BLOODSTREAM I NFECTI ONS AMONG PATI ENTS USI NG CENTRAL VENOUS
CATHETERS I N I NTENSI VE CARE UNI TS
Eni Rosa Air es Bor ba Mesiano1 Edgar Mer ch án - Ham an n2
Mesiano ERA, Ham ann EM. Bloodst r eam infect ions am ong pat ient s using cent r al v enous cat het er s in int ensiv e car e unit s. Rev Lat ino- am Enfer m agem 2007 m aio- j unho; 15( 3) : 453- 9.
Cent r al Venous Cat het er s ( CVC) , w idely used in I nt ensiv e Car e Unit s ( I CU) ar e im por t ant sour ces of bloodst r eam infect ions ( BSI ) . This pr ospect ive cohor t epidem iological analyt ical st udy, aim ed t o infer t he incidence of BSI , t he r isk fact or s associat ed and evaluat e t he car e act ions r elat ed t o t he use of t hese cat het er s in seven
I CU in t h e Feder al Dist r ict - Br asília, Br azil. Fr om t h e 6 3 0 pat ien t s u sin g CVC, 6 . 4 % dev eloped BSI ( 1 . 5 % dir ect ly r elat ed t o t he cat het er and 4 . 9 % clinic BSI ) . The hospit alizat ion t er m w as 3 . 5 t im es gr eat er am ong t hese pat ient s. Differ ent m odalit ies of cat het er inser t ion and ant isept ic subst ances use w er e obser ved. Tim e of
CVC per m anence w as significant ly associat ed t o infect ion incidence ( p< 1x 10- 8) as w ell as t he r ight subclav ian access and double- lum en cat het er s. Pat ient s w it h neur ological disor der s and t hose subm it t ed t o t r acheot om y w er e t he m ost affect ed. We suggest t he or ganizat ion of a “ cat het er gr oup” aim ing t o st andar dize pr ocedur es r elat ed t o t he use of cat het er s in or der t o r educe t he hospit alizat ion t er m and hospit al cost s.
DESCRI PTORS: cr oss infect ion; int ensiv e car e unit s; pr ev ent ion and cont r ol
I NFECCI ÓN DE CORRI ENTE SANGUÍ NEA EN PACI ENTES CON CATÉTER VENOSOS
CENTRAL EN UNI DADES DE CUI DADO I NTENSI VO
Los cat ét er es v enosos cent r ales ( CVC) ut ilizados pr incipalm ent e en unidades de cuidados int ensiv os -UCI s, son im por t ant es fuent es de infección de la cor r ient e sanguínea ( I CS) . Est e est udio epidem iológico analít ico, d e co r t e p r o sp ect i v o , en f o ca l a i n ci d en ci a d e I CS, f act o r es d e r i esg o aso ci ad o s y m ed i d as asi st en ci al es r elacionadas con el uso de est os cat ét er es en 7 UCI s del Dist r it o Feder al. Del t ot al de 630 pacient es con CVC,
6, 4% pr esent ar on I CS ( 1, 5% r elacionado al cat ét er y 4, 9% I CS- Clínica) . El t iem po de hospit alización fue 3, 5 veces m ayor par a est e gr upo de pacient es. Fuer on obser vadas difer ent es conduct as con r elación a la inser ción de cat ét er es y al uso de ant isépt icos. El t iem po de per m anencia del CVC est uv o asociado a la incidencia de
infección ( p< 1x10- 8) así com o a la punción en la vena subclavia der echa y al cat ét er de doble lúm en. Pacient es neur ológicos y con t r aqueot om ía fuer on los m ás afect ados. Se sugier e la for m ación de un “ gr upo de cat ét er ” , dest inado a est andar izar el uso de los cat ét er es, par a de est a for m a, se r eduzca el t iem po de hospit alización y los cost os hospit alar ios.
DESCRI PTORES: infección hospit alar ia; unidades de t er apia int ensiv a; pr ev ención & cont r ol
I N FECÇÕES DA CORREN TE SAN GÜÍ N EA EM PACI EN TES EM USO DE CATETER VEN OSO
CENTRAL EM UNI DADES DE TERAPI A I NTENSI VA
Os cat et er es v en osos cen t r ais ( CVC) , u t ilizad os, p r in cip alm en t e em u n id ad es d e t er ap ia in t en siv a-UTI s, são im por t ant es font es de infecção da cor r ent e sangüínea ( I CS) . Est e est udo epidem iológico analít ico, t ipo coor t e pr ospect iva, enfoca a incidência de I CS, fat or es de r isco associados e ações assist enciais r elacionadas
ao uso desses cat et er es em 7 UTI s no Dist r it o Feder al. Dos 630 pacient es com CVC, 6,4% apr esent ar am I CS ( 1,5% r elacionadas ao cat et er e 4,9% I CS- Clínica) . A per m anência de int er nação foi 3,5 vezes m aior par a esse gr upo de pacient es. Obser vou- se condut as diver sificadas com r elação à inser ção dos cat et er es e o uso de ant i-sépt ico. O t em po de per m anência do CVC m ost r ou- se associado à infecção ( p< 1x 10- 8) , assim com o à punção
em veia subclávia dir eit a e a cat et er de duplo- lúm en. Pacient es neur ológicos e os t r aqueost om izados for am os m ais acom et idos. Suger e- se a for m ação de um gr upo de cat et er , par a padr onizar r ot inas r elacionadas ao uso dos cat et er es no int uit o de r eduzir o per íodo de int er nação e os cust os hospit alar es.
