Rev. bras. farmacogn. vol.26 número4
Texto
Imagem
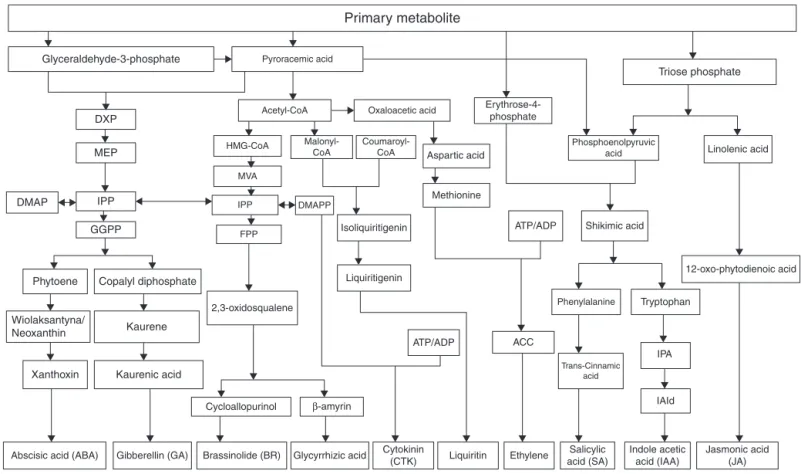
Documentos relacionados
The cholinesterase (both AChE and BuChE) inhibitory activities of the crude extract, fractions, precipitate, supernatant and isolated compounds were carried out using a 96
Although clinical biochemistry analysis showed liver and kidney damage, none of these organs from the BA extract treated rats showed any significant alteration in cell structure or
This was observed in the present study; however, when the group that received cisplatin was compared with the group that received cisplatin/bixin, it is evident that bixin
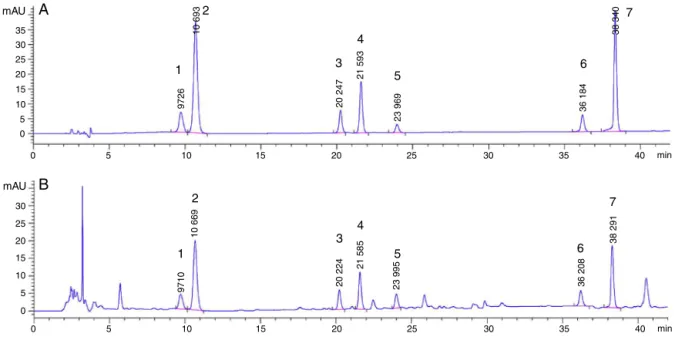
HPLC chromatograms of flavonoids standards (upper chromatogram; nor- malized view) and aqueous extracts of the leaves of Passiflora species.. For details of the chromatographic
Cross sections and scanning electron microscopy of leaves blade and petiole showed a simple organization with simple unicellular trichomes and cells containing tannins, and crystals
In order to understand the molecular basis for its traditional use in the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases and considering the pivotal role of T-cells on the maintenance
a Institut für Organische Chemie, Fakultät für Chemie und Mineralogie, Universität Leipzig, Leipzig, Germany b Herbarium Truxillense (HUT), National University of Trujillo,
Various other workers gave a comparative account of antioxi- dant activity of flavonoids in different in vitro antioxidant assays and attributed the difference in their activity to