Keratocystic odontogenic tumor : role of cone beam computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
This paper presents two cases of odontogenic lesions in children, one dentigerous cyst and one keratocystic odontogenic tumor, which were treated by marsupialization in order
The diagnostic and surgical management of a multifocal calciiyng epithelial odontogenic tumor in the mandible and maxilla associated with a squamous odontogenic tumor:
Computed tomography scan and magnetic resonance imaging showed a normal prostate and a 9.0 cm cystic tumor, replacing the left seminal vesicle.. The gross appearance and
Inclusion criteria for selecting articles were: » Studies based on magnetic resonance imag- ing (MRI), computed tomography (CT) and/ or volumetric cone-beam tomography, which assessed
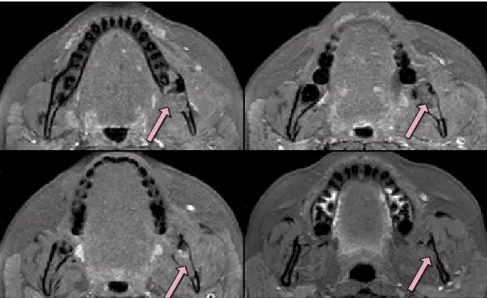
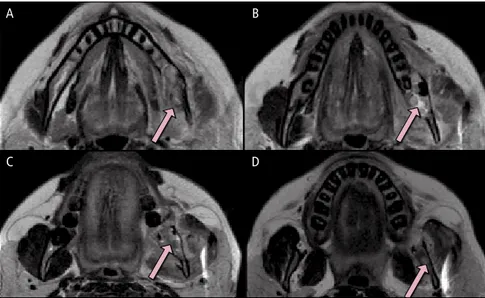
However, the appearance of this cyst on cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have received relatively little attention.. CBCT and
of glucose transporters 1 (GLUT-1) and 3 (GLUT-3) in keratocystic odontogenic tumors associated with Gorlin syndrome (SKOTs) and non-syndromic keratocystic odontogenic
On the right, typical epithelial lining of keratocystic odontogenic tumor presenting strong intensity and high syndecan-1 expression; on the left, decrease in syndecan-1
NA: not available, cSAH: convexity subarachnoid hemorrhage, CT: computed tomography; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; MRA: magnetic resonance angiography, RCVS: reversible