105
Original Article
REVISTA PAULISTA DE MEDICIN AIncide nce of
Gardnerella vaginalis, Candida sp
and
human papilloma virus in cytological sme ars
Discipline of Gynecology and O bstetrics,
Faculdade de Medicina do Triângulo Mineiro, Minas Gerais, Brazil
a b s t r a c t
CON TEX T: In spite o f the wide-rang ing literature o n the micro bio l-o g y l-o f nl-o rmal and abnl-o rmal fll-o ra l-o f the vag ina, there are few studies o n the relatio nship between human papillo ma virus (HPV) and o ther vag inal micro o rg anisms.
OBJECTIVE: To analyz e the frequency o f infectio n by human papil-lo ma virus (HPV) and o ther ag ents like Candida sp., G ardnerella vag inalis and Tricho mo nas vag inalis in cyto lo g ical smears.
DESIGN STUDY: Retro spective study
SETTIN G: A public tertiary referral center.
SAM PLE: An analysis o f 1 7 ,3 9 1 cyto lo g ies fro m o utpatients seen between January 1 9 9 7 and Aug ust 1 9 9 8 . The co ntro l g ro up was made up o f patients in the same ag e g ro up and same perio d with no cyto lo g ical evidence o f HPV infectio n. Patients with a diag no sis o f cervical intraepithelial neo plasia (CIN ) II o r III were excluded fro m this analysis.
M AIN M EASUREM EN TS: The diag no sis o f HPV infectio n was made in acco rdance with the criteria o f Schneider et al. and the diag no sis o f G ardnerella vag inalis was made with a finding o f clue cells.
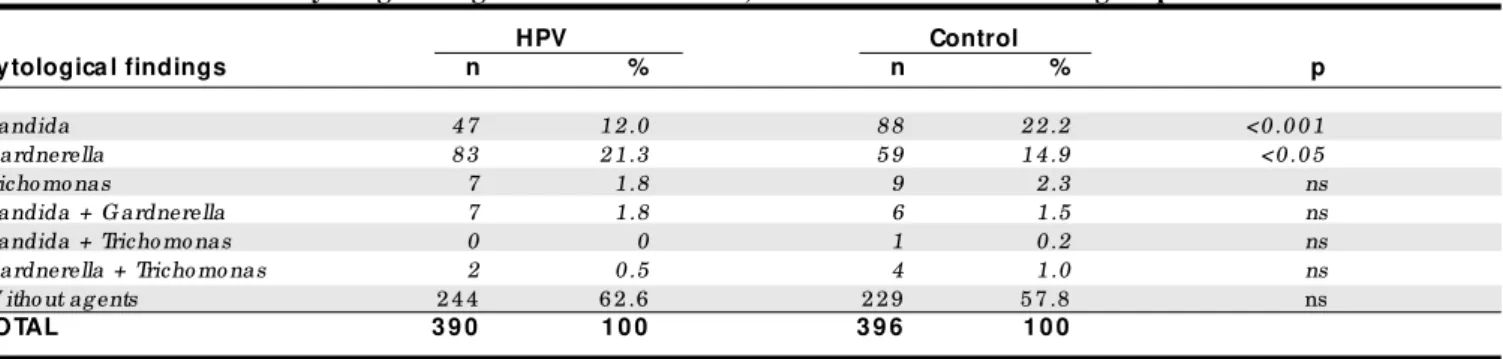
RESULTS: 3 9 0 (2 .2 4 %) had alteratio ns co nsistent with infectio n by HPV, so metimes a sso c ia ted with CIN I. The results sho wed tha t G ardnerella vag inalis was the mo st frequent ag ent in wo men with HPV infectio n (2 3 .6 % versus 1 7 .4 %; P <0 .0 5 ), while in the co ntro l g ro up the mo st frequent ag ent was Candida sp. (2 3 .9 % versus 1 3 .8 %; p <0 .0 0 1 ).
CON CLUSION : In spite o f this study being based so lely o n cyto lo g i-cal criteria, in which specific HPV and G ardnerella diag no stic tests were no t used, the cyto lo g ical smear is widely used in clinical prac-tice and the data presented in this investig atio n sho w that there is an asso ciatio n between G ardnerella vag inalis and HPV infectio n. It re-mains to be established whether the micro o rg anisms favo r each o ther.
KEY W ORDS: Human papillo ma virus. G ardnerella vag inalis. Can-dida sp. Cyto lo g ical smear.
