Article
J. Braz. Chem. Soc., Vol. 22, No. 6, 1183-1191, 2011. Printed in Brazil - ©2011 Sociedade Brasileira de Quím ica
0103 - 5 05 3 $ 6.00+ 0.00
A
* e-m ail: w y p y ch @ uf p r.b r
Effect of Coninement of Anionic
Organic Ultraviolet Ray Absorbers into
Two-dimensional Zinc Hydroxide N itrate G alleries
Ana Cristina T. Cursino,a Antonio Salvio Mangrich,b José Eduardo F. da Costa
Gardolinski,c Ney Mattosod and Fernando W y p y ch*,a
aCEPESQ - Research Centre of Applied Chemistry, Department of Chemistry,
bL ABPAM - L ab oratory of Env ironmental Proj ects and Processes, Department of Chemistry, cL AM I R - L ab oratory for Analysis of M inerals and Rock s, Department of G eolog y and
dDepartment of Physics, F ederal U niv ersity of Paraná, PO Box 1 9 0 8 1 ,
8 1 5 3 1 -9 8 0 Cu ritib a-PR, Brazil
E sp écies aniônicas ab sorv edoras de radiação ultrav ioleta ( U V) ( 4 -m etox ib enzoato, N-acetilantranilato, 4 -m etox icinam ato e 4 ,4 ' -diam ino-2,2' -estilb enodissulf onato) f oram intercaladas em h idrox initrato de zinco p elo m étodo de co-p recip itação ou reação de troca aniônica top otática.
A intercalação f oi conirm ada p or dif ratom etria de raios X de p ó ( X R PD ) , esp ectroscop ia na reg ião do inf rav erm elh o com transf orm ada de F ourier ( F T I R ) , análise térm ica ( T G A / D T A ) , m icroscop ia eletrônica de v arredura ( SE M ) , dif ração de elétrons em área selecionada ( SA E D ) , análise elem entar e esp ectroscop ia eletrônica na reg ião do ultrav ioleta-v isív el ( U V-Vis) . Na reação
de co-p recip itação um a intercalação com p leta f oi observ ada, enq uanto na reação de troca aniônica
os íons nitrato só f oram p arcialm ente sub stituídos p elos ânions org ânicos. A p ós a intercalação, a cap acidade de ab sorção de radiação U V f oi sim ilar à dos sais e ácidos sólidos, sendo o ef eito atrib uído ao coninam ento das esp écies aniônicas na g aleria b idim ensional da m atriz h osp edeira. E ssa ob serv ação ab re nov as op ortunidades p ara o uso de m atrizes lam elares alternativ as p ara a im ob ilização de ânions, na f orm ulação de p rotetores solares.
A nionic ultrav iolet ( U V) ray ab sorb ers ( 4 -m eth ox y b enzoate, N-acety lanth ranilate, 4 -m eth ox y cinnam ate and 4 ,4 ' -diam ino-2,2' -stilb enedisulf onate) w ere intercalated into zinc
h y drox ide nitrate, eith er b y direct alk aline co-p recip itation or top otactic ex ch ang e reactions. T h e
intercalation w as conirm ed b y X -ray p ow der dif f ractom etry ( X R PD ) , F ourier transf orm inf rared sp ectroscop y ( F T I R ) , th erm al analy sis ( T G A / D T A ) , scanning electron m icroscop y ( SE M ) , selected
area electron dif f raction ( SA E D ) , elem ental analy sis and ultrav iolet v isib le ( U V-Vis) sp ectroscop y . I n th e co-p recip itation reactions f ull intercalation w as ach iev ed, w h ile during th e ex ch ang e reactions nitrate anions w ere not com p letely rep laced b y th e org anic anions. A f ter th e intercalation, th e U V ab sorp tion cap acity w as sim ilar to th at of th e solid salts and acids, th e ef f ect b eing attrib uted to th e coninem ent of th e anionic sp ecies in th e h ost tw o-dim ensional g allery . T h is ob serv ation op ens new op p ortunities f or th e use of org anic anions im m ob ilized in alternativ e lay ered m atrix es f or th e f orm ulation of sunscreens.
K eywords: zinc h y drox ide nitrate, U V ray ab sorb ers, sunscreens, lay ered m aterials, intercalation
I ntrodu ction
H ealth p rob lem s related to th e ex p osure to solar ultrav iolet ( U V) radiation can b e m inim ized b y th e use of sunscreens and oth er cosm etic ilters. T h ese p roducts are reg ularly used b y m illions around th e g lob e. Because of
th eir f req uent and long -term use, sp ecial attention h as b een dev oted to th e ef iciency and saf ety of th ese f orm ulations.1
U V ray ab sorb ing org anic m olecules are w idely em p loy ed as activ e ing redients of sunscreens. A m ong such sub stances are anth ranilates and cinnam ates.2 A lth oug h
th ere are a larg e num b er of anth ranilates ( also k now n as
ortho-am inob enzoates) , only tw o of th em are com m only
l-anth ranilate and m eth y l-l-anth ranilate. A s th e U VA ray ab sorp tion of th ese com p ounds is low , th ey are usually used tog eth er w ith oth er U V ab sorb ers. T h ese com p ounds p resent g ood stab ility and solub ility in top ical p rep arations,
w ith ab sorp tion m ax im a around 336 nm f or th e ortho
and 300 nm f or th e para m olecules.3 O n th e oth er h and,
th e cinnam ates constitute a larg er g roup of com p ounds, sev enteen of th em h av ing b een ap p rov ed as sunscreens in E urop e and f our in th e U nited States. T h e cinnam ates are insolub le in w ater b ut h ig h ly solub le in alcoh ol, acetone and b enzene. T h ey act as ab sorb ers in th e U VB reg ion, w ith m ax im a around 300 nm .4 ,5
E v en th oug h th e use of U V ray ab sorb er m olecules, due to th eir h ig h af inity f or th e stratu m corneu m, is
v ery w idesp read, th ey can b e easily ab sorb ed b y th e b ody , leading to p h ototox ic and allerg ic reactions.6-8 T o
p rev ent th e direct contact of such m olecules w ith h um an tissues, th ey can b e intercalated into lay ered structures,
such as lay ered h y drox ide salts ( L H Ss)9 and oth er lay ered
m aterials.10-12
T h e structure of L H Ss is deriv ed f rom th at of a g eneric lay ered h y drox ide ( M2) , w h ere a f raction of th e ( O H ) h y drox y l sites are sub stituted b y oth er anions or by w ater m olecules, resulting in a structure w ith p ositiv ely ch arg ed lay ers th at are electrically b alanced b y intercalated anions.
