w ww.e l s e v i e r . c o m / l o c a t e / b j p
Original
Article
Isolation
and
identification
of
cytotoxic
compounds
from
a
fruticose
lichen
Roccella
montagnei,
and
it’s
in
silico
docking
study
against
CDK-10
Tripti
Mishra
a,
Shipra
Shukla
a,
Sanjeev
Meena
b,
Ruchi
Singh
c,
Mahesh
Pal
a,∗,
Dalip
Kumar
Upreti
d,
Dipak
Datta
baPhytochemistryDivision,CSIR-NationalBotanicalResearchInstitute,Lucknow226001,India bBiochemistryDivision,CSIR-CentralDrugResearchInstitute,Lucknow226031,India
cBiotechnologyDivision,CSIR-CentralInstituteofMedicinalandAromaticPlants,Lucknow226015,India
dPlantDiversity,SystematicsandHerbariumDivision,CSIR-NationalBotanicalResearchInstitute,Lucknow226001,India
a
r
t
i
c
l
e
i
n
f
o
Articlehistory:
Received6February2017
Accepted7July2017
Availableonline7September2017
Keywords:
Dockingstudy
Roccellicacid
Everninicacid
Cytotoxicactivity
a
b
s
t
r
a
c
t
RoccellamontagneiBél.belongstolichenfamilyRoccelleceaegrowingluxuriantlyalongthecoastalregions ofIndia.AsRoccellahasbeenshowntobebioactive,wepreparedmethanolicextractandassessedits anticancerpotential.Themethanolicextractshowedsignificantinvitrocytotoxicactivityagainstfour humancancercelllinessuchascolon(DLD-1,SW-620),breast(MCF-7),headandneck(FaDu).This promptedustoisolatebioactivecompoundsthroughcolumnchromatography.Twocompounds roccel-licacidandeverninicacidhavebeenisolated,outofwhicheverninicacidisreportedforthefirsttime. Boththecompoundshavebeentestedforinvitrocytotoxicactivityinwhichroccellicacidshowedstrong anticanceractivityascomparedtotheeverninicacid.CyclinDependentKinase(CDK-10)contributesto proliferationofcancercells,andaberrantactivityofthesekinaseshasbeenreportedinawidevarietyof humancancers.Thesekinasesthereforeconstitutebiomarkersofproliferationandattractive pharmaco-logicaltargetsfordevelopmentofanticancertherapeutics.Thereforeboththeisolatedcompoundswere testedforinsilicomoleculardockingstudyagainstCyclinDependentKinaseisomerenzymetosupport thecytotoxicactivity.
©2017SociedadeBrasileiradeFarmacognosia.PublishedbyElsevierEditoraLtda.Thisisanopen accessarticleundertheCCBY-NC-NDlicense(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Introduction
Lichenisasymbioticself-supportingmutualismshowsawide rangeof habitats throughout theworld.It is a stableorganism betweenmycobiontandphotobiont.(HawksworthandHonegger, 1994)Theyfoundgrowingonrocks,bricks,soil,rottingwoodetc. Lichensareapotentialsourceofdifferentbiologicalactivityas anti-tubercular(Marshak and Kuschner,1950), anticancer(Williams etal.,1998),anti-HIV(HuneckandYoshimura,1996)antipyretic analgesic(Müller,2001).
Thelichen species Roccellamontagnei Bél.belongs to family Roccellaceae,foundcommonasepiphytesalongtheCoromandel Coast,TamilNadu,IndiaanditisabundantinPichavaram man-groveforests.Itisafruticosegrowthform(Tehleretal.,2004).R.
montagneiisa richsourceof somanysecondarymetabolitesas
∗ Correspondingauthor.
E-mail:m.pal@nbri.res.in(M.Pal).
orcinol,montagnetol,-carotene,-sitosterol,erythritol,roccellic acid,lecanoricacidandmethylorsellinateetc.(Mittaletal.,1952). ApreviousreportconfirmsthebiologicalimportanceofR.
mon-tagneiforitsantimicrobialactivity(Balajietal.,2006),insecticidal
activity(Nanayakkaraetal.,2010)andanti-inflammatoryactivity (Cetinetal.,2008).
