Original Article
M ORPHOM ETRIC EVALUATION OF FORAM EN M AGNUM IN DRY
HUM AN SKULLS
Anil Kumar
* 1, M itesh Dave
2, Sanam Anw ar
3.
ABSTRACT
Address for Correspondence: Dr. Anil Kum ar, Depart m ent of Hum an St ruct ure and Neurobiology, Om an M edical College affiliated w it h West Virginia Universit y (USA), Sohar, Sultanate of Om an. E-M ail: anil@om c.edu.om
* 1 Depart m ent of Hum an St ruct ure and Neurobiology, Om an M edical College affiliated w it h West
Virginia Universit y (USA), Sohar, Sultanate of Om an.
2 Depart m ent of Hum an St ruct ure and Neurobiology, Om an M edical College affiliated w it h West
Virginia Universit y (USA), Sohar, Sultanate of Om an.
3
Depart m ent of Public Healt h and Epidemiology, Om an M edical College affiliated w ith West Virginia Universit y (USA), Sohar, Sultanate of Om an.
The foram en m agnum is an im port ant landm ar k in t he post erior part of t he cranial base, w hich is largely for m ed by t he occipit al bone. The dim ensions of t he foram en m agnum are clinically im port ant because of t he vit al st ruct ures passing t hrough it . We st udied t hirt y six dry hum an skulls of know n sex and m easured ant ero-post erior and t ransverse diam et ers w it h t he help of Vernier caliper. Addit ionally, sur face area and Index of for am en m agnum w ere also calculat ed. Oval shape is t he m ain t ype of m orphological variant f ound in t his st udy. The t ransverse diam et er of t he foram en m agnum w as in a range of 25.75-34.25m m in m ales, w hereas it w as bet w een 26-31.75m m in fem ales. The ant eropost erior diam et er w as in a range of 35 t o 39.75m m in m ales w hile it w as 29.5 t o 34.75m m in fem ales. The m ean area of f oram en m agnum in m ales w as 876.88±88.83m m w hereas it w as 776.87±68.51m m in fem ales. In cont r ast t o t he area, t he m ean foram en m agnum index w as higher in fem ales (89.01±6.84m m ) com pared t o m ales (81.75±5.99m m ) and t his difference w as also st at ist ically significant (p<0.01). The prospect ive st udy w ill help surgeon for reference value for det erm ining f easibilit y of t ranscondylar sur gical appr oach, w hich ar e being done in an increasing t rend in recent t im es f or br ain st em lesion.
KEY W ORDS:Foram en M agnum , Skull, M or phom et ry, Sexual dim orphism , Foram en m agnum index.
INTRODUCTION
Int J Anat Res 2015, Vol 3(2):1015-23. ISSN 2321- 4287 DOI: ht t p:/ / dx.doi.org/10.16965/ ijar.2015.154
Access this Article online
Quick Response code Web site:
Received: 31 M ar 2015 Accept ed: 18 Apr 2015 Peer Review : 31 M ar 2015 Published (O): 30 Apr 2015 Revised: None Published (P): 30 June 2015
Int ernat ional Journal of Anat om y and Research ISSN 2321-4287
ww w.ijmhr.org/ ijar.htm
DOI: 10.16965/ ijar.2015.154
A f u n dam ent al k n o w l ed ge o f t h e n o r m al anat om y of t he cranial base, especially t he foram en m agnum and associat ed st ruct ures, is im port ant t o t he clinician for accurat e diagnosis and t reat m ent of various diseases [ 1] . The foram en m agnum is an im port ant landm ark in t he post erior part of t he cranial base, w hich is largely form ed by t he occipit al bone. It lies in
w hich pr oject dow n t o ar t iculat e w it h t he superior art icular facet s on t he lat eral m asses of t he at las [2].
Foram en m agnum dim ensions can be used in t he f iel d o f f o r ensi c i d ent i f icat io n an d ant hropology for determination of t he gender of t he hum an skulls [3, 4, 5]. The region of foram en m agnum is covered and protected by large m ass of soft t issues. This know ledge can be applied in it s m or phom et r ic analysis w hen t her e is involvem ent of ot her part s of t he craniofacial skelet on, as in severe injuries, accident s, fire or explosion [6,7]. The cranial base has been not ed for it s abilit y t o rem ain int act in cases w here t he rest of t he cranium has been com prom ised and researchers have m ade use of t hat fact by analyzing sexually significant dim orphic t rait for t his anat om ic region [8,9]. Because of t he vit al an at o m ic st r u ct u r es p assi n g t h r ou gh t h e f oram en m agnum , it becom es essent ial t o m easure it s dim ensions, as t hese st ruct ures m ight get com pressed in various conditions such as foram en m agnum st enosis, achondroplasia and cerebral herniat ion. These m ay result int o life-threatening respirat ory com plications, lower cranial nerve palsies, and paresis of upper and low er ext rem it ies.
