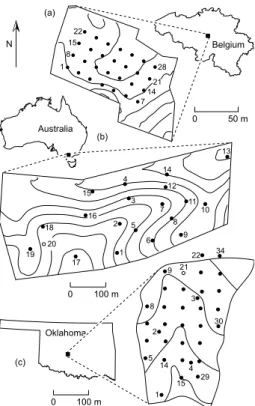
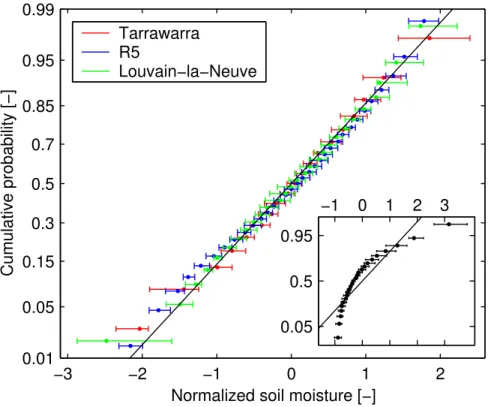
Estimating spatial mean root-zone soil moisture from point-scale observations
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
Mean annual values of soil temperature at 5 cm depth, soil moisture of the top 5 cm soil layer, soil respiration rate, fine root biomass and soil microbial biomass under
Moisture data for Station 84 (red clay): (a) Time series for each sensor; (b) Horizontal moisture isochrones A comparison between the precipitation and the gravimetric water content
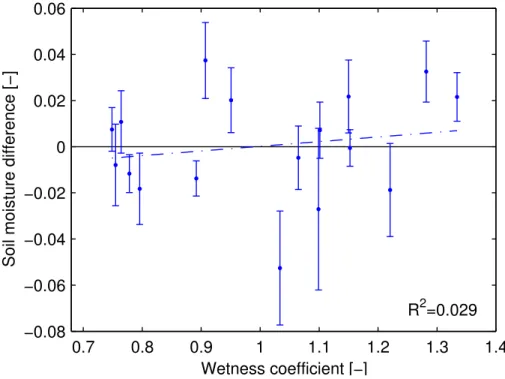
Semivariogram models, adjusted for soil moisture, had strong spatial dependence, but the relationship between soil moisture and soil ECa was obtained only in one of the
For the Red- Yellow Ultisol and Litholic Neosol, the largest amplitudes followed the sequence of the greatest water content retained by the soil (field capacity > wilting point
Decomposition of the Catchment near-surface soil moisture time series at Little River, using the harmonic (HA; black) and moving average (MA; cyan) methods, for (a) the original
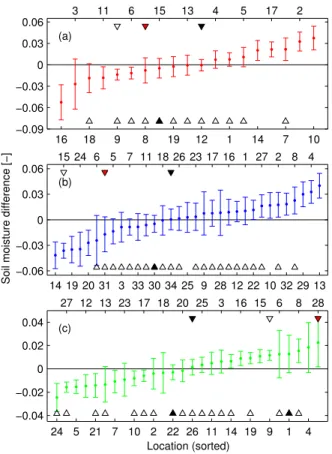
The main conclusions of this study are (1) soil moisture in near-surface and root zone layers in Oklahoma and Nebraska are strongly coupled, (2) the exponential filter method
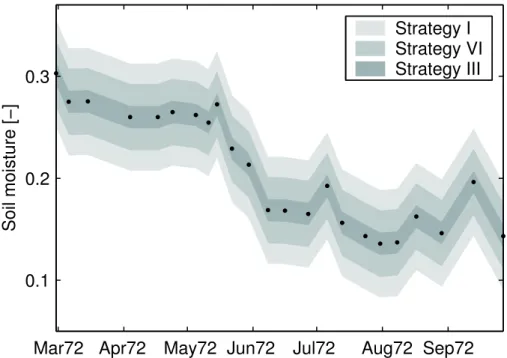
A linear interpolation of Ŵ soil between the six sampling dates in combination with hourly soil temperature measurements were used to generate a time series of soil compensation point
(2011) developed a dual Kalman filter for estimating the root zone soil moisture using a model based on the Richards equation, by combining the EKF to update the state variables,