Thepresentworkdealswiththeprimaryscreeningofcytotoxic activity of methanolicextract, isolation of bioactive molecules, structureelucidationofisolatedcompoundsandidentificationof compoundresponsibleforcytotoxicactivityofR.montagnei.
Materialsandmethods
Lichenmaterial
Inthepresentstudy,lichenmaterials(RoccellamontagneiBél., Roccellaceae)werecollectedfromKovalamSeashore Thirvananth-puram,Kerala,IndiagrownoverCocoesnuciferabarksinthemonth ofAugust2013andwereauthenticatedbyTaxonomyDivision,CSIR
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjp.2017.07.006
0102-695X/©2017SociedadeBrasileiradeFarmacognosia.PublishedbyElsevierEditoraLtda.ThisisanopenaccessarticleundertheCCBY-NC-NDlicense(http://
–NationalBotanicalResearchInstituteLucknow,India.Herbarium specimens(12634)werepreparedanddepositedattheHerbarium oftheInstitute.
Extraction
Driedlichenmaterial(100g)weremilledintopowderandthen extractedwithmethanol(2.5l)inanextractorfor36h.Theextract wasevaporatedinarotatoryevaporatoranddriedbyvacuumpump toaffordthe7.5gofmethanolicextract.
Compoundisolation
Methanolicfraction(5g)wassubjectedtochromatographyon silicagel(60–120mesh)elutedwithastepwisegradientof hexane-ethylacetate(9.5:0.5,9:1,8.5:1.5,8:2,7.5:2.5,7:3)byvolumeto affordatotalof500fractionsof50mleach.Columnfractionswere analyzedbyTLC,andfractionswithsimilarTLCpatternswere com-binedtogivefivemajorsubcolumnfractions.Columnfraction-1 wasfurtherpurifiedtogive21.5mgofeverninicacid(21.5mg)(1) whitecrystallinecompound(Yusofetal.,2015).Fraction2was fur-therpurifiedtogive16mgofwhitepowdered(2)Roccellicacid (HuneckandYoshimura,1996).
Cytotoxicactivity
Cellcultureandsamplepreparation
MethanolicextractalongwithisolatedcompoundofR. montag-neiweretestedforinvitrocytotoxicactivityagainstfivecancercell lines.Thehumancancercelllinessuchascolon(DLD-1)andbreast (MCF-7)weremaintainedinRPMI-1640medium,whereashead andneck(FaDu)andcoloncelllines(SW-620)inDMEMmedium. Thetestsamples/moleculesweighedinmicro-centrifugetubesand stocksolutionsof100mg/mlwerepreparedbydissolvingthe sam-plesinDMSO.Stocksolutionswerestoredat−20◦C. Aworking
solutionof100g/mlwaspreparedbydilutingthestocksolution inculturemedium(RPMI-1640with5%FBS)priortotheassay.
Cytotoxicityassay(SRBassay)
ThestandardcolorimetricSRBassaywasusedforthe measure-mentofcellcytotoxicity(Krishnaetal.,2014;Mishraetal.,2016).In brief,10,000–30,000cellsdependingonthedoublingtimeofeach celltypewereseededtoeachwellof96-wellplatein5%serum con-taininggrowthmediumandincubatedovernighttoallowforcell attachment.Cellswerethentreatedwiththetestsample(100l) togiveafinalconcentrationof100g/mlandduplicatewellswere included.Untreatedcellsreceivingthesamevolumeofvehicle con-tainingmediumservedascontrol.After48hofexposure,cellswere fixedwithice-cold50%TCA,stainedwith0.4%(w/v)SRBin1%acetic acid,washedandairdried.Bounddyewasdissolvedin10mMTris baseandabsorbancewasmeasuredat510nmonaplatereader (EpochMicroplate Reader,Biotek, USA).Thecytotoxiceffects of compoundswerecalculatedaspercentageinhibitionincellgrowth aspertheformula.
