Original Research Article
FACULTY AND STUDENT PERCEPTIONS ON THE INTRODUCTION
OF OBJECTIVE STRUCTURED CLINICAL EXAM INATION IN AN
UNDERGRADUATE PHYSIOTHERAPY COURSE: A PILOT STUDY
M ullai Dhinakaran *
1, Jugesh Chattwal
2, Dheeraj K.V
3.
* 1 Associate Professor, College of Physiot herapy, CM C & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. 2 Professor, Head of t he Depart ment , Depart ment of Paediat rics, CM C & Hospital, Ludhiana, India. 3 Professor, College of Physiot herapy, CM C & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India.
Background: The clinical educat ion m et hods in under graduat e physiot her apy t raining are w ell int egr at ed but t he m et hodology of t he clinical skill assessm ent st ill rem ains subject ive. Due t o lack of object ive clinical assessm ent , com pet ency in clinical skills becom es com prom ised.
Aim and Objectives: To int roduce Object ive St ruct ured Clinical Exam inat ion t o Physiot herapy facult y, st udent s and det erm ine t he percept ion of Physiot herapy facult y and st udent s about OSCE m et hod of clinical assessm ent .
M ethodology: OSCE w as conduct ed t o undergraduat e physiot herapy 4t h year st udent s (n – 20) by OSCE t rained staff m em bers (n -8) of College of Physiot herapy. CM C & H, Ludhiana. By t he end of exam , self-adm inist ered quest ionnair es w ere dist ribut ed and pilot ed t o bot h facult y and st udent s. They answ ered each it em on 5- point Likert scale from 1 (st rongly disagr ee) t o 5 (st rongly agree).
Results: The pilot ed dat a w as analysed w it h descript ive st at ist ics. The ent ire facult y perceived t hat OSCE helping t o enhance t he evaluat ion m et hod of clinical assessm ent . M ore t han 80% of t he st udent s felt t hat OSCE should be an ef fect ive clinical assessm ent t ool. Bot h facult y and st udent s felt t hat OSCE m et hod of clinical assessm ent is less st ressful but m ore exhaust ing and lengt hy. Bot h groups w ere sat isfied except m ore preparat or y per iod for t he exam as t hey expressed in open com m ent s.
Conclusions: This pilot st udy provided valuable feedback from facult y and st udent s w hen OSCE assessm ent w as int roduced int o undergraduat e physiot herapy course. It helps for st andardizat ion of Physiot her apy clinical assessm ent .
KEY W ORDS: OSCE, For m at ive PT assessm ent , facult y percept ion, St udent s’ percept ion.
ABSTRACT
INTRODUCTION
Address for correspondence: M ullai Dhinakaran, Associate Professor, College of Physiot herapy, CM C & H, Ludhiana. Punjab, India. E-M ail: mullaidhinakaran@ymail.com
DOI: ht t p:/ / dx.doi.org/10.16965/ ijpr.2015.196
Quick Response code
Access this Article online
International Journal of Physiotherapy and Research ISSN 2321- 1822
w w w.ijm hr.org/ ijpr.htm l
DOI: 10.16965/ ijpr.2015.196
Received: 11-10-2015 Peer Review : 11-10-2015 Revised: None
Accept ed: 16-11-2015 Published (O): 11-12-2015 Published (P): 11-12-2015
t heir application of t heory t o pract ice w hich w ill st rengt hen t he w ork readiness of graduat es [1]. But in curr ent syst em , t eaching st af f don’ t evaluat e t he clinical skills of t he st udent s. This is a crucial problem in physiot herapy educat ion. The cl in ical sk i ll assessm en t st i ll r em ain s subj ect ive due t o lack of obj ect ive clinical assessment [2].
The t radit ional clinical assessment met hod has In physiot herapy educat ion, skill t raining is an
import ant component of curriculum, Hence it is essent ial t o assess w het her object ive of skills acquisit ion has been met .
inabilit y t o assess communicat ion skill, pract ice of favourit ism and failure t o predict t he fut ure performance of t he st udent s [3].Oral and viva examinat ions have been replaced by object ive st ruct ured clinical examinat ion (OSCE) in clinical sciences t o overcome t he problems w hich are f aced in t r adit ional clinical exam inat ion in medical inst it ut ions [4].
