rev bras hematol hemoter. 2016;38(2):161–162
w w w . r b h h . o r g
Revista
Brasileira
de
Hematologia
e
Hemoterapia
Brazilian
Journal
of
Hematology
and
Hemotherapy
Case
report
Is
antenatal
RhIg
completely
safe?
Rajeswari
Subramaniyan
∗,
Karishma
Pereira
YashodaHospital,Hyderabad,India
a
r
t
i
c
l
e
i
n
f
o
Articlehistory:
Received12December2015 Accepted16January2016 Availableonline25March2016
The administration of antenatal and postnatal Rh immunoglobulin prophylaxis significantly prevents Rh D alloimmunizationduringpregnancy. Adoseof20ganti-D
IgGprotectsagainst1mLofD-positiveredbloodcellsor2mL ofwholeblood.RhD-negativewomenifunsensitizedreceive antenatalanti-Dprophylaxisof300gat28weeksof
preg-nancyandpostnatalprophylaxisifthebabyisRhDpositive. Initialtrialsconcludedthatpostpartumimmunoprophylaxis decreasedtheincidenceofRhDimmunizationfrom12–13% to 1–2% which was further shown to be reduced to 0.1% thankstoantenatalprophylaxis.1Rhimmunoglobulin(RhIg) administrationisquitesafeduringpregnancyalthoughRhIg cancrosstheplacentaandcausehemolysisoftheredcells ofD-positive fetuses. Unfortunatelydata is sparse on this serious adverse event.Herein wepresent an unusual case ofhemolyticdiseaseofnewborn(HDN)withpositiveDirect Coombs’Test(DCT)duetoantenatalRhIgprophylaxisinan Rh-negativemother.
Case
report
A 28-year-old primipara with blood group O Rh negative, deliveredamalebabyweighing2.6kgat37+2weeksby
emer-gencycesareansection inview offetal bradycardia.During 30weeksofpregnancy,herantibodyscreenwasnegativeand
∗ Correspondingauthorat:DepartmentofTransfusionMedicine,YashodaHospital,Malakpet,Hyderabad500036,India.
E-mailaddress:arthisoundarya@gmail.com(R.Subramaniyan).
shereceivedaprophylacticdoseof300gRhimmunoglobulin
(RhIg,Rhogam).Shehadanotherwiseuneventfulpregnancy. SincethemotherwasRhDnegative,arequisitionforblood grouping,Rhtyping andDCT ofthe babywas made.Blood groupofthebabywasORhDpositive(tubetechnique).DCT wasperformedusingcolumnagglutinationtechnology(Ortho clinical diagnostics,USA)andwasfoundtobepositive(3+) for polyspecificanti-human globulin(IgG+ C3d) having IgG
specificity.Anti-Dantibodywasidentifiedinthebaby’sserum (ResolvePanelA,OrthoClinicalDiagnostics,USA).
Antibodieswereelutedfromthebaby’sredcellsusingthe acidelutiontechnique(Diacidel,Bio-Rad,Germany).Antibody screeningwasnegativeforthesupernatantofthelastwash. Theeluatewaspositiveforanti-D.Themother’sbloodgroup wasORhDnegativewhilethefather’sbloodgroupwasORh Dpositive.Antibodyscreeningandidentificationofmother’s samplerevealedthepresenceofanti-D.Theanti-Dtitersofthe eluateandthemother’ssamplewere1:4and1:8respectively. Themotherwasgiven300gRhIg,6hpostpartum.
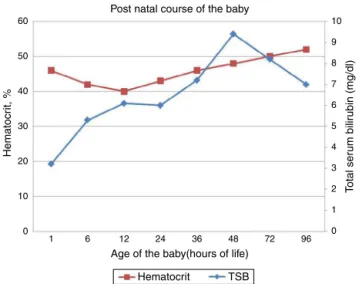
The baby’s Activity, Pulse, Grimace, Appearance, Respi-ration (APGAR) scores were 8 and 9 at 1min and 5min respectively. Atbirth, cord total serum bilirubin (TSB) and hematocrit were 3.2mg/dL and 46% respectively. At 6h of life, TSB was 5.3mg/dL and it was noticed that the baby had jaundice.Reticulocyteswere 6%(normal range0.5–2%). glucose-6-phosphatedehydrogenase(G6PD)deficiencytesting
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bjhh.2016.01.006
162
revbrashematolhemoter.2016;38(2):161–162Post natal course of the baby
T
o
tal ser
u
m bilir
ubin (mg/dl)
Age of the baby(hours of life)
Hematocrit TSB
Hematocr
it, %
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0 60
50
40
30
20
10
0
1 6 12 24 36 48 72 96
Figure1–Postnatalevolutionofthebabywithanincrease intotalserumbilirubin(TSB)anddropinhematocritvalues
thatrespondedtophototherapy.
was negative. There was no evidence of sepsis. Thechild receivedphototherapyinviewofhyperbilirubinemiaasper ourinstituteprotocol.Thepostnatalevolutionofthebabyis showninFigure1.Antibodyscreeningofthemotheraftersix monthswasnegative.Babyhadnoresidualsequelaeduring subsequentvisits.