DESCRI TORES : infecção hospit alar ; unidades de t er apia int ensiv a; pr ev enção & cont r ole
1 Doct oral St udent in Healt h Sciences Univer sit y of Brasília; Technical Consult ant of t he Gener al Managem ent of Saneant es - GGSAN/ ANVI SA; 2 PhD, Pr ofessor
Univer sit y of Br asília, Healt h Sciences School, Collect ive Healt h Depar t m ent
I NTRODUCTI ON
I
n t r a v a scu l a r ca t h e t e r s a r e e sse n t i a l i n m oder n m edicine, par t icular ly at int ensiv e car e unit s ( I CUs) . How ever, t hey const it ut e an im por t ant sour ce of pr im ar y blood st r eam infect ion. Appr oxim at ely 150 m i l l i o n c a t h e t e r s a r e p u n c t u r e d e v e r y y e a r a t hospit als and clinics in t he Unit ed St at es, m ore t han 5 m illion of w hich ar e cent r al v enous cat het er s( 1). As a r esu lt of t ech n olog ical ad v an ces, v en ou s access is m ain t ain ed lon ger an d u sed m or e fr equ en t ly, h en ce ent ailing an increased num ber of infect ions relat ed t o t h i s p r o ce d u r e . Th e h o sp i t a l s f r o m t h e N a t i o n a l Nosocom ial I n f ect ion Su r v eillan ce Sy st em ( NNI SS) of t h e Cen t er s f or Disease Con t r ol an d Pr ev en t ion ( CD C) i n t h e Un i t ed St a t es h a v e p u b l i sh ed b l o o d st r eam infect ion ( BSI ) r at es at int ensiv e car e unit s, w hich range from 4.9 at car diot horacic int ensive car e u n it s an d 1 1 . 9 at t r au m a u n it s, p er 1 , 0 0 0 cen t r al ca t h e t e r s- d ay, f o r t h e p e r i o d f r o m 2 0 0 2 - 2 0 0 4( 2 ). Bef or e, t h e NNI SS h ad alr ead y p u b lish ed a r at e of 3.48 per 1,000 dischar ges. Ar gent inean dat a r egist er 2.92% of t hese infect ions( 3).I n f ect ion r isk r elat ed t o v ascu lar access is a sso ci a t e d w i t h t h e a cce ss l o ca t i o n , t h e i n se r t e d so l u t i o n , t h e e x p e r i e n ce o f t h e p r o f e ssi o n a l w h o p e r f o r m s t h e p r o ce d u r e , d w e l l i n g t i m e , t y p e a n d cat h et er h an d l i n g , am o n g o t h er s( 4 ). Th ese f act o r s con st it u t e im p or t an t st r at eg ic p oin t s f or act ion s t o pr ev en t t h ese in fect ion s.
A l t h o u g h t h e i n c i d e n c e o f b l o o d s t r e a m infect ion is low er t han of ot her hospit al infect ions ( HI ) lik e lu n g , u r in ar y t r act an d su r g ical sit e in f ect ion s, blood st r eam in f ect ion s ar e im por t an t becau se t h ey ar e a cau se of su b st an t ial m or b id it y, m or t alit y an d i n cr eased h o sp i t al co st s( 3 - 4 ). No r t h Am er i ca n d a t a r egist er an ex t en ded h ospit alizat ion per iod, r an gin g fr om 6.5 t o 22 day s( 5). A st udy in Ar gent ina found a c o s t s u r p l u s o f $ 4 8 8 8 a n d a n e x t e n s i o n o f t h e hospit alizat ion per iod by 11.9 day s per blood st r eam infect ion episode( 3 ).
This st udy aim s t o calculat e t he incidence and r isk f act or s associat ed w it h blood st r eam in f ect ion s c a u s e d b y Ce n t r a l Ve n o u s Ca t h e t e r s ( CV C) a t int ensive care unit s from hospit als in t he Single Healt h Syst em ( SUS) hospit al net w or k of t he Feder al Dist r ict , Brazil. I n addit ion, t his research int ends t o cont ribut e t o t h e elabor at ion of act ion s t o pr ev en t an d con t r ol b l o o d st r e a m i n f e ct i o n s i n p a t i e n t s u si n g ce n t r a l
v enous cat het er s, as w ell as t o achiev e t he r at ional use of t his pr ocedur e.
PATI ENTS AND METHODS
We car r ied ou t an ep id em iolog ical- an aly t ic p r osp ect iv e coh or t st u d y in a clin ical en v ir on m en t , i n c l u d i n g a l l p a t i e n t s , i n d e p e n d e n t l y f r o m t h e b a se l i n e p a t h o l o g y, t y p e o f I CU, m e d i ca t i o n u se et c., ad m it t ed at 7 ad u lt in t en siv e car e u n it s f r om h osp it als in t h e Fed er al Dist r ict , in t h e p er iod f r om Feb r u ar y 2 1st t o Decem b er 2 6t h 2 0 0 3 . Th e p r esen ce of an y ear lier in f ect ion w as n ot con sid er ed eit h er, d u e t o t h e cr i t e r i o n u se d t o d i a g n o se t h e b l o o d st r e a m i n f e ct i o n , w h i ch co u l d n o t b e r e l a t e d t o an o t h er i n f ect i o n f o cu s.
St u d y p a r t i ci p a n t s w er e a l l a d u l t p a t i en t s hospit alized at t hese int ensive car e unit s w ho used a cen t r al v en ou s cat h et er for m or e t h an 2 4 h ou r s, t o adm inist er solut ions, m edicat ion and hem oder iv at iv e d r u g s. At t h at m o m en t , t h e I CUs w er e st u d i ed i n gener al, w it hout t ak ing int o account t heir t y pe. The st udy inv olv ed I CUs w it h m edical, sur gical or m ix ed clin ical p at ien t s. All cen t r al v en ou s cat h et er s u sed w er e m ade of poly ur et hane. Only pat ient s w ho w er e hospit alized and used a cat het er for less t han 24 hour s w er e excluded, as m ent ioned abov e. We car r ied out a pr et est w it h 40 pat ient s fr om an int ensive car e unit of anot her hospit al fr om t he Federal Dist r ict , used for t his goal only, dur ing a 30- day per iod, and m ade t he n e c e s s a r y a d j u s t m e n t s i n t h e d a t a c o l l e c t i o n inst r um ent . These pat ient s w er e not included in t he defin it iv e st u dy.