The Object ive St ruct ured Clinical Examinat ion (OSCE) int r o duced in 1979 b y Har den and Gleeson. It allow s t he act ual demonst rat ion of applied know ledge and skills rat her t han t est ing know ledge alone [5]. In recent years, research has focused on t he use of object ive st ruct ured clinical examinat ion (OSCE) w it h st andardized pat ient s t o im pr ove clinical assessm ent of st udent s, w hile simult aneously at t em pt ing t o recreat e realist ic pat ient s- care scenario during st udent s’ assessment [6]. OSCE is reliable and an est ablished m et hod w it h eff ect ive m ult i st at ion, t est for t he assessment of clinical skills in an object ive and t ransparent manner. It also provides opport unit y t o t est t heir at t it ude and communicat ion skills [7].
OSCE is used in several healt h pr ofessional educat ion including undergraduat e M edical st udent s, Radiography, Dent ist ry, Paediat rics, Opht halmology, Nursing and Pharmacy all over t he w orld. There are only one nat ional and few int er nat ional st udies r epor t ed on OSCE in physiot herapy field [8-11]. Therefore it requires more researches t o find out t he percept ion of st udent s as w ell as facult y about OSCE. The hypot hesis of t he st udy w as int roducing OSCE m et hod of assessm ent in an undergraduat e physiot herapy course t o provide opport unit y t o assess over all clini cal com p et ence o f t he st udent s and also t o det ermine t he percept ion of facult y and st udent s about int roducing OSCE met hod of object ive clinical assessment .
M ETHODOLOGY
st at ions, 2 rest st at ions) for physiot herapy in m usculoskelet al condit ion for 4t h year UG st udent s. A self-made quest ionnaire w as used t o assess t he percept ion about t he int roduct ion of t he OSCE for facult y and st udent s subject experts.
Tw ent y final year undergraduate st udent s w ere o r ien t ed abo u t OSCE m et h o d o f cl i n ical examinat ion t hrough pract ice session. Aft er t his, OSCE w as co n d uct ed u sin g st an dar d ized patient s. On t he day of exam, t he st udent s were rot at e t hrough each st at ion, complet ed a t ask and answ ered a relat ed t heoret ical quest ion. St udent s complet ed each st at ion in 5 minut es. In observed st at ion, t he quest ions w ere focused on specific issues like pain hist ory, M M T for specific m uscle (Fig- 1). The exam iner has a checklist for st at ion w it h each st eps carried a marks (marks w as deviat ed t o each st eps) t hat t hey w er e f il led out w hile ob ser ving each candidat e.
The f acul t y an d f i nal year un der gr adu at e st udent s of t he College of Physiot herapy, CM C & Hospit al w ere included in t his st udy w it h duly signed informed consent . Eight facult ies w ere sensit ized t o t he object ive st ruct ured clinical exam i n at i o n (OSCE) b y o r gan izi n g a m i n i w or kshop . Th e f acult y t hen developed 15 st at ions (5 observed st at ions, 8 non observed
Fig. 1: Observed stat ion Fig. 2: Non observed stat ion
In n o n -o b ser v ed st at i o n, St u d ent s hav e answ ered t he object ive quest ions (Fig -2). The examiners have a model answ er t o correct t he answ er w hich w as filled by st udent s. Facult y gave f eedback t o t he st udent s about t heir performances aft er t he exam.
Facult y and st udent s percept ion about OSCE, a closed ended quest ionnaire using 5 point Likert scale w as dist ribut ed and also included open comment s.
Data analysis: The pilot ed dat a of facult y and
students perception was analysed by descript ive st at ist ics in SPSS version 16.0.
RESULTS
A. Facu lt y p er cep t io n a b ou t O SCE: Eigh t
The 5 point Likert scale of percept ions w ere analysed w it h mean, st andard deviat ion and percentage of acceptance in Table- 1.
Table 1: Facult y percept ion about OSCE.