T h eir g eneral f orm ula is M2+( O H )
2−x( An−)x / n·y H2O , w h ere
M2+ is a m etal cation ( M g , Ni, Z n, C a, C d, C o and C u) and
A is th e n− ch arg ed anion, called th e counter-ion ( C l−, NO
3−,
SO4 2− and H
3C C O O
−) .13-16 D ue to th e structural ch aracteristics
of L H Ss, v arious k inds of anions can b e intercalated, f rom sim p le m onoatom ic sp ecies to com p lex m olecules.
T h e m ain g oal of th is w ork is to f urth er study th e intercalation of U V radiation ab sorb ers into L H Ss. T h is could p ossib ly g iv e rise to a new g eneration of sunscreens th at could sig niicantly reduce th e ab sorp tion of th e activ e m olecules b y th e h um an sk in, av oiding th e cause of m any allerg ic reactions and also slow ing th eir p h otodeg radation.
Exp erimental
Synthesis of zinc hydrox ide nitrate
T h e sy nth esis of zinc h y drox ide nitrate ( Z H N) w as carried out f ollow ing a p rocedure describ ed elsew h ere.17 ,18
I n sh ort, it w as p rep ared b y th e slow addition of an aq ueous NaO H solution ( 1 m ol L−1) into 7 0 m L of aq ueous
solution containing 17 .5 m m ol of Z n( NO3)2·6H2O , under
m ag netic stirring , w ith th e inal p H adj usted to around 6.5 . T h e solid w as sep arated b y centrif ug ing at 4 000 rp m f or 5 m in, f ollow ed b y ex tensiv e w ash ing w ith distilled w ater ( 5 tim es) . T h e inal w h ite solid w as dried under v acuum at 60 °C f or 24 h . T h e p rep ared Z H N w as used as a m atrix f or th e intercalation of sev eral org anic U V ray ab sorb er anions, w h ose acids are sh ow n in F ig ure 1.
Preparation of the intercalation compou nds
Ex chang e reaction
A n intercalation com p ound w ith 4 -m eth ox y b enzoate w as p rep ared b y th e slow addition of 5 0 m L of an aqueous solution of NaO H ( 1 m ol L−1) to 7 0 m L of a susp ension
containing 4 .7 m m ol of 4 -m eth ox y b enzoic acid ( F ig ure 1a) in decarb onated w ater, to ob tain a solution of sodium
4 -m eth ox y b enzoate salt. T o th is solution, Z H N ( 2 m mol) w as added and th e susp ension w as m ag netically stirred at
60 °C f or 4 day s, b ef ore b eing centrif ug ed and ex tensiv ely
w ash ed w ith distilled w ater ( 4 tim es) . T h e inal w h ite solid ( Z H N-M B) w as dried under v acuum at 60 °C f or 24 h . T h e sam e p rocedure w as f ollow ed to sy nth esize th e p roduct
w ith N-acety lanth ranilic acid ( F ig ure 1b , Z H N-NA A ) .
Synthesis b y co-precipitation
A s som e org anic anions do not h av e th e suf icient th erm ody nam ic driv ing f orces to disp lace th e intercalated nitrate anions f rom th e Z H N structure, new attem p ts
w ere m ade to p roduce th ese com p ounds b y direct co-p recip itation. T h e intercalation com p ound w ith
4 -m eth ox y cinnam ate ( F ig ure 1c) w as p rep ared b y dissolv ing 2.5 m m ol of 4 -m eth ox y cinnam ic acid in 20 m L of an aq ueous solution of NaO H ( 0.4 m ol L−1) .
T o th is, 20 m L of a solution containing 7 .5 m m ol of Z n( NO3)2·6H2O w as slow ly added and th e f inal p H
w as adj usted to around 7 b y th e addition of a NaO H ( 0.4 m ol L−1) solution. T h e susp ension w as m ag netically
stirred at room tem p erature f or 3 day s, b ef ore b eing centrif ug ed and w ash ed 5 tim es w ith distilled w ater. T h e
inal w h ite solid ( Z H N-M C ) w as dried under v acuum at 60 °C f or 24 h . T h e sam e p rocedure w as f ollow ed to sy nth esize th e p roduct w ith 4 ,4 ' diam ino2,2' -stilb enedisulf onic acid ( F ig ure 1d) , denoted Z H N-D SD .
