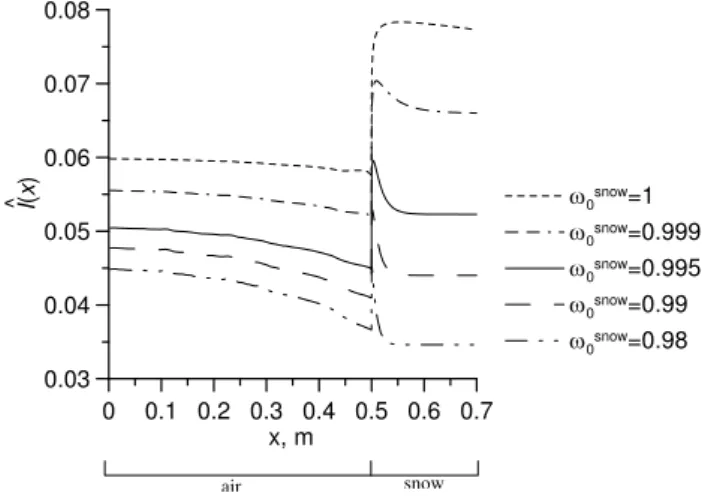
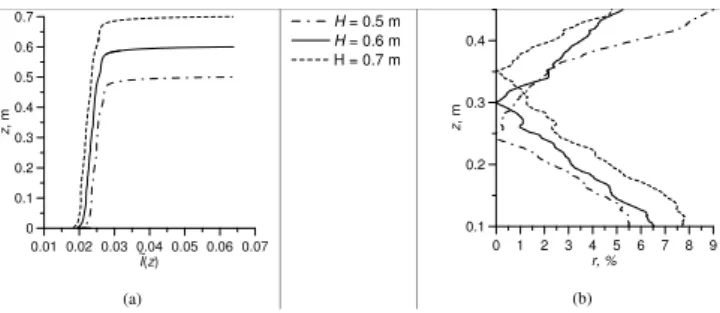
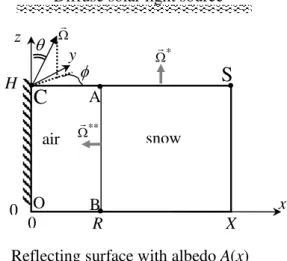
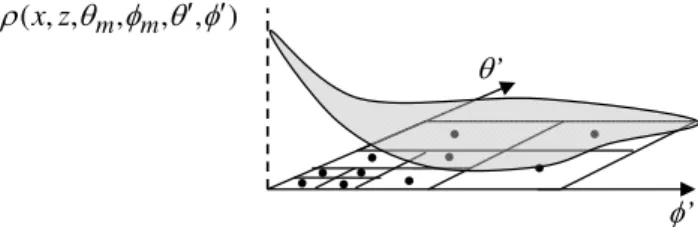
Theoretical study of solar light reflectance from vertical snow surfaces
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
Left panel is the false colour composite (red is 11 µm BT, green is 550 nm reflectance, blue is 1.6 µm reflectance) of initial AATSR scene; second left panel is the clear snow mask
The present study investigates the possibil- ity of a relationship between the coastal topography with steep slopes and sea-salt snow chemistry, using high reso- lution data from
The goals of this study included obtaining snow bidirectional reflectance at high 1 ◦ angular resolution from CAR measurements and using these data for an accuracy analysis
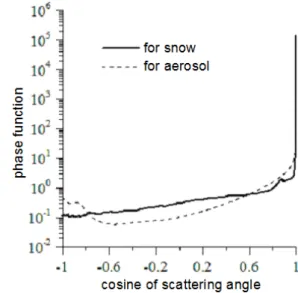
The effective diameter of snow for a given scene is estimated by matching the measured reflectance with an ice crystal model whose asymmetry parameter is consistent with that
Hydrologic response data include hourly stream discharge from the catchment outlet weir, continuous snow depths from one location, intermittent snow depths from 5 locations, and
The solid line is the theoretical error derived for an exponential decay exponent of 0.17 derived from the sampled correlation function of snow depth in FS, while the solid red
The two snow water contents from the microwave imagery (SMMR and SSM/I) and the Utah Energy Balance forced with the TRMM precipitation data were found to be unreliable sources
Spectral reflectance of (a) the natural snow surface and (b) bare ice with manually removed snow cover in the study lakes: 1, Lovojärvi; 2, Pääjärvi; 3, Iso Valkjärvi; 4, Peipsi;