SOCIEDADE BRASILEIRA DE ORTOPEDIA E TRAUMATOLOGIA
w w w . r b o . o r g . b r
Original
Article
Reliability
of
the
radiographic
union
scale
in
tibial
fractures
(RUST)
夽
Fernando
Antonio
Silva
de
Azevedo
Filho
a,b,∗,
Ricardo
Britto
Cotias
a,
Matheus
Lemos
Azi
b,
Armando
Augusto
de
Almeida
Teixeira
aaHospitaldoSubúrbio,Salvador,BA,Brazil
bHospitalManoelVictorino,Salvador,BA,Brazil
a
r
t
i
c
l
e
i
n
f
o
Articlehistory: Received13April2016 Accepted3May2016
Availableonline15December2016
Keywords: Tibia
Fracturehealing Radiography
a
b
s
t
r
a
c
t
Objective:Thisstudyaimedtoevaluatetheinter-andintraobserverreproducibilityofthe radiographicscoreofconsolidationofthetibiashaftfractures.
Methods:Fifty-onesetsofradiographsinanteroposterior(AP)andprofile(P)ofthetibial shafttreatedwithintramedullarynailwereobtained.TheanalysisofX-rayswasperformed
intwostages,witha21-dayintervalbetweenassessmentsbyagroupofnineevaluators. ToevaluatethereproducibilityofRUSTscorebetweentheevaluators,theintra-class corre-lationcoefficient(ICC)witha95%confidenceintervalwasused.ICCvaluesrangefrom+1, representingperfectagreement,to−1,completedisagreement.
Results:Therewasasignificantcorrelationamongallevaluators:ICC=0.87(95%CI0.81to 0.91).TheintraobserveragreementprovedtobesubstantialwithICC=0.88(95%CI0.85to 0.91).
Conclusion: ThisstudyconfirmsthattheRUSTscaleshowsahighdegreeofreliabilityand agreement.
©2016SociedadeBrasileiradeOrtopediaeTraumatologia.PublishedbyElsevierEditora Ltda.ThisisanopenaccessarticleundertheCCBY-NC-NDlicense(http:// creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Reprodutibilidade
do
escore
radiográfico
de
consolidac¸ão
das
fraturas
da
tíbia
(RUST)
Palavras-chave: Tíbia
Consolidac¸ãodafratura Radiografia
r
e
s
u
m
o
Objetivo:Avaliar a reprodutibilidade inter e intraobservador do escore radiográfico de consolidac¸ãodasfraturas(RUST)dadiáfisedatíbia.
Métodos:Foramobtidos51conjuntosderadiografiasnasincidênciasanteroposterior(AP)e perfil(P)dadiáfisedatíbiatratadascomhasteintramedular.Aanálisedasradiografiasfoi feitaemdoismomentos,comintervalode21diasentreasavaliac¸ões,pornoveavaliadores.
夽
StudyconductedatHospitaldoSubúrbio,Salvador,BA,Brazil.
∗ Correspondingauthor.
E-mail:azevedofilho@gmail.com(F.A.AzevedoFilho). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rboe.2016.05.006
ParaavaliarareprodutibilidadedoescoreRUSTentreosavaliadoresfoiusadoocoeficiente decorrelac¸ãointraclasse(CCI)comintervalodeconfianc¸ade95%.OvalordoCCIvariade
+1,querepresentaconcordânciaperfeita,a−1,quecorrespondeatotaldiscordância. Resultados: Houveumaconcordânciasignificativaentretodososavaliadores:CCI=0,87(IC 95%0,81a0,91).Aconcordânciaintraobservadormostrou-sesubstancial,comCCI=0,88(IC 95%0,85a0,91).
Conclusão: EstetrabalhoconfirmaqueaescalaRUSTapresentaumelevadograude confia-bilidadeeconcordância.
