DRUGS USE AND RI SK BEHAVI OR I N A UNI VERSI TY COMMUNI TY
1Ket t y Ar acely Piedr a Ch av ez2 Bev er ley O’Br ien3 Sandr a Cr ist ina Pillon4
Pied r a KAC, O’Br ien B, Pillon SC. Dr u g s u se an d r isk b eh av ior in a u n iv er sit y com m u n it y. Rev Lat in o- am En f er m agem 2 0 0 5 n ov em br o- dezem br o; 1 3 ( n ú m er o especial) : 1 1 9 4 - 2 0 0 .
The pur pose of t his st udy is t o evaluat e dr ug use and r isk behavior s am ong st udent s of t he Univer sit y
of Gu ay aq u il in Ecu ad or . To ev alu at e t h is issu e, w e u sed t h e q u est ion n air e “ You t h Risk Beh av ior Su r v ey ”
( YRBS) . The st udy sam ple consist ed of 751 under gr aduat e st udent s: 328 ( 44% ) m ale and 423 ( 56% ) fem ale.
Av er age age w as 20 y ear s old and 85, 5% of t he st udent s w er e single. Alcohol, t obacco and m ar ihuana w er e
t he m ost consum ed subst ances am ong st udent s, w ho use t hem for ent er t ainm ent . Dr ug consum pt ion ( legal or
illegal) am ong st udent s has becom e an issue for specialized r esear ch as w ell as an im por t ant field of int er vent ion
for public policies.
DESCRI PTORS: v iolen ce; st u den t s
USO DE DROGAS Y COMPORTAMI ENTOS DE RI ESGOS EN EL
CONTEXTO DE LA COMUNI DAD UNI VERSI TARI A
Est e est u d i o t i en e co m o o b j et i v o ev al u ar el u so d e d r o g as y co m p o r t am i en t o s d e r i esg o s en t r e
est u d ian t es d e la Un iv er sid ad d e Gu ay aq u il- Ecu ad or . Fu e u t ilizad o el cu est ion ar io d e Com p or t am ien t os d e
Riesgos en Est udiant es Adolescent es ( YRBS) . La m uest r a fue const it uida por 751 bachiller es - est udiant es del
pr im er año: 328 ( 44% ) er an hom br es y 423 ( 56% ) m uj er es, con edad pr om edia de 20 años y el 88, 5% er a
solt er o. Las subst ancias m ás ut ilizadas fuer on el alcohol, el t abaco y la m ar ihuana, que son usadas de for m a
r ecr eacional ent r e los est udiant es. El uso de dr ogas ( lícit as e ilícit as) ent r e los est udiant es se ha t or nado un
cam po de est udio bast ant e fav or able par a el est ablecim ient o de polít icas pr ev ent iv as.
DESCRI PTORES: v iolen cia; est u dian t es
USO DE DROGAS E COMPORTAMENTOS DE RI SCO NO
CONTEXTO DE UMA COMUNI DADE UNI VERSI TÁRI A
Est e est udo t em com o obj et ivo avaliar o uso de dr ogas e os com por t am ent os de r isco ent r e est udant es
d a Un iv er sid ad e d e Gu ay aq u il- Eq u ad or . Foi u t ilizad o o q u est ion ár io You t h Risk Beh av ior Su r v ey ( YRBS) . A
am ost r a f oi com post a por 7 5 1 est u dan t es de pr im eir o an o de gr adu ação: 3 2 8 ( 4 4 % ) er am h om en s e 4 2 3
( 56% ) m ulher es, com idade m édia 20 anos, e 88,5% solt eir os. As subst âncias m ais ut ilizadas for am o álcool,
o t abaco e a m aconha, que são usados de for m a r ecr eacional ent r e os est udant es. O uso de dr ogas ( lícit as e
ilícit as) ent r e est udant es t em se t or nado um cam po de est udo bast ant e fav or áv el par a o est abelecim ent o de
polít icas pr ev en t iv as.
DESCRI TORES: v iolên cia; est u dan t es
1
The opinions expr essed in t his ar t icle ar e t he sole r esponsabilit y of t he aut hor s and do not in any w ay r epr esent t he posit ion of t he or ganizat ion t hey w or k at or it s adm inist rat ion; 2 RN, Msc, Nur sing Facult y, Univer sit y of Guayaquil Ecuador ; 3 PhD, Nur sing Facult y at t he Univer sit y of Alber t a; 4 Facult y Mem ber, Univer sit y of São Paulo at Ribeir ão Pr et o College of Nur sing, WHO Collabor at ing Cent r e for Nur sig Resear ch Developm ent , Br azil, e- m ail: pillon@eer p.usp.br
I NTRODUCTI ON
A
ccording t o I nt er nat ional Or ganizat ion( 1), t he use of alcohol, t obacco and of illegal drugs cause greatproblem s t o public healt h in several count ries, m ainly am o n g y o u n g st er s. Th e r esu l t s o f sev er al st u d i es su p p o r t t h e n eed o f i n t er v en t i o n w o r k an d o f t h e
in cr ease in aw ar en ess of t h ese pr oblem s as w ell as of t h e r isk f act or s of t h e u se of d r u g s. Th e u se of such subst ances leads young people t o ear ly m or bidit y
a n d m o r t a l i t y r a t e s b o t h i n d e v e l o p e d a n d i n d ev elop in g cou n t r ies, sin ce t h ey ar e p r ob lem s t h at can b e p r ev en t ed an d t h at m an y in cases st ar t in
ad o l escen ce.