Characterization
X -ray p ow der dif f raction ( X R PD ) p atterns w ere recorded w ith a Sh im adzu X D R -6000 instrum ent using C uKα radiation (λ = 1.5 4 18 Å) in Brag g -Brentano g eom etry , w ith a dw ell tim e of 1° m in−1. T h e sam p les
w ere p laced and oriented b y h and b y p ressing on neutral g lass sam p le h olders.
T h e F T I R sp ectra w ere recorded w ith a Bio-R ad F T S 35 00G X and a Bom em M ich elson M B100 sp ectrop h otom eters, using ap p rox im ately 1% sam p le in 100 m g of sp ectroscop ic g rade K Br. T h e p ellets w ere p ressed at 10 ton. T h e m easurem ents w ere p erf orm ed in transm ission m ode w ith accum ulation of 32 scans and recorded w ith a nom inal resolution of 2 cm−1.
T h erm al analy ses ( th erm og rav im etry -T G A and dif f erential th erm al analy sis-D T A ) w ere p erf orm ed in 15 0 µL alum ina crucib les w ith a M ettler-T oledo T G / SD T A 85 1e T h erm oanaly ser under a 5 0 m L m in−1 ox y g en
low , at a h eating rate of 10 °C m in−1, in th e rang e of
30-1000 °C .
T h e dif f use relectance ultrav iolet-v isib le ( D R U V-VI S) sp ectra w ere ob tained at room tem p erature in th e reg ion of 24 0-800 nm , at interv als of 0.5 nm , w ith a
Sh im adzu U V-24 01PC sp ectrop h otom eter eq uip p ed w ith a M odel 24 0-5 24 5 4 -01 integ ration sp h ere.
Scanning electron m icroscop y ( SE M ) analy ses of th e sam p les w ere carried out ( af ter m etallization with
g old) w ith a J E O L J SM 6360 L V m icroscop e op erating at 15 k V. Selected area electron dif f raction ( SA E D )
m easurem ents w ere p erf orm ed w ith a J E O L J E M 1200 E X -I I transm ission electron m icroscop e ( T E M ) op erating at 80 k V f or p ure H Z N and 5 0 k V f or th e com p ounds ob tained b y co-p recip itation. C alib ration of th e electron dif f raction to SA E D m easurem ents w as carried out using an A u sam p le as ref erence.
Resu lts and D iscu ssion
T h e X R PD p atterns of Z H N and th e com p ound p rep ared b y co-p recip itation w ith 4 ,4 ' -diam ino-2,2' -stilb enedisulf onic acid are sh ow n in F ig ure 2.
T h e p roduct ob tained f rom th e alk aline p recip itation sh ow s th e f orm ation of a cry stalline p h ase of th e zinc h y drox ide nitrate ( Z n5( O H )8( NO3)2·2H2O = Z H N) ,
identif ied b y th e J C PD S f ile num b er 24 -14 60.19 T h e
dif f raction p attern sh ow s an intense relection due to th e ( 200) p lane of th e m onoclinic structure, w ith a b asal sp acing of 9.7 7 Å ( F ig ure 2c) .
F or th e direct sy nth esis f rom 4 ,4 ' diam ino2,2' -stilb enedisulf onic acid in th e p resence of zinc nitrate th roug h
alk aline co-p recip itation, th e b asal sp acing of th e p roduct
( Z H N-D SD ) w as m easured as 15 .4 8 Å ( F ig ure 2d) . T h is indicates th e p resence of th e org anic anion b etw een th e
inorg anic lay ers of th e m atrix , w ith a b asal ex p ansion of 5 .7 1 Å f rom th e orig inal com p ound. T h e p reserv ation of th e lay ered structure of th e m atrix is conirm ed b y th e p resence of th e b asal relections, w h ich are unif orm ly distrib uted betw een 5 ° and 35 ° ( in 2θ) . I n th e reg ion of 16° ( in 2θ) , th e sm all p eak indicated b y an “* ” is of one unk now n p h ase, b ut it is not attrib uted to th e 4 ,4 ' -diam ino-2,2' -stilb enedisulf onic acid.
T h e F T I R sp ectra of th e sam e com p ounds are sh ow n in F ig ure 3.
T h e F T I R sp ectrum of th e Z H N ( F ig ure 3c) p resents an intense b and at 1384 cm−1, ch aracteristic of th e nitrate ion w ith
F igu re 2. X R PD p atterns of 4 ,4 ' -diam ino-2,2' -stilb enedisulfonic acid
D3h sy m m etry (ν3 m ode)18. A b road b and around 35 00 cm−1 is
also seen, attrib uted to th e v ib ration of th e h y drox y l g roup s,
w h ich h av e m ultip le h y drog en b onds w ith p h y sisorb ed/ intercalated w ater m olecules. A narrow b and p resent at
35 7 5 cm−1 is also attrib uted to h y drox y l g roup s, b ut in th is case
f rom th e cry stal lattice, w ith a w ell deined v ib ration energ y .20
T h e F T I R sp ectrum of th e 4 ,4 ' diam ino2,2' -stilb enedisulf onic acid ( F ig ure 3a) p resents a b and
b etw een 314 0 and 2920 cm−1 th at is attrib uted to th e
ax ial def orm ation of arom atic N−H and C−H alip h atic
g roup s. Norm ally th e sy m m etric and asy m m etric ax ial def orm ations of th e S= O g roup s are v isib le around 135 0-134 2 cm−1 and 1165 -115 0 cm−1, resp ectiv ely . H ow ev er, it
w as not p ossib le to identif y th ese b ands b ecause such v alues
are due to th e anh y drous f orm of th e acid, w h ich p rom p tly h y drates to a h y dronium -sulf onate, th us g iv ing rise to b ands
around 1230-1120 cm−1.21 T h ese h y drated f orm b ands are
p resent in th e acid at 1200 cm−1 and also in its sodium salt
( F ig ure 3b ) and in th e Z H N-D SD com p ound ( F ig ure 3d) . T h e ax ial def orm ation b ands of th e arom atic C = C g roup s around 1613 and 14 82 cm−1 seen in th e acid, its sodium salt
and, m ost im p ortantly , in th e Z H N-D SD com p ound, f urth er conirm th e intercalation of th e org anic anion.
