First-Priniples Calulations of the Eetive Mass
Parameters of Al
x Ga
1 x
N and Zn
x Cd
1 x
Te Alloys
R. de Paiva,R. A.Nogueira, C. de Oliveira,
Departamentode Fsia,ICEx,UFMG,
C.P.: 702,CEP:13.081-970,BeloHorizonte,MG,Brazil
H. W. Leite Alves, J. L. A.Alves,
Departamento deCi^eniasNaturais-FUNREI,
C.P.: 110,CEP:36300-000, S~ao Jo~aodelRei,MG,Brazil
L.M. R. Solfaro, and J.R. Leite
LNMS,Departamento deFsiadosMateriais eMe^ania-USP
C.P.: 66.318,CEP:05389-970,S~aoPaulo,SP,Brazil
Reeivedon23April,2001
First-priniples alulations of eletroni band strutures of the ordered ubi alloys
Al
x Ga
1 x
N and Cd
x Zn
1 x
Te are arried out. The band strutures are used to provide
eetivemassesand Luttingerparameterswhihareusefulin theparametrizationof
theo-riesbasedoneetivehamiltonians.
I Introdution
The wide bandgaps of GaN and AlN make them
idealmaterialsfortheonstrutionofblue/green
light-emittingdevies(LED 0
sandlasers)andoftransistors
intended to operate at high power and temperatures
[1, 2℄. The alloyingbetweenGaN andAlN,produing
Al
x Ga
1 x
N, allowsthe \engineeringofthe band gap"
from6.28eVforAlNto3.44eVforGaNbyontrolling
theomposition x.
On the other hand the II-VI semiondutor
om-pounds ZnTeand CdTe and their alloys Zn
x Cd
1 x Te
haveimportantappliationssuhasinfrareddetetors,
solarellsandotherdevies[3,4℄.
Despitethereentintensiveexperimentaland
theo-retialstudyofthese materialssomeofthe
fundamen-talparameterswhihareessentialtotheoretialmodels
usedtoaountforthebehaviorofthealloysareeither
unknown or the subjet of some debate. In
partiu-lar, although theeetivemass approximationisused
extensivelythroughoutintheliterature,theatual
ele-tronandholeeetivemassesforthealloysinthewhole
range of x, are unknown. The transport and optial
phenomenausuallyaregovernedbythebandstrutures
in the immediateviinity ofthe Brillouinzone enter.
Thus the eetive mass approximation turn to be an
troni properties of materials amenable. The purpose
of the present study is to obtain the eletroni
stru-ture of those zin-blende (ubi) materials and their
alloysonthebasisof rst-priniplesband alulations
andthenlinktheeletronibandalulationswiththe
eetive-masstheory. Therefore,wefousoneletroni
struturesaround the valene-band maximum (VBM)
andtheondution-bandminimum(CBM)andobtain
theeletroneetivemasses,holeeetivemasses,and,
equivalently,theLuttinger-likeparameters[5℄. Asa
re-sult,wepresentsigniantparametersofthese
materi-als,whihanbeusedforthedesignofopto-eletroni
devies.
II Theoretial Framework
AlNandGaNusuallyhavewurtzitestrutureand
zin-blende struture as well; ZnTe and CdTe have the
zin-blende struture. In the present study we
on-siderthezin-blendephaseforallompoundsand
per-form eletroni struturealulationsby meansof the
abinitiofull-potentiallinearizedaugmentedplane-wave
(FLAPW)method[6,7℄. WeusetheCeperley-Alder[8℄
ofloal-densityapproximation(LDA)forthe
TableI.Calulatedeetiveeletronmasses(m
e
),atCBM,light-hole(m
lh
)andheavy-hole(m
hh
)eetivemasses,
at VBM, along [111℄, [100℄ and [110℄ diretions for the Zn
x Cd
1 x
Te and Al
x Ga
1 x
N alloys (in the unit of free
eletronmassm
o ).