Th e collect ed d at a w er e r eg ist er ed b y t h e r esear cher in indiv idual files w it h t he daily ev olut ion, from t he pat ient ’s ent ry at t he int ensive care unit unt il h i s/ h er d i sch a r g e o r t r a n sf er en ce. D i sch a r g e w a s consider ed t o be t he m om ent w hen t he pat ient w as sen t t o an ot h er place ou t side t h e h ospit al of or igin and t r ansfer ence w hen t he pat ient w as sent t o a unit in t h e sam e h ospit al. I n t h is case, t h e pat ien t w as follow ed for t w o m or e day s.
w er e r eg i st er ed . Th e cat h et er i n ser t i o n t ech n i q u e an d t h e p r of ession al w h o car r ied ou t t h e p r oced u r e w e r e n o t a s s e s s e d , a s a l a r g e m a j o r i t y o f t h e p at ien t s w er e cat h et er ized at t h e em er g en cy u n it s. Pe r i p h e r a l b l o o d cu l t u r e s w e r e ca r r i e d o u t i n a l l p a t i e n t s w i t h a f e v e r o r o t h e r si g n s o f i n f e ct i o n . Th e ca t h e t e r s w e r e r e m o v e d w h e n t h e i r u se h a d b e c o m e u n n e c e s s a r y, i n c a s e o f o b s t r u c t i o n o r a cci d en t a l l o ss, a n d su b m i t t ed t o cu l t u r es ( sem i -q u a n t i t a t i v e i n f i v e i n t e n s i v e c a r e u n i t s a n d quant it at ive in t he rest ) . To obt ain t he diagnosis of blood st ream infect ion, a t echnique was used wit h t he cat het er in place, wit hout t he need t o rem ove it .
Th is ar t icle r ep or t s in it ial r esu lt s of a lar g er p r o j e c t , a i m e d a t a s s e s s i n g t h e i n c i d e n c e o f i n f e ct i o n s i n p a t i e n t s a t t h e m e n t i o n e d i n t e n si v e car e u n i t s, an d w as ap p r ov ed b y t h e I n st i t u t i on al Re v i e w B o a r d f r o m t h e Fe d e r a l D i s t r i c t H e a l t h Se cr e t a r y ( SES- D F) .
The cr it er ia r ecom m ended by t he CDC( 6) w ere used for t he diagnosis. Cat het er s w it h negat ive r esult s of m icr oor g an ism cu lt u r es w er e con sid er ed st er ile. Clinical Blood St r eam I nfect ion ( C- BSI ) w as diagnosed w hen t he pat ient pr esent ed at least one of t he signs or sy m pt om s w it hout anot her ident ified cause: fev er ( t em per at u r e e” 3 8 º C) , pain , er y t h em a or h eat of t h e in v olv ed v ascu lar sit e an d > 1 5 Colon y For m in g Unit s ( CFU) , isolat ed fr om t he t ip of t he int r avascular cat het er, and blood cult ur e w it h a negat iv e r esult or n o t acco m p l i sh ed . Cat h et er - Rel at ed Bl o o d St r eam I n f e c t i o n ( CR- B S I ) o c c u r r e d w h e n t h e p a t i e n t pr esent ed t he abov e cr it er ia associat ed w it h posit iv e blood cult ur e, w it h t he sam e m icr oor ganism isolat ed fr om t he cat het er t ip.
STATI STI CAL ANALYSI S
Dat a w er e analy zed using EPI I NFO, v er sion 6 . 2 . Fr equ en cy t ables w er e u sed t o su m m ar ize t h e diagn oses of pat ien t s u sin g a cat h et er, accor din g t o gen der an d cat h et er dw ellin g t im e. Th e per cen t age of pat ient s w it h blood st ream infect ion, w it h or w it hout a r isk fact or, was com par ed using Fisher ’s Ex act t est o r Pe a r so n ’s Ch i - Sq u a r e t e st . We ca l cu l a t e d t h e Relat iv e Risk ( RR) , a 9 5 % Con f id en ce I n t er v al an d t h e associat ed p - v alu e. Th e sig n if ican ce lev el w as p< 0.05. Mean/ m edian t est s ( St udent ’s t and Kr uskal-Wallis) w er e car r ied ou t t o ch eck f or dif f er en ces in
t h e n u m e r i ca l v a r i a b l e s b e t w e e n p a t i e n t g r o u p s, m aint aining t he sam e significance lev el.
RESULTS
Dur ing t he st udy per iod, 1,165 pat ient s w er e h ospit alized at t h e 7 in t en siv e car e u n it s, 1 , 0 0 6 of w h o m ( 4 9 . 4 % f em al e an d 5 0 . 6 % m al e) r em ai n ed h ospit alized at t h ese u n it s f or m or e t h an 2 4 h ou r s. The m ean age w as 48 ± 20.5 y ear s and t he m edian 47 year s; t he m ean st ay in hospit al last ed 11.5 ± 15 d a y s a n d t h e m e d i a n 6 d a y s. I n t h e t o t a l g r o u p ( 1,006) , 630 ( 62.6% ) used a cent ral venous cat het er, 4 0 . 8 % of w hom w er e w om en and 5 9 . 2 % m en, w ho const it ut ed t he final st udy populat ion ( RR= 1.64; 95% CI = 1 . 4 1 - 1 . 9 0 ; p= 1 x 1 08) .
Am ong t he 630 pat ient s w ho used a cent r al v enous cat het er, 4 0 ( 6 . 4 % ) pr esent ed blood st r eam i n f ect i o n , 9 ( 1 . 5 % ) o f w h i ch cat h et er - r el at ed an d 4 1 ( 4 . 9 % ) cl i n i cal . Th e d i f f er en ce o b ser v ed i n t h e in cid en ce of b lood st r eam in f ect ion ( 5 7 . 5 % f em ale and 42.5% m ale cases) w as not st at ist ically significant ( RR= 0.84; 95% CI = 0.58- 1.21; p= 0.30) . On t he ot her hand, t he presence of infect ion significant ly increased t he dur at ion of t he pat ient s’ st ay at t he I CUs, w it h a m ean st ay of 4 0 . 3 d ay s, ap p r ox i m at el y 3 . 5 t i m es lon ger t h an pat ien t s w it h ou t in f ect ion , w it h a m ean st ay of 1 1 . 5 d ay s ( Kr u sk al- Wallis t est ; p < 1 x 1 0- 8) . D e f i n i t e l y, t h i s i n c r e a s e i n t h e d u r a t i o n o f hospit alizat ion is dir ect ly r elat ed w it h t he sev er it y of t he pat ient ’s case, and not only w it h t he pr esence of in f ect ion .