Th e r elat ion sh ip b et w een t h e u se of d r u g s and v iolence has cr eat ed a lot of int er est in sev er al
social d iscip lin es in clu d in g Ep id em iolog y, Sociolog y, M e d i c i n e , Ed u c a t i o n a n d Ps y c h o l o g y( 2 - 3 ). Th i s r elat ion sh ip occu r s at d if f er en t lev els - in d iv id u al,
fam ilial, and at com m unit y level, and it is affect ed by t h e k in d of dr u g u sed an d t h e n at u r e of beh av iou r ex h ibit ed. Th e u se of t obacco, alcoh ol an d of ot h er
i l l eg al d r u g s h av e ser i o u s i m p l i cat i o n s f o r h eal t h , including acut e as w ell as cronic diseases t hat lead t o h ig h r at es of ear ly m or t alit y. Th er ef or e, t h e u se of
dr ugs account s for one of t he gr eat est Public Healt h pr oblem s( 1 ).
I n o r d e r t o u n d e r s t a n d t h e c o m p l e x
relat ionship bet w een t he use of drugs and violence, it i s e s s e n t i a l t o u n d e r s t a n d t h e p h a r m a c o l o g i c a l part icularit ies of t he drugs as w ell as t he social cont ext
in w h ich an in div idu al is in ser t ed. Th e u se an d t h e abu se of su bst an ces occu r in social, sit u at ion al an d cult ur al cont ex t s, t hat ex ponent ially influence v iolent
r esult s( 4 ).
Am on g d if f er en t k in d s of v iolen ce, t h er e is t h e p h ar m acolog ical on e t h at occu r s as a r esu lt of
t he use in t he short and t he long r un of cer t ain drugs t h at pr odu ce beh av iou r s.
Acco r d i n g t o t h e l i t e r a t u r e( 4 ) o n k i n d s o f
v iolence, t he v iolence m ost com m only found am ong gr ou ps of st u den t s is t h e ph ar m acological on e. For ex am ple, st u den t s w h o dr iv e af t er dr in k in g accou n t
for higher risks of accident s. I n ot her cases, st udent s w ho dr ink and use dr ugs account for higher pr obabilit y of unpr ot ect ed sex and sex abuse( 5).
The pr esence of dr ugs in violent event s does n o t n e ce ssa r i l y i m p l y t h a t t h e su b st a n ce s a f f e ct p e r p e t r a t o r s ’ o r v i c t i m s ’ b e h a v i o u r s( 4 ). Be s i d e s ,
different subst ances affect individuals in different iat ed
way s, based on t heir phy siology, psychology, hist or y,
gender and ot her per sonal and cult ur al fact or s( 6). Alm ost all com m on illegal dr ugs can lead t o v iolent behav iour s how ever, it fr equent ly happens by
m e a n s o f d i f f e r e n t m e ch a n i sm s( 7 ). Th e t y p e s o f violence depend on t he use of legal and illegal dr ugs as w e w ill see:
- The use of legal dr ugs
Alcohol is t he m ost fr equent ly cit ed subst ance as far as r isk behav iour s ar e concer ned, due t o t he
effect s on behav iour, and it is appar ent ly inv olved in t he v iolence t hat occur s under t he effect of t he use. Th e d ir ect an d m ost com m on r elat ion sh ip b et w een
a l c o h o l a n d a g g r e s s i o n o c c u r s b y m e a n s o f int ox icat ion. Resear ch indicat es t hat t he m echanism s t hat ex plain how alcohol induces t o aggr ession occur
because of t he lack of fear inhibit ion by t he ansiolit ic act ion( 7). For exam ple, alcohol can affect t he cognit ive fu n ct ion in su ch a w ay t h at t h e in div idu al su ffer s a
d e c r e a s e o f h i s / h e r c a p a c i t y t o p l a n a c t i o n s i n r esponse t o t hr eat ening sit uat ions.
Alcohol can also boost pain percept ion, w hich
m i g h t b e o n e o f t h e ca u se s o f g r e a t e r d e f e n si v e a g g r e s s i o n . Th e i n d i v i d u a l c a n h a r d l y t o l e r a t e aggr ession an d pr om pt ly st ar t s f igh t in g. St ill it can
s e r v e a s a t r i g g e r i n g m e c h a n i s m t o p r o m o t e aggression act s in t hose w ho really have an inclinat ion t o v iolence and w hen t hey find t hem selv es ex posed
t o v u ln er ab le sit u at ion s( 8 ). I t h as b een r ep or t ed in sever al st udies, for exam ple, t hat people w ho have a gr eat er inclinat ion t o being aggr essive, t end t o exhibit
high lev els of aggr ession, but t hey do not dr ink . - Nicot ine
As f ar as t h e u se of n icot in e is con cer n ed,
not hing has been found in t he lit erat ure t hat links it t o v iolence, unless t her e ar e ot her addict ions inv olv ed. Heav y use of t obacco has not been r ecognised as a
pr oducer of psy chological dist ur bs, ot her t han t hose w ho feel lik e giv ing up but ex per ience difficult ies in d o i n g so . Sm o k i n g , h o w e v e r, a s o t h e r a d d i ct i v e
b eh a v i o u r s, i s k ep t b eca u se i t p r o v i d es a w a y t o m inim ize negat iv e effect s ( t hat is t o say, st ress, rage, f e a r, sh a m e , d e sp i se ) a n d e v o k e s t h e e f f e ct s o f
ex cit em en t , pleasu r e an d su r pr ise. - Sedat iv es - Hy pnot ic dr ugs
H y p n o t i c d r u g s c a n b e a s s o c i a t e d w i t h
phar m acological violence due t o ir r it abilit y and anxiet y, w hich m any t im es ar e t he r esult s of int ox icat ion and a b s t i n e n c e( 7 ). H y p n o t i c s e d a t i v e s s u c h a s
c o m m o n l y p r e s c r i b e d t o m i n i m i z e s y m p t o m s o f
in som n ia an d an x iet y.
