Hot-Spots in Plasma-Fous Disharges as Intense
Soures of Dierent Radiation Pulses
L.Jakubowskiand M.J. Sadowski
TheAndrzejSoltanInstitute forNulearStudies
05-400Otwok-Swierk byWarsaw,Poland.
Reeivedon26June,2001
ThepaperonernspulseddishargesofthePlasma-Fous(PF)type,andinpartiularthe
forma-tionofmiro-regions(so-alledhotspots)withveryhigheletrononentrationandrelativelyhigh
eletrontemperature. PartiularattentionispaidtotheorrelationbetweenX-raypulsesemitted
fromthehotspotsandtheemissionofpulsedeletronbeams,ionbeams,andthepulsedneutron
uxes.
I Introdution
It is well known that a urrent sheath layer, whih is
formed by a high-urrent disharge within a
Plasma-Fous(PF) system,undergoesrst theaxial
aelera-tion,andafterreahingtheeletrodeendsitissubjet
to the radialollapse [1-3℄. This proess leadsto the
formation of the dense magnetized plasmaolumn on
the z-axis. In suh a olumn there appear
magneto-hydrodynami(m =0)instabilities,whihprodue
lo-al plasmaregionsofsmalldimensions(oftheorderof
severalor dozen mirometers), but with high eletron
onentrations (10 20
10 21
m 3
) and relatively high
eletron temperatures (0.5 - 5 keV) [4℄. Suh plasma
miro-regions, so-alled \hot spots", are well visible
partiularly in PF disharges performed within a
hy-drogen (ordeuterium) mixture withsomeheavygases
(e.g. argon). The hot spots are identied as soures
of intense X-ray emission as well as pulsed
eletron-andion-beams[5℄. IfthePFdishargesarearriedout
within puredeuterium,as aresultofnulearfusion
D-Dreations,thereareemittedalsoneutronpulseswith
thetotalyield,whihisameasureofthePFdisharge
quality. Themainaimofthispaperwastostudya
or-relation between the appearane of hot spots and the
emission of dierent radiation pulses. The desribed
experimentswerearriedoutwithintheMAJA-PF
de-vie [4-5℄,operatedatIPJin Swierk,Poland.
II Experimental setup
The MAJA-PFfaility was equippedwith twooaxial
eletrodesoftheMathertype. Theseeletrodesare72
eletrodes are 300 mm in length. The front plate of
theinnereletrodehasaentral10-mm-diameterhole,
whih is used for the observation of pulsed eletron
beams emitted in the upstream diretion. The
ele-trodesystemissuppliedfromaondenserbank,whih
isusuallyoperatedat45kJbytheinitialhargingupto
35kV. Atthis operationalvoltage, themaximum
dis-harge urrent amounts to about 500 kA. During the
PFexperimentsdesribedinthispaperthe
experimen-talhamberoftheMAJA-PFdeviewaslledupwith
puredeuterium oramixture ofdeuterium and(up to
20%)argon.
III Experimental studies
During numerous PF disharges performed within
the MAJA-PF faility, there were performed
time-integrated and time-resolved measurements of
X-rays, fast eletrons, and aelerated ions, and
fusion-produedneutrons.
III.1Time-integrated observationsof hot
spots
Aording to the known proess, after the
appli-ation of high voltage between the eletrodes a
dis-tintplasmalayer(so-alledurrentsheath)wasformed
upontheinsulatorsurfae,anditwasaeleratedinthe
axial diretion by the interation of quasi-radial
ur-rentsandtheazimuthalmagnetield. Whenthis
ur-rentsheathreahedtheeletrodeendsitwasdeformed,
and after that it was subjet to the radial ollapse.
Atthez-axistherewasformed adenseplasmaolumn
miro-Figure1. X-raypinholeimagesfromdierentdishargesperformedintheMAJA-PFfaility.