No ca t h e t e r i n se r t e d i n a n o t h e r u n i t w a s c h a n g e d w h e n t h e p a t i e n t w a s a d m i t t e d a t t h e in t en siv e car e u n it , ex cep t on on e occasion , w h en t he cat het er w as changed using t he guide w ir e. None of t he I CUs had an est ablished Cat het er Com m ission. As t hese hospit als had a m edical r esidence pr ogr am , usually, t he pr ocedur e was car r ied out by t he r esident ph y sician s, su per v ised by t h e ph y sician r espon sible for t he unit . Only one of t he I CUs referred it s pat ient s for cat het erizat ion at t he Surgery Cent er. Despit e t he absen ce of st an dar dized r ou t in es for all I CUs, in all punct ur es, t he physicians used sur gical gloves, m ask, cap and gow n.
a t t h e t i m e o f ca t h e t e r i n st a l l m e n t a n d d r e ssi n g r eplacem en t . I n m ost cases, PVPI w as u sed an d, if absent , cleaning w as done using physiological ser um . This lack of st andardizat ion did not allow us t o assess t he use of ant isept ic agent as a r isk fact or for blood st r eam in f ect ion .
The dr essing used on t he punct ur e sit e should b e p er m eab le t o w at er st eam , com f or t ab le f or t h e pat ien t an d easy t o h an dle f or h ealt h pr of ession als and/ or pat ient s. I t can be t r anspar ent or using gauze f i x e d w i t h a d h e s i v e t a p e . Th e a d v a n t a g e o f t r a n s p a r e n t d r e s s i n g s i s t h a t t h e y p e r m i t t h e visualizat ion of t he insert ion orifice, prom ot e a barrier again st dir t an d t h at ch an ges ar e less f r equ en t , as t h e y f a v o r c o n s t a n t a s s e s s m e n t b y h e a l t h pr ofessionals. Ther e is no consensus about infect ion r isk an d it s associat ion w it h in t r av ascu lar cat h et er dr essings. What is im por t ant is t hat t he gauze dr essing sh ou ld be r eplaced w h en ev er h u m id, dir t y or loose. I n t he cat het er s follow ed in t his st udy, t he dr essings of t h e in ser t ion sit e w er e r eplaced by n u r ses ev er y 48 hours or w henever necessary, in line w it h t he above or ien t at ion s, u sin g st er ile g au ze an d t h e av ailab le ant isept ic agent . The sit e w as pr ot ect ed w it h st er ile gauze and adhesive t ape. As t he used ant isept ic agent w as not st andar dized, dr essing change could not be assessed eit her as a r isk fact or for infect ion.
Am ong t he com plicat ions r elat ed t o t he CVC, 4 5 . 4 % o f t h e p a t i e n t s p r e s e n t e d f e v e r, 3 . 5 % p n eu m ot h or ax , 2 . 5 % p r esen ce of secr et ion on t h e inser t ion sit e and 1% accident al cat het er loss. All 40 pat ient s w ho dev eloped blood st r eam infect ion had a t em per at u r e e” 3 8 º C.
Table 1 – Fr equency dist r ibut ion of pat ient s w it h and w it hout infect ion, according t o cat het er dw elling t im e, at 7 I CUs from t he SUS net w ork in t he Feder al Dist r ict , 2 0 0 3
g n i l l e w d r e t e h t a C e m i t n o i t c e f n
I Noinfection Total
N % N % N %
7 o t
1 1 2,5 307 52* 308 48,9
4 1 o t
8 7 17,5 155 26,2 162 25,7
1 2 o t 5
1 7 17,5 70 18,9 77 12,2
1 2 n a h t e r o
M 25 62,5* 58 9,8 83 13,2
l a t o
T 40 6,4 590 93,7 630 100
p< 0.05
I t is obser v ed in Table 1 t hat 6 2 . 5 % of t he pat ient s w it h blood st r eam infect ion used a CVC for m o r e t h a n 2 1 d a y s . Th e d i f f e r e n c e w a s h i g h l y s i g n i f i c a n t f r o m a s t a t i s t i c a l p e r s p e c t i v e w h e n
c o m p a r i n g t h e c a t h e t e r d w e l l i n g t i m e w i t h t h e p r e se n ce o f i n f e ct i o n ( p < 1 x 1 0- 8) . Mo r e t h a n h a l f ( 52% ) of t he pat ient s w ho did not pr esent infect ion used a CVC for up t o 7 days.
Table 2 – Fr equency dist r ibut ion of pat ient s w it h and w it hout infect ion accor ding t o cat het er inser t ion sit e, at 7 I CUs fr om t he SUS hospit al net w or k in t he Feder al Dist r ict , 2003
e t i s n o i t r e s n i r e t e h t a
C Infection Noinfection Total
N % N % N %
n i e v l a r o m e f t f e
L 0 0 4 0,7 4 0,6
n i e v l a r o m e f t h g i
R 0 0 0 0 0 0
m r a t f e
L 0 0 1 0,2 1 0,2
m r a t h g i
R 0 0 0 0 0
n i e v r a l u g u j t f e
L 3 7,5 1 0,2 4 0,6*
n i e v r a l u g u j t h g i
R 7 17,5 44 7,5 51 8,1*
n i e v n a i v a l c b u s t f e
L 10 25* 130 22 140 22,2
n i e v n a i v a l c b u s t h g i
R 20 50* 410 69,5 430 68,2
l a t o
T 40 6,4 590 93,7 630 100
( * ) p< 0.05
Table 2 r egist er s t hat 68.2% of t he cat het er s w er e inser t ed in t he r ight subclav ian v ein, w hich can j ust ify t he incidence of 50% of BSI w hen t his access w as used, and 75% w hen adding t he access t hr ough t he left subclav ian v ein. The occur r ence of infect ions w as ver y consider able w hen t he r ight and left j ugular v ein w er e used.