Alt hough sever al user s t ake t hese subst ances
because of t heir sedat ive effect s, people w ho use t hem
f r eq u en t l y b eco m e sh y. Th ese ar e t h e f i r st ab u se
dr ugs and t hey ar e usually t aken w it h ot her subst ances
- The use of illegal drugs
Th e u se of illeg al d r u g s is con n ect ed w it h
violent crim es, alt hough t here ar e r ar ely any dat a on
t he pat t er n of dr ug use and violence( 6). Crim inals w ho
u se illeg al d r u g s ar e m or e f r eq u en t ly in t o st ealin g
an d assau lt s t h an cr im in als w h o do n ot t ak e dr u gs
and t hey com m it cr im es m or e oft en in per iods w hen
t hey t ak e dr ugs m or e heav ily( 6).
- Mar ij uana
Mar ij u an a is t h e illeg al d r u g w h ich is m ost
com m only used and has been consum ed for cent ur ies
f or it s alt er at ion s in m ood( 9 ). Th e m od er at e u se of
m ar ij uana has been found t o t em por ar ily inhibit violent
an d ag g r essiv e b eh av iou r p at t er n s in h u m an s an d
anim als( 6). I n gener al, t he use of m ar ij uana has been
found as a w ay t o inhibit act ivit ies.
- Am ph et am in es an d m et h am ph et am in es
Th e r e a r e co n si d e r a b l e i n v e st i g a t i o n s o f
possible link s bet w een t he use of am phet am ines and
v i o l e n c e . A m p h e t a m i n e s , e s p e c i a l l y
m et ham phet am ines ar e am ong t he illegal st im ulat ing
dr ugs in sever al count r ies. Am ong t he m ost im por t ant
effect s of am phet am ines on behaviour is m ood, w hich
can occur w it h t he adm inist rat ion of bot h chronic and
acu t e u se( 1 0 ). On e of t h e g r eat est con seq u en ces of
t h e c h r o n i c a b u s e o f a m p h e t a m i n e s i s t h e
dev elopm ent of pat hologic behav iour( 1 0 ).
- Cocain e
The use of cocaine has been associat ed w it h
cr im e and v iolence( 9). The int r a- nasal use of cocaine
a n d t h e u se o f t h e cr a ck h a v e b een f o u n d t o b e
associat ed w it h ph ar m acological v iolen ce( 4 ). Cocain e
is one of t he illegal st im ulant ing drugs usually abused
i n t h e U S A , w i t h s i m i l a r c h a r a c t e r i s t i c s t o
a m p h e t a m i n e s , r e g a r d i n g i t s m o o d c h a n g i n g
p r o p e r t i e s a n d t h e d e v e l o p m e n t o f c o n d u c t
pat hology( 10). Violence is pr esent am ong dr ug user s,
t he sam e w ay it is pr esent am ong alcohol dr ink er s;
aggr essiv e behav iour is not only lim it ed t o addict ed
indiv iduals, but also occasional user s.
Th e ab u se of p sy ch oact iv e su b st an ces h as
b e e n p a i n st a k i n g l y i n v e st i g a t e d , w i t h t h e a i m o f
especifically cont ribut ing t o prevent ion act ions t ow ards
t he use of drugs( 11). I nform at ion on t he int eract ion of
r isk behav iour s and t he use of subst ances at schools is necessar y so t hat pr ev ent ion act ions can be t ak en
an d en v ir on m en t s can r em ain f r ee f r om d r u g s an d
v i o l en ce. Co n si d er ab l e ef f o r t s h av e b een m ad e i n or der t o under st and t he causes of t he use of dr ugs so
t h a t m o r e e f f e ct i v e p r e v e n t i o n p r o g r a m s ca n b e
id en t if ied . Man y of t h ese w or k s h av e b een car r ied
ou t esp ecially at sch ools/ u n iv er sit ies, f or t h ese ar e
places w her e a gr eat num ber of individuals can have easy access t o t hem . Schools/ univer sit ies populat ions
ar e consider ed ideal for pr ev ent ion cam paigns( 1 2 ).
I n Ecuador t her e is a lack of st udies in t he
lit erat ure t hat assess t he relat ionship bet w een t he use of dr u gs an d v iolen ce am on g y ou n gst er s, m ain ly in
Lat in Am er ica. Th is w or k p r op oses t o in cr ease ou r
u n der st an din g of t h is r elat ion sh ip am on g u n iv er sit y st u den t s. A bibliogr aph ic su r v ey w as car r ied ou t in
t he dat abase of MedLine and CI NADHL, in an at t em pt
t o assess exist ing st udies, how ever, m ost of t hem have
been con du ct ed in dev eloped coun t r ies.