Suh images were registeredby meansof anX-ray
pinholeameraequippedwitha100-m-diameter
open-ing,whihwasoveredwitha12-m-thikBe-foil. To
redue the absorption of soft X-rays, the amera
vol-ume (ontainingan X-raylm) waspumped outwith
an auxiliarypumping-stand (Fig.1a). It wasobserved
that thehotspotsareformed rst inproximityofthe
eletrode outlets. They have form of bright
miro-regionssurroundedbylowertemperatureplasma. The
appliation ofanadditionalabsorptionlter, e.g. a
5-m-thiklayerofairunderatmospheripressure,
elimi-natesX-raysfromthislowertemperatureplasma. This
tehniqueenables theregistration of the most intense
soures, emitting X-rays of energy above 5 keV, as
showninFig.1b. Itshouldbenotedthatduringasingle
PFdishargeseveralormore(evenadozen) hotspots
are formed mostly at the z-axis, although sometimes
theyappearalso otheaxis(see Fig. 1). Onthe
ba-sis ofthe earlierstudies [6℄,it wasfound that the hot
spotsareformedsuessively,startingat theeletrode
endsandmovingastheurrentsheathollapsesatthe
z-axis. Theregionofthemaximumompressionmoves
alongthisaxis(withanaverageveloityequaltoabout
3:10 7
m/s). Lifetimesofindividual hotspots amount
to about 10 ns, and thehot spot population exits for
about100ns,ountingfromthemomentwhenthe
ol-lapsingurrentsheathreahesthez-axis. OtherX-ray
pinhole images,whih showtheformationand motion
ofdistinthotspots, arepresentedin Fig. 2.
In some ases there appear many hot spots
loal-ized losely eah other within the PF pinh olumn,
asshown inFig. 2a. Sometimes, oneanalso observe
thebrightplasmaobjetsmovingnearbythez-axis(see
Fig. 2b). Thedesribedimages anbeinterpreted as
examplesofhotspotsmotion. Takingintoaount
life-timesofthesehotspotsandtheirspatialdisplaement,
oneanestimatethattheirveloitieswereoftheorder
of5:10 7
m/s. Inotherwords,itwasthephaseveloity
of the displaement of the maximum plasma
onen-tration. It should benotedthat spatial displaements
ofthe hotspots havebeen onrmedbysome
inlina-rystal spetrometers. Those inlinations ould result
fromthehotspotdisplaemento thez-axisandfrom
theDopplereet induedbythemovingobjet. This
questionrequiresmoredetailed investigations.
Figure2. Examplesofx-raypinholeimagesshowinga
dis-plaementofthedistinthotspots.
III.2 Spae-resolved x-ray spetra
Thehigh-temperatureplasmaproduedbyPF
dis-harges, performed with a deuterium-argon lling,
emits intense X-raypulses. Inorder todetermine
val-uesofeletrontemperatureandonentration,onean
useharateristiX-rayspetrallinesorrespondingto
highlyionizedargonions. Intheexperimentswithinthe
MAJA-PFfailitytheuse wasmadeofaJohann-type
spetrometer,whih wasequippedwith aquartz
rys-tal bent ylindrially. This X-ray spetrometer made
possible theregistration of spetral lines in the range
from3.8Ato4.2
A.Theoptialaxisoftherystalwas
perpendiularto thePFpinh olumn. Toobserve
X-rayspetrallinesfromindividualhotspotsdistributed
alongthez-axis,theusewasmadeofanadditionalslit
of 600 m in width, whih was plaedin frontof the
spetrometer. This slit ensured a satisfatory spatial
resolution to registerX-ray spetrafrom the separate
hotspots. ThesespetrawereomparedwiththeX-ray
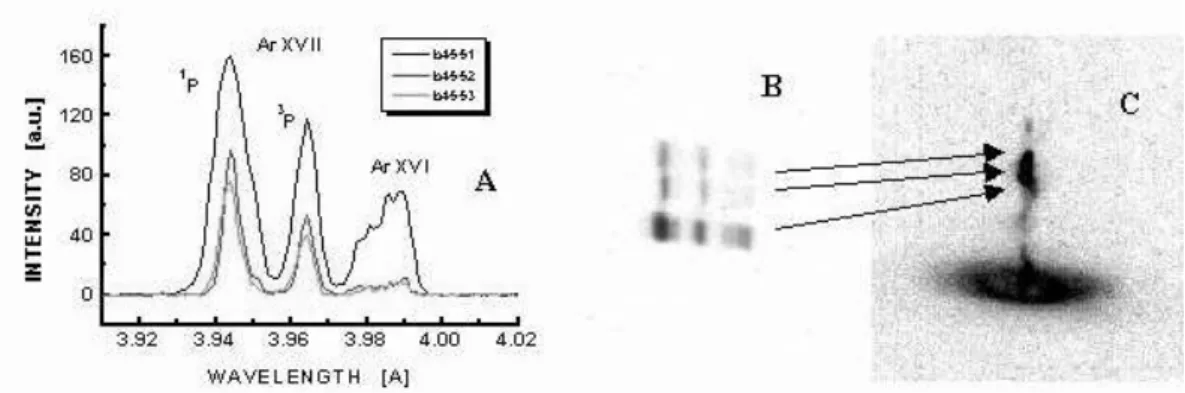
Figure 3. X-ray lines intensities (A)and orrespondingX-ray spetra (B), as obtainedfrom highly ionizedargon-ions, in
aomparison withthe X-raypinholepiture (C),whihshows thespatialdistributionofhot spotsintheinvestigatedPF
disharge.