We f o u n d a h i g h er b l o o d st r eam i n f ect i o n coef f icien t in pat ien t s w er e n eu r ological pat h ologies ( 3 0 % ) , f o l l o w e d b y h e a r t d i se a se s ( 1 7 . 5 % ) . Th e r em ain d er w as d ist r ib u t ed in sm aller p er cen t ag es: p at ien t s w it h g ast r o- in t est in al ( 1 2 . 5 % ) , r esp ir at or y ( 1 2 . 5 % ) , o r t h o p e d i c ( 1 0 % ) , k i d n e y ( 7 . 5 % ) , g y n e c o l o g i c a l - o b s t e t r i c ( 5 % ) a n d i n f e c t i o u s pat h ologies ( 5 % ) .
Table 3 – Fr equency dist r ibut ion of pat ient s w it h and w it h ou t in f ect ion accor din g t o n u m ber of lu m en s in t he cat het er s, at 7 I CUs fr om t he SUS hospit al net w or k in t he Feder al Dist r ict , 2003
s n e m u l f o r e b m u
N Infection Noinfection Total
N % N % N %
n e m u l e l g n i
S 6 15 129 21,9 135 21,4
n e m u l e l b u o
D 34 85* 460 78 494 78,4
n e m u l e l p i r
T 0 0 1 0,2 1 0,1
l a t o
T 40 6,4 590 93,7 630 100
( * ) p< 0.05
k s i r f o e c n e s e r P s r o t c a f n o i t c e f n
I No
n o i t c e f n
i RR CI P-value
% % r o t a r i p s e
R 87,5 79,1 1,3 1.16-1,49 0,0061
e b u t l a e h c a r t o r
O 87,5 78,1 1,3 1.16-1,49 0,0059
n o i s u f s n a r t d o o l
B 77,5 45,8 1,9 1.60-2,31 0
n i a r d c i c a r o h
T 20 26,8 0,9 0.50-1,76 0,833
y m o t o e h c a r
T 77,5 16,3 4,9* 3.68-6,60 0
r e t e h t a c n e m u l e l b u o D s i s y l a i d o m e
h 30 10,2 2,9* 1.75-4,85 0
y m o t o b e l h
P 27,5 8,1 2,5 1.45-4,22 0,0016
l n o i t i r t u n l a r e t n e r a p l a t o
T 10 4,4 3,0* 1.26-7,21 0,01251
con sider ed a r isk f act or f or blood st r eam in f ect ion , w e f ou n d n o st at ist ical d if f er en ce w h en com p ar in g p a t i en t s w h o u sed a cen t r a l v en o u s ca t h et er a n d display ed infect ion w it h t he num ber of lum en in t he u sed cat h et er ( p = 0 . 9 3 ) . We ob ser v ed a p r ef er en ce for using double lum en cat het er s ( 78.4% ) and higher infect ion levels ( 85% ) w hen t his t ype of cat het er w as u sed .
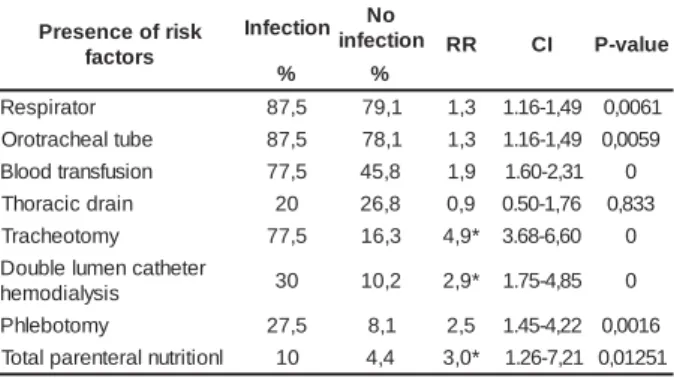
Table 4 – Fr equency dist r ibut ion of pat ient s w it h and w i t h o u t i n f e c t i o n a c c o r d i n g t o u s e d i n v a s i v e pr ocedur es, at 7 I CUs fr om t he SUS hospit al net w or k in t he Feder al Dist r ict , 2003
( * ) p< 0.05
I n Ta b l e 4 , w e o b se r v e t h a t m o st o f t h e invasive pr ocedur es used in t he pat ient s at t he 7 I CUs r e v e a l e d t o b e a sso ci a t e d w i t h t h e b l o o d st r e a m infect ion, w it h a high lev el of st at ist ical significance. I n t r acheot om y pat ient s, a r elat iv e r isk ( RR) of 4.93 is obser v ed, follow ed by t h e u se of t ot al par en t er al nut rit ion and double lum en cat het er for hem odialysis, w it h an RR of 3 and 2.9 r espect ively.
Table 5 – Fr equency dist r ibut ion of pat ient s w it h blood st r eam in f ect ion accor din g t o in f ect iou s agen t , at 7 I CUs f r om t h e SUS h ospit al n et w or k in t h e Feder al Dist r ict , 2003
t n e g a s u o i t c e f n
I Infection
N % e v i t a g e n -m a r G a s o n i g u r e a s a n o m o d u e s
P 13 32,5*
i n n a m u a b r e t c a b o t e n i c
A 7 17,5
e a i n o m u e n p a ll e i s i b e l
K 1 2,5
e v i t i s o p -m a r
G Staphylococcusaureus 14 35*
a v i t a g e n e s a l u g a o c s u c c o c o l y h p a t
S 3 7,5
s u g n u
F Cândidaalbicans 2 5
l a t o
T 40 100
( * ) p< 0.05
As t o i n f e ct i o u s a g e n t s ( Ta b l e 5 ) , g r a m -p o si t i v e St a -p h y l o ccu s a u r e u s a n d g r a m - n e g a t i v e Pse u d o m o n a s a e r u g i n o sa st a n d o u t a s t h e m o st
f r eq u en t ly isolat ed m icr oor g an ism s, w it h 3 5 % an d
3 2 . 5 % , r esp ect iv ely. How ev er, in t h e g en er al su m , g r a m - n e g a t i v e o r g a n i sm s w e r e m o r e p r e v a l e n ce , w hich goes against ot her publicat ions( 7- 8).
