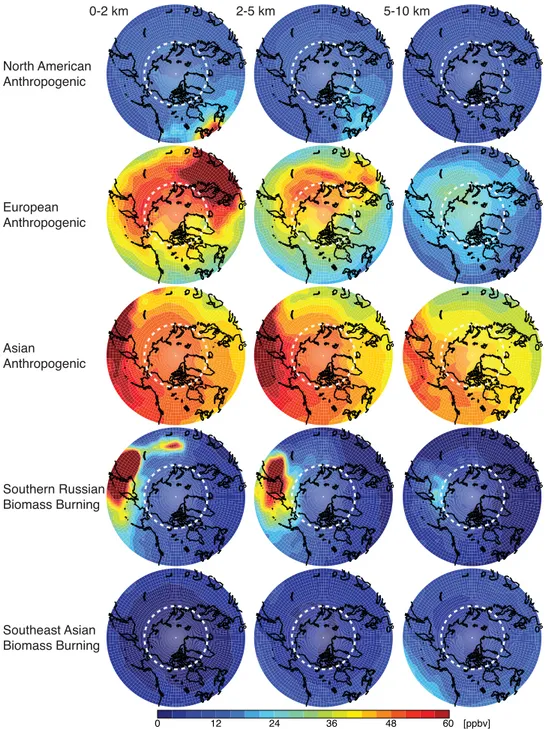
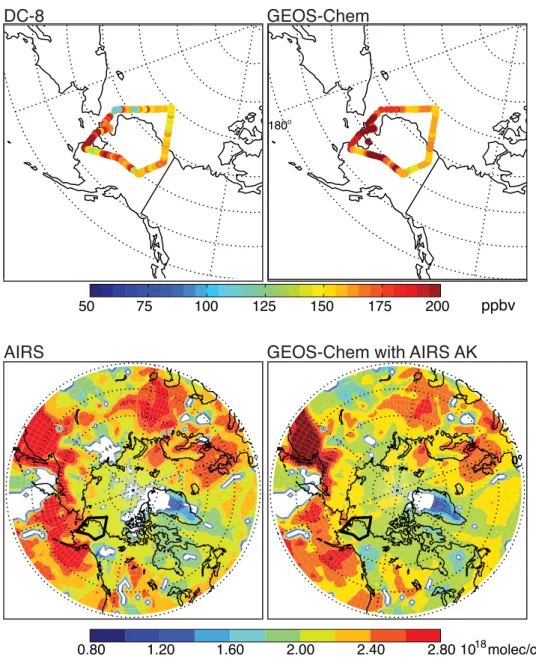
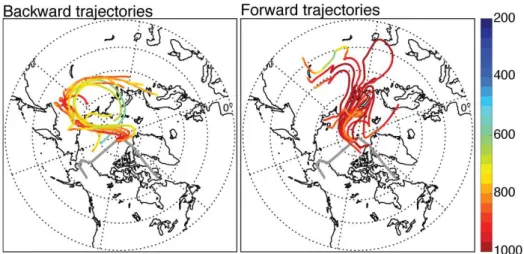
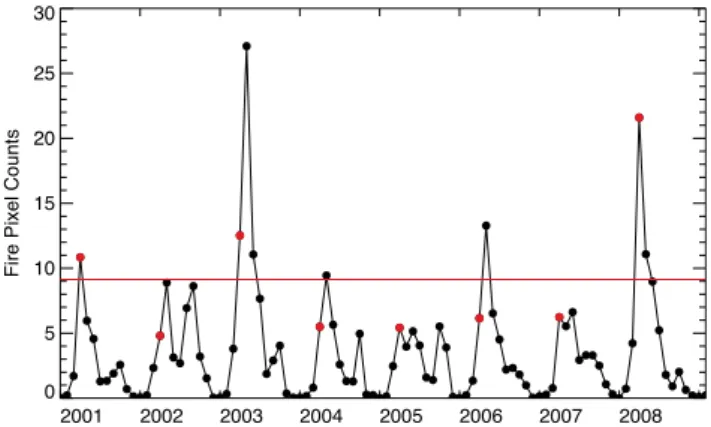
Source attribution and interannual variability of Arctic pollution in spring constrained by aircraft (ARCTAS, ARCPAC) and satellite (AIRS) observations of carbon monoxide
Texto
Imagem

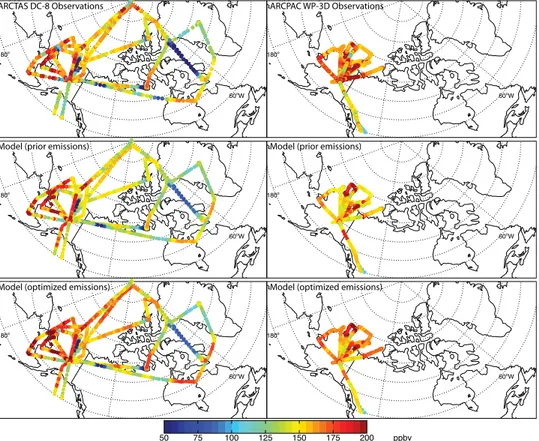
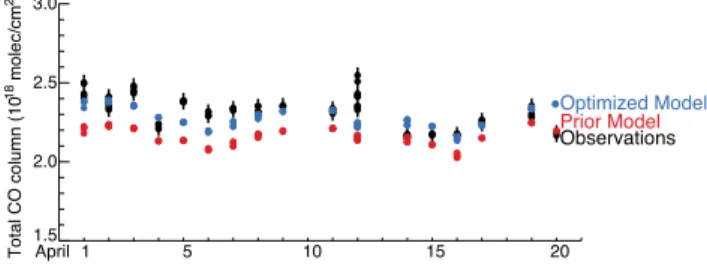
Documentos relacionados
The highest monthly average values of IO slant columns are found for October and March (springtime and autumn) close to the Antarctic continent, especially in the Weddell Sea,
Comparison of AIRS satellite observations (top, left) and MPTRAC simulation results on 13 June 2011, 06:00 UTC based on the equal-probability strategy (top, right), the mean
We use satellite observations of aerosol optical depth (AOD) from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spec- trometer (MODIS) together with the GEOS-Chem global chemical transport model
Abstract: This paper proposes a systematic method for the simultaneous determination of adjusted ranks of sample observations and their sums and products adjusted for
However, carbon monox- ide (CO), sulfur dioxide (SO 2 ), and toluene have been ob- served co-emitted with carbonyl compounds from industrial facilities at various locations and
Similar discrepancies are found when using the HYSPLIT trajectory model at different altitudes (10–13 km) or the wind speeds and directions, actually measured on board of the
tions from aircraft (NCAR C-130 and NASA DC-8) and from the Tropospheric Emission Spectrometer (TES) satellite during the MegaCity Initiative: Local and Global Research
The goals of this study included obtaining snow bidirectional reflectance at high 1 ◦ angular resolution from CAR measurements and using these data for an accuracy analysis