Covered in w ide knowledge 4.0 + 0.92 87.5
Easy to pass 3.63 + 0.92 62.5
Viva – voice is better 2.75 + 1.16 37.5
Fair 4.0+ 0.76 75
Personality, ethnicity, face value doesn’t affect the OSCE
score
4.13 + 0.99 87.5
Cheating was minimized 4.5 + 0.53 100
Less stressful 3.75 + 0.89 75
Exhausting and Lengthy 3.63 + 1.06 75
Suitable for all level of students 3.38 + 1.19 75
Help to assess future
performance 3.88 + 0.83 87.5 Enhances teaching level 3.63+ 0.92 62.5
Enhances evluation method 4.3 + 0.52 100
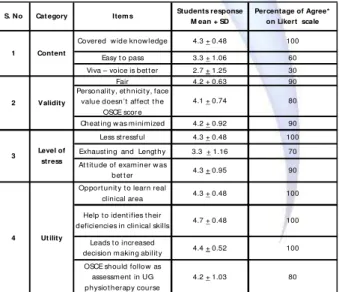
Content 1
Students response (M ean + SD)
Percentage of Agree* on Likert scale Items Category S.No 2 Validity Level of stress 3 Utilit y 4
Some of t he responses to the open comments
of t he facult y percept ion are as follow s
· OSCE i s f o r m at i v e t y p e o f t i m e savi n g comparing w it h t radit ional exam.
· It w ill help in addressing more clinical aspect as co m p ar ed t o t r adi t i on al w ay of t ak in g examinat ion.
· Easy t o administer.
· Overall know ledge of t he st udent s in each t op-ic can be assessed.
OSCE is f easible m et hod of evaluat ing t he individual st udent t o know t heir skills.
B. St udent s’ perce pt ion a bout OSCE: The
st udent s’ per cept ions Quest ionnair es it em s w er e divided int o f our cat egories (Cont ent , Validit y, St ress level, ut ilit y). The 5 point Likert scale of percept ions w ere analysed by M ean, SD and percentage of acceptance in Table 2.
Table: 2: Percept ion of St udent s about OSCE.
Easy t o pass 3.3 + 1.06 60 Viva – voice is bet t er 2.7 + 1.25 30 Fair 4.2 + 0.63 90
Cheat ing w as minimized 4.2 + 0.92 90 Less st ressf ul 4.3 + 0.48 100 Exhaust ing and Lengt hy 3.3 + 1.16 70
Percentage of Agree* on Likert scale
Covered w ide know ledge
Personalit y, et hnicit y, face value doesn’t affect t he
OSCE scor e
At t it ude of examiner w as bet t er Opport unit y t o learn real
clinical area
100
S. No Cat egory Item s Students response M ean + SD
Content 1
4.3 + 0.48
2 4.1 + 0.74 80
Level of stress 3
90 4.3 + 0.95
Validity
4
4.7 + 0.48
4.4 + 0.52
4.2 + 1.03 80 100 100 4.3 + 0.48 100
Ut ility
Leads t o incr eased decision making abilit y OSCE should follow as assessment in UG physiot herapy course Help t o ident ifies t heir deficiencies in clinical skills
* = Agree and st rongly agree com bined t oget her
The follow ing are some of t he responses t o t he
open comments of the students’ percept ion
about OSCE met hod of assessment . One of t he student s perceived t hat durat ion of each st at ion should be more t han 5 minut es.
· OSCE is t he best met hod for clinical exam. · No Performance pressure
· Fear of facing t he examiner is minimized. · In fut ure, exam should be conduct ed in t he OSCE met hod.
· No bias.
· Act ual decision making, communicat ion ability, and clinical know ledge are judged.
· Timing of each stat ion should be more t han 5 minute
All t he st udent s have agreed t hat OSCE has covered a w ide know ledge, less st ressful and it pr o vides oppor t unit y t o lear n r eal clini cal scenario, leads t o increased decision m aking ability. They perceived that OSCE helps t o identify t heir deficiencies in clinical skills. M ore t han 80% of t he st udent s felt t hat OSCE should be an assessment t ool for t he physiot herapy course in w hich manipulat ion of score on t he basis of personalit y, et hnicit y and face value is not possible and it should be im plem ent ed as a clinical assessment .