For t y - f iv e per cen t ( 1 8 ) of t h e pat ien t s w it h blood st r eam infect ion w ere t r ansfer r ed t o ot her unit s in t he sam e hospit al; 40% ( 16) died due t o a cause t hat w as not specified as r elat ed t o t he infect ion. I n t he r em aining gr oup, 5% ( 2) w er e r efer r ed t o ot her in st it u t ion s an d 1 0 % ( 4 ) r em ain ed at t h e I CU u n t il t he end of t he st udy.
DI SCUSSI ON
Al t h o u g h i t i s a ck n o w l e d g e d t h a t ce n t r a l v en o u s cat h et er s ar e i m p o r t an t f o r p at i en t s, t h ey en t ail a pr edisposit ion t o in fect iou s com plicat ion s( 9 ). I n t his st udy, t he 6. 4% infect ion r at e w e found w as associat ed w it h t he durat ion of hospit alizat ion, cat het er dw ellin g t im e, locat ion in t h e r igh t su bclav ian v ein , u se of d ou b le lu m en cat h et er an d t h e con com it an t presence of t racheot om y, parent eral nut rit ion cat het er and double lum en cat het er for hem odialy sis.
These findings ar e in line w it h ot her st udies t hat appoint t he dur at ion of t he cat het er izat ion as a r i sk f a ct o r f o r b l o o d st r ea m i n f ect i o n( 1 ). Ef f ect i v e m easur es t o r educe t he r isk associat ed w it h cat het er d w ellin g in clu d e t h e cau t iou s in d icat ion of cat h et er use, as w ell as a w ell t rained t eam for t heir insert ion, m aint enance and r em ov al( 4 , 1 0 ).
Ot h er st u dies, in clu din g t h is on e, f ou n d an ex t en si on of t h e h osp i t al i zat i on p er i od d u e t o t h e incidence of blood st r eam infect ion( 10). The ex t ension of t he hospit al st ay in it self fav or s an incr eased r isk of infect ion, t he r educed av ailabilit y of beds and t he incr ease of hospit al cost s, am ong ot her s.
W h e n t h e c a t h e t e r i s i n s e r t e d i n a n em er gency sit uat ion, t his can lead t o t he br eaking of a sep si s t ech n i q u es, b esi d es t h e r i sk o f t r a u m a t i c v essel in j u r ies. I n t h ese cases, t h e cat h et er sh ou ld b e ch an g ed as q u i ck l y as p o ssi b l e. Ho w ev er, w i t h r e s p e c t t o t h e f r e q u e n c y o f c e n t r a l c a t h e t e r r ep l acem en t , n o ad v an t ag e h as b een o b ser v ed i n t er m s of infect ion r educt ion. The pr ogr am m ed r out ine r eplacem ent , using t he guide w ir e or a new punct ur e, is not indicat ed because it does not r educe infect ion r at es( 5 ).
t h e cen t r al v en ou s cat h et er is in ser t ed b y sp ecif ic t eam s or duly t rained st aff, infect ion rat es ar e r educed, a s t i s s u e d a m a g e d e c r e a s e s a n d t h e u s e a n d p e r m a n e n ce o f t h e CVC i s r e d u ce d , w i t h a cl e a r adv an t age in t h e cost / ben ef it assessm en t( 5 ). I n t h is st u d y, w e a l e r t t o t h e i m p o r t a n ce o f t h e t e a m ’s au t on om y t o im plan t a ch an ge in t h e pr of ession als’ b eh a v i o r, a n d t h e n eed f o r su p p o r t f r o m h o sp i t a l m an ag er s. I t i s h i g h l i g h t ed t h at t h e NNI SS f o u n d h ig h er BSI r at es in lar g e t each in g h osp it als ( m or e t han 500 beds) .
As opposed t o ot her r efer ences( 8), t his st udy f ou n d a h ig h er in cid en ce of in f ect ion in su b clav ian vein cat het er izat ions. How ev er, cat het er izat ion of t he f e m o r a l v e i n i s a sso ci a t e d w i t h a h i g h e r r i sk o f i n f ect i o u s a n d t h r o m b o si s co m p l i ca t i o n s t h a n t h e subclavian vein in I CU pat ient s ( 11). I t is also associat ed w it h h ig h er r at es of m ech an ical com p licat ion s lik e ar t er ial punct ur e and hem at om a( 12). Despit e a low er r isk of com plicat ions caused by t he inser t ion, j ugular v ein cat h et er s con cu r f or t h e h igh est pr obabilit y of d ev elop in g in f ect ion ( 1 2 ). I n a st u d y car r i ed ou t i n ch ildr en , t h e m ost u sed cat h et er in ser t ion sit e w as t he int er nal j ugular v ein, follow ed by t he subclav ian v ein( 9).
Ce n t r a l c a t h e t e r s c a n b e i n s e r t e d per ipherally, by m eans of a punct ur e in t he cephalic or basilic v ein as, fav or ed by t he low er colonizat ion, oilin ess an d h u m idit y of t h e an t ecu bit al f ossa, t h ey pr ovide for easy m aint enance and longer dw elling t im e and pr esent low er infect ion r at es t han non- im plant able cent r al cat het er s. These r out es can be an opt ion for t h e p r oced u r e, also d u e t o t h e h ig h con t am in at ion pr obabilit y of t he cat het er inser t ed in t he subclav ian and j ugular v eins, due t o t he dr ainage of r espir at or y secr et ion f ou n d in p at ien t s u sin g or ot r ach eal t u b es an d t r ach eot om ies w h ich , in t h is st u dy, r epr esen t ed im por t ant r isk fact or s for infect ion. Venous dissect ion sh o u l d b e a v o i d e d b e ca u se o f t h e h i g h e r r i sk o f in f ect ion t h an p u n ct u r e, d u e t o t issu e t r au m a an d b eca u se t h er e i s n o a p p r o p r i a t e ca t h et er f o r t h i s p r oced u r e( 8 ).