• Eddie Fernando Candido Murta • Maria Az niv Haz arabedian de So uz a • Eduardo Araújo Júnio r • Sheila Jo rg e Adad
INTRODUCTION
An extensive and diverse spectrum o f patho -genic and no n-patho -genic o rganisms may be o bserved in vaginal micro flo ra. In spite o f the wide-ranging lit-erature o n the micro bio lo gy o f no rmal and abno rmal flo ra o f the vagina, many questio ns have still no t been co mpletely answered.1,2 Vario us infectio us pro cesses
in the vagina are the result o f disequilibrium o f this flo ra1, such as that o ccurring during pregnancy.2 The
mo st co mmo n infectio ns are caused by Candida sp., Gardnerella vaginalis, Trichomonas vaginalis and Chlamydia trachomatis,who se frequencies vary amo ng no n-preg-nant wo men fro m 7 to 20.5%, 2 to 58%, 9 to 12% and 8 to 40%, respectively.3-5 Human papillo ma virus (HPV)
infectio n is also co mmo n and presents a frequency that varies fro m 13 to 46%, depending o n the po pula-tio n studied and the study metho d used.6,7
So me o f the epidemio lo gical facto rs related to greater incidence o f HPV infectio n are well-kno wn: yo ung wo men, especially tho se who start to be sexually active at a very early age, smo kers, pregnant wo men o r tho se using o ral co ntraceptives.8,9 Ho wever, there are few
stud-ies o n the relatio nship between HPV and o ther vaginal micro -o rganisms. The o bjective o f this wo rk was to study a gro up o f wo men with a cyto lo gical diagno sis o f HPV, to verify the frequency o f o thers agents, especially Candida sp., Gardnerella vaginalis and Trichomonas vaginalis.
METHODS
An analysis was made o f 17,391 cyto lo gies fro m o utpatients attended to in the perio d fro m January
106
1997 until August 1998. Of the to tal o f 17,391 cyto lo -gies, 390 (2.24%) had a cyto lo gical repo rt diagno sing HPV infectio n, so metimes asso ciated with cervical intrae pithe lial ne o plasia (CIN) grade I (lo w-grade squamo us lesio n). Patients with a diagno sis o f CIN II o r CIN III were excluded fro m this analysis.
The diagno sis o f HPV infectio n was made in ac-co rdance with the criteria o f Schneider et al.10 which
are based o n the presence o f classic co ilo cyto sis o r the presence o f six o r mo re o f the nine no n-classic criteria (mild co ilo cyto sis, mild dekerato sis, cyto plas-mic clarificatio n, kerato hyalin granules, cyto plasplas-mic striatio n, dekerato tic fusifo rm cells, nuclear hyperchro -matism, bi- o r multi-nucleatio n and perinuclear halo ). The diagno sis o f Gardnerella vaginalis was made with a finding o f clue cells. The co ntro l gro up was made up o f patients in the same age gro up and same perio d with no cyto lo gical evidence o f HPV infectio n. The co nco mitant presence o f fungus (Candida sp.), bacte-ria (Gardnerella and Actinomyces), pro to zo ans ( Trichomo-nas vaginalis) and infectio n by Herpes virus was ana-lyzed fo r bo th gro ups.
The X2 test was used fo r statistical analysis with
the significance level set at less than 0.05.
RESULTS
A distrib utio n o f patients with HPV infectio n is sho wn in Tab le 1, matched with the co ntro l gro up acco rding to age gro up. It can b e seen that 83.6% o f the patients with HPV infectio n were aged 40 o r un-der, and 38.7% were b etween 21 and 30. In the gro up with HPV infectio n, o ther agents were detected in 146 (37.4%) o f the 390 cases and in the co ntro l gro up, in 167 (42.2%) o f the 396 cases. Ho wever, this difference was no t c o nsid e re d statistic ally signific ant (
χ
2 =1.839; Yates co rrectio n = 1.647). There were 61 (15.6%) p re gnant p atie nts in the gro up with HPV and 70 (17.6%) in the co ntro l gro up. Tab le 2 sho ws the fre-q uency o f the mo st co mmo n infectio us agents in cy-to lo gical exams in the gro up with HPV, in relatio n cy-to the c o ntro l. It m ay b e o b s e rve d that G ardnerella vaginalis was the mo st freq uent agent in the gro up with HPV infectio n, while in the co ntro l gro up the mo st co mmo n agent was Candida sp. There was no statistically significant difference between the gro ups in relatio n to infectio n b y Trichomonas vaginalis. No cases o f Herpes virus and/o r Actino myces were o b -served in any o f the patients in the study gro ups.