In forensic or archaeological cont ext est im at ion o f sex i s a v er y i m p o r t an t st ep i n t h e ident ificat ion of any hum an skelet al rem ains discovered [10]. Foram en m agnum is an int egral com ponent of st udies on skull in par t icular int erest for ant hropology, anat om y, forensic m edicine, and ot her m edical fields[11]. The diameters and area of t he foram en magnum are, in general, m ore in m ales t han in f em ales. Furt her, foram en m agnum index is a param eter w hich, alon g w it h cr anial index and o t her dim ensions, is ut ilized in craniom et ry t hat helps in m easuring t he skull for m aking com parisons am ong races [ 12]. Also, t her e exist s som e cor relat ion bet w een t he shape of f oram en m agnum and ancest ry of an individual. Thus, v ar i at io n s i n it s sh ap e h ave got cli n i cal , radiological and diagnost ic im port ance [13].
The m orphom etric analysis of foramen m agnum and it s var iat ions is im por t ant not only f or an at o m ist s b u t al so t o t h e an est h et ist , neurosurgeons, ort hopedicians, radiologist s.
M ATERIALS AND M ETHODS
Th ese var i at io ns h av e beco m e signi f i cant because of new er im aging t echniques such as com put ed t om ography and magnet ic resonance im aging in t he field of diagnost ic m edicine. Considering t he above m ent ioned param et ers in relat ion w it h t he foram en m agnum , t he aim of present research st udy w as t o m easure t he lengt h, w idt h, area and index of t he foram en magnum in dry human skulls, and document their relat ions t o t he gender, as w ell as t o analyze t he variat ions in it s shape.
The st udy sam ple included random collect ion of 36 adult hum an dry hum an skulls (19 m ales and 17 fem ales). M orphological invest igat ion of foram en m agnum was carried out in t he Hum an structure and Neurobiology departm ent of Oman M edical College, Sohar, Om an. The skulls t hat w ere dam aged or incom plet e and t hose of children w ere excluded from t he st udy. The sex w as det er m ined by considering t he classic anat o m i cal ch ar act er i st i cs [ 14, 15] . All param eters w ere m easured independently by t w o different observers, w it h a predet erm ined methodology to prevent inter-observer and intra-observer error. M easurem ent s w ere perform ed by means of Vernier calipers accurate t o 0.01m m on Foram en m agnum of dry hum an skulls.
The p ar am et er s m easu r ed i ncl u ded t h e follow ing:
1. Foram en m agnum lengt h (FM L)/ Ant ero-p ost er i o r d i am et er : M axi m um st r ai gh t ant eropost erior diam et er from basion (m edian point on t he ant erior m argin of t he foram en m agnum ) t o opist hion (m edian point on t he post erior m argin of t he foramen m agnum ). [Fig. 1A]
2. Foram en m agnum w idt h (FM W)/ Transverse d iam et er : M axim u m st r ai gh t t r an sv er se diam et er bet w een t w o point s of t he foram en m agnum on m ost lat erally placed m argins. [Fig. 1B]
3. Area of foram en m agnum (FM A): The area of Foramen m agnum w as calculat ed using form ula derived by Radinsky [16].
Radinsky’s Form ula (FM A): 1/4 X X FM L X FM W
W here, (m at hem at ical const ant ) = 22/7, FM L = Foram en m agnum lengt h and FM W = Foramen m agnum width.
4. Foram en m agnum index (FM I): Calculat ed by: For am en m agnum w idt h X 100 / For am en m agnum lengt h.
5. Shape of foram en m agnum – The different shap es o f t h e f o r am en m agnu m w er e m acroscopically not ed and classified as oval, round, tet ragonal, hexagonal and irregular. [Fig. 2]
St at ist ical analysis: The dat a w as collect ed, t abulat ed and st at ist ically analyzed. Dat a w as analyzed using SPSS 17.0 program . Descript ive st at ist ics including range, m ean and st andard deviat ion was calculated for each param eter. Unp ai red ‘ t ’ t est w as used as t h e t est o f signif icance t o t est t he difference in m eans bet w een m ales and fem ales at an alpha of 0.05.
Fig. 1: Phot ograph show s m easurem ent s undert aken in t he foram en m agnum . AB- Ant eropost erior diam et ers, CD- Transverse diam et ers.
Fig. 2: M orphological variant s of t he shape of Foram en m agnum : (A) Oval, (B) Round, (C) Tet ragonal, (D) Hexagonal, (E) Ir regular.
RESULTS
p value was <0.01 (Table 3). In cont rast t o t he area, t he m ean foram en m agnum index w as higher in fem ales (89.01±6.84m m ) com pared t o m ales (81.75±5.99m m ) and t his difference w as also st at ist ically significant (p<0.01).
The most common shape of the foramen magnum was oval follow ed by round and irregular. The m ean ant eropost erior diam et er and foram en m agnum area w as higher in m ales com pared t o f em ales (p<0.01). Th e m ean di f f er ence of t ransverse diam et er w as also m ore in m ales how ever t he difference w as not st at ist ically significant . One very int erest ing fact can be observed t hat all values of fem ale are lower t han m ales, w hich show s t hat t hese param et ers are ver y im por t ant f or sex det er m inat io n and const it ut ion of biological profile. In cont rast t o t hese t hree param et ers, t he foram en m agnum i nd ex w as si gni f i can t ly h igh er i n f em al es com pared t o m ales (p<0.01).