%ofcellskilled=100−
MeanODtestMeanODcontrol×100
Moleculardockingstudies
Compoundroccellicacidand everninic acidisolated fromR.
montagneihavebeenevaluatedforcytotoxicactivityandfurtheras
asupportivestudythesetwocompoundsalongwiththestandard drugdoxorubicinhavebeenevaluatedforinsilicomolecular dock-ingstudy.Therefore,inthisstudythecompoundswereselected astheligandbyusingHomosapiensCyclinDependentKinase-10
100.00
80.00
0.00 20.00 40.00 60.00
DLD-1 SW620 FaDu MCF-7
Cancer cell line
% Inhibition
MeoH Extract Conc_ 100µg/ml
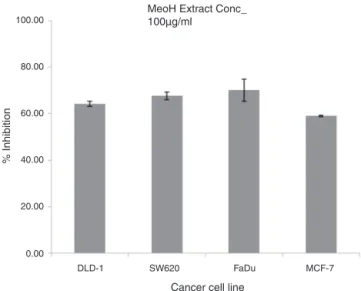
Fig.1. Cytotoxicactivityofthemethanolextract(100g)againstbreastandcolon
cancercelllines.
(CDK-10isomer)asthebaseenzyme.Theproteinencodedbythis genebelongstotheCDKsubfamilyoftheSer/Thrproteinkinase family.TheCDKsubfamilymembersareknowntobeessentialfor cellcycleprogression.Thiskinasehasbeenshowntoplayarolein cellularproliferationanditsfunctionislimitedtocellcycleG2-M phase.Cyclindependentkinasescontributestoproliferationof can-cercells,andaberrantactivityofthesekinaseshasbeenreported inawidevarietyofhumancancers.Thesekinasestherefore con-stitutebiomarkersofproliferationandattractivepharmacological targetsfordevelopmentofanticancertherapeutics.(Peyressatre et al., 2015). The autodock 4.2 docking software was used to performmoleculardockingsimulationbetweenCDK-10andthe compounds isolatedfromR. montagneialong withdoxorubicin. SequencehasbeenobtainedbyNCBIandmodelofCDK-10hasbeen preparedfromITASSERserver(Zhang,2007).MGLTools-1.4.6was usedtoprepareprotein(protein.pdbqt)andtowritegridparameter file(protein.gpf)anddockingparameterfile(ligand.dpf).Protein preparation includes:(i)removalofwater andionsand extrac-tion of co-crystallized ligand; (ii)addition of polar hydrogens; (iii)assignmentofAD4atomtype;andfinally(iv)assignmentof Gasteigercharges.Thegridmapsrepresentingthenativeligandin theactualdockingtargetsitewerecalculatedwithautogrid4with boxdimensionof126×126×126 ˚Aandspacingof0.375 ˚Aby
tak-ingthecenteroftheligandasthecenterofthegrid.Dockingofthe ligandwasdonewithdefaultparameters.
Resultanddiscussion
Cytotoxicactivity
Roccella montagnei thallus was extracted in methanol and
IsolationofpurecompoundsfrommethanolicextractofRoccella montagnei
Themethanolicextractwascolumnchromatographedover sil-ica to obtainpure compounds. Isolated pure compounds were identifiedbymeansofspectroscopicanalysis,andtheywere iden-tifiedaseverninic acid(1)and roccellicacid(2).Everninicacid (1) resultedas a white crystallinesolid and its mass spectrum exhibited molecular ion peak at m/z 182, with the molecular formulaC9H10O4.UVspectroscopysignifiesabsorptionbandsat
550nm,moreoverIRspectraofcompound1showedfrequencies at3390cm−1and3400cm−1indicatingthepresenceofaromatic
hydroxyl group.MS spectra shows basepeak at m/z 149were attributed to orsellinic acid moiety. Proton NMR spectroscopy showspeakat11.58forhydroxylgroup.Twosignalsat6.19and 6.20 attributed to aromatic proton methyl singlet at 2.438 for methylgrouppresentatbenzenering.Signalat3.93denotesfor methoxygroup.The13CNMRspectrashowedninecarbons,
sig-nalat␦173.559showedpresenceofcarboxylicgroupandsignalat 52.344showspresenceofmethoxygroupwhichwerethe charac-teristicsignalsof thecompound(1).Signalat166.031,163.803, 144.684 and 106.073 indicated quaternary carbons along with 101.867,112.640fortertiarycarbononesignalat24.271shows methylgrouppresence(Yusofetal.,2015).Allthespectroscopic detailsindicatedthatitisorsellinicacid-4-methylether(everninic acid)withmolecularformulaC9H10O4.Roccellicacid(2)resulted
aswhiteamorphoussolidanditsmassspectrumshowsmolecular ionpeakatm/z300,withthemolecularformulamoreoverIR spec-traofcompound2showsfrequenciesat3000,2900corresponds tocarboxylicgroup.MSspectrashowsbasepeakat283.Proton NMRspectroscopyshowspeakat0.88(t, CH3),1.17(d, CH3),
1.284(s, CH2).The13CNMRspectrashowedninecarbons,
Sig-nalat␦178.988and178.244showedpresenceoftwocarboxylic groups.Signalat30.822showstripletandat30.51doubletsand at30.684singletpeak.Allthespectroscopicdataindicated that thecompoundisRoccellicacidwithmolecularformulaC17H32O4
(HuneckandYoshimura,1996).