©2016SociedadeBrasileiradeOrtopediaeTraumatologia.PublicadoporElsevier EditoraLtda.Este ´eumartigoOpenAccesssobumalicenc¸aCCBY-NC-ND(http:// creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Introduction
Tibialshaftfractureisthemostcommonamongthoseoflong bones;ithasahighincidenceandmainlyaffectsyoungmales ofworkingage.Theseinjuriesresultfromhigh-energykinetic trauma,suchasfallfromheightandcaraccidents;thelatter areamajorcauseoffracturesandleadtodisability,withhigh socioeconomiccosts.1–6
Theuseofreamedlockedintramedullarynailsforthe inter-nalfixationinthe treatmentoftibiashaftfracturesiswell establishedin the literature.2 Despite advances in surgical techniques,localanatomicalconditionsmaycontributetothe onset ofcomplications, such asdelayed consolidationand pseudoarthrosis.7,8
Theincidence ofpseudoarthrosis after internalfixation withintramedullarynailhasbeenreportedintheliterature asrangingfrom5%to33%,whichoftenresultsintheneedfor secondaryinterventionoradditionaltreatmenttostimulate boneunion.2,3,9,10
Bone consolidation process is a simple biological phe-nomenon that occurs in stages: hematoma, inflammation, angiogenesis, cartilage formation (with subsequent calcifi-cation, cartilage removal, and then bone formation), and boneremodeling.Completefracturehealingmaytakeseveral months,andonlyoccursafterthecompletionofallstages.2,4,11 Fromaclinical standpoint,afracture canbeconsidered consolidatedattheendoftherepairphase.Thecriteriaused forthisdefinitioncanbesubdividedintoclinicalexamination data(e.g.,weightbearingwithoutlocalpainandlackof mobil-ityatthefracturesite)andpatient-relatedfactors(qualityof life).4,7,12,13
Corralesetal.,13inareviewof77clinicalstudiesthatused clinicalcriteriatodefinetheconsolidationoflongbone frac-tures,foundthatthethreemostcommonlyusedcriteriawere absenceofpainortendernesswithweightbearing,absenceof painortendernessatthefracturesiteduringtheexamination. Fortheradiologicalevaluationoffractures,plain radiogra-phyremainsthemostcommonmethodtoassess healing.7 Someauthorssuggestasacriteriontodeterminefracture con-solidationthepresenceofatleastthreeconsolidatedcortices observedintworadiographicviews(anteroposterior[AP]and lateral[L]).14
Panjabietal.,15 inanexperimentalstudy,demonstrated that cortical continuity was the best predictor of fracture healing,whilecallusareawastheleastimportantpredictor.
McClellandetal.,15 whenstudyingpatientswithtibial frac-tures treated with external fixation, observed a moderate correlationbetweenradiographichealingandstiffnessatthe fracture site.These authorssuggestedthatthe presenceof bonecallusintwocorticeswasthebestindicatortoconsider afractureashealed.
Variousscalesand classificationshavebeenproposedto define fracture consolidation, withacombination of radio-graphiccriteria.5,7,9,10,16
Kooistra et al.2 recommendthe use oftheRadiographic UnionScaleforTibialFractures(RUST)forassessing consol-idation.Thismethodevaluatestwoorthogonalradiographic views;eachcortexisattributedpointsrangingfrom1to3.A fractureintheimmediatepostoperativeperiodwillreceivethe minimumscore,4,andafullyconsolidatedconsidered frac-turewillbeassignedthemaximumscore,12.Studiesshow thatRUSTisasimple,systematic,andcontinuousindicatorin theevaluationoftibialfracturestreatedwithintramedullary nail.2
Thisstudyaimedtoevaluatetheinter-andintraobserver reproducibility of the RUST scale in patients treated with reamedlockedintramedullarynail.
Material
and
methods
Aretrospectivestudywasconductedtoevaluatetheintra-and interobserverreproducibilityoftheRUSTscale.
Thestudyincludedradiographsofpatientswithfractures ofthetibialshafttreatedwithreamedlockedintramedullary nail,agedover16years,ofbothsexes;theexamshadgood technicalquality,andweremadeduringthefollow-upperiod (eightweekstoninemonths)inAPandL.Patientswith patho-logical fractures,who presentedinfection or consolidation delay,orwho evolvedtopseudarthrosisandneededanew procedurewereexcluded.
