireitosreservados.
Introduction
Traumaticinjuriesofthedistalinsertionofthetendonofthe bicepsbrachii muscle(TBBM)areuncommon1 and an inci-denceof1.24casesper100,000inhabitantshasbeenreported.2 Ifthebicepsbrachiimuscleisconsideredinitsentirety,only 3%ifitsinjuriesaffectthedistalportionand1%theshorthead, whilethegreatmajority(96%)affectthelonghead.3
TearingoftheTBBMisattributedtodegeneration, hypo-vascularization and/or friction on the tendon.4,5 Morrey suggestedthatinflammationofthedeepradialbursacould contributetowardtendondegeneration,6andalsothatbone irregularitiesatthetuberosityoftheradiuscouldcause rub-binginthedistalportionoftheTBBM,therebycontributing towardtearingit.5Thisregionhasahypovascularzoneand azoneoffibrocartilaginoustissuethat,onaverage,islocated 2.14cmfromthedistalregion.7
Smokers present greater predisposition toward tendon avulsion,2alongwithathleteswhousedanabolicsteroids.8,9
Itgenerallyoccursinmenbetweentheirfourthandsixth decades of life.7,10 The commonest injury mechanism is abruptflexionoftheelbowagainstresistance,withthe fore-arminsupination.7Patientsusuallyreportthattherewasan audible sound ofsomethingsnapping and palpable retrac-tion ofthe bicepstendon.1 The initialsymptomsare pain, edema,ecchymosis,changestothereliefofthearm(Fig.1)and diminishedelbowsupinationandflexionstrength.11Ifthere isstillany doubtaboutthe diagnosis,ultrasonography (US) and/ormagneticresonance imaging(MRI)are thepreferred examinations.12
In the literature, several different types ofconservative and/orsurgicaltreatment havebeenreported, and thereis stillmuchcontroversywithregardtowhichtreatmentoption is best.7 Patients who are treated conservatively present strengthandfunctiondeficitsinvariousactivities.7Surgical treatmentbymeansofasingleextendedrouteoradouble route has shown the best results, but complications often occur.3,7,10
Theaimofthepresentstudywastoevaluatetheclinical andfunctionalresultsfrompatientswithtraumaticinjuries ofthedistalinsertionoftheTBBMwho weretreated surgi-cally.
Fig.1–Clinicalimageshowingtearingofthedistaltendon ofthebiceps(arrow).
Sample
and
methods
Between April2002and June2011,the ShoulderandElbow GroupoftheDepartmentofOrthopedicsandTraumatologyof SantaCasadeMisericórdiadeSãoPaulo,Fernandinho Simon-senWing,operatedon15elbowsof14patientswithinjuries to the distalinsertion of the TBBM. The inclusion criteria werethatallthepatientsneededtobeadultswhounderwent surgicaltreatmentforreinsertionoftheTBBMandwhohad beenfollowedupforatleastsixmonthsaftertheoperation. Patients whosefollow-up had been less than this duration wereexcluded.Thus,thereevaluationswereconductedon14 elbowsof13patients(Table1).
Allthepatientsweremale,withameanageof40yearsand arangefrom28to62.Thedominantlimbwasaffectedinnine cases(64.2%)(Table1).Regardingthetraumamechanism,all thepatientsreportedthattheirelbowhadbeenflexedandthat theyhadbeenexertingforceagainstresistance.Theirforearm hadthenbeensubjectedtoabruptextensionasthetrauma mechanism.
Table1–Epidemiologicaldataonpatientswithdistal injuryofthetendonofthebicepsbrachiimuscle.
Initials Age(years) Sex Dominantlimb
1 PTP 50 M +
2 CMA 32 M
3 FE 34 M +
4 ETJ 56 M +
5 CM 33 M
6 CM 34 M +
7 ECIPR 28 M +
8 DN 32 M +
9 ACGS 51 M
10 COCJ 45 M +
11 AOM 39 M
12 GAG 38 M +
13 MVS 34 M +
14 GION 62 M
Source:Hospitalmedicalfiles.