As t o t h e ch oice of t h e cat h et er t y p e w it h r esp ect t o t h e n u m b er of lu m en s, t h e n eed an d / or sev er it y of t he pat ient ’s case should be assessed, as w ell as t h e n u m b er of m ed icat ion s an d n u t r it ion al support . References indicat e t hat each lum en increases handling by 15 t o 20 t im es per day( 5). A r andom ized st udy in pat ient s using subclav ian v ein cat het er s for m or e t han a w eek for an incidence lev el of 2. 6% of blood st ream infect ion for single lum en, against 13.1%
f or t r iple lu m en cat h et er s( 1 3 ). How ev er, gen er ally, it ar e t he m ost sev er e pat ient s w ho ar e hospit alized at I CUs, m ost fr equent ly use m ult i- lum en cat het er s and, consequent ly, pr esent gr eat er infect ion r isk s. I n t his st u d y, w e f o u n d h i g h er u sa g e a n d , co n seq u en t l y, higher incidence lev els of infect ion in case of double lu m en cat h et er s.
Gr a m - p o si t i v e St a p h y l o co ccu s a u r eu s a n d coagulase- negat ive St aphylococcus ar e t he or ganism s m ost frequent ly involved in vascular access infect ions, m a i n l y i n p a t i e n t s w h o s e i m m u n e s y s t e m i s com p r om ised an d h av e u sed a cat h et er f or a lon g t im e. Can dida spp h as r ev ealed t o be an im por t an t an d em er g in g p at h og en in r ecen t y ear s, in cr easin g it s part icipat ion in blood st ream infect ions( 5). Pr obably, t h i s o c c u r r e n c e i s p a r t i a l l y r e l a t e d w i t h t h e i n d i scr i m i n at e u se of l ast - g en er at i on an t i m i cr ob i al agent s and w it h t he incr eased use of CVC.
S t u d i e s a p p o i n t t h a t t h e h e a l t h t e a m ’ s ed u cat i o n can b e t h e m o st i m p o r t an t m easu r e t o pr event com plicat ions der iving fr om t he use of cent r al v enous cat het er s( 10). Hand w ashing is highlight ed as a pr im or dial m easu r e t o pr ev en t h ospit al in fect ion s. Therefore, in com binat ion w it h t he sensit izat ion of t he p r of ession al t eam , ad eq u at e con d it ion s n eed t o b e fav or ed t o car r y out t he pr ocedur e.
We consider t h e follow ing st udy lim it at ion s: r ealizat ion at I CUs w it h dist inct peculiar it ies, each of w hich w it h different risks of acquiring HI ; t he presence of m ult iple t eam s for cat het er inser t ion and t he non st andar dizat ion of cr it er ia for t he dur at ion of it s use. Th e u se of t h e t ot al n u m ber of pat ien t s u sin g CVC and not of pat ient s per day and cat het er s per day t o calculat e t he indicat or s, w hich w ould help t o cont r ol for t he var iat ion in t he pat ient ’s st ay at t he I CU, w as also consider ed a lim it ing fact or.
Cult ur e of t he cat het er t ip t hr ough t he sem i-q u an t i t at i v e m et h o d h el p s t o d i st i n g u i sh b et w een in f ect ion an d con t am in at ion , p r ov id in g f or a m or e specific diagnosis of cat het er- relat ed sepsis. How ever, t he quant it at ive m et hod can be used t hr ough vigor ous shak ing in t he cult ur e m edium or t hr ough ult r asonic t r eat m ent , in or der t o incr ease t he specificit y of t he diagnosis( 8). Using qualit at iv e t echniques t o diagnose cat h et er - r elat ed in f ect ion s is n ot r ecom m en d ed , as one single cont am inat ing m icr oor ganism can lead t o a posit iv e cult ur e( 8).
a n t i se p t i c a g e n t s, a n t i b i o t i cs a n d h a n d w a sh i n g pr odu ct s w er e fr equ en t ly lack in g.
We hope t hat t hese result s w ill st im ulat e t he im plan t at ion of BSI pr ev en t ion act ion s, su ch as t h e cr eat ion of t he Cat het er Gr oup t o st andar dize cat het er i n se r t i o n , m a i n t e n a n ce a n d w i t h d r a w a l r o u t i n e s, besides orient at ions for caut ious cat het er use and care pr ofessionals’ adher ence t o t he st andar dized pr ot ocols f or cat h et er car e. An ot h er i m p or t an t f act or i s t h e i n c o r p o r a t i o n o f k n o w l e d g e i n t o h a n d w a s h i n g pr act ices, w hich w ill fav or t he r educt ion of infect ions in gener al, and not only of blood st r eam infect ions.
I t is im por t an t t o car r y ou t specif ic st u dies per I CU t ype, as t he dur at ion of t he pat ient s’ st ay at t hese unit s varies and, consequent ly, cat het er dw elling t i m es, l ead i n g t o v ar i at i o n s i n t h e i n f ect i o n r at es r elat ed t o t he inv asiv e pr ocedur es. I n t his sense, w e agr ee w it h t h e or ien t at ion t h at , in or der t o pr ev en t h o s p i t a l i n f e c t i o n , b o t h p h y s i o p a t h o l o g y a n d epidem iology sh ou ld be k ept in m in d( 1 4 ). Th er ef or e, accom panying hist or ical ser ies of infect ion occur r ence
is r ecom m endable in or der t o apply hospit al infect ion cont r ol and pr ev ent ion m easur es. The elabor at ion of i n ci d en ce d en si t y i n d i cat o r s, u si n g t h e n u m b er o f cent ral venous cat het er s- day, w ill help t o cont r ol for t he pat ient ’s per m anence t im e at t he I CU. Alt hough t her e does not ex ist an accept able v alue for hospit al i n f e c t i o n s , A r g e n t i n e a n d a t a r e g i s t e r 2 . 9 2 % o f cat h et er - r elat ed blood st r eam in f ect ion s in m edical/ su r gical an d car diology( 3 ) I CU pat ien t s, t h at is, w it h sim ilar charact er ist ics t o t his st udy.
