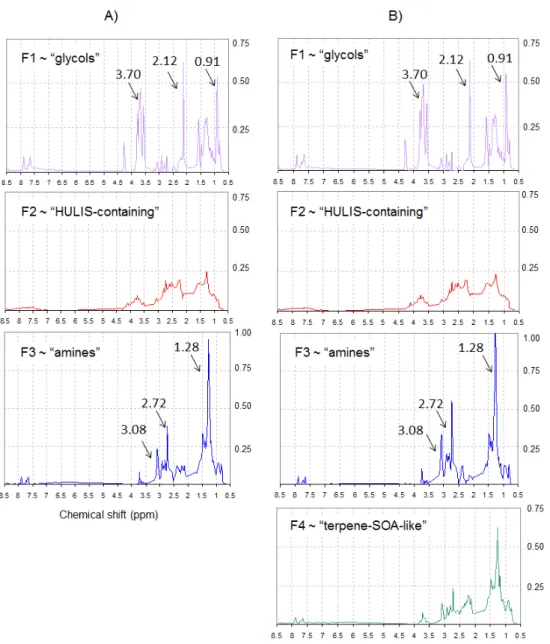
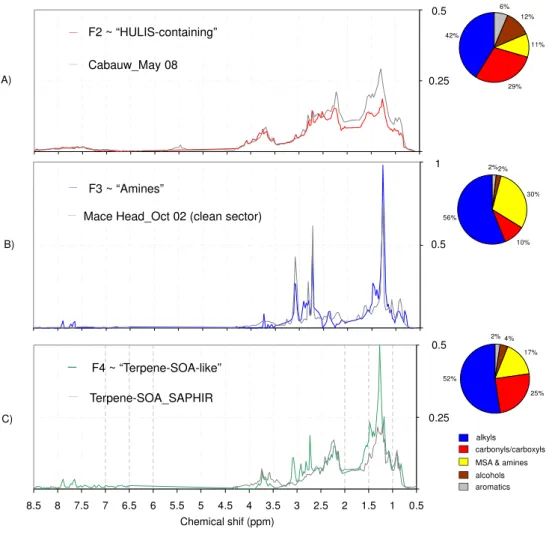
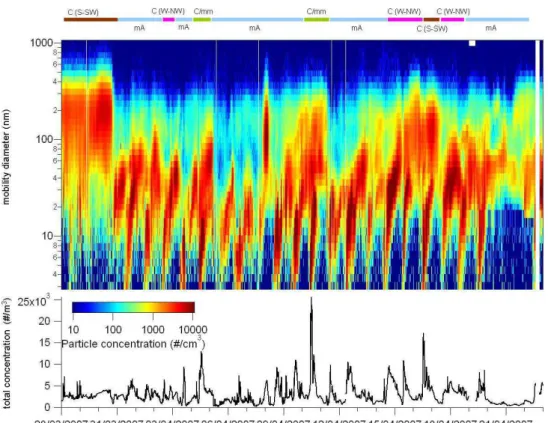
Determination of the biogenic secondary organic aerosol fraction in the boreal forest by NMR spectroscopy
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
The volatile and hygroscopic properties of ammonium sulphate seeded and un-seeded secondary organic aerosol (SOA) derived from the photo-oxidation of atmospherically
aerosols (SOA) from anthropogenic sources (ASOA), biogenic sources (BSOA), and glyoxal (GLSOA), and semi-volatile organic aerosol (SVSOA) over Australia, Europe, North America,
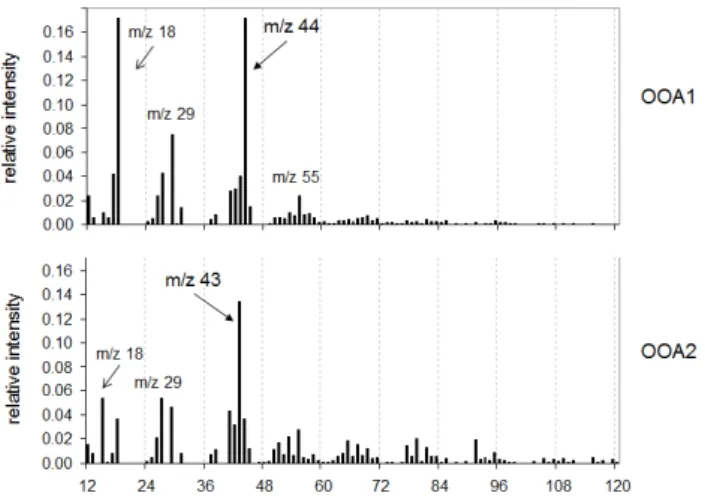
Positive matrix factorization analysis of the TPOT AMS organic mass spectra yielded a primary biomass burning factor and four oxygenated organic aerosol factors directly..
Predicted seasonal average SOA concentrations due to contributions from different precursors in (a) spring (March, April and May), (b) summer (June, July and August), (c)
In regions like the San Joaquin Valley, the mass of biogenic emissions from agricultural crops during the summer (with- out flowering) and the potential ozone and secondary
The aim is to eval- uate how the mass spectral signatures of the photooxidation products of 1,3,5-TMB and α -pinene observed in this study compare to mass spectral signatures of
(2011) found that organic aerosol particles measured at the PUY site during summer 2010 were likely linked to biogenic sources: the mass spectra of OOA (oxygenated organic aerosols)
At these sites, about 30% of measured organic carbon was found in the coarse mode and was to a certain level attributed to primary biogenic organic aerosol (Puxbaum et al., 2003),