DISCUSSION
The presence o f genital co -infectio ns, whether se xually transm itte d o r no t, m ay have im po rtance in the ce ll pro life ratio n asso ciate d with HPV. This pro b ab ly o ccurs thro ugh an incre ase in m o istne ss in the vaginal e nviro nm e nt.11 Kingho rn12 diagno se d
o the r ge nital infe ctio ns in 32% o f m e n and 61% o f wo me n who pre se nte d co ndylo mato us le sio ns, with 29% o f the m e n 28% o f the wo m e n having se xually transm itte d dise ase s (STD). In a study o f 179 m e n and 168 wo men with co ndylo mato us lesio ns, Carne13
fo und c o -infe c tio ns in 34% and 54% re sp e c tive ly,
Table 2 - Fre que ncy of infe ction by various age nts in the group of patie nts with cytological signs of HPV infe ction, in re lation to the control group
HPV Control
Cytologica l findings n % n % p
Candida 4 7 1 2 .0 8 8 2 2 .2 <0 .0 0 1
G ardnerella 8 3 2 1 .3 5 9 1 4 .9 <0 .0 5
Tricho mo nas 7 1 .8 9 2 .3 ns
Candida + G ardnerella 7 1 .8 6 1 .5 ns
Candida + Tricho mo nas 0 0 1 0 .2 ns
G ardnerella + Tricho mo nas 2 0 .5 4 1 .0 ns
W itho ut ag ents 2 4 4 6 2 .6 2 2 9 5 7 .8 ns
TOTAL 3 9 0 1 0 0 3 9 6 1 0 0
χ2 test ; ns = no t sig nificant.
Table 1 - Distribution of patie nts with cytological signs of HPV, compare d to the control group,
according to age group
HPV Control
Age group (yea rs) n % n %
< 2 0 9 9 2 5 .4 1 0 0 2 5 .3 2 1 -3 0 1 5 1 3 8 .7 1 5 3 3 8 .6 3 1 -4 0 7 6 1 9 .5 7 7 1 9 .5
4 1 -5 0 3 4 8 .7 3 5 8 .8
5 1 -6 0 1 8 4 .6 1 8 4 .5
> 6 1 1 2 3 .1 1 3 3 .3
TOTAL 3 9 0 1 0 0 3 9 6 1 0 0
107
with 80% o f the m e n and 51% o f the wo m e n having STD. Strand e t al.14 de te cte d HPV infe ctio n via PCR
in 30.5% o f the patie nts (66 m e n and 65 wo m e n) who we nt to an STD clinic fo r co nsultatio n b e cause o f sym p to m s, o r fo r tre atm e nt o f so m e se xually transm itte d dise ase . Vo o g, e t al.15 studie d the pre
s-e ncs-e o f Candida via culture in patie nts po sitive to DNA HPV, in re latio n to tho se ne gative to DNA HPV. A fre q ue ncy o f 26% in the first gro up and 16% in the se co nd was fo und. The pre vale nce o f Chlamydia was 6% in patie nts po sitive to DNA HPV, co m pare d to 12% in patie nts ne gative to DNA HPV. Othe r stud-ie s have d e m o nstrate d a p re vale nc e o f Chlamydia
varying fro m 12 to 18%.16,17
In o ur wo rk, we did no t analyze the fre q ue ncy o f Chlamydia, as cyto lo gy is no t the m e tho d re co m m e nde d fo r its diagno sis due to the m e tho d’s lo w se nsitivity,18 which wo uld thus
unde re stim ate the num b e r fo und.
Infectio n by Candida has been fo und in appro xi-mately 25% o f patients with HPV infectio n.12,15 Vo o g,
et al.15 raised the po ssibility that infectio n by Candida
co uld activate latent HPV infectio n. In o ur material, cyto lo gical diagno sis o f Candida was made in 13.8% o f the cases with HPV infectio n and in 23.9% o f the co n-tro l gro up (P < 0.001), the inverse o f the results o b-tained by Vo o g, et al.15 Ho wever, these autho rs did no t
age-match the gro ups which were po sitive and nega-tive to DNA HPV by age.
Studies o f vaginal flo ra in healthy wo men have d e m o nstrate d p e rc e ntage s o f 25% fo r Gardnerella vaginalis,4 and 10 to 55% fo r Candida sp.19 In o ur
mate-rial, independent o f the set o f sympto ms, respectively 23.9 and 17.4% o f wo men in the co ntro l gro up pre-sented Candida and Gardnerella vaginalis upo n cyto lo gical examinatio n, while in the gro up with HPV the pro -po rtio ns were 13.8 and 23.6%. This led us to questio n whether wo men who present Gardnerella in the vaginal flo ra co uld have a greater predispo sitio n to HPV in-fectio n. The risk facto rs fo r HPV inin-fectio n are already well kno wn and it is no t within o ur kno wledge that alteratio ns in the vaginal flo ra co uld have a ro le in predispo sitio n to this infectio n. On the o ther hand, there is no data in the literature indicating that HPV infectio n co uld favo r the gro wth o f Gardnerella in the vaginal flo ra. Platz-Christensen, et al.20
suggested that bacterial vagino sis is in so me way asso ciated with the develo pment o f CIN, i.e., as a co facto r to HPV.