Th e aim of t h is st u d y is t o ch ar at er ize t h e u se of psy ch oact iv e su bst an ces an d r isk beh av iou r s
am on g u n iv er sit y st u den t s.
METHODOLOGY
Ecuador is a count ry w hich is insert ed in t he “ I nt er nat ional Rout e” of dr ugs bet w een t he nor t h and
t h e so u t h . W i t h o u t r e st r i ct i o n s, i t h a s p r o g r a m s,
policies, and funds t o handle t he Use of Dr ugs am ong
i t s ci t zen s. Ho w ev er i n cl ea r d i sa d v a n t a g e, si n ce Ecuador is dependent on I nt er nat ional Or ganizat ions.
Due t o t he lack of inform at ion on t his area, t his st udy
also aim s t o in cr ease t h e k n ow led g e of t h e n at u r e
and m agnit ude of t he use of dr ugs and t he r elat ionship
bet w een t he use and r isk behav iour s.
Dat a w er e collect ed bet w een Oct ober 2 0 0 3
a n d Ja n u a r y 2 0 0 4 u s i n g a ( YRB S ) Yo u t h Ri s k
Behaviour s Quest ionnair e( 13) t hat ident ifies t he use of p sy ch o act i v e su b st an ces ( ex p er i m en t al , m o d er at e
an d h eav y u ses) on t h e last 3 0 day s, in t h e last 6
m ont hs inside and out side univer sit y and general use
pr ot ect ion, dr unk dr iving, being under t hr eat ening and
being caught by t he police.
The sam ples consist ed of st udent s in t he fir st
y ear of gr aduat e cour ses in t he ar ea of Hum anit ies, Biolog ical an d Ex act Scien ces. An au t h or izat ion f or
t he ut ilizat ion of t he quest ionnaire w as obt ained from
t h e Cen t er f or Disease Con t r ol - USA. Th e p r esen t
pr oj ect has been assessed and appr oved by t he Et hics
Com m it t ee of Alber t a Univer sit y and t he Univer sidade
de Guay quil- Equador. This is a descr ipt ive st udy.
Fr o m t h e t w o u n i v e r s i t y s c e n a r i o s , t h e
select ed on e w as Un iv er sidad de Gu ay aqu il, t h at is
sit uat ed in t he area of Salado in t he cit y of Guayaquil
– Pr ov in ce of Gu ay as. Th e sam p le ch osen f or t h is st udy com pr ised 751 st udent s dur ing t he fir st year in
t h e colleg es b elon g in g t o t h e u n iv er sit y m en t ion ed
ab ov e. Th e r esu lt s can n ot b e g en er alized b ecau se
t his st udy w as conduct ed based on a sam ple t hat w as
n ot r epr esen t at iv e of st u den t s in t h eir f ir st y ear of
g r ad u at e cou r ses.
RESULTS
Th e ( YRBS) qu est ion n air e f in din gs h igh ligh t
dem ogr aphic char act er ist ics in a sam ple w it h n.= 751
( 100% ) st udent s. The dist r ibut ion accor ding t o gender
w as as follow : 328 ( 44% ) m en and 423 ( 56% ) w om en,
w it h av er age age of 20. 3 y ear s, r anging fr om 18 t o
3 1 ( SD 2 . 7 4 ) . No st at ist ically sig n if ican t d if f er en ce
found bet w een age and sex. Am ong all t he st udent s,
665 ( 88.5% ) ar e single, 491 ( 65,4% ) live w it h r elat ives
and 473 ( 63% ) live in t heir ow n par ent s’ hom es. The
a v e r a g e f a m i l y m e m b e r s w e r e 5 . 4 9 ( SD = 2 . 0 3 ) m inim um 1 and m axim um 17 people in t he fam ily. As
far as religion is concerned, t he m aj orit y w as cat holic
- 561 ( 73% ) . We found t hat for 356 ( 100% ) st udent s,
t he fat her of 165 ( 22% ) dr ank alcohol and 165 ( 22% )
sm o k ed .
Fiv e h u n dr ed an d for t y - on e st u den t s ( 7 2 % )
hav e alr eady had alcohol, and w om en t ur ned out t o
be m or e abst em ious t han m en, t he lat t er abused of
it , w it h st at ist ically sign if ican t dif f er en ce X2= 3 1 , 8 9 p.000. The sam e w as t r ue of t hose w ho sm oked, t hat
i s , 4 8 5 ( 6 4 , 5 % ) o f s t u d e n t s , w h e r e t h e g e n d e r
dist r ibut ion is 248 ( 51% ) m en and 237 ( 49% ) w om en
w it h st at ist ically significant difference X2= 31,22 p.000.
When com par ed t o t he av er age age and t he
l a t n e m i r e p x E e s U e t a r e d o M e s U y v a e H e s
U Total
o .
N % N.o % N.o % N.o %
* r e e
B 326 43 141 19 23 3 470 62.5
* e n i
W 236 31.4 28 4 6 .8 270 36
* a li u q e T , y k s i h
W 187 25 43 6 10 1.3 240 32
s r e z il i u q n a r T ) x a r o l , m u il a V
( 19 2.5 5 .7 - - 24 3
a n a u ji r a
M 13 2 3 .4 2 .3 18 2.4
s t n a l a h n
I 6 1 - 7 0.9
e n i a c o
C 4 .5 2 .3 1 .1 7 0.9
use of alcohol and t obacco, w e did not find significant
r elat ion for t his sam ple.