T o study th e b eh av ior of th e p roduct in th e ultrav i olet-v isib le reg ion, D R U V-VI S sp ectroscop y w as conducted ( F ig ure 4 ) . T h e K ub elk a-M unk f unction w as ap p lied to th e study of op tically th ick sam p les, w h ere m ore than 5 0%
of th e lig h t is relected and less th an 20% is transm itted.22
T h e ex p erim ental relectance sp ectra w ere conv erted b y th e reem ission f unction of K ub elk a-M unk , def ined as:
f ( K M ) = ( 1 − R )2 / 2R = k / s, w h ere R is th e relectance, k is
th e ab sorp tion coef icient and s is th e disp ersion coef icient.23
A ssum ing th at th e disp ersion coef icient v aries m inim ally as a f unction of th e w av eleng th , th e reem ission f unction areas and th e ab sorp tion f unction areas of th e sp ectra should b e v ery near each oth er.
T h e y ellow ish 4 ,4 ' -diam ino-2,2' -stilb enedisulf onic acid h as an ab sorp tion m ax im um in th e reg ion around 25 0-35 4 nm ( F ig ure 4 b ) , cov ering th e entire U VB reg ion and p art of th e U VA reg ion. I ts orang e colored sodium salt ab sorb s in th e reg ion around 24 0-37 9 nm , cov ering th e U VC to U VA reg ions ( F ig ure 4 c) .
T h e Z H N-D SD p roduct h as a lig h t b eig e color, w h ich can b e considered esth etically m ore p leasing and thus m ore
usab le th an th e strong -colored f ree acid and its sodium
salt. I t h as a sig niicant ab sorp tion in th e w h ole ultrav iolet reg ion, f rom U VA to U VC ( F ig ure 4 d) , slig h tly less intense in th e h ig h er w av eleng th s th an th e f ree sodium salt due to th e dilution ef f ect af ter intercalation into th e Z H N lay ered m aterial. T h e org anic m olecule slig h tly increases its rang e to ab sorb U V lig h t, and th is ef f ect can b e interp reted on th e b asis of th e sp atial coninem ent of th e anionic sp ecies
in th e interlay er L H S sp ace, low ering th e sy m m etry of th e intercalated anion in com p arison to th e m olecules in th e
solid salt or acid, and also to sup ram olecular h ost-g uest interactions ( electrostatic attraction, h y drog en b onding and v an der W aals f orces) .24 ,25
F igu re 3 . F T I R sp ectra of 4 ,4 ' -diam ino-2,2' -stilb enedisulf onic acid ( a) , 4 ' ,4 -diam ino-2,2' -stilb enedisulf onic acid sodium salt ( b ) , Z H N ( c) and Z H N-D SD ( d) .
T h e stab ility of th e Z H N-D SD p roduct w as tested b y stirring in w ater f or 2 h . A f ter th is treatm ent, th e
ab sorp tion in th e ultrav iolet reg ion w as v irtually unch ang ed
(F ig ure 4 e) . I n addition, th e X R PD p attern of th is p roduct ( not sh ow n) sh ow ed no ch ang es in relation to th e orig inal p roduct.
T h erm al analy sis ( T G A / D T A ) results f rom Z H N ( not sh ow n) rev eal a com p lex decom p osition p roile w ith a
series of endoth erm ic ev ents around 200 °C ( 129, 163,
214 and 262 °C ) , attrib uted to loss of w ater, b oth adsorb ed and structural, w h ich com p rises 6% of th e total m ass up to 131 °C . Betw een 131 and 5 5 2 °C a m ass loss of 27 % occurs, attrib uted to th e m atrix deh y drox y lation along w ith
nitrate decom p osition.26 T h e m ass losses are consistent
w ith th e f orm ula Z n5( O H )8( NO3)2·1.7 4 H2O , close to th e
th eoretical f orm ula.
T G A / D T A m easurem ents w ere p erf orm ed to estim ate th e com p osition of th e intercalation com p ounds ( F igure 5 ) .
T h e th erm al analy sis curv es of Z H N-D SD sh ow th ree m ain th erm al ev ents. T h e f irst tw o corresp ond to the
rem ov al of p h y sisorb ed/ intercalated w ater m olecules, associated w ith tw o D T A p eak s at 160 and 215 °C . T h e th ird th erm al ev ent is attrib uted to th e ox idation of organic m atter and deh y drox y lation of th e lay ered m atrix , p roducing Z nO ,
as attested b y X R D ( not sh ow n) . W ith th is inf orm ation, it w as p ossib le to estim ate th e com p osition of th e comp ounds
as b eing Z n5( O H )8( NO3)0.04( C14H12N2O6S2)0.98·0.84 H2O ,
close to th e stoich iom etric v alue. T h e th erm al stability of Z H N-D SD is around 25 0 °C , under dy nam ic h eat conditions.