CHO
H
H O
HO
HO OH
O O O
CH3
CH3
OCH3
1 2
ItisknownthattheeverninicacidisalreadyreportedinCladonia
multiformis,however,tothebestofourknowledge,theisolation
andcharacterizationofeverninicacidfromR.montagneihasnot beenreportedearlier.Boththeisolatedcompoundswereidentified onthebasisofUV,IRand1HNMRdataandcomparedandvalidated withtheexistingliterature.
Cytotoxicactivityofisolatedcompound
Isolatedcompounds have beenevaluated at100g/ml dose
wereforinvitrocytotoxicactivityagainsttwocancercelllinesi.e.
breastcancer(MCF-7,MDAMB-231)andcoloncancer(DLD-1, SW-620)(Fig.2).Itisneededtomentionherethatthedosesofpure compoundsmayvaryatmicromolelevel.Thedoseof100g/ml ofeverninicacidandroccellicacidare548.92Mand332.85M respectivelyaspercalculation,thustheeverninicacidshowslower cellgrowthinhibitionpercentageathigherdoseatmicromolescale androccellicacidfoundtohavesignificantcellgrowthinhibition
100.00
80.00
60.00
40.00
20.00
0.00
DLD-1 MCF-7 MDAMB-231 SW620
Cancer cell lines
Everninic Acid
Roccellic Acid Drugs Conc_100µg/ml
% Inhibition
Fig.2.Cytotoxicactivityofisolatedcompoundsagainstbreastandcoloncancercell
lines.
at100g/ml(332.85M)doseagainstMCF-7andDLD-1i.e.75.84 and87.90%,respectively,howeveritwaseffectiveagainst MDAMB-231with65.30%cellgrowthinhibition.Outofisolatedcompounds roccellicacidwasfoundtobecytotoxicagainstdifferentcancercell linesbutshowsmostsignificantcytotoxicactivityincoloncancer i.e.DLD-1.ThusIC50ofboththecompoundshavebeencalculated
asperdoseresponsecurveagainstDLD-1tocomparethe cyto-toxiceffects(Fig.3).IC50ofroccellicacidwasfound71.26g/ml
(237.18M)whereaseverninicacidshowsIC50valuemorethan
100g/ml.
In-silicocomparativemoleculardockingstudiesofisolated
compoundsagainstCDK-10
Toinvestigatetheeffectofdifferentcompoundsoncancercell linewehavechosenCyclinDependentKinase-10(CDK-10isomer)
ofHomosapiensassubstratebecauseitisanimportantenzymein
thegrowthphaseofthecancerouscells.Everninicacidandroccellic acidhavechosenasligands.Moleculardockingisthesimulations ofbindingofeverninicacidandroccellicacidwithactivesiteof CDK10wascarriedoutusingAutodock4.2.Fromthisstudywecan concludeaboutH-bondinteractionswiththeactivesiteresidues. EverninicacidformsoneHbondwiththehydrogenofARG71:HH11 alongwiththecarbonyloxygenofeverninicacidLIG1:O.(Fig.4)The estimatedfreebindingenergyofeverninicacidis−6.65kcal/mol
withthe estimated inhibition constant, Ki=13.37M. Roccellic acidformstwohydrogenbonds,onewiththehydrogenofroccellic acidalongwithnitrogenofALA187andotherisbetweenoxygen ofroccellicacidwithhydrogenofASN343HD22(Fig.5).Roccellic acidhasshownestimatedfreeenergyofbinding−6.75kcalmol−1
estimatedinhibitionconstant,Ki=11.35M.