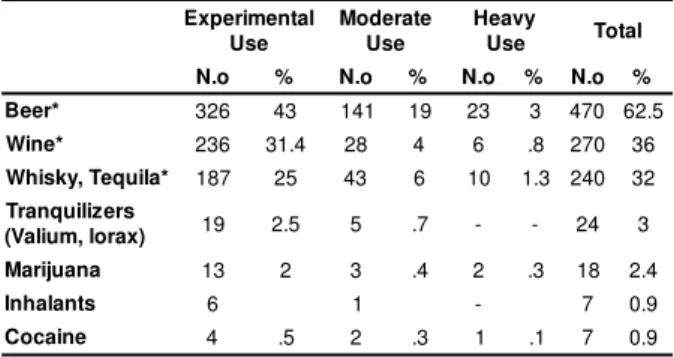
Tab le 1 - Nu m er ical an d p er cen t ag e r ep r esen t at ion
of st an dar ds of psy ch oact iv e su bst an ces u se am on g
st udent s ( n.o = 751) in t he last 6 m ont hs
* Significant differ ence bet w een gender s p< 005
Ta b l e 1 sh o w s t h a t m o st st u d e n t s “ u se d
alcoh ol ex per im en t ally ” ( w in e, t equ ila, beer ) in t h e
last 6 m ont hs, w hen w e com par ed gender s, w e found
t hat m en use alcohol m or e heavily t han w om en, w it h
st at ist ically sign ifican t differ en ce.
Table 2 - Repr esen t at ion of life u se of psy ch oact iv e
su bst an ces am on g u n iv er sit y st u den t s
s e Y N % f o s s a l g a , n a c r e e b e n o ( l o h o c l a f o e s o d e n O * ) k n i r d d e ll i t s i d f o l m 0 4 , e n i
w 424 57
* e c n o g n il a h n i y l n o g n i e b n e v e , e t t e r a g i
C 422 63.2
* e t t e r a g i c e l o h w
A 297 45
o c c a b o
T 33 6
* a n a u ji r a
M 25 3
t u o h t i w e n i c i d e m ( s g u r d l a g e ll i e m o S . ) n o i t p i r c s e r
p 14 2.4
) t n i a p ,l o s o r e a , e u l g , e n il o s a g ( s t n a l a h n
I 13 2
) k c a r c ( e n i a c o
C 10 1.7
* Significant differ ence bet w een gender s p< 005
Tab le 2 r ep r esen t s lif e u se of p sy ch oact iv e subst ances am ong st udent s, 424 ( 57% ) had alr eady
had a dose of alcohol and 422 ( 63,2% ) had inhaled a
c i g a r e t t e a t l e a s t o n c e . W h e n g e n d e r s w e r e
com par ed, m en w er e fou n d t o h av e u sed cigar et t es
and m ar ij uana m or e oft en.
I n g e n e r a l , t h e u s e o f d r u g s s t a r t e d o n
av er age at t he age of 16 ( Dp = 2.09) , r anging fr om
t he age of 10 t o 18.
As for t he t y pes of psy choact iv e subst ances
Tab le 3 - Nu m er ical an d p er cen t ag e r ep r esen t at ion
of dr u gs u sed in side an d ou t side u n iv er sit y an d t h e t y pes of use. ( n.o= 751)
e s u e fi
L Useinthe
s h t n o m 6 t s a l t s a l e h t n o e s U e d i s t u o s y a d 0 3 y ti s r e v i n u t s a l e h t n o e s U e d i s n i s y a d 0 3 y ti s r e v i n u o .
N % N.o % N.o % N.o %
l o h o c l
Á 524 83 420 56 252 33.5 86 11
o c c a b o
T 485 65 360 48 52 7 150 20
Table 3 r epr esent s “ life use” of t obacco and alcohol, w hich w er e used in higher pr opor t ion am ong st udent s, and t obacco w as m or e used at univer sit y.
Regar ding “ life use”, 294 ( 39% ) st udent s used alcoh ol ab u siv ely, r esu lt in g in d r u n k en n ess. Am on g t hese, 188 ( 64% ) got dr unk fr om 1 t o 2 t im es, m en acco u n t ed f o r t h e m aj o r i t y o f t h em . D r u n k en n ess happened in low er pr opor t ion, t o 25( 3% ) st udent s.
As f o r t h e f a ct o f e n j o y i n g d r i n k i n g , 1 6 1 ( 2 1 , 4 % ) st u d e n t s p o i n t e d o u t t h a t t h e y e n j o y e d dr inking fr om 1 t o 2 doses, w hile 106 ( 14% ) st udent s enj oy dr inking t o get a lit t le bit high, w hat show s t hat m en get dr unk m or e oft en t han w om en.
Am ong t he st udent s, 177 ( 23,5% ) dr ove aft er dr in k in g an d am on g t h ese 3 0 ( 1 7 % ) h ad been f in ed or got inv olv ed in accident s aft er hav ing dr unk .
As for sexual behaviour s, 443 ( 59% ) st udent s had sexual int er cour se and am ong t hese 245 ( 55,3% ) had had alcohol befor e t he sex ual int er cour se. Most o f t h e m w e r e m e n a n d o n l y 7 2 ( 1 6 , 2 % ) w o r e co n d o m s.