[111℄ [100℄ [110℄
Ligas m e m lh m hh m e m lh m hh m e m lh m hh CdZn (0:0)
Te 0.135 0.106 1.099 0.135 0.137 0.490 0.122 0.101 0.424
Cd
(0:75) Zn
(0:25)
Te 0.142 0.103 1.096 0.142 0.132 0.496 0.130 0.098 0.418
Cd
(0:50) Zn
(0:50)
Te 0.140 0.101 1.058 0.147 0.130 0.464 0.127 0.096 0.414
Cd
(0:25) Zn
(0:75)
Te 0.143 0.100 1.001 0.141 0.132 0.435 0.131 0.096 0.387
Cd
(0:0)
ZnTe 0.129 0.102 0.960 0.129 0.139 0.419 0.148 0.098 0.365
GaAl
(0:0)
N 0.186 0.153 1.895 0.185 0.190 0.848 0.169 0.144 0.738
Ga
(0:75) Al
(0:25)
N 0.223 0.181 2.430 0.223 0.231 1.018 0.201 0.171 0.847
Ga
(0:50) Al
(0:50)
N 0.267 0.285 2.711 0.321 0.284 1.098 0.235 0.294 0.920
Ga
(0:25) Al
(0:75)
N 0.268 0.231 3.752 0.268 0.304 1.287 0.239 0.217 1.117
Ga
(0:0)
Al N 0.305 0.252 4.289 0.306 0.330 1.395 0.271 0.236 1.206
TheGa(3d)-,Zn(3d)-,Cd(4d)-andTe(4d)-eletronsare
treated as partof the valene-band states, sinethey
are relatively high in energy even thoughthey
onsti-tuteawell-loalizednarrowband. InsidethemuÆn-tin
spheres,theangularmomentumexpansionistrunated
at ` =9for the wavefuntions. Weuse the
parame-ter R
mt K
max
= 9whih yields to a set of about 10 4
LAPW basis funtions. The harge density was
self-onsistently determined using 63 k-points in the
irre-duible wedge of the rst Brillouin zone. The total
energyriterionforonvergenewas10 7
Ry.
In order to simulate the ordered alloys with
zin-blende strutureand ompositions x=0.0; 0.25; 0.50;
0.75;1.00,weadoptaveryapproximatemodelbasedon
an eight-atoms superell with ubi symmetry. Large
superells that would be neessary to allow a more
ontinuous variation of the omposition x would be
more omputationally demanding. The alloy
on-sists of a ation sublattie where the metals are
in-terhanged (Ga and Al; Zn and Cd) and of an
an-ion sublattie (N;Te), both originated from the
zin-blende struture. The ubi superells were built by
plaingtheanionsatthepositions(0,0,0),(0,1/2,1/2),
(1/2,0,1/2) and (1/2,1/2,0); Zn(Al) atoms replaing
suessively the Cd(Ga) atoms initially plaed at the
positions (1/4,1/4,1/4), (1/4,3/4,3/4), (3/4,1/4,3/4)
and(3/4,3/4,1/4)simulate theompositionsx =0.25;
0.50;0.75;1.00,respetively. Thelattieparameters,a,
wereoptimizedforeahompositionxbymeansoftotal
energy andfore alulations. The resultswere found
to obeya Vegard-typelaw[9℄. The muÆn-tin sphere
radiiforallatomsweretakenwiththesamevalue0.21
a, sine the use of the full-potential ensures that the
alulation is independent of the hoie of the sphere
III Results and Disussion
We alulate the bottom of the ondution band and
theheavyholeandlightholebandsat21 ~
k-pointswith
j ~
k j ranging from 0:05(2=a) to 0:05(2=a). The
orrespondingeetivemassesanbettedusingE=
h 2 j ~ k 2 =2m
j. The heavy holeand the light hole
ef-fetivemasses,m
hh andm
lh
,andtheeletroneetive
masses,m
e