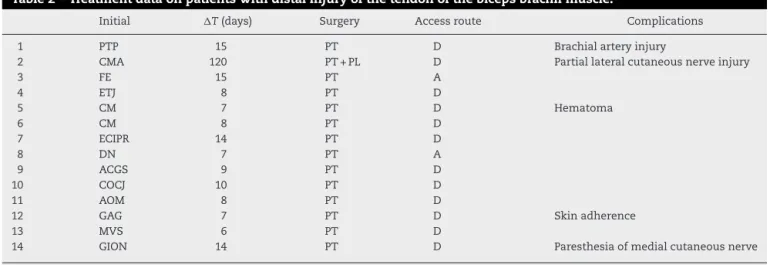
Themeanlengthoftimebetweenthedateofthetrauma andthesurgerywas17days, witharangefrom sixto120. Allthepatientsunderwenttheiroperationsinthehorizontal dorsaldecubitusposition,withtheaffectedlimbsupported onahandaccesstable.Adoubleaccessroutewasusedin12 cases(85.7%)(Fig.3)andanextendedanteriorrouteintwo cases(14.3%)(Table2).
Elbow mobility was measured by means of goniome-try, using the parameters of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS).13 Thelength ofthe postop-erative follow-up ranged from six to 98 months (mean of
Fig.2–MRIoftheelbow(sagittalslice),showingtear (arrow)withretractionoftheinsertionofthetendonofthe bicepsmuscle.
28months).Thepatientswereevaluatedwithregardtothe degreeofjointrangeofmotion(flexion–extensionand prono-supination),presenceofpainanddegreeofsatisfaction.All thepatientswerereassessedsixmonthslaterusingthe crite-riaoftheAmericanMedicalAssociation(AMA),asmodified byBruceetal.14Radiographsproducedatthislate postopera-tivestagewereusedtoevaluatethepresenceofheterotopic ossificationand/orproximalradioulnarsynostosis.
Thepresentstudywasinitiallysubmittedforappraisalby thehospital’sresearchethicscommitteeandwasapproved.
Results
All the patients were satisfied with the treatment. Twelve cases(85.7%)wereconsideredtopresentexcellentresultsand two(14.3%)wereconsideredtobegood,accordingtothe crite-ria ofthe AMA, as modified byBruce et al.14 None of the patientsreportedhavinganypainandallofthemreturned totheirnormaldailyactivities.
Thejointrangeofmotionremainedunchangedin compar-isonwiththatoftheunaffectedlimb,andnoclinicalchanges tomusclestrengthwere observed.Therewasnoclinicalor radiographicevidenceofheterotopicossificationorradioulnar synostosisaftersixmonthsofevolution.
Complications occurred infive cases (35.7%). In case 1, duringthe operation,therewasaniatrogenicinjury tothe brachialartery andaninterventionbythevascularsurgery teambecamenecessary,inwhichanend-to-endrepairwas performedusinganinvertedsaphenousveingraft.Thepatient evolvedwithagoodresult.Incase2,theinjurytothe dis-tal tendonofthebiceps hadoccurred 120daysearlier and itwasnecessarytouseagraftfromtheipsilaterallong pal-martendon.Thispatientpresentedpartialinjuryofthelateral cutaneousnerveoftheforearmandevolvedwithparesthesia onthelateralfaceoftheforearm,whichimprovedoverthe courseofthefollow-up.Incase5,thepatientevolvedwitha largehematomaintheimmediatepostoperativeperiod,with theneedfordrainage,whichdidnotinterferewiththefinal result.Incase12,thepatientevolvedwithasmallskin adher-enceinthesurgicalwound.Incase14,thepatientpresented transitoryparesthesiaofthemedialcutaneousnerveofthe forearm(Table2).
Discussion
ItisknownthatdistalinjuriesoftheTBBMareuncommon.1,2 The average number of such cases seen at our service is 1.6 cases per year, and this is concordant with the literature.1,2,4,7,10,15Thisinjuryisalsoobservedpredominantly in males,who formed100% ofoursample.1,2,4,7,10,15 These injuriesgenerallyoccurbetweenthefourthandsixthdecades oflife.1,2,4,7,10,15Themeanageinourstudywas40years,with arangefrom28to62.
Table2–Treatmentdataonpatientswithdistalinjuryofthetendonofthebicepsbrachiimuscle.