Table 4 - Repr esent at ion of t y pes of r isk behav iour s as v ict im s, an d t h e u se of psy ch oact iv e su bst an ces am ong univ er sit y st udent s in t he last 1 2 m ont hs at u n iv er sit y
s e Y o . N % . r o z a r a r o e fi n k a , n u g a h ti w t r u h r o d e n e t a e r h T
* 193 25.7
r e h t o / r o z a r , e fi n k , n u g a h ti w e n o e m o s w a S * s n o p a e
w 158 21
. n e t a e b g n i e b f o d i a r f a e r e W
* 158 21
. s t h g i f n i d e v l o v n i t o
G 124 16.5
e n o e m o s y b d e k c i k r o ti h , d e p p a l s , d e ll u p e r e W * . g n i y a l p t o n s a w o h
w 76 10
s e il r o p i s s o g f o s m i t c i v e r e
W 44 6
. s t n e m m o c d e t a l e r x e s r o s e k o j f o s m i t c i v e r e
W 33 4.4
r i e h t r o s k o o l r i e h t o t e u d g n i y ll u b f o s m i t c i v e r e W . g n i k a e p s f o y a
w 15 2
* Significant differ ence p< 005
Tab l e 4 r ep r esen t s ( 2 5 , 7 % ) st u d en t s w h o w er e t h r eat en ed or h u r t w it h a gu n , k n if e or r azor,
( 21% ) saw som eone w it h a gun, knife or a r azor and t h e sam e n u m b er of st u d en t s w er e af r aid of b ein g
beat en w hen t hey used alcohol in t he last m ont hs at u n iv er sit y.
Com par in g t h e st u den t s w h o u sed an y k in d of psy ch oact iv e su bst an ces, or u sed gu n s eit h er t o in t im id at e or t h r eat en , or g ot in v olv ed in f ig h t s or had pr oblem s w it h t he police, w e found t hat ( dist illed or fer m ent ed) alcoholic bev er ages show ed a r elat ion bet w een dr ink ing and being a v ict im ( p. 0 0 0 ) , w hich did not happened in r elat ion t o ot her dr ugs.
DI SCUSSI ON
Th i s i s t h e f i r s t t i m e t h a t a s t u d y t h a t invest igat es t he use of dr ugs and r isk behaviour s has b een co n d u ct ed am o n g st u d en t s d u r i n g t h ei r f i r st college y ear at Un iv er sidade de Gu ayaqu il, Ecu ador. The pr esent st udy has m ade it possible t o point out t hat t he use of alcohol and of ot her dr ugs is pr esent not only on t he college prem ises. How ever, it has been ident ified t hat once t he age at w hich t he beginning of t h e u se of dr u gs h appen s lies bet w een 1 0 an d 1 8 , ag e t h at p r eced es u n iv er sit y en t r an ce. Th e st u d ied populat ion is com posed of youngst er s, m ainly w om en, single indiv iduals, w ho liv e w it h t heir par ent s, w her e at least one m em ber of t he fam ily uses subst ances, esp ecially f at h er s.
The age at t he beginning of t he use and t he p r e s e n c e o f a m e m b e r o f t h e f a m i l y w h o u s e s p sy ch oact iv e su b st an ces can con t r ib u t e d ir ect ly or in dir ect ly t o t h e st u den t s’ u sin g of su ch su bst an ces t h r ou gh m odels an d r ein for cin g beh av iou r s.
Alt h ou gh t h e sam ple w as com posed m ain ly of w om en , ab u siv e u se of alcoh ol am on g st u d en t s occu r r ed m or e sign ifican t ly am on g m ale in div idu als, as w ell as t he r elat ion bet w een r isk behaviour s. St ill, w om en drink w it hin t he lim it s of norm al drinking, w hile m en enj oy dr ink ing t o get t he high of alcohol or t o get slight ly dr unk . Such a fact is in accor dance w it h int er nat ional st udies( 1 4 ) t hat st at e t hat in st udies on gender, alcohol use is a predict or t o such behaviours, an d t h e k in d s of b eh av iou r s ar e d if f er en t b et w een g en d er s.
Sev er al psy ch oact iv e su bst an ces h av e been asso ci at ed w i t h r i sk b eh av i o u r s, h o w ev er, f o r t h i s sam p le, on ly alcoh ol ex h ib it ed an associat ion w it h t h em , w h at t h e au t h or( 1 0 ) p u t s as p h ar m acolog ical v i ol en ce.
As for t he use of t obacco, it t ook place m or e fr equent ly inside t he univ er sit y w hen com par ed w it h
a l c o h o l . Th i s f a c t c a n b e a s s o c i a t e d w i t h t h e per m issiv en ess of it s in side t h e u n iv er sit y, alt h ou gh
t h is v ar iab le h as n ot b een m easu r ed in t h is st u d y. What leads us t o t hink t hat alcohol is usually used in
social occasions such as par t ies and ot her gat her ings and one can suppose t hat t he univer sit y cam pus poses rest rict ions or has cont rol t hrough t he legislat ion over
alcoholic dr ink s, r egar ding bot h t heir sales and t heir con su m p t ion , w h ich d oes n ot h ap p en in r elat ion t o
ci g ar et t es. Al t h o u g h t h e sal es m i g h t b e f o r b i d d en inside t he cam pus, t here is no rest rict ion t ow ards t he
use of cigar et t es.