Discussion
TSBconcentrationsabove5mg/dLondayoneoflifeinaterm neonate indicates pathologic jaundice. Hemolytic anemia should beconsidered inthe setting ofABO/Rh incompati-bility,jaundicewithin24h,positiveDCT,raisedreticulocyte count,raisedserumbilirubin,presenceofpallororevidence ofhemolysisinperipheralblood smear.Inthis case,along withthesefeatures,antibodytiterswerelowandsix-months follow-up analysis showed negative antibody screening in motherfavoringRhIginducedHDN.Suchsecondary hemol-ysis is transient. ABO incompatibility was ruled out. Rh alloimmunizationhasoccurredeveninfirstpregnancy lead-ingtoHDNduetoearlytrimesterfetomaternalhemorrhage or failure of RhIg. In such cases, anti-D will be persistent beingdetectedinearly trimester ofsecond pregnancy.2 Rh Immunoglobulin generally disappears within 6–8 weeks of administration.
Tothebestofourknowledge,thisrarecaseisthefirstreport fromIndia.Incidenceofpositivedirectantiglobulintest(DAT)
inbabiesborntoRhnegativemothersrangesfrom2to30%. WhenmothersweregiventwodosesofantiD immunoglobu-linantenatally,20%oftheRhDpositivebabiesshowedpositive DAT. In another study, twoout of 1238(0.16%) Rhpositive newbornswereaffectedbypassivetransferofmaternalRhIg. Cohenetal.in2014reportedacaseofpassivetransferofRhIg inducingHDN.3AlsoahighgradeDATisastrongpredictor ofphototherapy.4 Maayan-Metzgeretal.,intheir retrospec-tive analysis, concluded that there was no significant risk ofhemolysisduetoRhIg amongpreterm(28–34 weeks)Rh D positivebabies born toRhnegativemothers andfurther prospectivestudieswererequiredtoconfirmthecorrelation.5 Toconclude,antenatalandpostnatalRhIgprophylaxisfor allRh-negativemotherswhoareunsensitizedisthestandard practiceinvogue.BloodgroupingandDCTismandatoryfor allnewbornsofRh-negativemothers.AlthoughRhIg admin-istrationtoRhDnegativemothersisconsideredsafe,positive DCTinthoseDpositiveneonatesshouldbefurtherevaluated to rule out thepossibility ofRhIg induced HDN. Follow-up ofmother and babywill assistindifferentiatinghemolysis causedbyRhimmunizationfromthatofRhIgprophylaxis.6
Conflicts
of
interest
Theauthorsdeclarenoconflictsofinterest.
r
e
f
e
r
e
n
c
e
s
1.LiumbrunoGM,D’AlessandroA,ReaF,PiccininiV,CatalanoL, CalizzaniG,etal.Theroleofantenatalimmunoprophylaxisin thepreventionofmaternal-foetalanti-Rh(D)
alloimmunisation.BloodTransfus.2010;8(1):8–16.
2.ToveyLA,TownleyA,StevensonBJ,TheTavernerJ.Yorkshire antenatalanti-Dimmunoglobulintrialinprimigravidae. Lancet.1983;2(8344):244–6.
3.CohenDN,JohnsonMS,LiangWH,McDanielHL,YoungPP. Clinicallysignificanthemolyticdiseaseofthenewborn secondarytopassivetransferofanti-DfrommaternalRhIg. Transfusion.2014;54(11):2863–6.
4.DillonA,ChaudhariT,CrispinP,ShadboltB,KentA.Hasanti-D prophylaxisincreasedtherateofpositivedirectantiglobulin testresultsandcanthedirectantiglobulintestpredictneed forphototherapyinRh/ABOincompatibility?JPaediatrChild Health.2011;47(1–2):40–3.
5.Maayan-MetzgerA,SchwartzT,SulkesJ,MerlobP.Maternal anti-Dprophylaxisduringpregnancydoesnotcauseneonatal haemolysis.ArchDisChildFetalNeonatalEd.2001;84(1):F60–2.