The ent ire facult y perceived t hat OSCE helping t o enhance t he evaluat ion met hod of clinical assessm ent . M ore t han 85 % of t hem agreed t hat it covers w ide know ledge and helps t o assess future performance without the influence of personalit y, et hnicit y, and face value.
Bot h facult y and student s felt that OSCE met hod of clinical assessment is less st ressful but more exhaust ing and lengt hy. Only less t han 40 % of t he st udent s and facult y w ere comfort able w it h t radit ional viva voice of clinical assessment . Both groups w ere satisfied except t hat it require more preparat ory period for t he exam, as t hey expressed in open comment s.
DISCUSSION
OSCE has been int roduced int o predominant ly m ed ical ed ucat i on an d o t h er f i el ds as an assessm ent t ool t hat enables t he object ive evaluat ion of t he clinical skills. The OSCE can eval u at e t he p sych om o t o r, af f ect i v e an d
cognit ive domain bet t er t han exist ing w rit t en exam.
Clinical competence includes t he ability t o solve problems, t o t hink crit ically in order t o apply clinical reasoning, t o w ork as a t eam and t o com m unicat e effect ively in bot h ver bal and w r it t en f o r m s. All o f t h ese sk il ls ar e also necessary for a physiot herapist w hich could be assessed by OSCE. So t hat w e need t o ident ify t he level of stake holders acceptance by pilot st udy of percept ion.
In Erfanian and Khadivzadeh st udy, 80 percent of mid w ife st udent s of M ashhad universit y of M edical Science (Iran) report ed t hat t hey are highly and very highly sat isfied w it h OSCE t est [12].
Amiri M , Nickbakht M st at ed t hat highest level of sat isfact ion among audiology st udent s w it h t he equipment used in OSCE [13]. In our st udy, st udent s and facult y w ere sat isfied about OSCE and recommended t o implement in t he fut ure exam.
Sadia S et al st at ed t hat st udent s rat ed OSCE t o be bet t er and large number of st udent s felt t hat OSCE was easier than ot her evaluat ion met hods. Their result s show ed t hat medical st udent s had a po si t i v e at t it u d e t o w ar d s OSCE as an alt ernat ive t o assess clinical skills [14]. The present study results, bot h groups were st rongly agreed and show ed posit ive at t it ude t ow ards OSCE.
Saadeldin et al st udy concluded t hat st udent s an d t each er s accep t ed t hat t h i s t y p e o f exam inat ion is bet t er t han t he t r ad it ional examination. M ost of t he st udent s and t eachers agreed t hat examiner bias may be eliminat ed by follow ing t his t ype of assessment . OSCE w as considered as quit e st ressful. Bot h w ere agreed t hat t his t ype of examination may be exhausting and st ressful w it h increased number of st at ion and t im e of t he exam4. The sam e kind of st at em ent w as present ed in our st udy. But according to stress as concern bot h st udent s and facult y felt less t han ot her met hod of exams.
Limit at ions of t he st udy: Sampling size is small, only one exam w as conduct ed.
facult y and st udent s of Physiot herapy w hen int roducing t he OSCE assessment format int o undergraduat e Physiot her apy cur riculum . It helps t o st andar dize physiot her apy clinical assessm ent am ong st udent s t hose w ho are appearing for examinat ion. Our fut ure aim is t o implem ent OSCE in Physiot herapy educat ion syst em t o cult ivat e good clinical t herapist
Conflicts of interest: None
REFERENCES
[1]. Naumann F.L. & M oore K.M . Developing an Objective St r uct ur ed Clinical Exam inat ion t o assess Clinical Com pet ence. Aust ralian Collaborat ive educat ion net work National conrference M elbourne/ Geelong 2012.
[2] . Hiroaki Sakurai, Yoshikiyo Kanada, Yoshit o Saugi-ura, Ikuo M ot oya, M a yuki Yam aka, M asao Tom aita, Toshio Teranishi, Shigeo Tanabe . Standardizat ion o f cl i n i cal ski l l e v al u at i o n i n Ph y si cal / Occupat ional educat ion – Effect s of Int r oduct ion o f an ed u cat i o n syst em u si n g OSCE. Jo u r n al Physical t herapy Science.2013;25:1071-1077. [3] . Wass V Van der Vhat zer J , Jones R. Assessm ent of
clinical com pet ence. Lancet . 2001;357(9260):945-949.