ACKNOW LEDGEMENTS
To t h e D i r ect o r s a n d p r o f essi o n a l s a t t h e I CUs, Lab or at or ies an d File Sect or of t h e h osp it als t h at par t icipat ed in t h e st u dy : Hospit al Region al da Asa Nor t e, Hospit al Regional de Sobr adinho, Hospit al
Reg ion al d a Asa Su l, Hosp it al d e Base d o Dist r it o
Fe d e r a l ( 3 a d u l t I CUs ) , Ho sp i t a l Un i v e r si t á r i o d e
Br asília an d Hospit al das For ças Ar m adas.
REFERENCES
1. McGee DC, Gould MK. Pr ev ent ing com plicat ions of cent r al venous cat het erizat ion. N Engl J Med 2003 Mar, 348: 1123- 33. 2 . Cen t er s f o r D i sea se Co n t r o l a n d Pr ev en t i o n . Na t i o n a l Nosocom ial I n f ect ion s Su r v eillan ce( NNI SS) Sy st em r ep or t , dat a sum m ar y fr om Januar y 1992- hy be 2004m . Am J I nfect Co n t r o l 2 0 0 4 ; ( 3 2 ) : 4 7 0 - 8 5 .
3 . Ro se n t h a l VD , Gu sm a n S, Mi g o n e O, Cr n i ch CJ. Th e at t r ib u t ab le cost , len g t h of h osp it al st ay, an d m or t alit y of cen t r al l i n e- asso ci at ed b l o o d st r eam i n f ect i o n i n i n t en si v e car e d ep ar t am en t s i n Ar g en t i n a: A p r o sp ect i v e, m at ch ed an aly sis. Am J I n f ect Con t r ol 2 0 0 3 ; 3 1 : 4 7 5 - 8 0 .
4 . Fer n an d es AT, Rib eir o NF. I n f ecção d o Acesso Vascu lar. I n: Fer nandes AT, Fer nandes MA, Ribeir o N F, or ganizador es. I nfecção Hospit alar e suas I nt er faces na Ár ea da Saúde. São Pau lo ( SP) : At h en eu ; 2 0 0 0 . p. 5 5 6 - 7 9 .
5 . Associação Pau list a d e Est u d os e Con t r ole d e I n f ecção H o s p i t a l a r. I n f e c ç ã o Re l a c i o n a d a a o u s o d e Ca t e t e r e s Vascu l ar es. São Pau l o ( SP) : APECI H; 2 0 0 5 .
6. Cent er s for Disease Cont r ol and Pr ev ent ion. Guideline for t he Pr ev ent ion of I nt r av ascular Cat het er - Relat ed I nfect ions. MMW R 2 0 0 2 ; 5 1 ( RR- 1 0 ) : 1 - 2 9 .
7. O‘Gr ady NP, Alexander M, Dellinger EP, Geber ding JL, Hear d S O , M a k i D G, e t a l . Gu i d e l i n e s f o r t h e p r e v e n t i o n o f i n t r a v a s c u l a r c a t h e t e r - r e l a t e d i n f e c t i o n . M M W R 2 0 0 2 ; 3 4 : 1 3 6 2 - 8 .
8. Marangoni D, Santos M. I nfecção Hospitalar e seu Controle. I n: Coura JR, editor. Dinâm ica das Doenças I nfecciosas e Parasitárias. Rio de Janeiro ( RJ) : Guanabara- Koogan; 2005. p. 435- 59.
9 . Car r ar a D . I n f l u ên ci a d o Si st em a Fech ad o d e I n f u são Venosa sem Agulha na I ncidência das I nfecções de Cor r ent e Sa n g ü ín e a ( I CS) e m Cr i a n ça s Op e r a d a s n o I NCOR – H C-FMUSP. [ t ese] . São Pau lo ( SP) : Facu ldade de Medicin a/ USP; 2 0 0 4 .
1 0 . Hig u er a F, Rosen t h al VD, Du ar t e P, Ru iz J, Fr an co G, Safdar N. Th e effect of pr ocess con t r ol on t h e in ciden ce of cen t r al v en ou s cat h et er - associat ed b lood st r eam in f ect ion s and m or t alit y in int ensive car e unit s in México. Cr it Car e Med 2 0 0 5 ; 3 3 ( 9 ) : 1 - 6 .
11. Mer r er J, De Jonhghe B, Golliot F, Lefrant J, Raffy B, Bar r e E, et al. Com p licat ion s of f em or al an d su b clav ian v en ou s cat het er izat ion in cr it ically ill pat ient es. JAMA 2 0 0 1 August ; 2 8 6 ( 6 ) : 7 0 0 - 7 .
1 2 . Slon im AD, Sin gh N. Nosocom ial Bloodst r eam in f ect ion an d cost . Cr it Car e Med 2 0 0 1 ; 2 9 ( 9 ) : 1 8 4 9 .
1 3 . Clar k C, Ch r ist of f N, Wat t er s VA, Sp ar k s W, Sn y d er P, Gr a n t JP. U s e o f t r i p l e l u m e n s u c l a v i a n c a t h e t e r s f o r adm inist r at ion of t ot al par ent er al nut r it ion. J Par ent er Ent er al Nu t r 1 9 9 2 ; 1 6 ( 5 ) : 4 0 3 - 7 .
1 4 . Rich t m an n Rosan a. I n f ecções da Cor r en t e San gü ín ea e Relacion ad as a Disp osit iv os I n t r av ascu lar es. I n : Rod r ig u es EAC, Mendonça JS, Am ar ant e JMB, Alves MB Filho, Gr inbaum RS , Ri c t m a n n R. I n f e c ç õ e s H o s p i t a l a r e s : Pr e v e n ç ã o e Con t r ole. São Pau lo ( SP) : Sav ier ; 1 9 9 7 . p. 1 9 1 - 2 0 8 .