A total of77 sets of APand L radiographs ofthe tibial shaftofoutpatientstreatedwithintramedullarynailsin2014 wereretrieved;51setsmetallinclusioncriteria.Examswere selectedfromtheelectronichospitalrecords,invariousstages ofconsolidation.
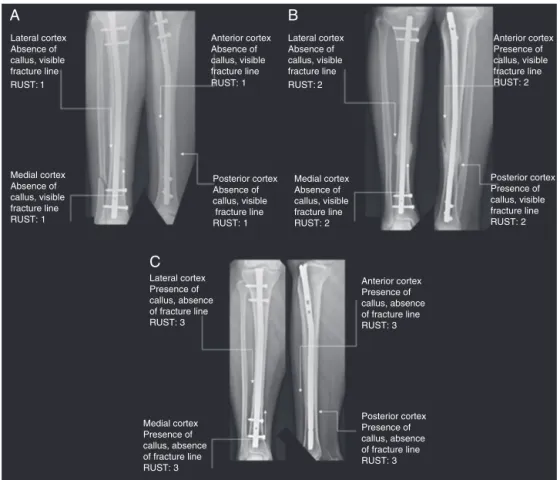
Table1–Radiographicscaleoftibialfractureconsolidation.
Cortex Visiblefractureline,
withoutcallus Score=1
Visiblefractureline, withcallus
Score=2
Nofractureline, withvisiblecallus
Score=3
Totalscore
Minimum4
Maximum12
Lateral Medial Anterior Posterior
Images were simultaneously presentedto all evaluators in
an air-conditioned environment using Sony VPL-DX130B®
image projector. Radiographs in AP and L of each patient
were projected simultaneously, with one minute for each
evaluation.
TheRUSTscaleassignsascoreforagivensetofAPand
Lradiographs,basedontheassessmentofhealingineachof
thefourcorticesvisibleontheseprojections(medialand
lat-eralcorticesinAP,andanteriorandposteriorcorticesinL).
Eachcortexisassigned1pointifafracturelinewithoutthe
presenceofcallusisobserved;2,ifthereiscallus,buta
frac-turelineisstillvisible;and3,ifthereiscalluswithnoevidence
offractureline(Table1).
The scores on each cortex are added, resulting in a total valuefor each set of radiographs; 4 isthe minimum score, indicative that the fracture is not healed and 12 is themaximumscore,indicatingthatthefracturecompletely cured.2,10,17Ascore≥7isequivalenttoaminimumofthree
corticeswithbonecallus.Afracturewiththisscorecanbe consideredasradiologicallyconsolidated17(Fig.1).
Theexaminersdidnothaveaccesstopatienthistory,age, fracturetime,andanyotherclinicalinformation.Radiographs wereidentifiedbynumbersandonlythemainresearcherhad accesstothisidentification.
Theinterobserverreproducibilitywasassessedby compar-ing thetotalscoresofeachobserver obtainedintheinitial visualization of the radiographs. The intraobserver repro-ducibilitywasdeterminedbythecomparisonofthescoresof thefirstandsecondevaluationbyeachparticipant.
ToevaluatethereproducibilityoftheRUSTscoreamong raters, the intraclasscorrelation coefficient (ICC) was used witha95%confidenceinterval.ICCvaluesrangefrom+1, rep-resentingperfectagreement,to−1,completedisagreement.
ThestudywasapprovedbytheResearchEthicsCommittee oftheHealthSecretariat oftheStateofBahia,OpinionNo. 788,655.