M orp h olog ical analy ses of th e Z H N ( F ig ure 6a) and
Z H N-D SD ( F ig ure 6b ) w ere p erf orm ed b y SE M . T h e
p recursor Z H N is ch aracterized b y tab ular p articles w ith w ell def ined corners and a w ide size distrib ution, in
accordance to w h at h as already b een rep orted f or sim ilar com p ounds.16 T h e co-p recip itated Z H N-D SD com p ound
w as also ch aracterized b y tab ular p articles w ith w ell deined
corners, th ese h ow ev er b eing m uch larg er th an th ose of th e Z H N and v ery f rag m ented, due to th e m ag netic stirring .
F ig ure 7 p resents th e X R PD p atterns of th e Z H N deriv ativ es w ith 4 -m eth ox y b enzoate, Z H N-M B
( F ig ure 7 b ) , 4 -m eth ox y cinnam ate, Z H N-M C ( F ig ure 7 c) and N-acety lanth ranilate, Z H N-NA A ( F ig ure 7 d) .
T h e b asal sp acing of th e Z H N-M B and Z H N-M C com p ounds increased f rom th e orig inal 9.7 7 Å of th e
p ristine Z H N to 18.67 and 20.13 Å, resp ectiv ely . T his strong ly indicates th e sub stitution of th e orig inally intercalated nitrate anion b y th e corresp onding org anic anions em p loy ed. I t can also b e seen th at th ese p roducts
are p ossib ly contam inated w ith p h ases p resenting v arious deg rees of h y dration or f orm ation of stag e interm ediate
p h ase, ch aracterized b y low intensity p eak s at 26.5 and
26.9 Å f or Z H N-M C and Z H N-M B, resp ectiv ely . T h e X -ray dif f raction p atterns of th e Z H N-NA A com p ound ( F ig ure 7 d) sh ow no clear distinction in th e b asal distances f rom th e orig inal Z H N, sug g esting th at th e org anic anion w as not intercalated. T h is is p rob ab ly due to th e
incom p atib ility b etw een th e p ositions of th e neg ativ e ch arg es in th e N-acety lanth ranilate and th e p ositiv e ch arg es
in th e Z H N structure. H ow ev er, no dif f raction p eak s due to th e f ree acid or its sodium salt could b e detected.
T h e F T I R s p e c t r a o f 4 - m e t h o x y c i n n a m a t e , 4 -m eth ox y b enzoate, N-acety lanth ranilate and th eir Z H N
deriv ativ es can b e seen in F ig ure 8. Bands attrib uted to v ib rational m odes f rom th e N-acety lanth ranilate anion are
p resent in th e F T I R sp ectrum of th e Z H N-NA A p roduct ( F ig ure 8g ) . I n th is case, th e b ands at 15 15 and 14 15 cm−1
are attrib uted to th e asy m m etric and sy m m etric carbox y late stretch ing m odes. Betw een 2900 and 285 0 cm−1, w eak
b ands f rom th e ax ial def orm ation of m eth y l C−H b onds are also p resent. I n addition, th e ch aracteristic nitrate b and at 1384 cm−1 is still p resent. T h e p resence of th ese
org anic b ands and th e f act th ere w as no ch ang e in th e b asal sp acing of th e m atrix sug g ests th at th e N-acety lanth ranilate
m olecules are adsorb ed on th e surf ace of th e Z H N p articles.
F or th e Z H N-M B and Z H N-M C com p ounds, th e p resence of th e intercalated org anic U V ray ab sorb ing
anions can b e attested b y th eir F T I R sp ectra ( F ig ures 8c and 8e) . A round 15 4 0 and 14 20 cm−1, b ands attrib uted to
carb ox y late asy m m etric and sy m m etric stretch ing m odes are ob serv ed, as w ell as b ands b etw een 307 0 and 2840 cm−1,
attrib uted to th e ax ial def orm ation of C−H g roup s in arom atic ring s and m eth y l g roup s,27 along side oth er b ands
p resented in T ab le 1. Bands attrib uted to th e inorganic
m atrix are also p resent, lik e th e b road sig nal b etw een 3600 and 335 0 cm−1, ch aracteristic of lattice h y drox y l g roup s.
T h e th erm al p roiles of th e Z H N-M B and Z H N-M C com p ounds ( not sh ow n) are v ery sim ilar, p resenting tw o m aj or ev ents, th e irst one attrib uted to w ater loss
( endoth erm ic ev ent around 15 0 °C ) and th e second one attrib uted to th e deh y drox y lation of th e m atrix and b urning
of th e org anic m atter ( ex oth erm ic ev ent around 4 00 °C ) .
A s discussed f or th e Z H N-D SD , th e T G A / D T A analy sis allow s us to estim ate th e f orm ula of th e com p ounds as
Z n5( O H )8( NO3)0.4 6( C10H9O3)1.5 4·3.4 H2O f or Z H N-M C and
Z n5( O H )8( NO3)0.4 8( C8H7O3)1.5 2·4 .6H2O f or Z H N-M B, w h ere
not all th e nitrate anions w ere rep laced b y th e organic anions. T h e adsorp tion of th e N-acety lanth ranilate anions
onto Z H N is f urth er attested b y th e T G A / D T A results ( not sh ow n) , since th ey are clearly distinct f rom th e th erm al p roile of th e orig inal Z H N.
T h e D R U V-VI S sp ectroscop ic analy sis of th e Z H N-NA A com p ound ( F ig ure 9d) p resented ab sorp tion b ands sim ilar to th ose of th e f ree acid ( F ig ure 9c), its
sodium salt ( F ig ure 9b ) and also th e Z H N ( F ig ure 9a) . H ow ev er, in th e U VA reg ion, a sh if ted ab sorp tion m ax im um not seen in any of th e p recursors can b e ob serv ed in th e p roduct. T h is is anoth er indication th at th e U V-ab sorb ing org anic m olecules are adsorb ed on th e Z H N p articles outer surf aces.