In summary, in spite o f this study b eing b ased so lely o n cyto lo gic criteria, in which specific HPV and
Gardnerella diagno stics tests were no t used, the cyto -lo gical smear is widely used in clinical practice and the greater freq uency o f Gardnerella in patients with HPV infectio n fo und in this wo rk deserves deeper in-vestigatio n. The data presented in this inin-vestigatio n sho w that there is an asso ciatio n b etween Gardnerella vaginalis and HPV infectio n. It remains to b e estab -lished whether the micro o rganisms favo r each o ther. Better understanding o f vaginal physio lo gy and the po ssib le direct o r indirect relatio n b etween HPV and
Gardnerella vaginalis co uld lead to great strides fo rward in the understanding o f the physio patho lo gy o f HPV infectio n.
1. Faro S. Bacterial vaginitis. Clin Obstet Gyneco l 1991;34:582-6. 2. Slo tnick IJ, Hildebrandt RJ, Prysto wsky H. Micro bio lo gy o f the female
genital tract. Obstet Gyneco l 1963;21:312-7.
3. Fleury FJ. Adult vaginitis. Clin Obstet Gyneco l 1981;24:407-8. 4. Hammill HA. No rmal vaginal flo ra in relatio n to vaginitis. Ob stet
Gyneco l Clin No rth America 1989;16:329-6.
5. McCue JD, Ko maro ff AL, Pass TM, Co hen AB, Friedland G. Strategies fo r diagno sing vaginitis. J Fam Pract 1979;9:395-2.
6. Fis h e r M, Ro s e n fe ld WD, Bu rk RD. Ce rvic o vag in al h u m an papillo mavirus infectio n in suburban ado lescents and yo ung adults. J Pediat 1991;119:821-5.
7. Bauer HM, Ting Y, Greer CE, et al. Genital human papillo mavirus infectio n in female university students as determined by a PCR-based metho d. J Am Med Asso c 1991;265:472-7.
8. Bo sch FX, Muno z N, De-Sanjo se S, et al. Risk facto rs fo r cervical cancer in Co lo mbia and Spain. Int J Cancer 1992;52:750-8.
9. Mu rta EFC, So u za MAH, Lo m b ard i W, Bo rg e s LS. As p e c to s e pide mio ló gico s da infe cção pe lo papilo mavírus humano . J Bras Gineco l 1997;107:95-9.
10. Schneider A, Meinhardrat G, de Villers EM, Gismmann L. Sensitivity o f the cyto lo gic diagno sis o f cervical co ndylo ma in co mpariso n with HPV-DNA hybridizatio n studies. Diagn Cyto patho l 1987;3:250-5. 11. Mo o re DE, Spado ni LR, Fo y HM, et al. Increased frequency o f serum
antibo dies to Chlamydia tracho matis in infertility due to distal tubal disease. Lancet 1982;2(8298):574-7.
12. Kingho rn GR. Genital warts: incidence o f asso ciated genital infectio ns. Br J Dermato l 1978;99:405-9.
13. Carne CA, Do ckerty G. Genital warts: need to screen fo r co -infectio n. Br Med J 1990;300:459.
14. Strand AE, Ryland e r E, Evand e r M, Wad e ll G. Ge nital hum an papillo mavirus infectio n amo ng patients attending an STC clinic. Genito urin Med 1993;69:446-9.
15. Vo o g E, Bo lmstedt A, Olo fsso n S, Ryd W, Lo whagen G-B. Human papillo mavirus infectio n amo ng wo men attending an STD clinic co rrelated to reaso n fo r attending, presence o f clinical signs, co nco mitant infectio ns and abno rmal cyto lo gy. Acta Derm Venereo l 1995;75:75-8.
16. Ylisko ski M, Tervahanta A, Saariko ski S, Mantyjarvi R, Syrjanen K. Clinical co urse o f cervical human papillo mavirus lesio ns in relatio n to co existent cervical infectio ns. Sex Trans Dis 1992;19:137-9.