A m o n g t h e d r u g s u s e d b y s t u d e n t s a r e ( d i s t i l l e d a n d f e r m e n t e d ) a l c o h o l i c b e v e r a g e s ,
t r anquillizer s, t obacco and m ar ij uana. Most st udent s
ex per ience lifet im e use, how ev er t his use decr eases a s t i m e g o es b y. No t a l l ca ses d ev el o p i n t o d r u g addict ion, w hat can be obser v ed is t he gr adual dr op
fr om life use t o use in t he last 6 m ont hs and in t he last m ont h, such r esult s w er e found in int er nat ional
st u d ies.
St udies( 14) show t hat dur ing t he phases of t he
involvem ent w it h psychoact ive subst ances, individuals begin w it h legal dr u gs ( alcoh ol and cigar et t es) , and t h en st ar t u si n g m ar i j u an a an d l at er o t h er i l l eg al
d r u g s.
Se x u a l a c t i v i t i e s c a n b e c o n s i d e r e d r i s k
a ct i v i t i es a m o n g st u d en t s si n ce t h ese y o u n g st er s h ar dly w ear con dom s u n der t h e effect of alcoh ol or
aft er hav ing used ot her dr ugs. Such a fact has been happening not only on t he last 30 day s, but also in
t he last 6 m ont hs. Ther efor e, unpr ot ect ed sex can be pu t t in g t h ese y ou n gst er s at t h e r isk s of con t r act in g
sex u ally t r an sm it t ed diseases.
As for dr unk dr iving is concer ned, 1/ 3 of t he st u d en t s h av e alr ead y d r iv en u n d er t h e ef f ect s of
alcohol and half of t hem have been fined or involved i n a c c i d e n t s , t h i s f a c t m a k e s u s r e - t h i n k t h e s e
y ou n gst er s’ aw ar en ess of t h e r isk s of dr u n k dr iv in g and t he accident s t hat m ay end up in deat hs.
There is an associat ion bet w een using alcohol and being a v ict im ( t hr eat s, fear s, inv olv em ent w it h
f i g h t s) i n t h e l a st 1 2 m o n t h s a t u n i v e r si t y. Th e lit er at ur e show s( 5) t h at t h e y ou n gst er s w h o u se an y k in d of psy ch oact iv e su bst an ces ar e m or e pr on e t o
get inv olv ed in fight s and becom e v ict im s.
This st udy has som e lim it at ions, since it has
b e e n c a r r i e d o u t w i t h a n o n - r e p r e s e n t a t i v e con v en ien ce sam p le, an d alt h ou g h it is a st u d y of
c h a r a c t e r i z a t i o n o f t h e u s e o f d r u g s a n d r i s k beh av iou r s am on g st u den t s, t h e size of t h e sam ple
m i g h t h a v e i n f l u e n c e d t h e a s s e s s m e n t o f s o m e v ar i ab l es. An ot h er q u est i on t h at m i g h t h av e b een
invest igat ed are t he law s in force, in relat ion t o int ernal u n iv er sit y p olicies g ear ed t ow ar d s t h e con t r ol ov er t h e u se of alcoh ol an d t ob acco, w h ich m ig h t h av e
im p r ov ed t h e lev el of d iscu ssion in r elat ion t o t h is p r o b l em .
CONCLUSI ON
I n Ecuador, st udies on t he ident ificat ion and
a s s o c i a t i o n b e t w e e n t h e u s e o f d r u g s a n d r i s k
beh av iou r s am on g st u den t s or am on g ot h er gr ou ps ar e h ar d l y co n d u ct ed . Ho w ev er, t h er e ar e sev er al r easons t hat j ust ify t he pr esence of t he use of dr ugs
an d r isk b eh av iou r s at u n iv er sit y. St u d ies lik e t h is ar e con sid er ed t o b e im p or t an t an d ar e seen as a
w ay t o develop educat ional pr ogr am s t hat aim at t he r e d u c t i o n o f r i s k b e h a v i o u r s a n d a l s o o f t h e
con su m pt ion s of psy ch oact iv e su bst an ces.
Th e n u r sin g colleg es at t h e Un iv er sid ad d e Guay aquil along w it h CI CAD/ OEA ar e in a pr ev ileged
sit uat ion t o urge t he invest igat ion in t he area of drugs u s e a n d r i s k b e h a v i o u r s i n o r d e r t o d e v e l o p
e d u c a t i o n a l a n d p r e v e n t i v e s k i l l s t o f a c e t h i s p h en om en on .
Th e issu e of alcoh ol an d d r u g s u se am on g univer sit y st udent s m ust be faced as a t op pr ior it y in
a l l a r ea s, w i t h t h e a i m s o f p r o m o t i n g p r ev en t i o n p r og r am s g ear ed t ow ar d s t h is p op u lat ion , in w h ich
p r o f esso r s’ p ar t i ci p at i o n sh o u l d b e i n cl u d ed . Bo t h m andat or y and opt ional subj ect s on t he use of dr ugs and alcohol in t he gr aduat e and post - gr aduat e cour se
should com pr ise m or e hour s. This r esear ch pr esent s on ly p ar t of t h e r ealit y of t h e u se of d r u g s in t h e
u n iv er sit y set t in g an d it con sider s t h at t h is k in d of st udy should be m or e w idely conduct ed, t ak ing int o
con sider at ion m or e r epr esen t at iv e popu lat ion s.