F igu re 6. SE M im ag es of Z H N ( a) and Z H N-D SD ( b ) .
F igu re 7 . X R PD p atterns of Z H N ( a) , Z H N-M B ( b ) , Z H N-M C ( c) and Z H N-NA A ( d) .
F igu re 8 . F T I R sp ectra of Z H N ( a) , sodium m eth ox y cinnam ate (b ) , Z H N-M C ( c) , sodium m eth ox y b enzoate ( d) , Z H N-M sodium B ( e) ,
N-acety lanth ranilate ( f ) and Z H N-NA A ( g ) .
Table 1 . W av enum b ers ( cm−1) of som e v ib rational m odes in th e Z H N-M B and Z H N-M C com p ounds and th e resp ectiv e org anic sodium salts
C om p ound C O O−
( as) C O O
−
( sy m )C = C( arom ) C−O−C( as)C−O−C( sy m )
Na-M C 15 5 4 14 33 15 12 124 3 1033 Z H N-M C 15 4 2 14 23 15 17 125 9 1027 Na-M B 15 96 14 19 15 4 1 125 1 1029 Z H N-M B 1606 14 17 15 4 8 125 9 1032
T h e w h ite-colored sodium 4 -m eth ox y b enzoate p resented an ab sorp tion m ax im um around 25 0-290 nm , cov ering th e U VC to th e U VB reg ions, as seen f rom th e D R U V-VI S results ( F ig ure 10d) . A f ter intercalation, th e Z H N-M B p roduct, also w h ite, p resented one ab sorp tion m ax im um around 25 3 nm ( F ig ure 10e) . R esults f rom th e D R U V-VI S sp ectroscop y analy sis of th e Z H N-M C com p ound ( F ig ure 10c) p resented one ab sorp tion m ax im um
around 297 nm , not ab sorb ing in th e v isib le reg ion (λ> 4 00 nm ) . T h is ch aracteristic is p ossib ly an adv antag e to th e cosm etics industry , w h ere colored additiv es are
not alw ay s desired. I n addition, th is p roduct ab sorb s in
a b road sp ectral rang e, including U VC and U VB reg ions and a sm all p art of th e U VA reg ion. T h is b eh av ior is closely related to th e sodium 4 -m eth ox y cinnam ate, w ith an ab sorp tion rang e b etw een 24 0 and 308 nm ( F ig ure 10b ) ,
b ut sig niicantly dif f erent th an th e 4 -m eth ox y cinnamic acid ( not sh ow n) , w ith a m ax im um around 264 -387 nm .
A s in th e case of th e Z H N-D SD com p ound, scanning electron m icroscop y im ag es of th e p roducts ob tained b y co-p recip itation ( Z H N-M C ) and ex ch ang e reaction ( Z H N-NA A ) ( F ig ures 11b and 11c) sh ow ed tab ular p articles w ith larg er size and w ider size distrib ution th an
th ose of Z H N ( F ig ure 11a) . T h e cry stal g row ing p rocess can b e attrib uted to dissolution and re-p recip itation during
th e ex ch ang e reaction.
T h e SA E D p attern of th e com p ounds ob tained b y co-p recico-p itation conirm ed th at th e b asic structure is f rom
th e Z H N and th e only dif f erence b etw een th e p roducts is th e b asal distance ob serv ed b y X R D m easurem ents
F igu re 9 . D R U V-VI S sp ectra of : Z H N ( a) , sodium N-acety lanth ranilate ( b ) , N-acety lanth ranilic acid ( c) and Z H N-NA A ( d) .
F igu re 1 0. D R U V-VI S sp ectra of : Z H N ( a) , sodium 4 -m eth ox y cinnam ate
( b ) , Z H N-M C ( c) , sodium 4 -m eth ox y b enzoate ( d) and Z H N-M B ( e) .
F igu re 1 2 . SA E D p attern of Z H N ob tained at 80 k V and at room tem p erature ( a) , Z H N-D SD ob tained at 5 0 k V and at room tem p erature ( b ) and Z H N-M C ob tained at 5 0 k V at −4 3 °C ( c) . T h e SA E D p attern in ( c) w as ob tained using a cooled sp ecim en h older ( G atan m odel 636) .
h av e interesting U V ray ab sorb ing p rop erties, som etim es ev en enh ancing th e ab sorp tion rang e of th eir p recursors. F urth er research on th ese com p ounds could b e v ery fruitf ul to th e cosm etics industry , esp ecially b ecause zinc ox ide is g enerally recog nized as saf e ( G R A S) and is w idely used as antisep tic and w h itening p ig m ent in cosm etic f orm ulations.
Ack nowledgments
W e g ratef ully ack now ledg e th e Brazilian R esearch A g encies C NPq , C A PE S and F I NE P f or th eir inancial sup p ort of th is w ork . A . C . T . C ursino th ank s C NPq f or th e m asters research g rant. W e also ack now ledg e th e use of
th e E lectron M icroscop y C enter of th e F ederal U niv ersity of Paraná.
References
1. W issing , S. A .; M üller, R . H .; I nt. J. Pharm. 2 0 0 2, 2 4 2, 37 3. 2. U rb ach , F .; J. Photochem. Photob iol., B 2 0 0 1, 6 4, 99.