Initial T(days) Surgery Accessroute Complications
1 PTP 15 PT D Brachialarteryinjury
2 CMA 120 PT+PL D Partiallateralcutaneousnerveinjury
3 FE 15 PT A
4 ETJ 8 PT D
5 CM 7 PT D Hematoma
6 CM 8 PT D
7 ECIPR 14 PT D
8 DN 7 PT A
9 ACGS 9 PT D
10 COCJ 10 PT D
11 AOM 8 PT D
12 GAG 7 PT D Skinadherence
13 MVS 6 PT D
14 GION 14 PT D Paresthesiaofmedialcutaneousnerve
Source:Hospitalmedicalfiles.
Legend:D,doubleaccess;A,extendedanterioraccess.
Thebicepsbrachiimusclefunctionsasanimportantflexor oftheelbowandisthemainsupinatoroftheforearm. Sur-gical repair should beindicated mainly in cases ofyoung patients,manualworkersandathletes,especiallywhenthe dominantsideis affected.3,9 In 1985,Morrey et al.16 found through isometric tests on three patients who had been treatedconservativelythat theyhad lost 31% oftheir flex-ionstrengthand40%oftheirsupinationstrength,whereas
sixpatientswhohadbeentreatedsurgicallypresentedlosses of 6% of flexion strength and 19% of supination strength. Oursampledidnotpresentanylossesofflexionand supina-tion strength. However, we used subjective criteria based oninformationfromthepatientsand theevaluationswere performed by means ofmanual measurements, without a dynamometer,whichcanbeconsideredtobeadeficiencyof thisstudy.
AnatomicalrepairofthedistalinsertionoftheTBBMhas nowbecomethepreferredprocedurefortraumaticinjuries, particularlybecausegood resultshavebeenreportedinthe greatmajorityofstudieswithregardtorestorationof supina-tionandflexion,andthiswasalsoourexperience.
Thevarioustechniquesthatweredevelopedovertheyears weredirectedtowardreducingthecomplicationsassociated with repairs. Historically, surgical treatment for the distal insertionoftheTBBMstartedbymeansofasingleextended anteriorincision.However,somecasesofinjurytothe poste-riorinterosseousnervehavebeenreported.17,18Inoursample, we made an extended anterior access route in two cases and did nothave any neurologicalinjuries. Our two cases ofneurologicalinjuries(8.3%)affectedthelateralandmedial cutaneousnervesoftheforearmandoccurredwhenweused adoubleaccess.
ThedoubleaccessroutetechniquewasdescribedbyBoyd andAnderson18in1961.Althoughitpresentsfavorableresults, itevolveswithheterotopicossificationandproximal radioul-narsynostosisascomplicationsinsomecases.In1990,Faila et al.19 reported on four cases ofradioulnarsynostosis, of whichonlytworecoveredmovementaftertheresection.In 1985, Morrey et al.16 modified this technique by dividing thedorsalmusculatureandavoidingsubperiostealdissection ofthe ulnaalong theinterosseousmembranetothe radial tuberosity.Thesemodificationsledtodiminutionoftherates ofheterotopicboneformationandsynostosis.Overthelast fewyears,severaltechniquesandvarious fixationmethods have been described. However, there is still no consensus regardingthebestrouteandthebesttechniquetouseinthese cases.WeusedthedoubleaccesstechniquedescribedbyBoyd andAnderson,asmodifiedbyMorreyetal.,16in12casesand didnotobserveanyproximalradioulnarsynostosisor hetero-topicossificationinoursample.
Duringthe1990s,withthedevelopmentofsutureanchors, the anterior single incision via Henry’s access route was reintroduced.3,10In2000,Bainetal.20publishedatechnique usingEndobuttonforfixationofthetendonofthebicepsatthe tuberosityoftheradiusandshowedfavorableresults.In2009, Fentonetal.1publishedatechniqueusingfixationwith bio-tenodesisscrewsandGregoryetal.15describedfixationusing anchorsunderendoscopicviewing.
In2007,Mazzocaetal.17conductedabiomechanicalstudy in which they compared four techniques for distal biceps repair.Endobuttonshowedbetterresultsthansutureanchors, transosseousstitchesorinterferencescrews.Nonetheless,we chosetousetransosseousstitchesinallofourpatients, with-outlossoffixationinanycase.
Conclusions
Weobservedthatsurgicaltreatmentisagoodoptionfor dis-talinjuriesoftheTBBMwhenyoungandactivepatientsare affected,sincewefoundthat85.7%oftheresultswere excel-lentand14.3%weregood.