,werethendeterminedalongthe[111℄,[100℄
and [110℄ diretions, and are shown in Table I.Using
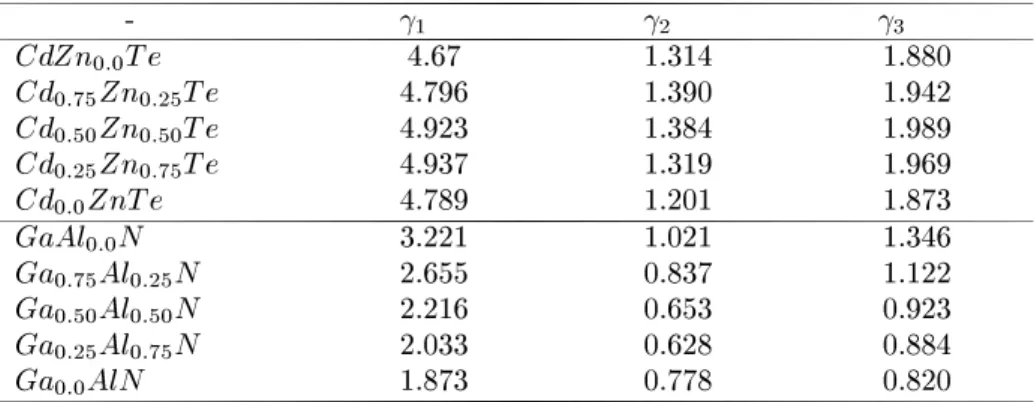
1 =1=2(1=m 100 lh +1=m 100 hh ); 2 =1=4(1=m 100 lh 1=m 100 hh ) and 3 =1=4(1=m 100 lh +1=m 100 hh 2=m 111 hh
weobtainthe
Luttingerparameters[5℄whihareshownin TableII.
IV Disussion
The literature is sare in experimental and
rst-priniples alulatedvalues of the eetivemasses for
the materials studied in this work. There is a broad
general agreement between the results presented here
and those of other alulations. For instane m
e
forGaN is0:17m
o
in ouralulation,0:15m
o
obtained
byeletronspin-resonane experiment[10℄, 0:21m
o by
a rst-priniple pseudopotential alulation [11℄ and
0:13m
o
by an empirial pseudopotential alulation.
Ontheotherhandoureetivemassesalongthe[100℄
diretion for CdTe, m e = 0:13m o , m lh = 0:14m o and m hh =0:42m o
are to be ompared to the values
m e =0:11m o , m lh =0:18m o and m hh =0:60m o ,
ob-tained by empirial pseudopotential alulations [12℄,
while,inpartiular,theheavy-holeeetivemassalong
thegrowth(z)diretionofamultiple-quantum-wellhas
beenassignedvaluesrangingfrom0:4m
o
to0:6m
o [13℄.
Theeetivemassesweobtainforthealloysarealmost
TableII.LuttingerparametersfortheZn
x Cd
1 x
TeandAl
x Ga
1 x
Nalloys.
-
1
2
3
CdZn
0:0
Te 4.67 1.314 1.880
Cd
0:75 Zn
0:25
Te 4.796 1.390 1.942
Cd
0:50 Zn
0:50
Te 4.923 1.384 1.989
Cd
0:25 Zn
0:75
Te 4.937 1.319 1.969
Cd
0:0
ZnTe 4.789 1.201 1.873
GaAl
0:0
N 3.221 1.021 1.346
Ga
0:75 Al
0:25
N 2.655 0.837 1.122
Ga
0:50 Al
0:50
N 2.216 0.653 0.923
Ga
0:25 Al
0:75
N 2.033 0.628 0.884
Ga
0:0
AlN 1.873 0.778 0.820
Aording to our rst-priniples alulations, the
energy dispersion of the lowest ondution band has
some anisotropy for ~
k diretions. On the other hand
the hole masses have non-negligible ~
k-diretional
de-pendene whih is important when designing devies
like laser diodes (LD's). So theLuttinger parameters
i
, in the zin-blende struture, may be very useful
for tehnologialappliations. The eetivemasses of
Ga
1 x Al
x
Nalloysexhibitastrongerdependeneonthe
ompositonthantheCd
1 x Zn
x
Tealloys. Thisbehavior
mayreetthedehibridizationofthed-eletronsofGa
atomwiththetopofvalenebandastheompositionx
inreases. IntheaseoftheCd
1 x Zn
x
Tealloysthe
hi-bridizationoftheCd(4d)-eletronswiththetopofthe
valeneband isontinouslysubstitutedbythe
Zn(3d)-eletrons. Theeetivemasses oftheCd
1 x Zn
x Te
al-loys have an almost linear dependene on x, showing
small bowing fators. The alulated eetivemasses
along the [110℄ diretion are slightly smaller ( 4%)
thanthealulatedmassesalongthe[100℄and[111℄
di-retions,whihareoinident. Thealulatedeetive
masses of the light holes along the[100℄ diretion are
bigger (29%) than thealulatedmasses along the
[111℄and [110℄diretions whih arealmostoinident.