Table 1: Com parison of m orphological t ypes of foram en m agnum and frequency of occurrence w it h previous st udies.
Types of foram en
m agnum M urshe d e t al [19]
Radhakrishna et al [20]
P.Chet han et al [13]
Radhika P.M [38]
Present st udy
Oval 9 (8.1%) 3 9 (39 %) 8 (15 .1%) 60 (4 0%) 18 (50 %)
Round 24 (21.8 %) 2 8 (28 %) 12 (22.6%) 30 (2 0%) 7 (20 %)
Tet ragonal 14 (12.7 %) 1 9 (19 %) 10 (18.9%) 9 (6 %) 2 (6 %)
Hexagonal 19 (17.2 %) - 3 (5.6 %) 9 (6 %) 3 (8 %)
Irregular 22 (19.9 %) - 8 (15 .1%) 24 (1 6%) 6 (16 %)
Table 2: Descript ive stat ist ics: Dim ensions, Area and Index of t he foram en m agnum .
Table 3: M ean differences in dim ensions, area and index of foram en m agnum across gender.
M ean S.E. M ean S.E.
Transverse diam e t er (m m ) 30.05 0.54 2 9.49 0.4 >0.05
Ant eropost erior diam et er (m m ) 36.78 0.35 3 3.22 0.49 <0.01
Foram en m agnum Are a (m m2) 8 76.88 20 .38 776.87 1 6.6 2 <0.01
Foram en m agnum Index 81.75 1.37 8 9.01 1.66 <0.01
Param et er M ales (n=1 9) Fe m ales (n=17) p value
* p value < 0.05 m eans dat a is st at ist ically significant
DISCUSSION
Foram en m agnum is m orphologically variable ost eological feat ur e in t he skull w hich has undergone evolut ionary changes [17]. There is great variat ion in t he m orphological t ypes of foram en m agnum (Fig. 2). In t he present st udy, t he var io u s v ar i an t s (sh apes) o f f or am en m agnum were described as oval (50%), rounded (20%), t et ragonal (6%), hexagonal (8%) and irregular (16%) shapes (Table 1). The shape of t he foram en m agnum w as sim ilar in bot h sexes and oval shape is m ost com m only observed. Zaidi and dayal [18] also observed t hat t he oval shape (64%) is t he m ain t ype. The shape and m orphological variat ions of foram en m agnum are im port ant in neurological int erpret at ion. In an ovoid t ype of t he foram en m agnum , t he surgeon m ay find it difficult t o explore t he ant erior port ion of t he foram en m agnum. In t he lit erat ure, t here is great discordance regarding
M inim um M axim um M inim um M axim um
Transverse diam e t er (m m ) 25.75 34.25 30.05 ± 2.36 26.00 31.75 29.49 ± 1.66
Ant e ropost e rior diam et e r (m m ) 35.00 39.75 36.78 ± 1.52 29.5 34.75 33.22 ± 2.00
Foram e n m agnum Area (m m2) 734.65 1031.44 876.88 ± 88.83 607.85 848.77 776.87 ± 68.51
Foram e n m agnum Index 71.53 90.13 81.75 ± 5.99 83.45 105.83 89.01 ± 6.84
Param et e r
M ales (n=1 9 ) Fem ale s (n=1 7)
Range
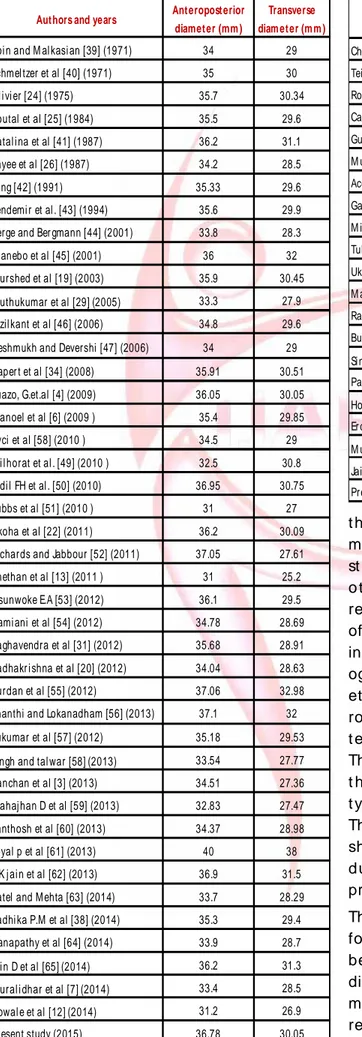
Table 4: com parison of foram en m agnum (m ale) dim ensions in var ious st udies.