Table1: Resultsofthespetralmeasurements.
Spetrum
number I
R I
I I
S n
e [m
3
℄ T
e [eV℄
45-51 195.0 137.7 89.9 3
10 20
255
45-52 109.8 60.0 13.9 1:6
10 21
790
45-53 86.1 52.9 12.9 1:0
10 21
650
The spae-resolved X-ray spetra (shown in
Fig.3a,b) originated from dierent hot spots formed
along the disharge axis. The omparison of those
spetra with the orresponding X-ray pinhole piture
(Fig. 3) onrmed that they were evidently emitted
from dierenthotspots. Thedesribed measurements
showed that the most intense were helium-like argon
lines, and in partiulartheresonaneline ArXVII-1
P,
theinterombinationline ArXVII-3
P,andsatellitelines
ArXVI,aspresentedinTable1.
Thevaluesoftheeletrononentrationn
e
were
es-timatedonthebasisoftheI
R /I
I
ratio[7℄observedfor
individual hot spots. Theobtained valueswere
dier-ent,as shown inTable1,buttheyhangedwithin the
rangeof10 20
10 21
m 3
. Itshouldbenotedthatthese
valueswerealulatedunderassumptionthateletrons
havetheMaxwelliandistribution funtion. Therefore,
theresultsmustbetreatedasapproximateones.In
or-dertodeterminetheseparameterswithbetterauray,
oneneeddataaboutdiretedeletronbeamsandtheir
inueneonthepopulationofdierentenergylevelsin
the argon ions. The values of the eletron
tempera-tureT
e
werealulatedfrom theratioof satellitelines
ArXVIandtheresonaneline ArXVII-1
Pforindividual
hotspots. Theresultspresentedin Table1showthat
hotspots (formed within the samePF disharge)an
havedierenteletrontemperatures(200 -700eV).It
shouldbenotedthat suh eletrononentration-and
temperature-valueswere determinedfor manyPF
dis-hargesandnumeroushotspots. Onthebasisofa
om-parativeanalysis ofsubsequenthotspotsit wasfound
[4℄thattheformationofthehotspotshasastohasti
harater. Theloationsaswellastheeletron
onen-trationandtemperaturevaluesseemtobeindependent
of neighboring hot spots. A ompletely dierent
on-lusionwasobtained when then
e and T
e
valueswere
omparedasafuntionofadistanefromtheeletrode
outlet,asshowninFig. 4.
Figure4. Eletrononentration n
e
andeletrontemperatureT
e
spot. The above interpretation does not refer to all
the ases beause there appear dierent loal
ondi-tions (e.g. strong eletrial and magneti elds), but
thisquestionrequiresmoredetailed investigations.
III.3 Studies of pulsed eletron beams
The appearane of loal strong eletromagneti
eldswithinthePFpinholumn(i.e. insideornearby
thehotspots)wasonrmedbyobservationsofintense
eletronbeams,emittedmainlyin theupstream
dire-tion (towards the anode). The earlier experimental
studies [9℄ showed the emission of X-ray pulses from
theobservedhotspotsisaompaniedbytheemission
ofpulsedeletronbeamswitharelativelywideenergy
spetrum. Thesephenomenawerealsoanalyzedonthe
basisofatheoretialmodelassumingthegenerationof
so-alled\runaway"(fast)eletrons. Themodel
om-putations were performed for the experimental
ondi-tionsourringin theMAJA-PFfaility,and their
re-sults were in agreementwith theobserved emissionof
pulsedeletronbeams[10℄. Experimentalstudiesofthe
fasteletronbeamsin theMAJA-PFdevie were
ar-riedoutbymeansofCerenkov-typedetetors
ontain-ingtheradiatorsmadeofquartzorrutilrystals. These
partiular materials were applied beause oftheir low
energythreshold(equaltoabout50keV).Itwasfound
that the fast eletron pulses an last about 7-10 ns,
and thenumberofsuhpulses dependson anamount
oftheappearinghotspots. Theemissionoftheeletron
pulses wasobserved during about 100ns. Inorder to
investigatean energy distributionof the emitted
ele-Time-resolvedmeasurementsofeletronpulseswere
performed by means of miniature sintillation
dete-tors, whih werexedupon thedetetionplaneof the
same magneti analyzer. It made possible to observe
temporal hanges of the eletron emission in the
se-leted energy ranges. A omparison of the registered
eletron signalsonrmed that individual pulsed
ele-tronbeamsareemittedfromdierenthotspots,whih
are formedwith sometimedelays. Detailed
investiga-tions of energy spetra of the pulsed eletron beams,
emittedfromdierenthotspots, haveshownthat:
1. The eletron energy spetra from the PF
dis-harges, whih were arried outwith pure deuterium,
haveextendedoverarelativelywiderangefrom about
10keVtoabout600keV.Onontrary,thespetra
reg-isteredforPFshotsperformedwithanargonadmixture
(up to 20%) have been limited to arelatively narrow
energyband.
2. Energyranges of the eletron beams from
dif-ferent hot spots have varied from shot to shot under
the sameexperimental onditions. An example of
os-illograms,whihwereregisteredfortwosuessivePF
dishargeswithintheMAJA-PFfaility,ispresentedin
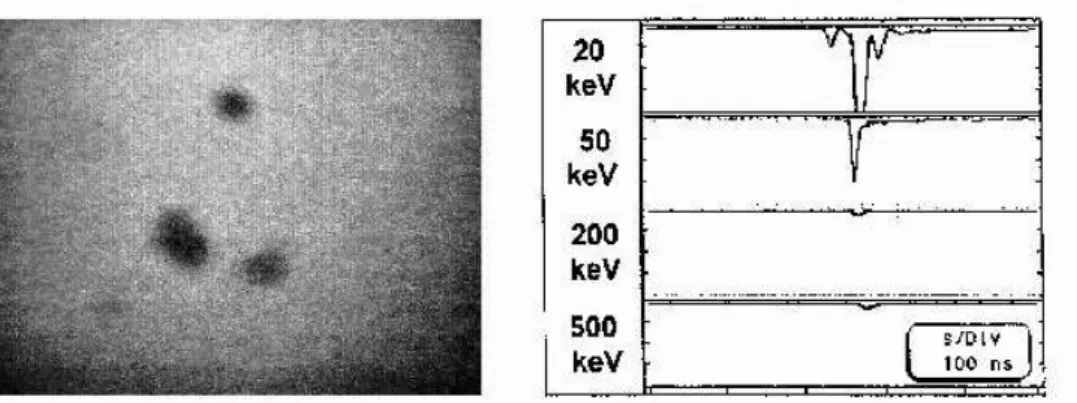
Fig. 5.
Duringtherstshottherewereemittedeletronsof
energy200-500keV,whileduringtheseondshot
(per-formedat thesameonditions)onlylowenergy(20-50
keV)eletronswereobserved. It shouldbenotedthat
inthebothasesthetime-integratedX-raypinhole
im-ageswereverysimilar.
Figure5. Comparisonofeletronpulses,emittedfromtwosuessivePFshotswithin theMAJA-PFfailityandmeasured
3. Oneouldsuspetthatthepulsedeletronbeams
emittedfrom thehotspots, whih wereformed within
the PF disharges with the deuterium-argon mixture,
havehaddierentenergyharateristisindependene
on theplae and time of theirgeneration. Ingeneral,
thehotspots,whihwereformedlater(atalarger
dis-tane from the anode end), have emittedthe eletron
beamsof higherenergy,asshowninFig. 6.
Figure 6. Inrease inenergyof thepulsedeletron beams
emitted by the hot spots, whih wereformed suessively
duringthePFdishargewithintheMAJA-PFdevie.
III.4 Studies of pulsed ion beams
Inorder to investigatethe orrelationbetween the
formation of thehot spots and thepulsed emissionof
ionstreams,theusewasmadeofanionpinholeamera
equipped with solid-state nulear trak detetors [11℄.
This amerawasadjustedalong thez-axis,and its
in-letdiaphragmwasplaedatadistaneof280mmfrom
the inner eletrode (anode)end plate. An analysis of
theirradiated and ethed detetors made possiblethe
investigation of aspatialdistribution oftheregistered
ionbeams,andthedeterminationofabsolutevaluesof
theion uxes. Examples of theion images and
orre-spondingeletron-induedsignals,whihwereobtained
fromasinglePFdishargeintheMAJA-PFfaility,are
presentedin Fig.7.
Onthebasisofaomparisonoftheionpinhole
im-ages(registered along thez-axis) and the
orrespond-ing eletronsignals (registered in theupstream
dire-tion) one ould suspet the simultaneous emission of
the investigated ions and fast eletrons [11℄.
Consid-eringthe experimental results presented in Fig. 7, it
seemsreasonableto assumethatthepulsedionbeams
areemittedfromdierentminiatureionsoures,whih
aredistributedalongthePFpinholumn andanbe
identiedwithsuessivehotspots.
From the detailed analysis of the ion pinhole
pi-tures, whih were taken for the investigated PF
dis-hargesperformedwithintheMAJA-PFfaility,itwas
estimated that the total ion ux amounted to about
10 12
deuterons/stereo-radian. It should also benoted
thatreentlysomeeortshavebeenundertakento
an-alyzetheorrelationofthehotspotswiththeemission
of fast neutrons (produed by D-D fusion reations).
For this purpose a neutron sintillation detetor has
beenplaednearbytheMAJA-PFexperimental
ham-ber,andneutron-induedsignalshavebeentransmitted
toafastphoto-multiplier(through anappropriate
op-tial able). Theexperimental resultsobtained sofar
haveappearedtobediÆultfortheinterpretation,
be-auseneutronssatteredfromthelaboratorywallsand
equipmentdisturbtheregisteredsignals. Somespeial
measureshavetobeundertakentoperformthestudies
inquestion.
Figure7. Ionpinholeimage,whihshowsthetraksproduedbythepulsedionbeams,andtheosillogramofthe
eletron-beamsignals,whihwereregisteredduringthesamePFdishargewithintheMAJA-PFdevie.
IV Summary and onlusions
The mostimportant resultsof theexperimental
inves-follows:
whihwereemittedfromdierenthotspots.
4. Alsomeasuredwereion(deuteron) beams
emit-ted along the z-axis, and registered by means of
CN-typetrakdetetors. Dierentgroupsoftheiontraks,
asobtainedafter theething of theirradiated CN
de-tetors,wereidentiedwithdierenthotspots. An
op-tial analysis of the registered ion traks enabled ion
uxes (of about 10 12
deuterons/stereo-radian) to be
measured.
Reently, someeortshavebeenundertakento
in-vestigatetimeorrelationoffastneutronpulses,whih
originatefromD-Dfusionreationsourringinsideor
nearbydierenthotspots. Suhmeasurementsrequire
moredetailedstudies,beausedisturbanesinduedby
satteredneutronsmustbeeliminated.
Beams(Haifa,1998),Pt.2,p.615.
[6℄ L. Jakubowski, and M. Sadowski, Pro. 22nd EPS
Conf.CF&PP (Bournemouth,1995),Pt.2,p.181.
[7℄ A.V. Vinogradov, et al., Kvantovaya eletronika (in
Russian)2,1165(1975).
[8℄ E.V. Aglikiy, etal., Kvantovayaeletronika(in
Rus-sian)1,579(1974).
[9℄ L. Jakubowski, and M. Sadowski, Pro. 1996 Intern.
Conf.onPlasmaPhys.(Nagoya,1996),Pt.2,p.1326.
[10℄ L.Jakubowski,M.Sadowski,E.O.Baronova,andV.V.
Vikhrev, Pro. 4th Intern. Conf. onDense Z-Pinhes
(Vanouver,1997),p.443.
[11℄ L.Jakubowski,M.Sadowski,andJ.Zebrowski.,Pro.
18thFusionEnergyConferene (Sorrento, 2000);