Conclusion
60
60 80
40
40
20
20
0
0
-20 -20
-40 -40
100µg 50µg 25µg 12.5µg 12.5µg 6.25µg 6.25µg 100µg 50µg 25µg
Drug Conc_ Drug Conc_
% Inhibition % Inhibition
Everninic Acid
IC50 Value>100
Roccellic Acid
Ic50 Value 71.26±2.0
Fig.3.Doseresponsestudyofeverninicacidandroccellicacidagainstcoloncancercellline(DLD-1).
Everninic Acid
Cyclin Dependent k
inase-10
1 H-Bonds
Fig.4. Moleculardockingstudyofeverninicacidagainstcyclindependentkinase-10.
2 H-Bonds
Cyclin Dependent Kinasa-10
Roccellic acid
Fig.5. Moleculardockingstudyofroccellicacidagainstcyclindependentkinase-10.
knowledgeeverninicacidisreportedforthefirsttimeinR.
mon-tagnei.Itisbelievedthatmajorityofcompoundsoriginatedfrom
fungalcomponent. Probablyeverninic acidmight beoriginated fromfungalcomponentofR.montagneiasitisalreadyreported
fromCladoniamultiformis(Yusofetal.,2015).Boththecompounds
havebeenevaluatedagainsthumancancercelllines.At100g roccellicacidshowssignificantactivityagainstbreast andcolon cancercelllines.Roccellicwasfoundtohavesignificantcellgrowth inhibitionagainstDLD-1withIC50value71.26g/mlasperdose
responsecurvestudy.Itis alsosupportedbyinsilicomolecular dockingstudywhichshowedthateverninicacidformoneand
roc-cellicacidshowedtwohydrogenbondingwithfreebindingenergy
−6.65kcal/moland−6.75kcal/molrespectively.Althoughroccellic
acidformtwohydrogenbondinteractionbutfreebindingenergy ofroccellicacidfoundtohavelesserthaneverninicacidthusitis confirmedthatroccellicacidfoundtohavebettercytotoxicactivity overeverninicacid.
someothernovelcompoundresponsibleforsignificantcytotoxic activityofR.montagnei.
Ethicaldisclosures
Protectionofhumanandanimalsubjects. Theauthorsdeclare thattheproceduresfollowedwereinaccordancewiththe regula-tionsoftherelevantclinicalresearchethicscommitteeandwith thoseoftheCodeofEthicsoftheWorldMedicalAssociation (Dec-larationofHelsinki).
Confidentialityofdata. Theauthorsdeclarethattheyhave fol-lowed theprotocolsof theirworkcenter onthepublication of patientdata.
Right to privacy and informed consent. The authors have obtainedthewritteninformedconsentofthepatientsorsubjects mentionedinthearticle.Thecorrespondingauthorisinpossession ofthisdocument.
Authors’contributions
Conceivedanddesigntheexperiments:MPDDDKU.Performed theexperiments:TMSS,SM,andRS.Analyzedthedata:MPDD. Contributedreagents/material/analysistools:DDDKU.Wrotethe paper:MPTMSSSM.
Conflictsofinterest
Theauthorsdeclarenoconflictsofinterest.
Acknowledgements
TheauthorsarethankfultotheDirector,CSIR-NationalBotanical Research Institute, Lucknow, Indiafor facilities and encourage-ments.ThefinancialsupportreceivedfromtheCouncilofScientific andIndustrialResearch,NewDelhiundertheproject ‘Bioprospec-tionofPlantResourcesandOtherNaturalProducts(BSC-0106)’is dulyacknowledged.