Authors and years Anteroposterior diameter (mm )
Transverse diam eter (m m )
Coi n and M al kasi an [39] (1971) 34 29
Schmel tzer et al [40] (1971) 35 30
Ol i vi er [24] (1975) 35.7 30.34
Routal et al [25] (1984) 35.5 29.6
Catal i na et al [41] (1987) 36.2 31.1
Sayee et al [26] (1987) 34.2 28.5
Lang [42] (1991) 35.33 29.6
Sendemi r et al . [43] (1994) 35.6 29.9
Berge and Ber gmann [44] (2001) 33.8 28.3
W anebo et al [45] (2001) 36 32
M urshed et al [19] (2003) 35.9 30.45
M uthukumar et al [29](2005) 33.3 27.9
Ki zil kant et al [46] (2006) 34.8 29.6
Deshmukh and Devershi [47] (2006) 34 29
Gaper t et al [34] (2008) 35.91 30.51
Suazo, G.et.al [4] (2009) 36.05 30.05
M anoel et al [6] (2009 ) 35.4 29.85
Avci et al [58] (2010 ) 34.5 29
M i l horat et al . [49] (2010 ) 32.5 30.8
Erdi l FH et al . [50] (2010) 36.95 30.75
Tubbs et al [51] (2010 ) 31 27
Ukoha et al [22] (2011) 36.2 30.09
Ri chards and Jabbour [52] (2011) 37.05 27.61
Chethan et al [13] (2011 ) 31 25.2
Osunwoke E.A [53] (2012) 36.1 29.5
Dami ani et al [54] (2012) 34.78 28.69
Raghavendra et al [31] (2012) 35.68 28.91
Radhakr i shna et al [20] (2012) 34.04 28.63
Burdan et al [55] (2012) 37.06 32.98
Shanthi and Lokanadham [56] (2013) 37.1 32
Sukumar et al [57] (2012) 35.18 29.53
Si ngh and tal war [58](2013) 33.54 27.77
Kanchan et al [3] (2013) 34.51 27.36
M ahaj han D et al [59] (2013) 32.83 27.47
Santhosh et al [60] (2013) 34.37 28.98
Loyal p et al [61] (2013) 40 38
S.K j ai n et al [62] (2013) 36.9 31.5
Patel and M ehta [63] (2014) 33.7 28.29
Radhi ka P.M et al [38] (2014) 35.3 29.4
Ganapathy et al [64] (2014) 33.9 28.7
Jai n D et al [65](2014) 36.2 31.3
M ural i dhar et al [7](2014) 33.4 28.5
Howal e et al [12](2014) 31.2 26.9
Pr esent study (2015) 36.78 30.05
Table 5: Com parison of Area and Index of foram en m agnum (m ale) in various st udies.
Authors and years Foram en m agnum area (mm2)
foram en magnum Index
Chaturvedi and Har nej a [66] (1963) - 83.81
Tei xei ra [30] (1982) 963.73
-Routal et al [25] (1984) 819
-Catal i na et al [41] (1987) 888.4
-Gunay and Al ti nkok [36] (2000) 909.91
-M ur shed et al [19] (2003) 931.7
-Acer et al [67] (2006) 760
-Gapert et al [34] (2008) 862.41
-M i l horat et al [50] (2010) 787.7
-Tubbs et al [51] (2010) 558
-Ukoha et al [22] (2011 ) 857
-M acal uso [68] (2011) 854
-Raghavendra et al [31] (2012) 811.67
-Bur dan et al [55] (2012) 877.4 89.34
Si ngh and tal war [58](2013) 733
-Patel and M ehta [63] (2014 755.37
-Howal e et al [12](2014) - 84.85
Er di l FH et al [50] (2010) - 83.7
M ur al i dhar et al [7](2014) 748.6
-Jai n D et al [65](2014) - 86.69
Present study 876.88 81.75
t he predom inant m orphological type of foramen m agnum . The dat a obt ained from t he present st udy w as compared with few m ore reports from o t her au t h or s an d t he sam e has been represent ed in t able 1. The difference in shapes of t he foram en m agnum from various report s indicat es racial variabilit y am ong t he m orphol-ogy. According t o M urshed et al. [19], Chet han et al. [ 13] and Radhakr ishna et al. [ 20], t he rounded shape is t he m ain t ype, w hile it is t he t et ragonal shape according t o Sindel et al. [21]. These variat ions m ight have been at t ribut ed by t he fact ors such as sexual dim orphism [22], t ypes of populat ion [13], and et hnic groups [23]. Therefore the variat ion in t he foram en m agnum sh ape shou ld be t aken in t o con sid er at i on du r i ng cli nical and r adi ol ogical di agno st ic procedures and t he surgical approach [13].
larger t han t he t ransverse diam et er and also bot h diam et ers are slight ly sm aller in fem ales t han in m ales. Sim ilar finding is report ed by Ol iv ier (1975) w h o also f ou nd co r r elat i on bet w een t hese t w o variables [24]. St udies by Rout al et al. [25] and Sayee et al. [26] also suggested that the foramen magnum dimensions in m ales are significant ly higher t han in fem ales. Th is i s u sef u l f i n di n g f o r f o r ensi c an d paleo-ant hropology, because one can, t herefore est im at e sizes in fragm ent ed foram en m agnum rem ains. Ford [27] report ed t hat t he lengt h of t he foram en m agnum increases m ore rapidly during prenat al period w hen com pared t o it s w idt h. A great er degree of cerebellar t onsillar herniat ion is associat ed w ith a w ider ant eropos-t erior diam eeropos-t er of foram en m agnum [28]. Ieropos-t has been report ed t hat longer ant eropost er ior dim ension of f or am en m agnum per m it t ed gr eat er cont r alat er al sur gical exposur e f or condylar resect ion in t ranscondylar approach [29].
