rev bras ortop.2015;50(3):352–355
w w w . r b o . o r g . b r
Case
Report
Bryan
and
Morrey
type
IV
intra-articular
fracture
of
the
distal
extremity
of
the
humerus
treated
surgically
with
anterior
access:
case
report
夽
Hugo
Bertani
Dressler
∗,
Ricardo
Nunes
Borges
de
Paula
SantaCasadeBeloHorizonte,BeloHorizonte,MG,Brazil
a
r
t
i
c
l
e
i
n
f
o
Articlehistory:
Received23May2014 Accepted25June2014 Availableonline27April2015
Keywords:
Humeralfractures/surgery Elbow
Bonescrews Capitellum Trochlea
a
b
s
t
r
a
c
t
Withinthecontextofelbow-leveltrauma,fractureswithacoronallineatthedistalextremity ofthehumerusarerareandresultfromindirectaxialtraumawiththearmextended.These aredifficult-to-treatintra-articularfractures,sincetheyrequirestableanatomicalreduction inordertomaintainjointcongruenceanddiminishcomplicationssuchasstiffness.This paperreportsacasethatoccurredinayoungmanwhosufferedafallfromaladderthat resultedinaBryanandMorreytypeIVintra-articularfractureofthehumerus.Theinjury wastreatedsurgicallybymeansofananterioraccess,usingosteosynthesiswithtwoHerbert screwsthatwereinsertedfromanteriortoposterior.
©2014SociedadeBrasileiradeOrtopediaeTraumatologia.PublishedbyElsevierEditora Ltda.Allrightsreserved.
Fratura
intra-articular
da
extremidade
distal
do
úmero
tipo
IV
de
Bryan
e
Morrey
tratada
cirurgicamente
com
acesso
anterior:
relato
de
caso
Palavras-chave:
Fraturasdoúmero/cirurgia Cotovelo
Parafusosósseos Capitelo Tróclea
r
e
s
u
m
o
Nocontextodos traumatismos ao nível docotovelo,as fraturas comtrac¸o coronal da extremidadedistal do úmerosão rarase resultam de trauma axial indireto no mem-brosuperiorestendido.Sãofraturasintra-articularesdedifíciltratamentopordemandar reduc¸ãoanatômicaeestávelparaamanutenc¸ãodacongruênciaarticularereduc¸ãodas complicac¸õescomorigidez.Reporta-senesteartigoumcasoocorridoemumjovemdosexo masculino,vítimadequedadeescadaqueresultouemumafraturaintra-articulardoúmero distaltipoIVdeBryaneMorreyequefoisubmetidoatratamentocirúrgicoporviadeacesso anterioreosteossíntesecomdoisparafusosdeHerbertinseridosdeanteriorparaposterior. ©2014SociedadeBrasileiradeOrtopediaeTraumatologia.PublicadoporElsevierEditora Ltda.Todososdireitosreservados.
夽
WorkdevelopedattheOrthopedicsandTraumatologyServiceofSantaCasadeBeloHorizonte,BeloHorizonte,MG,Brazil.
∗ Correspondingauthor.
E-mail:hugobertani@hotmail.com(H.B.Dressler). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rboe.2015.04.008
rev bras ortop.2015;50(3):352–355
353
Introduction
Fracturesofthecapitellumandtheirvariantsextendingtothe trochleaarerareandaccountforaround1%ofthefractures atelbowleveland6%ofthefracturesatthelevelofthedistal humerus.1,2Thisinjurypatternresultsfromashearingforce
transmittedfromtheproximalextremityoftheforearmbones totheproximalextremityofthehumerusbymeansofaxial loading.Theseareintra-articularfracturesthatrequirecareful treatmentandanatomicalreductioninordertodiminishthe complications,suchasjointstiffness.3
Case
report
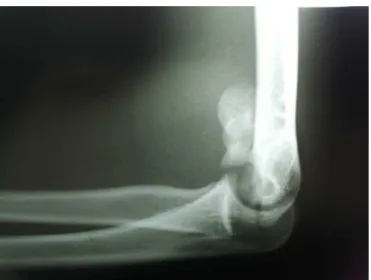
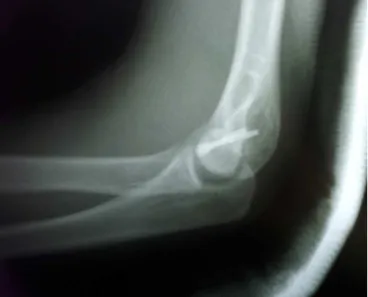
Thepatientwas a16-year-oldright-handedmale who suf-fered afall from a ladder in whichhis left hand took the force of the impact on the ground. This resulted in axial transmissionofenergythroughtheextendedleftarm.Inthe admissionexaminationattheemergencyservice,significant localpainwasnoted,withincreasedvolumeandlimitationof leftelbowmovement.Therewerenoskininjuries. Neurovas-cularexaminationoftheextremitydidnotdemonstrateany abnormalities. The initial radiographic evaluation revealed fracturingofthedistalextremityofthelefthumerus,without goodcharacterizationofthepattern(Figs.1and2).Inlateral view,the“doublearchsign”couldbeseen(Fig.2).4Todefine
Fig.1–Anteroposteriorradiographicview,whichdoesnot
showthefracturepatternclearly.
