Vertical profiling of aerosol hygroscopic properties in the planetary boundary layer during the PEGASOS campaigns
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
The comparison of the total aerosol number size distribu- tions, including BC-free particles (representing the largest fraction, and a minor fraction of BC-containing particles), of
Figure 10 does not show a large inter-annual variability of the air masses circulation over the three sites ; the main dif- ferences are observed over the Cinzana site in summer
Overall, mass transfer effects in hygroscopic measurements of ambient particles and laboratory generated particles are possible if the particles are not allowed to have sufficient
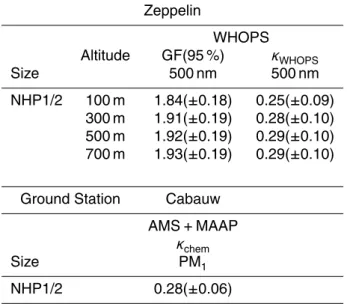
In this study, we analyzed number concentration and size distribution of aerosol particles, together with the mass concentration and chemical composition of UFPs and PM 1
Measurements of aerosol chemical composition and aerosol optical depth in the Nepal Himalaya have clearly shown the build up of aerosols in the pre-monsoon season during the winter
The reported method decouples any change in the charge transfer properties of the particles from the measurement signal, so the e ff ect of particle phase changes on bounce alone can
The change of phase can be clearly seen in the bounce dia- gram of 115 nm (mobility size), ammonium sulfate (Fig. 4), where the fraction of the bounced particles reduce almost with
Basing on the results of MANOVA test it has been observed that the strongest significant effect on an increase of the tensile strength R m exerted the addition of Mg, followed by