REFERENCES
108
r e s u m o
CON TEX TO: Apesar da extensa literatura so bre a micro bio lo g ia da flo ra vag inal no rmal e ano rmal, há po uco s trabalho s so bre a relação e ntre p a p ilo ma vírus huma no (HPV) e o utro s mic ro o rg a nismo s vag inais.
OBJETIVO: Analisar a freqüência de infecção po r HPV e o utro s ag entes co mo Candida sp., G ardnerella vag inalis e Tricho mo nas vag inalis no exame cito ló g ico .
TIPO DE ESTUDO: Estudo retro spectivo .
LOCAL: Centro público de referência terciária.
AM OSTRA: 1 7 .3 9 1 cito lo g ias de pacientes ambulato riais atendidas entre janeiro de 1 9 9 7 e ag o sto de 1 9 9 8 . O g rupo co ntro le fo i co mpo sto po r mulheres da mesma idade sem sinais cito ló g ico s de infec ç ã o po r HPV. As pa c ientes c o m dia g nó stic o de neo pla sia intraepitelial cervical (N IC) II o u III fo ram excluídas desta análise.
VARIÁVEIS ESTUDADAS: O diag nó stico cito ló g ico de infecção po r HPV fo i feito seg undo o s c ritério s de Sc hneider, et a l. e o diag nó stico de G ardnerella vag inalis fo i feito pelo achado de “ clue cells” .
RESULTADO S: 3 9 0 (2 ,2 4 %) tinham alteraçõ es co mpatíveis co m infecção po r HPV asso ciada o u não a N IC I. O s resultado s mo straram que a G ardnerella vag inalis fo i o ag ente mais freqüente nas mulheres co m infecção po r HPV (2 3 ,6 % versus 1 7 ,4 %; P <0 ,0 5 ), enquanto no g rupo co ntro le o ag ente mais frequente fo i a Candida sp. (2 3 ,9 % versus 1 3 ,8 %; P <0 ,0 0 1 ).
CON CLUSÃO: Apesar deste estudo ser baseado so mente em critério s cito ló g ico s, em que testes diag nó stico s específico s não fo ram usado s, o exame cito ló g ico é larg amente usado na prática clínica e o s dado s apresentado s nesta investig ação mo stram a asso ciação entre a G ardnerella vag inalis e a infecção po r HPV. Se o s micro o rg anismo s favo recem um ao o utro , isto ainda está po r ser estabelecido .
PALAVRAS-CHAVE: Papilo mavírus humano . G ardnerella vag inalis. Candida sp. Exame cito ló g ico .
Acknowle dgme nts
We thank the Cyto patho lo gy Service o f the Faculdade de Medicina do Triângulo Mineiro and Co nselho Nacio nal de Desenvo lvimento Científico e Tecno ló gico (CNPq).
Eddie Fe rnando Candido Murta, MD, PhD. Assistant Pro fesso r, Discipline o f Gyneco lo gy and Obstetrics, Faculdade de Medicina do Triângulo Mineiro , Minas Gerais, Brazil.
Maria Azniv Hazarabe dian de Souza, MD. Assistant Pro fesso r, Discipline o f Gineco lo gy and Obstetrics, Faculdade de Medicina do Triângulo Mineiro , Minas Gerais, Brazil.
Eduardo Araújo Júnior. Undergraduate student, Faculdade de Medicina do Triângulo Mineiro , Minas Gerais, Brazil.
She ila Jorge Adad, MD, PhD. Assistant Pro fesso r, Discipline o f Special Patho lo gy, Faculdade de Medicina do Triângulo Mineiro , Minas Gerais, Brazil.
Source s of funding: No t declared
Conflict of inte re st: No t declared
Last re ce ive d: 25 No vember 1999
Acce pte d: 01 December 1999
Addre ss for corre sponde nce :
Eddie Fernando Candido Murta Rua Alfen Paixão , 170 – Apto ,. 202 Uberaba/MG - Brasil - CEP 38060-230 E-mail: eddiemurta@ mednet.co m.br
p u b lis hin g in fo r m a t io n
17. Andersso n-Ellstro m A, Fo rssman L. Genital papillo mavirus infectio n in wo men treated fo r Chlamydia infectio n. Int J STD AIDS 1992;3:42-5. 18. Rettig PJ. Perinatal infectio ns with Chlamydia trachomatis. Clin Perinato t
1988;15:321-50.
19. So bel JD. Candidal vulvo vaginitis. Clin Obstet Gyneco l 1993;36:153-65. 20. Platz-Christensen JJ, Sundstro m E, Larsso n PG. Bacterial vagino sis and c e rvic al intrae p ithe lial ne o p las ia. Ac ta O b s te t Gyne c o l Sc and 1994;73:586-8.