Conflicts
of
interest
Theauthorsdeclarenoconflictsofinterest.
r
e
f
e
r
e
n
c
e
s
1.FentonP,QureshiF,AliA,PotterD.Distalbicepstendon rupture:anewrepairtechniquein14patientsusingthe biotenodesisscrew.AmJSportsMed.2009;37(10):2009–15. 2.SafranMR,GrahamSM.Distalbicepstendonruptures:
incidence,demographics,andtheeffectofsmoking.Clin OrthopRelatRes.2002;(404):275–83.
3.LintnerS,FischerT.Repairofthedistalbicepstendonusing sutureanchorsandananteriorapproach.ClinOrthopRelat Res.1996;(322):116–9.
4.PeetersT,Ching-SoonNG,JansenN,SneyersC,DeclercqG, VerstrekenF.Functionaloutcomeafterrepairofdistalbiceps tendonrupturesusingtheendobuttontechnique.JShoulder ElbowSurg.2009;18(2):283–7.
5.Seiler3rdJG,ParkerLM,ChamberlandPD,SherbourneGM, CarpenterWA.Thedistalbicepstendon.Twopotential mechanismsinvolvedinitsrupture:arterialsupplyand mechanicalimpingement.JShoulderElbowSurg. 1995;4(3):149–56.
6.MorreyBF.Theelbowanditsdisorders.2nded.Philadelphia: Saunders;1993.
7.ChillemiC,MarinelliM,DeCupisV.Ruptureofthedistal bicepsbrachiitendon:conservativetreatmentversus anatomicreinsertion–clinicalandradiologicalevaluation after2years.ArchOrthopTraumaSurg.2007;127(8):705–8. 8.VisuriT,LindholmH.Bilateraldistalbicepstendonavulsions
withuseofanabolicsteroids.MedSciSportsExerc. 1994;26(8):941–4.
9.D’AlessandroDF,ShieldsJrCL,TiboneJE,ChandlerRW.Repair ofdistalbicepstendonrupturesinathletes.AmJSportsMed. 1993;21(1):114–9.
10.ChakkourI,LopesEI,GomesMD,FilhoJDL,CostaAC, FernandesMS.Lesãodotendãodistaldomúsculobíceps braquial:tratamentocomousodeâncorasósseas.RevBras Ortop.1998;33(3):195–8.
11.LouisDS,HankinFM,EckenrodeJF,SmithPA,WojtysEM. Distalbicepsbrachiitendonavulsion.Asimplifiedmethodof operativerepair.AmJSportsMed.1986;14(3):234–6.
12.WeissC,MittelmeierM,GruberG.DoweneedMRimagesfor diagnosingtendonrupturesofthedistalbicepsbrachii?The valueofultrasonographicimaging.UltraschallMed. 2000;21(6):284–6.
13.AmericanAcademyofOrthopaedicsSurgeons:JointMotion. Methodofmeasuringandrecording.Chicago:AAOS;1965. 14.BruceHE,HarveyJP,WilsonJrJC.Monteggiafractures.JBone
JointSurgAm.1974;56(8):1563–76.
15.GregoryT,RoureP,FontèsD.Repairofdistalbicepstendon ruptureusingasutureanchor:descriptionofanew endoscopicprocedure.AmJSportsMed.2009;37(3):506–11. 16.MorreyBF,AskewLJ,AnKN,DobynsJH.Ruptureofthedistal
tendonofthebicepsbrachii.Abiomechanicalstudy.JBone JointSurgAm.1985;67(3):418–21.
17.MazzoccaAD,BurtonKJ,RomeoAA,SantangeloS,AdamsDA, ArcieroRA.Biomechanicalevaluationof4techniquesof distalbicepsbrachiitendonrepair.AmJSportsMed. 2007;35(2):252–8.
18.BoydJB,AndersonLD.Amethodforthereinsertionofthe distalbicepsbrachiitendon.JBoneJointSurgAm. 1961;43:1041–113.
19.FaillaJM,AmadioPC,MorreyBF,BeckenbaughRD.Proximal radioulnarsynostosisafterrepairofdistalbicepsbrachii rupturebythetwo-incisiontechnique.Reportoffourcases. ClinOrthopRelatRes.1990;(253):133–6.