Teixeria in 1983 was probably one of t he first resear cher s w ho published his resear ch on est im at ion of sex based on t he size of foram en m agnum [30]. The present st udy show ed t hat t he lev el of st at i st i cal si gn i f i can ce in sex difference is however higher for t he lengt h, area and index w hereas t he t ransverse diam et er is not stat ist ically significant (Table 3). M uralidhar et al. also report ed that the t ransverse diam et er of m ales w as not st at ist ically significant in his st udy [7]. A recent st udy [31] has report ed a low predict ive accuracy of foram en m agnum lengt h in sex est im at ion based on BLR analysis w hile foram en magnum breadth (width) was not found t o be a useful crit erion for sex est im at ion. Uysal et al. [32] have report ed st at ist ically significant sex differences in the w idt h of foram en m agnum diam et ers by using t hree-dimensional comput ed t omography (3D CT) m easurement s. Populat ion differences are also im port ant in defining sexual differences in t he cranium . Therefore sexual differences in t he foram en m agnum have been st udied in various populations. The com parative analysis of t he dim ensions of foram en m agnum of our dat a supplem ent ed by lit erat ure and observat ional dat a of t he previous st udies is show n in t able 4. A variat ion in t he m ean values of foram en m agnum m easurem ent s in m ales
and fem ales is obvious ow ing t o t he populat ion differences. Sexual dim orphism was found in the present st udy in bot h ant er opost erior and t r ansv er se di am et er s. Th e col lect ed d at a indicat es a sexual dim orphism of t he foram en m agnum but only in relat ion t o it s size (Table 4). Gruber et al. [33] did not find any sexual d im o r p h ism i n t h e d i am et er s o f f or am en m agnum in Cent ral Eur opean dr y specim en dat ing f r om Pleist ocene t o m oder n t im es. Ragh av en d r a et al . [ 31] f o un d t h at t h e ant eropost erior diameter to be t he m ost reliable variable for sex est im at ion. How ever Gapert et al. [34] report s t he w idt h of foram en m agnum t o b e t h e m o st r el iab l e v ar iab l e i n sex est im at i on . Di f f er ence i n o bser vat io ns o f dif ferent aut hors m ay be at t r ibut ed t o t he d if f er en ces i n t h e p o pu l at i o n gr o up s, m et hodology, and stat ist ical analysis.
In t his st udy, the mean area of foramen m agnum in fem ales w as found sm aller t han m ales. Our f in d i ngs sh o w ed st at i st i cal l y si gni f i can t differences exist bet w een t he areas est im at ed using form ula derived by Radinsky [16] .This result is in agreem ent w it h Teixeria [30] and Fatteh [35]. In a Turkish populat ion, Gunay and Alt inkok [36] also observed t hat m ean area of foram en m agnum in fem ales w as significant ly low er t han in m ales. Ut hm an et al [37] report ed t hat f o r am en m agn um ar ea is t he b est discrim inant param et er t hat could be used t o st ud y sexu al d im o r ph i sm w i t h an o v er al l accuracy 69.3%. The m ean values of foram en m agnum area and index m easurem ent s of t he present st udy are com pared w it h t he values p r esen t ed by m ost of t he o t h er au t ho r s (Table 5). Foram en m agnum index in m ale was st at ist ically significant correlat ed w it h fem ale, but w as significant ly larger in fem ale t han in m ale foram en m agnum (Table 5). Though t he diff erences in t he obser vat ions of previous researchers are at t ribut ed t o t he variat ions in t he st udy sam ples, m et hodology, and stat ist ical analysis em ployed.
CONCLUSION
procedures. M orphom et ric analysis of foram en m agnum can be used as support ive findings in est im at ion of sex of fragm ent ed, incom plet e or dam aged dry hum an skulls. The know ledge of m orphology and m orphom et r y of f or am en m agnu m is i m p o r t an t f o r n eu r o su r geo ns, radiologist s as w ell as ant hropologist s.
Et hical Approval:
This st udy w as approved by t he Inst it ut ional Review Board (IRB) of Om an m edical college. The Inst it ut ional Review Board (IRB) regist ration num ber is OM C/ IRRB/2015/005/ C
Acknow ledgem ent :
We are t hankful for t he support provided by t he Om an M ed i cal Co l l ege, Al - Tar eef, So h ar, sult anat e of Om an.
Conflicts of Interests: None
REFERENCES
[1] . Gaut am Kanodia, Vijay Parihar, Yad R Yadav, Pushp R Bhat ele and Dhananjay Sharm a. M orphom et ric analysis of post erior fossa and for am en m agnum . J Neurosci Rural Pract . 2012; 3(3): 261–266. [2] . Standarding S. Gray’s anat om y. The anat om ical
basis of clinical pract ice. 39t h ed. London: Elsevier Churchill Livingst one; 2005: 460.
[ 3] . Tanuj kanchan, anadi gupta, and kew al kr ishan. Cr aniom et r i c analysis of f or am en m agnum f or est im at ion of sex. Int ernat ional journal of m edical, Heal t h , b i o m ed i cal an d p h ar m aceu t i cal engineering. 2013; 7(7): 111-113.