3. A g rap idis-Paloy m p es, L . E .; Nash , R . A .; Sh aath , N. A .; J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1 9 8 7, 3 8, 209.
4 . C osta, E . J .; L acaz, E .; M ed Cu tán I b ero-L atino Am. 2 0 0 1, 2 9, 14 5 .
5 . H oy o, C .; Vicente, M . A .; R iv es, V.; Clay M iner. 2 0 0 1, 3 6, 5 4 1.
6. Perioli, L .; A m b rog i, V.; Bertini, B.; R icci, M .; Nocch etti, M .; L atterini, L .; R ossi, C .; Eu r. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2 0 0 6, 6 2,
185 .
7 . Perioli, L .; Nocch etti, M .; A m b rog i, V.; L atterini, L .; R ossi, C .; C ostantino, U .; M icroporou s M esoporou s M ater. 2 0 0 8, 1 0 7,
180; C ostantino, U .; A m b rog i, V.; Nocch etti, M .; Perioli, L .;
M icroporou s M esoporou s M ater. 2 0 0 8, 1 0 7, 14 9.
8. R ietsch el, R . L .; F ow ler, J . F .; F isch er, A . A .; F isher’s Contact Dermatitis, 6th ed., BC D eck er I nc.: O ntario, 2008.
9. C ursino, A . C . T .; G ardolinsk i, J . E . F . C .; W y p ych , F .; J. Colloid I nterface Sci. 2 0 1 0, 3 4 7, 4 9.
10. H oy o, C .; Appl. Clay Sci. 2 0 0 7, 3 6, 103. ( see F ig ures 2 and 7 ) . F ig ure 12 sh ow s th e standard SA E D
f or th e Z H N m atrix and f or th e com p ounds ob tained by co-p recico-p itation. T h e Z H N m atrix co-p resented g ood structural stab ility to p erf orm th e analy sis, as did th e co-p recip itated sam p le w ith stilb enedisulf onate ( Z H N-D SD ) , b oth of th em p resenting larg e sing le cry stals. I n th e case of th e sam p le
co-p recip itated w ith m eth ox y cinnam ate ( Z H N-M C ) , th e cry stals are too sm all, g enerating a standard p oly cry stal,
as sh ow n in F ig ure 12c. I n addition, th e structural stab ility of th is sam p le is too low to b e analy zed under normal conditions. T h e analy sis th en needs to b e carried out at
−4 3 °C w ith a low -energ y electron b eam .
T h e index ed sp ots f or th e Z H N corresp ond to th e non b asal direction contrib utions, sh ow ing th at th e lay er stack ing occurs along th e [ 100] ax is. T h is cry stallog rap h ic orientation is th e sam e in all sam p les analy zed b y SA E D and no ch ang es w ere ob serv ed in th e sp acing p erp endicular
to th e lay ers. T h is sh ow s th at th e stilb enedisulf onate and m eth ox y cinnam ate anions, in th e co-p recip itation p rocess, are only intercalated b etw een th e lay ers, as ob serv ed b y X R D in F ig ures 2 and 7 , p reserv ing th e lay er as in th e Z H N structure. Prob ab ly th e b asal sp acing of 20.13 Å ob tained f or th e sam p le co-p recip itated w ith cinnam ate reduces th e coh esion b etw een th e lay ers, causing th eir low stab ility under th e electron b eam .
Conclu sion
L ay ered zinc h y drox ide nitrate w as used as h ost f or org anic U V ray ab sorb ing anions. 4 -M eth ox y cinnam ate, 4 - m e t h o x y b e n z o a t e a n d 4 , 4 ' - d i a m i n o 2 , 2 ' -stilb enedisulf onate ions w ere intercalated b etw een th e Z H N lay ers, w h ereas th e N-acety lanth ranilate anion w as m ostly
lik ely adsorb ed on th e outer surf aces of th e h y drox ide salt p articles. T h e p roducts w ere ch aracterized b y X R PD , F T I R ,
11. F eng , Y . J .; L i, D . Q.; W ang , Y .; E v ans, D .G .; D uan, X .; Polym. Deg rad. Stab. 2 0 0 6, 9 1, 7 89.
12. R ossi, C .; Sch oub b en, A .; R icci, M .; Perioli, L .; A m b rog i, V.; L atterini, L .; A loisi, G . G .; R ossi, A .; I nt. J. Pharm. 2 0 0 5, 2 9 5, 4 7 .
13. X ue, M .; C h itrak ar, R .; Sak ane, K .; O oi, K .; K ob ay ash i, S.; O h nish i, M .; D oi, A .; J. Solid State Chem. 2 0 0 4, 1 7 7, 1624 .
14 . Nish izaw a, H .; Y uasa, K .; J. Solid State Chem. 1 9 9 8, 1 4 1, 229.
15 . M arang oni, R .; Bub niak , G . A .; C antão, M . P.; A b b ate, M .; Sch reiner, W . H .; W y p y ch , F .; J. Colloid I nterface Sci. 2 0 0 1,
2 4 0, 24 5 .
16. A rizag a, G . G . C .; Saty anaray ana, K . G .; W y p y ch , F .; Solid State I onics 2 0 0 7, 1 7 8, 114 3.
17 . Stäh lin, W .; O sw ald, H . R .; Acta Crystallog r., Sect. B: Stru ct. Sci. 1 9 7 0, 2 6, 860.
18. New m ann, S. P. J ones, W .; J. Solid State Chem. 1 9 9 9, 1 4 8, 26.
19. D ata C ollection of th e J oint C om m ittee on Pow der D if f raction Standard, PC PD F W I N, Version 2.2, C op y rig h t, 2001.