On the other hand the alulated eetive masses of
theheavyholesalongthe[111℄diretionarebigger(
134%)thanthemasses alongthe[100℄and[110℄
dire-tions,whiharealsoalmostoinident.
The eetive masses of the Ga
1 x Al
x
N alloy,
ex-ept for x = 0.5, also have an almost linear behavior
with theompositionx, andexhibit thesamefeatures
as desribed for the Cd
1 x Zn
x Te: m
110
e
is about 5%
smaller than m 110
e
m
111
e . m
100
lh > m
111
lh
m
110
lh ;
m 111
hh >>m
100
hh m
110
hh
. Thelostofsymmetryouring
forx=0.25;0.50or0.75shouldberesponsibleforsome
oftheseutuations. Ontheotherhand,asmentioned
before, these resultsalso depends on thesmall size of
V Conlusions
Wehaveperformedrst-priniplesFLAPWband
alu-lationswithintheLDAforthezin-blendeGa
1 x Al
x N
andCd
1 x Zn
x
Tealloys(x=0.0;0.25;0.50;0.75;1.00).
The eletron eetive mass, hole eetive masses, or
equivalently, the Luttinger parameters, were derived
fromthealulatedbandstruturesneartheCBMand
VBM.Theseresults providethebasis forthestudy of
the eletroni struture and physial properties of
al-loysofvaryingompositions. A moredetailed analysis
ofthestrutural, eletroni andthermodynami
prop-ertiesof thesealloyswillappearsoonelsewhere.
Aknowledgements
Theauthors are thankfulto theBrazilian agenies
CNPq, FAPEMIG and CAPES for nantial support,
andtoCENAPAD-MG-COforomputationalsupport.
Referenes
[1℄ S. Nakamura, and G. Fasol, The Blue Laser Diode,
Springer:Berlin(1997).
[2℄ Y. Wu, B. P. Keller, S. Keller, D. Kapolnek, P.
Kosodoy,S.P.DenbaarsandJ.K.Mishra.Appl.Phys.
Lett.69,1438(1996).
[3℄ R. Dornhaus and G. Nimitz, Narrow-Gap
Semion-dutors,Eds. G.Hohlerand E.A.Nikish(Springer,
Berlin)pp119(1983).
[4℄ J. P. Faurie, J. Reno and M. Boukerhe, J. Crystal
Growth72,111(1985).
[5℄ R.Enderlein,G. M. Sipahi, L. M. R.Solfaro and J.
R.Leite.Phys.Stat.Sol(b)206,623(1998).
[6℄ E.Wimmer,H.Krakauer,M.WeinertandA.J.
Free-man,Phys.Rev.B24,864(1981).
[7℄ X.Zhun,S.B.Zhang,S.G.Louie,andM.L.Cohen,Phys.
Rev.Lett.63,2112(1989).
[9℄ A. B. Chen and A. Sher,"Semiondutor Alloys:
Physis and Materials Engineering". Plenum Press
(1996).
[10℄ M.Faniulli,T.Lei,andT.D.Moustakas,Phys.Rev.
BB48,15144(1993).
[11℄ K. Miwa and A. Fukumoto, Phys. Rev. B48,
7897(1993).
[12℄ W. J.Fan, M. F.Li, T. C.Chong, and J.B. Xia,J.
Appl.Phys.79,188(1996).
[13℄ F. Long,P.Harrison, W.E. Hagston, J.Appl. Phys.