[4]. Suazo, G. I. C. Russo, P. P., Zavando, M . D. A.; & Sm ith, R. L. Sexual dim or phism in t he f oram en m agnum dim ensions. Int .J. M or phol., 2009; 27(1): 21-23. [5] . K. Edw ards, M .D. Viner, W. Schw eit zer, M .J. Thali.
Sex det er m inat ion f r om t he f oram en m agnum . Journal of f orensic radiology and im aging. 2013; 1(4): 186-192.
[6] . M anoel, C., Prado, FB., Caria, PHF.and Groppo, FC. M orphom et r ic analysis of t he foram en m agnum in hum an skulls of brazilian individuals: it s r elat ion t o gender. Braz. J. M orphol. Sci., 2009; 26(2): 104-108.
[ 7]. M uralid har P Shepur, M agi M , Nanjundappa B, Pavan P Havaldar, Prem alat ha Gogi, Shaik Hussain Saheb. M orphom et ric analysis of foramen magnum . Int J Anat res., 2014; 2(1):249-55.
[8]. Holland TD. Sex det erm inat ion of fragment ary crania by analysis of cr ania base. Am J Phys. Ant hropol. 1986; 70: 203-208.
[9]. Graw M . M orphom et rische and M orphognost ische. Ge sch l ect h sd i agn o st i k an d er m e n sch l i ch en Schadelbasis. In: Oehm icen M , Geserick G (eds) Ost eologische Ident ifikat ion and Alt ersschat zung Schm idt -Rom hild, Lubeck, 2001: 103- 121.
[10]. Barut N, Kale A, Turan Suslu H, Ozt urk A, Bozbuga M , Sahinoglu K: Evaluat ion of t he bony landm arks in t ranscondylar approach.,Br J Neurosurg., 2009; 23: 276-281.
[11]. Furtado SV, Thakre DJ, Venkatesh PK, Reddy K, Hegde AS:M or phom et r ic analysis of f oram en m agnum dim ensions and int racranial volum e in pediat r ic chiari I m alform at ion. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2010; 152: 221-227.
[12]. Deepak S. How ale, Anil Bat hija, Sudarshan Gupt a, D P Pandit . Correlat ion bet w een cranial index and f or am en m agnum index in hum an dr ied skulls. GJRA. 2014; 3(1): 3-6.
[13]. P. Chet han, K.G. Prakash, B.V. M ur lým anju, K.U. Prashant h, Lat ha V. Prabhu, Vasudha V. Saralaya, Ashw in Kr ýshnam urt hy, M .S. Som esh, C. Ganesh Kum ar. M orphological analysis and m or phom et ry o f t h e f o r am en m agn u m : an an at o m i cal invest igat ion. Turkish Neurosurgery. 2012; 22(4): 416-419.
[14]. Test ut L, Latarjet A. Trat ado de anat om ia hum ana, Salvat . Barcelona. 1977.
[15]. Gr ay H. Car act er ist icas Craneles en las diff erent es edades; in William s and Warw ick, Anat om ia Salvat . Bar celona. 1985.
[16]. Radinsky L. Relat ive brain size e a new m easure. Science. 1967; 155: 836-838.
[17]. Nevell L, Wood B. Cranial base evolut ion w it hin t he hom inin clade. J Anat ., 2008; 212: 455-468. [ 18] . Zai di SH, Dayal SS. Var iat ions in t he shape of
for am en m agnum in Indian skulls. Anat Anz Jena. 1988; 167: 338-340.
[19]. M urshed K, Çiçekcibasi A, Tuncer I. M orphom et ric evaluat ion of t he for am en m agnum and var iat ions in it s shape: a st udy on com put erized t om ographic im ages of nor m al adult s. Turk J M ed Sci. 2003; 33: 301-306.
[ 20] . Radhakr ishna S, Shivar am a C, Ram akr ishn a A, Bh agya B. M o r ph om et r i c an al ysi s of f or am en m agnum f or sex det er m inat ion in sout h Indian p o p ul at i o n . Ni t e u ni ver si t y j o u r nal o f h eal t h science. 2012; 2(1): 20-22.
[ 21] . Si ndelM , Özkan O, Uçar Y, Dem ir S. For am en M agnu m ’un An at om i k Var yasyo nl ar ý. Akdeni z Üniversit esi Týp Fakült esi Dergisi. 1989; 44(6): 97-102. Annual Research & Review in Biology, 4(9): 1372-1378.
[22]. Ukoha U, Egw u O, Okafor I, Anyabolu A, Ndukw e G, Okp al a I. Sexual Dim or ph i sm i n t he Fo r am en M agnum of Nigerian Adult . Int J Biol M ed Res., 2011; 2(4): 878-881.
[23]. Espinoza E, Ayala C, Ort ega L, Collipal E, Silva H, M orf om et r ía t om ogr áf ica delf oram en m agno y surelaciónco nel sexo y la et nia m apuche. Rev. ANACEM (Im presa). 2011; 5(1): 28-31.
[24]. Olivier G. Biom et ry of t he hum an occipit al bone. J Anat ., 1975; 120: 507–518.