20. A rizag a, G . C . G .; M ang rich , A . S. M .; W y p y ch , F .; J. Colloid I nterface Sci. 2 0 0 8, 3 2 0, 238.
21. Silv erstein, R . M .; W eb ster, F . X .; K iem le, D . J .; Spectrometric I dentiication of O rg anic Compou nds, 7th ed., J . W iley & Sons:
H ob ok en, U SA , 2005 .
22. K ub elk a, P.; M unk , F .; Z . T ech. Phys. 1 9 3 1, 1 2, 5 93. 23. Sh erm an, D . M .; W ait, T . D .; Am. M ineral. 1 9 8 5, 7 0, 1262. 24 . C h ai, H .; L in, Y . J .; E v ans, D . G .; L i, D . Q.; I nd. Eng . Chem.
Res. 2 0 0 8, 4 7, 285 5 .
25 . C ui, G . J .; X u, X . Y ; Y an, J . L .; E v ans, D . G .; D ian, Q. L .; I nd. Eng . Chem. Res. 2 0 1 0, 4 9, 4 4 8.
26 W y p y ch , F .; A rizag a, G . G . C .; G ardolinsk i, J . E . F . D .; J. Colloid I nterface Sci. 2 0 0 5, 2 8 3, 130.
27 . Nak am oto, K .; I nfrared and Raman Spectra of I norg anic and Coordination Compou nds, 4th ed., J oh n W iley & Sons: New
Y ork , 1986.
Supplementary Information
J. Braz. Chem. Soc., Vol. 22, No. 6, S1-S7, 2011. Printed in Brazil - ©2011 Sociedade Brasileira de Química
0103 - 5053 $6.00+0.00
S
I
*e-mail: delgado@unam.mx
Biotransformation of Sclareolide by Filamentous Fungi:
Cytotoxic Evaluations of the Derivatives
Arturo Cano,a María Teresa Ramírez-Apanb and Guillermo Delgado*,b
aFacultad de Estudios Superiores Zaragoza, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México,
Av. Guelatao no. 66 (Eje 7 Oriente), Col Ejército de Oriente, Iztapalapa 09230, Mexico, D.F.
bInstituto de Química, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Ciudad Universitaria,
Circuito Exterior, Coyoacán 04510, Mexico, D.F.
Figure S1. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl
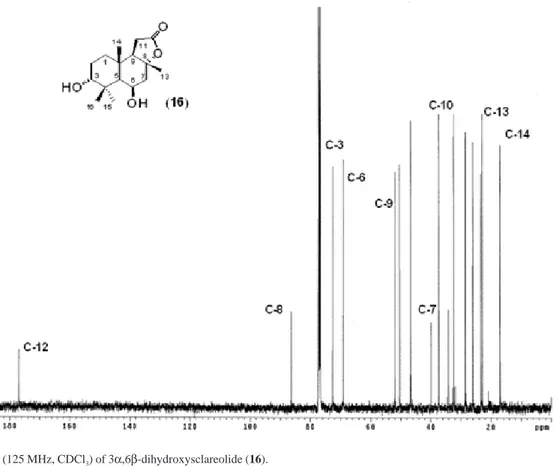
Figure S2. 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) of 3α,6β-dihydroxysclareolide (16).
Figure S4. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) of 1-ketosclareolide (17).
Figure S6. HMBC (500 MHz, CDCl3) of 1-ketosclareolide (17).
Figure S8. 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) of 3-keto-15-hydroxysclareolide (18).
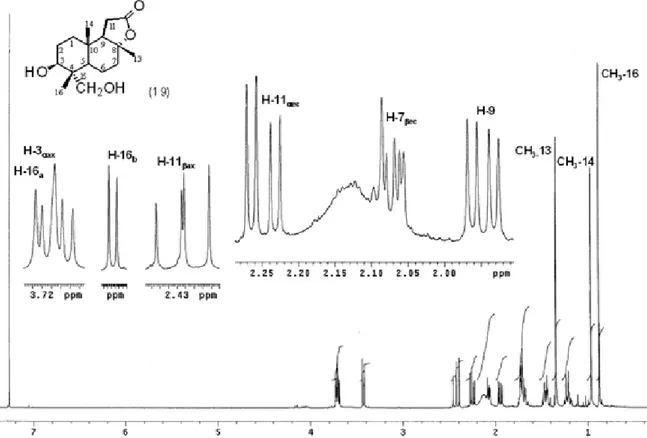
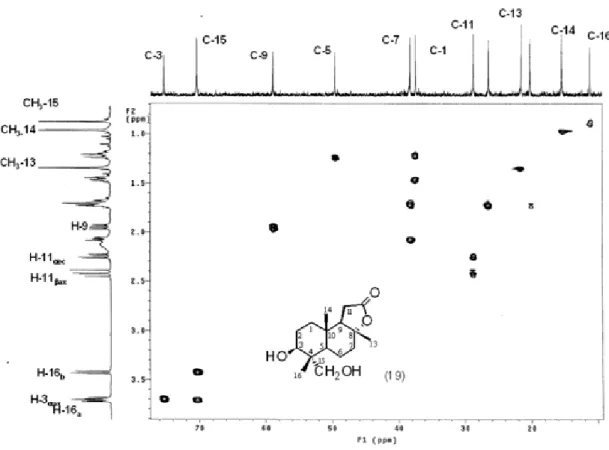
Figure S10. 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) of 3β,15-dihydroxysclareolide (19).