Fig.2–Lateralradiographicviewshowingfracturewith
displacementanddouble-archsign.
thefracturepatternandenablebetterpreoperativeplanning, atomographicevaluationwasmade.Thisdefinedthecoronal outline,extendingfromthecapitellumtothetrochleaina sin-glefragment(Figs.3and4).Inthelightoftheimagingstudy, thefracturewasclassifiedastypeIVaccordingtothe classifi-cationofBryanandMorrey,1asmodifiedbyMcKeeetal.,4or
astype13B3.3accordingtotheAOclassification.5
Aftertheinitialevaluationhadbeenmade,fromwhich pro-visionalplaster-castimmobilizationwasperformedandother injuriesandcomorbiditieswereruledout,surgicaltreatment wasindicated.Thepatientwaskeptinhospitalforcare,and toawaitschedulingoftheoperationatthesamepublic ortho-pedicandtraumatologyservice.
After a hospitalstay of 14 days, the surgical treatment wasperformed. Itwasdecidedtouse ananterioraccessin the elbow, on a proximal internervous plane between the
Fig.3–Three-dimensionaltomographicreconstructionin
354
rev bras ortop.2015;50(3):352–355Fig.4–Three-dimensionaltomographicreconstructionin
medialviewshowingdisplacedbonefragment.
brachioradialismuscle(innervatedbytheradialnerve)and thebrachialismuscle(innervatedbythemusculocutaneous nerve),anddistallybetweenthebrachioradialisandthe prona-torteres muscle(innervated bythe mediannerve),6 under
leftbrachial plexusblockinassociationwithsedation.The patientwaspositionedindorsaldecubituswiththeleftarm abductedandsupinatedonalateralsupporttable.After per-formingrigorousantisepsisandpreparationoftheskinusing achlorhexidinesolution,andplacementofsterilefields,the pneumatictourniquetwasinflated.Afterlayer-bylayer dis-section andidentification ofthe fracturefocus,anatomical reduction was performed, with fixation using two Herbert screwsthatwereinsertedfromanteriortoposterior.7
Discussion
Sincethiswasanintra-articularfracturepatternwith signif-icantdisplacement,asurgicalapproachbecamenecessaryin ordertoreestablishtheanatomyandjointcongruence.Inthis regard,openreductionwithstableinternalfixationbecause imperative.8Sincetheusualradiographicviewsdonotallow
detailing of the fracture pattern, tomographic assessment plays an important role in understanding the injury and enablesbettersurgicalplanning.9
Inmostoftheseries,2–4,7thesurgicalapproachwaslateral,
medialorposteriorandthesynthesismaterialwaspositioned fromposteriortoanterior.However,inthecasereportedhere, giventhatthetreatmentwasimplemented14daysafterthe fractureoccurred,thepossibilityofreductionbymeansofan anterioraccesswasconsideredtoallowforthepossibilityof osteoclasis(“calloclasis”),therebyexplainingthechoice.
Afteranatomicalreductionwith satisfactorypositioning of the bone fragment in its bed had been achieved, fix-ation was performed using two Herbert screws (Zimmer, Warsaw, Indiana) inserted from anterior to posterior. This
Fig.5–Anteroposteriorradiographicviewshowing
positioningofthesynthesismaterial.
couldbeobservedinthepostoperativeradiographic evalua-tion(Figs.5and6).
Althoughthesurgicalmethodusedinthis casewasnot the one chosenbythe majority ofthe surgeonswho treat this typeofinjury,thereisbackingforourapproachinthe
Fig.6–Lateralradiographicviewshowingpositioningof
thesynthesismaterialandanatomicalreductionofthe
rev bras ortop.2015;50(3):352–355
355
literature.1,3,4,6–8,10 Itsdisadvantageisitstechnicaldifficulty,
giventheriskofneurovascularinjurytothestructuresofthe cubitalfossacubital.Ontheotherhand,itenablesextensive viewingofthefocusofthefracture,whichisespeciallyhelpful foranatomicalreduction,andthisisadecisivefactorforgood evolutionofthecase.10
Conflicts
of
interest
Theauthorsdeclarenoconflictsofinterest.
r
e
f
e
r
e
n
c
e
s
1. BryanRS,MorreyBF.Fracturesofthedistalhumerus.In: MorreyBF,editor.Theelbowanditsdisorders.Philadelphia: Saunders;1985.p.302–39.
2. DubberleyJH,FaberKJ,MacdermidJC,PattersonSD,KingGJ. Outcomeafteropenreductionandinternalfixationof capitellarandtrochlearfractures.JBoneJointSurgAm. 2006;88(1):46–54.
3.SenRK,TripahtySK,GoyalT,AggarwalS.Coronalshear fractureofthehumeraltrochlea.JOrthopSurg(HongKong). 2013;21(1):82–6.
4.McKeeMD,JupiterJB,BambergerHB.Coronalshearfractures ofthedistalendofthehumerus.JBoneJointSurgAm. 1996;78(1):49–54.
5.RüediTP,MurphyWM.PrincípiosAOdotratamentode fraturas.SãoPaulo:Artmed;2002.
6.PollockJW,AthwalGS,SteinmannSP.Surgicalexposuresfor distalhumerusfractures:areview.ClinAnat.
2008;21(8):757–68.
7.SinghAP,SinghAP,VaishyaR,JainA,GulatiD.Fracturesof capitellum:areviewof14casestreatedbyopenreduction andinternalfixationwithHerbertscrews.IntOrthop. 2010;34(6):897–901.
8.SimpsonLA,RichardsRR.Internalfixationofacapitellar fractureusingHerbertscrews.Acasereport.ClinOrthop RelatRes.1986;(209):166–8.
9.RingD,JupiterJB,GulottaL.Articularfracturesofthedistal partofthehumerus.JBoneJointSurgAm.2003;85(2): 232–8.