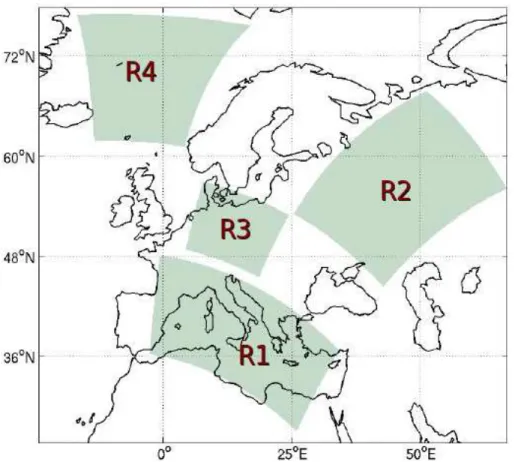
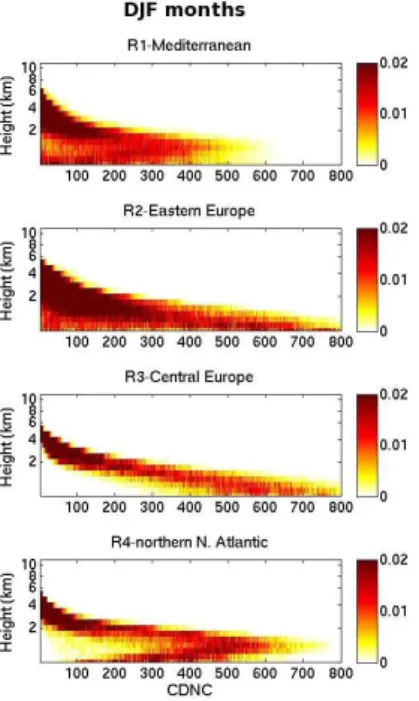
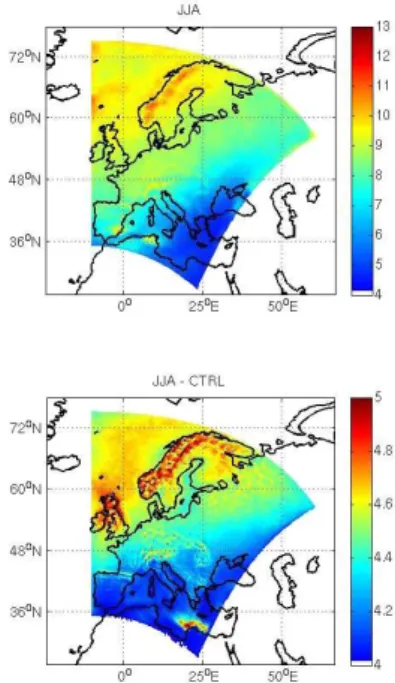
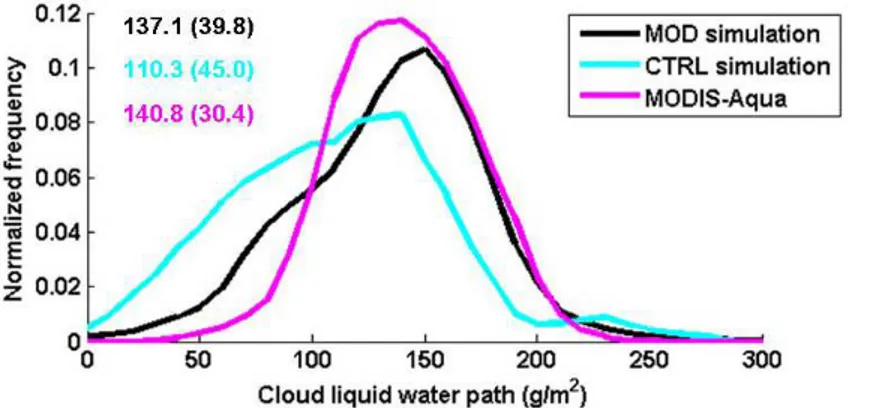
Development of prognostic aerosol–cloud interactions combining a chemistry transport model and a regional climate model
Texto
Imagem

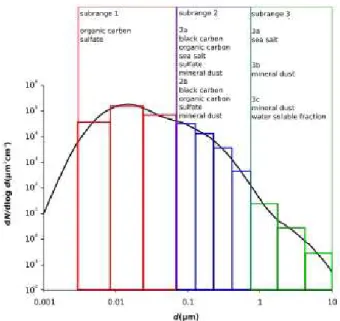
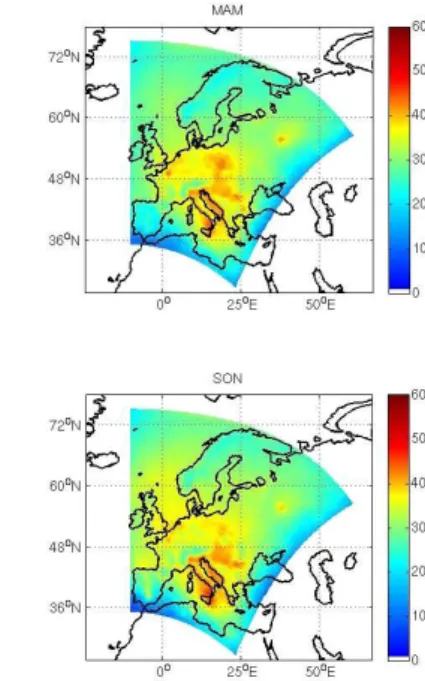
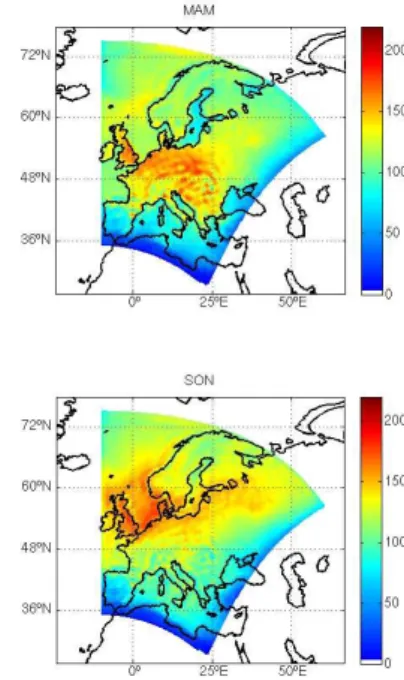
Documentos relacionados
When droplets condensed on CCN grow large enough to be distinguished from non- activated nuclei, the cloud droplets’ size distribution calculated by the parcel model is assigned to
It is shown that subgrid treatment of cloud activation and autoconversion of cloud water to rain reduce the impact of anthropogenic aerosols on cloud properties and thus reduce
A coupled atmospheric chemistry and climate system model was developed using the modal aerosol version of the National Center for Atmospheric Research Community Atmosphere
Coupled Chemistry Aerosol-Tracer Transport model to the Brazilian developments on the Regional Atmo- spheric Modeling System (CCATT-BRAMS, version 4.5) is an on-line regional
A regional climate model study has been performed to investigate the transport and atmospheric loss rates of emissions from Indonesian volcanoes and the sensitivity of these
Thus, rain profiles are found by integration of the microphysical process rates over height but not time (diagnostic rain) as described in Morrison and Gettelman (2008, Sect. In
Prognostic treatment of the aerosol concentrations in the explicit cloud droplet nucleation scheme of the model, improved the model performance for the twenty-four hour
We analyze the modeled microphysical properties under the different aerosol conditions to gain insights into the effects of aerosols on cloud development, precipitation, and