References
Balaji,P.,Bharath,P.,Satyan,R.,Hariharan,G.,2006.Invitroantimicrobialactivity
ofRoccellamontagneithallusextracts.J.Trop.Med.Plant7,169–173.
Cetin,H.,Tufan-Cetin,O.,Turk,A.O.,Tay,T.,Candan,M.,Yanikoglu,A.,Sumbul,
H.,2008.Insecticidalactivityofmajorlichencompounds,(−)-and(+)-usnic
acid,againstthelarvaeofhousemosquito,CulexpipiensL.Parasitol.Res.102, 1277–1279.
Hawksworth,D.,Honegger,R.,1994.Thelichenthallus:asymbioticphenotypeof
nutritionallyspecializedfungianditsresponsetogallproducers.In:Williams, M.A.J.(Ed.),PlantGalls.Organisms,Interactions,Populations,TheSystematics AssociationSpecialVolume,vol.49.ClarendonPress,Oxford,pp.77–98.
Huneck,S.,Yoshimura,I.,1996.IdentificationofLichenSubstances.Springer,Berlin.
Krishna, S.,Singh, D.K.,Meena, S.,Datta, D.,Siddiqi, M.I., Banerjee, D.,2014.
Pharmacophore-basedscreeningandidentificationofnovelhumanligaseI inhibitorswithpotentialanticanceractivity.J.Chem.Inf.Model.54,781–792.
Marshak,A.,Kuschner,M.,1950.Theactionofstreptomycinandusnicacidonthe
developmentoftuberculosisinguineapigs.PublicHealthRep.(1896–1970), 131–144.
Mishra,T.,Pal,M.,Meena,S.,Datta,D.,Dixit,P.,Kumar,A.,Meena,B.,Rana,T.,Upreti,
D.,2016.Compositionandinvitrocytotoxicactivitiesofessentialoilof
Hedy-chiumspicatumfromdifferentgeographicalregionsofwesternHimalayaby principalcomponentsanalysis.Nat.Prod.Res.30,1224–1227.
Mittal,O.,Neelakantan,S.,Seshaadri,T.,1952.ChemicalinvestigationofIndian
lichens.XIV.ChemicalcomponentsofRamalinacalicarisandRamalinasinensis. J.Sci.Ind.Res.IndiaB11,386–387.
Müller,K.,2001.Pharmaceuticallyrelevantmetabolitesfromlichens.Appl.
Micro-biol.Biotechnol.56,9–16.
Nanayakkara,C.,Bombuwala,K.,Kathirgamanathar,S.,Adikaram,N.,Wijesundara,
D.,Hariharan,G.,Wolseleys,P.,Karunaratne,V.,2010.Effectofsomelichen
extractsfromSriLankaonlarvaeOfaedesaegyptiandthefungusCladosporium cladosporioides.J.Natl.Sci.Found.SriLanka33,147–149.
Peyressatre,M.,Prével,C.,Pellerano, M.,Morris,M.C., 2015.Targeting
cyclin-dependent kinases in human cancers: from small molecules to peptide inhibitors.Cancers7,179–237.
Tehler,A.,Dahlkild,Å.,Eldenäs,P.,Feige,G.B.,2004.Thephylogenyandtaxonomy
ofMacaronesian,EuropeanandMediterraneanRoccella(Roccellaceae, Artho-niales).Symb.Bot.Upsal.34,405–428.
Williams,D.E.,Bombuwala,K.,Lobkovsky,E.,deSilva,E.D.,Karunatne,V.,Allen,
T.M.,Clardy,J.,Andersen,R.J.,1998.AmbewelamidesAandB,antineoplastic
epidithiapiperazinedionesisolatedfromthelichenUsneasp.TetrahedronLett. 39,9579–9582.
Yusof,H.,Azahar,H.,Din,L.B.,Ibrahim,N.,2015.Chemicalconstituentsofthelichens
CladoniamultiformisandcryptotheciaSP.Malay.J.Anal.Sci.19,930–934.
Zhang,Y.,2007.Template-basedmodelingandfreemodelingbyI-TASSERinCASP7.