ACKNOW LEDGEMENTS
Sch olaish ip Pr og r am , t h e Gov er n m en t of Jap an , all
Facult y of t he Univ er sit y of Alber t a/ Canada, and t he e l e v e n r e p r e s e n t a t i v e s f r o m t h e s e v e n La t i n
-A m e r i c a n c o u n t r i e s t h a t p a r t i c i p i t e d i n t h e “ I
I nt er nat ional Resear ch Pr ogram ”, im plem ent ed at t he Univ er sit y of Alber t a/ Canada in 2 0 0 3 - 2 0 0 4 .
REFERENCES
1 . Pan - Am er ica Healt h Or g an izat ion . PAHO. Healt h in t h e Am er icas. Vol I . Scient ific and Technical Publicat ion n. 5 8 7 ; 2 0 0 2 .
2. De la Rosa M, Lam ber t EY, Gr opper BA. Dr ugs and violence: cau ses, cor r elat es, an d con seq u en ces. Rock v ille ( MD) : US Dep ar t m en t of Healt h an d Hu m an Ser v ices, Pu b lic Healt h S e r v i c e , Á l c o o l , D r u g A b u s e , a n d M e n t a l H e a l t h A d m i n i s t r a t i o n , N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e o n D r u g A b u s e a n d Álcoolism ; 1 9 9 0 . ( NI DA Resear ch Mon og r ap h No. 1 0 3 ) 3 . Ch er m ack ST, Gian cola PR. Th e r elat ion b et w een álcool a n d a g g r e s s i o n : a n i n t e g r a t e d b i o p s y c h o s o c i a l con cep t u alizat ion . Clin ica Psy ch olog ical Rev iew Sep t 1 9 9 7 ; 1 7 ( 6 ) : 6 2 1 - 4 9 .
4 . Fagan J. Set an d set t in g r ev isit ed: in f lu en ces of alcoh ol an d illicit d r u g s. I n : Mar t in SE. Alcoh ol an d in t er p er son al v iolen ce: f ost er in g m u lt id iscip lin ar y p er sp ect iv es. Rock v ille ( MD) : US Depar t m ent of Healt h and Hum an Ser v ices, Public H e a l t h Se r v i c e , N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h , N a t i o n a l I n st i t u t e on Al coh ol Ab u se an d Al coh ol i sm ; 1 9 9 3 . p . 1 6 1 -9 2 .
5. Fur long M, Casas JM. Dr ugs and School Violence. Educat ion & Tr eat m en t of Ch ildr en 1 9 9 7 ; 2 0 ( 3 ) : 2 6 3 - 8 1 .
6. Reiss AJJr, Rot h JA. Under st anding and Pr evening Violence. Wash in gt on ( DC) : Nat l. Acad Pr ess; 1 9 9 3 .
7. Lav ine R. Psy chophar m acological t r eat m ent of aggr ession a n d v i o l e n c e i n t h e s u b s t a n c e u s i n g p o p u l a t i o n . J Psy ch o act i v e D r u g s 1 9 9 7 ; 2 9 ( 4 ) : 3 2 1 - 9 .
8 . Feldm an M. Cr im in al beh av ior : a psy ch ological an aly sis. Lon don : Wiley ; 1 9 7 7 .
9 . Gold MS, Tullis M. Cannabis. I n: Galant er M, Kleber HD. Tex t book of subst ance abuse t r eat m ent . 2 ª ed. Washingt on ( DC) : Am er ican Psy ch iat r ic Pr ess; 1 9 9 9 . p . 1 6 5 - 8 1 . 10. Fischm an MW, Haney M. Neur obiology of st im ulant s. I n: Ga l a n t e r M, K l e b e r H D . Te x t b o o k o f S u b s t a n c e A b u s e Tr eat m en t . 2 ª ed . Wash in g t on ( DC) : Am er ican Psy ch iat r ic Pr ess; 1 9 9 9 . p . 2 1 - 3 1 .
1 1 . La n g e JE, Cl a p p JD, Tu r r i si R, Re av y RL, Ja cca r d J, Johnson MB, et al. College Binge Dr ink ing: What I s I t ? Who D o es I t ? Al co h o l i sm Cl i n Ex p Res 2 0 0 2 May ; 2 6 ( 5 ) : 7 2 3 -3 0 .
1 2 . B o t v i n GJ, B o t v i n EM , Ru c h l i n H . S c h o o l - b a s e d a p p r o a c h e s t o d r u g a b u s e p r e v e n t i o n : e v i d e n c e f o r e f f e c t i v e n e s s a n d s u g g e s t i o n s f o r d e t e r m i n i n g c o s t ef f ect iv en ess. I n : Nat ion al I n st it u t e on Dr u g Ab u se. Cost -benefit / cost - effect iveness r esear ch of dr ug abuse pr event ion: im plicat ion s for pr ogr am m in g an d policy. Wash in gt on ; Gov t Pr int Off. ; 1 9 9 8 . ( NI DA Resear ch Monogr. n. 1 7 6 ) .
1 3 . Cen t er For Disease Con t r ol an d Pr ev en t ion . You t h r isk b e h a v i o r su r v a i l l a n ce - Un i t e d St a t e s, 1 9 9 7 . MMW R CD C Su r v eill Su m m 1 9 9 8 ; 4 7 : 3 .
1 4 . Fr ied m an AS. Su b st an ce u se/ ab u se as a p r ed ict or t o illegal and violent behavior : a r eview of t he r elevant lit er at ur e. Ag g r ession an d Violen t Beh av ior 1 9 9 8 ; 3 ( 4 ) : 3 3 9 - 5 5 .