[4] . Saadeldin A. Idris, Aam ir A. Ham za, M oham m ed M .Haf iz, M oham m ed Eltayeb A: Teachers’ and st udent s’ percept ions in surgicasl OSCE exam : A p i l o t st u d y. Op en sci e n ce Jo u r n al o f educat ion.2014;2(1):15-19.
[5] . Sood R. A rat ional appr oach for t he assessm ent of clinical com pet ence of undergraduat e m edical st u d en t s. J Asso ci at i o n Ph y si ci an s I n d i a. 1999;47:980-4.
[6]. Sharon l. Gorm an, Rolando lazaro, Judit h Fairchild. Developm ent and im plem ent at ion of an object ive st r u ct u r ed cl i n i cal e xam i n at i o n ( OSCE) i n Ne u r o m u scu l ar Physi cal Th er ap y. Jo u r n al o f physical t herapy Educat ion.2010;24(3):62-68. [7] . Agarw al A, Bat ra B, Sood AK, Ram akant an R,
Bhar-gava SK, Chidam bar anat han N, et al. Object ive st r uct ured clinical exam inat ion in radiology. Indian J Radiology Im aging. 2010;20:83-8.
[8] . Cibele C.B.M . Silva, Adriana C. Lunardi, Felipe A.R. M en des, Fl avi a F.P.So u za, Cel so R.F.Car val h o . Ob ject i ve St r u ct u r ed cli nical eval uat io n as an assessm en t m et h od f or u n der gr ad u at e chest physical t herapy st udent s: a cross – sect ion st udy. Revista Brasiler ia De Fisiot erapia. 2011;15(6):481-486.
[9] . Sharon l.Gor m an, Rolando lazaro, Judit h Fairchild. Developm ent and im plem ent at ion of an object ive st r u ct u r ed cl i n i cal e xam i n at i o n ( OSCE) i n Ne u r o m u scu l ar Physi cal Th er ap y. Jo u r n al o f physical t her apy Educat ion.2010; 24(3):62-68.
CONCLUSION
[10]. Am er Al Saif, and Sam ira Alsenany. The Object ive Struct ured Clinical Exam (OSCE): A Qualit at ive St udy exploring Physical Therapy St udent ’s Experience. Journal of Am erican Science 2013;9(6):615-621. [11].M arcie Sw if t ; Ellen Spake, Byron J Gajew ski. The
Rel i ab i l i t y o f a M u scu l o sk e l e t al Ob j e ct i v e St r uct ur ed Clinical Exam inat ion in a Prof essional Physical Ther apist Pr ogr am . Journal of Physical Therapy Educat ion 2013;27(2):41.
[12]. Erfanian F, Khadivzadeh T, Evaluat ion of m idw ifery st udent s com pet ency in pr oviding int raut er ine device services using object ive st r uct ured clinical exam i n at i o n . Ir an i an j o u r n al o f n u r si n g an d m idw ifery resear ch, 2011;16(3):191-6.
[13]. Am iri M , Nickbakht M . The object ive st r uct ured clinical exam inat ion: A st udy on sat isficat ion of t he st udent s, f acult y m em bers and t ut or s. Lif e science jour nal 2012;9(4):4909- 4911.
[14]. Sadia S, Sultana S, Waqar F, Original art icle- SCE as an Assessm e n t To o l : Pe r ce p t i o n s o f Undergraduat e M edical St udent s. An int ernat ional jou r nal o f anaest hesiology, pain m anagem ent , i n t e n si v e car e & r esu sci t at i o n . h t t p :/ / w w w.apicareonline.com / ?p=1637
How to cite this article:
M ullai Dhinakaran, Jugesh Chatt wal, Dheeraj K.V. FACULTY AND STUDENT PERCEPTIONS ON THE INTRODUCTION OF OBJECTIVE STRUCTURED CLINICAL EXAM INATION IN AN UNDERGRADUATE PHYSIOTHERAPY COURSE: A PILOT STUDY. Int J Physiot her Res 2015;3(6):1307-1311. DOI: