Microphysical processing of aerosol particles in orographic clouds
Texto
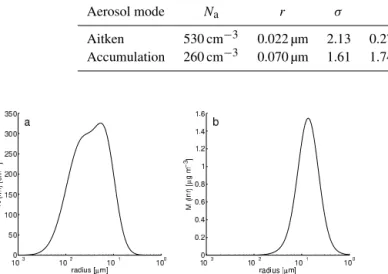
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
changes in wind speed over the ocean on aerosols characteristics using collocated measurements of aerosol number size distribution, mass concentration, and spectral aerosol
Large variation in microphysical characteristics of the boundary layer clouds and the aerosol concentration were found, and in particu- lar the CDP cloud droplet number concentration
We find that the variability in the CCN concentrations in the central Amazon is mostly driven by aerosol particle number concentration and size distribution, while variations in
The well- predicted aerosol quantities, such as aerosol number, mass composition and optical properties, and the inclusion of full aerosol-cloud couplings lead to
The comparison of the total aerosol number size distribu- tions, including BC-free particles (representing the largest fraction, and a minor fraction of BC-containing particles), of
In this study, we analyzed number concentration and size distribution of aerosol particles, together with the mass concentration and chemical composition of UFPs and PM 1
The atmospheric visibility was dependent on aerosol number size distribution and its impairment during the hazy episodes was mostly caused by the enhancement of aerosol concentration
Then global simulations will analyze the sen- sitivity of ACI to many different aspects of cloud micro- physics, including sensitivity to (1) activation, (2) precipi- tation, (3)