[26]. Sayee R, Janakiram S, Thomas IM . Foramen m agnum m easurem ent s of Cr ania from Karnat aka. J Anat Soc India. 1987; 36: 87-89.
[27]. Ford HER. Grow t h of t he f oet al skull. J Anat ., 1956; 90: 63–72.
[28]. Duft on JA, Habeeb SY, Heran M K, M ikulis DJ, Islam O. Post erior fossa m easurem ent s in pat ient s w it h and w it hout Chiar i I m alform at ion. Can J Neurol Sci., 2011; 38: 452–455.
[ 29]. M ut hukum ar N, Sw am inat han R, Venkat esh G, Bham um at hi SP. A m orphom et r ic analysis of t he f o r am en m agn u m r egi o n as i t r e l at e s t o t r anscondylar appr oach. Act a neurochir (Wien). 2005; 147(8): 889- 895.
[30]. Teixeria WR. Sex ident ificat ion ut ilizing t he size of Foram en M agnum . Am J Forensic M ed pat hol., 1983; 3: 203-206.
[ 31] . Y.P. Raghavendra Babu, Tanuj Kanchan, Yam ini At t iku, Prashant h Narayan Dixit , M .S. Kot ian. Sex est im at ion f rom f oram en m agnum dim ensions in an Indian populat ion. Jour nal of forensic and legal m edicine. 2012; 19: 162-167.
[32]. Uysal S, Gokharm an D, Kacar M , Tuncbilek I, Kosa U. Est im at ion of sex by 3D CT m easurem ent s of t he for am en m agnum . J For ensic Sci, 2005; 50: 1310– 1314.
[33]. Gr uber P, Henneberg M , Böni T, Rühli FJ. Var iabilit y o f h u m an f o r am e n m agn u m si ze. An at Re c (Hoboken). 2009; 292: 1713-9.
[34]. Gapert R, Black S, Last J. Sex determ inat ion from t he occipit al condyle; discrim inant funct ion analysis is an eight eent h and ninet eent h cent ur y Brit ish sam ple. Am J Physical Ant hropology. 2008; (138): 384-94.
[35] . Fat t eh, A.: handbook of forensic pat hology. J.B. Lippincot t , Philadelphia,1973.
[36]. Gunay Y, Altinkok M . The value of the size of foramen m agnum in sex det erm inat ion. J Clin Forensic M ed., 2000; 7: 147-9.
[37]. Ut hm an AT, Raw i NA and Tim im i JA. Evaluat ion of for am en m agnum in gender det erm inat ion using helical CT Scanning. Dent om axillof acial Radiol., 2012; 14: 197-202.
[ 38 ] . Rad h i ka.P. M , Sh ai l aj aSh e t t y ,Pr at h ap K.J, C.Sheshgiri, Jyot hi K.C. M orphom et ric st udy of t he for am en m agnum in adult hum an skulls in indian populat ion. Asian J M ed Clin Sci., 2014; 3 (2): 68-72.
[ 39] .Coin CG, M alkasian DR. For am en m agnum . In: New t on TH, Pot t s DG eds. Radiology of t he skull and brain: t he skull. M osby, St . Louis. 1971: 275– 347.
[40] . Schm elt zer A, Babin E, Wenger JJ: M easurem ent of t he f or am en m agnu m in chi ld r en an d ad ul t s. Neuroradiology. 1971; 2(3): 162-163.
[41]. Cat alina-Her rera CJ. St udy of t he anat om ic m et ric values of t he for am en m agnum and it s relat ion t o sex. Act a Anat ., 1987;(130):344–347.
[42]. Lang J. Clinical anat om y of t he post erior cranial fossa and it s f oram ina. Thiem e M edical Publishers, Ber lin. 1991.
[43].Sendem ir E, Savci G, Cim en A. Evaluat ion of t he for am en m agnum dim ensions. Kaibogaku Zasshi. 1994; 69: 50–52.
[44]. Berge JK, Bergm an RA (2001) Variat ions in size and in sym m et ry of foram ina of t he hum an skull. Clin Anat ., 2001;14: 406–413.
[45]. Wanebo JE, Chicoine M R: Quant it at ive analysis of t h e t r an sco n d yl ar ap p r o ach t o t h e f o r am en m agnum . Neurosurgery. 2001; 49: 934-941. [ 46 ] . Ki zi l kan at Em i n e Do n d u , Bo yan N esl i h an .
M o r p ho m et r y of h yp o glo ssal canal , o ccip i t al co nd yl e and f or am en m agnu m . Neu r osur ger y quart er ly. 2006; 16(3): 121- 125.
[47]. Deshm ukh AG, Devershi DB. Com par ison of cranial sex det erm inat ion by univariat e and m ult ivariat e analysis. J Anat Soc India. 2006; 55: 48-51. [48]. Avic E, Dagt ekin A, Ozt urk AH, Kara E, Ozt urk NC,
Uluc K et .al. Anat om ical variat ions of t he foram en m agnum , occipit al condyle and jugular t ubercle. Tur k Neurosurg. 2011; 21(2): 181-190.
[49]. M ilhorat TH, Nishikaw a M , Kula RW, Dlugacz YD. M echan ism s o f cer eb ellar t onsil h er n iat ion in pat ient s w it h Chiar i m alf or m at ions as guide t o clinical m anagem ent . Acta Neurochir. 2010; 152: 1117–1127.
[50]. Edril FH, Saban V, Cim en M , Isi k O: M orphom et ric
Evalu-ation of the foramen magnum by CT. Ericyes Medical Jour-nal. 2010; 32(3): 167-170.
[51]. Tubbs RS, Griessenauer CJ, Loukas M , Shoja M M , Coh en- Gado l AA. M o r ph o m et r i cs an alysi s o f f o r am en m agn u m : an an at o m i c st u d y. Neurosurgery. 2010; 66(2): 385-88.
[ 52] . Ri char d s GD, Jabb o u r RS. Fo r am en m agn u m ont ogeny in Hom o sapiens: a f unct ional m at rix per spect ive. Anat Rec.,2011; 294: 199–216. [ 53] . Osu n w o ke EA, Ol ad i p o GS, Gw u n i r eam a IU,
Ngaokere JO. M orphometric analysis of t he foram en m agnum and jugular foram en in adult skulls in sout her n Nigerian populat ion. Am . J. Sci. Ind. Res., 2012; 3(6): 446-448.
[ 54] . Dam iani, Borelli, NS., M elo, HJF, Lim a, RS and Nobeschi. M orphom et ry and spat ial correlat ion of t he foram en magnum and spinal cord t hrough M RI. J. M orphol. Sci., 2012; 29(2): 87-90.
[55]. F. Burdan, J. Szum i³o, J. Walocha, L. Klepacz, B. M adej, W. Dw orzañski,R. Klepacz, A. Dw or zañska, E. Czekajska-Chehab, A. Dr op. M orphology of t he f o r am en m agn um in yo ung East er n Eur o pean adult s. Folia M or phol.2012; 71(4): 205–216. [56]. Shant hi CH, S.Lokanadham . M orphom et r ic st udy
on foram en m agnum of hum an skulls. M edicine Science. 2013; 2(4): 792-798.
[ 57 ] . S. Su ku m ar, S. yad av an d H B M an j u . 3 D Reconst r uct ion com put er t om ography of foram en m agn u m an d f r o n t o n asal j u n ct i o n f o r se x det erm inat ion in sout h indian populat ion. Int J Pharm Bio Sci. 2012; 3(4): (B)615 – 619.
[ 59] . Divya M ahajan, Gaurav Agnihot r i, Abha Shet h, Rahat Brar. An anat om ical perspect ive of hum an occipit al condyles and f or am en m agn um w it h neurosur gical corr elat es. Int ernat ional journal of clinical and exper im ent al anat om y. 2013; 6(7): 29-33.
[ 60] .San t h osh CS, V i sh w an at han KG, Asho k Gu pt a, Si dd esh RC, an d Tejas J. M or ph om et r y o f t h e Fo r am en M agn u m : An Im p o r t an t To o l i n Sex Det erm inat ion. Resear ch and Review s: Journal of M edical and Healt h Sciences. 2013; 4(2): 88-91. [61]. Loyal P, Onget i K, Pulei A, M andela P, Ogeng’o J,
Gen d e r r el at ed p at t er n s i n t h e sh ap e an d dim ensions of t he foram en m agnum in an adult kenyan populat ion. Anat J Afr. 2013; 2(2): 138-141. [62]. S.K. Jain, Alok Kum ar Choudhar y, Pankaj M ishra. M orphom et ric evaluat ion of foram en m agnum for sex det erm inat ion in a docum ent ed nort h indian sam ple. Journal of Evolut ion of M edical and Dent al Sciences.2013; 2(42): 8093-8098.
[63]. Rom a Pat el, C. D.M eht a. M orph m et ric st udy of For am en M agnum at t he base of hum an skull in So ut h Gu jar at . Jour nal of Dent al and M edical Sciences. 2014; 13(6): 23-25.
How to cite this article
:
Ani l Kum ar, M it esh Dave, Sanam Anw ar. M ORPHOM ETRIC EVALUATION OF FORAM EN M AGNUM IN DRY HUM AN SKULLS. Int J Anat Res 2015;3(2):1015-1023. DOI: 10.16965/ ijar.2015.154
[ 64 ] . Ar t h i Gan ap at h y, Sad e esh T. , Su d h a Rao . M orphom et r ic analysis of f or am en m agnum in adult hum an skulls and ct im ages. Int J Cur Res Rev., 2014; 6(20): 11-15
[65]. Jain D, Jasuja O P, Nat h s. Evaluat ion of foram en m agnum in sex det erm inat ion from hum an crania b y u si n g d i scr i m i n an t f u n ct i o n an al y si s. E1 m ednifco jour nal. 2014; 2(2): 89-92.
[66]. Chaturvedi R.P. & Harneja N.K. A Craniomet ric Study of Hum an Skull; Jour nal of Ant om ical Societ y of India. 1963; 12: 93 -96.
[67]. Acer N, Sahin B, Ekinci N, Ergür H, Basaloglu H. Relat ion bet w een int r acr anial volum e and t he sur face area of t he f oram en m agnum . J Cr aniofac Sur g., 2006;17: 326–330.