Lateral cortex Absence of callus, visible fracture line RUST: 1
Lateral cortex Absence of callus, visible fracture line RUST: 2
Medial cortex Absence of callus, visible fracture line RUST: 1
Anterior cortex Absence of callus, visible fracture line RUST: 1
Posterior cortex Absence of callus, visible fracture line RUST: 1
Lateral cortex Presence of callus, absence of fracture line RUST: 3
Anterior cortex Presence of callus, absence of fracture line RUST: 3
Medial cortex Presence of callus, absence of fracture line RUST: 3
Posterior cortex Presence of callus, absence of fracture line RUST: 3 Medial cortex Absence of callus, visible fracture line RUST: 2
Anterior cortex Presence of callus, visible fracture line RUST: 2
Posterior cortex Presence of callus, visible fracture line RUST: 2
B
A
C
20
15
10
%
5
0
7 6 5
4 8
RUST score
1st assessment 2nd assessment 10
9 11 12
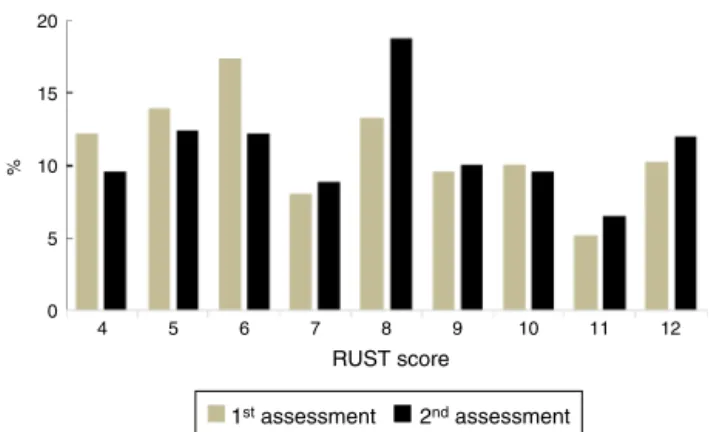
Fig.2–DistributionoftheRUSTscoreinthe1stand2nd assessment.
Table2–RUSTscoreinter-andintra-observerinterclass correlationcoefficient.
Inter-observerICC
95%CI
Intra-observerICC
95%CI
Traumatologists 0.94(0.90–0.96) 0.94(0.91–0.95)
3rdyear-resident 0.90(0.84–0.94) 0.83(0.71–0.90)
2ndyear-resident 0.92(0.87–0.95) 0.89(0.84–0.93)
1styear-resident 0.80(0.67–0.88) 0.87(0.79–0.90)
General 0.87(0.81–0.91) 0.89(0.85–0.91)
Results
The RUST score of the 51 sets of radiographs (AP and L)
rangedfrom4to12,withascoreof7.53± 2.53(median7)in
thefirstassessmentand7.88±2.49(median8)inthesecond
(Figs.2and3).
Therewasasignificantcorrelationamongtheevaluators, with ICC of 0.87 (95% CI: 0.81–0.91). Among traumatolo-gists,therewasgreaterreliabilitywhencomparedwithfirst-, second-,and third-yearresidents (ICC: 0.94,0.80,0.92,and 0.90,respectively;Table2).
12
11
10
9
8
RUST
7
6
5
4
a1 a2 a3 a4 a5 a6 a7 a8 a9
Fig.3–ComparisonofthemeanRUSTscoreamong evaluators.
a1,a2,a3;traumatologists;a4,a5,third-yearresidents;a6, a7,second-yearresidents;a8,a9,first-yearresidents.
Intraobserveragreementwassubstantial,withICCof0.88 (95%CI:0.85–0.91).Byanalyzingtheevaluatorsaccordingto thedegreeoftraining,itwasobservedthattraumatologists showedanear-perfectreproducibility(ICC0.94;95%CI0.91 to0.95).Amongtheresidents,thehighestICCwasobserved forsecond-yearresidents(ICC0.89),followedbyfirst-year(ICC 0.87)andfinallythird-year(ICC0.83;Table2).
Discussion
Despitethenumerousstudiesrelatedtothedevelopmentof scalestoassesstheradiographicconsolidationoftibial frac-tures,areliableandeffectivemethod,agoldstandard,isnot yetestablishedintheliterature.18,19
The definition of radiological union isinconsistent due tothedegreeofimprecisionoftheselectedvariables.Some investigationsuseasingleparameter,suchasthepresenceof callusinatleasttwocortices.5
Several variables are observedwhen analyzing the evo-lutionoffracturehealing,includingnumberofconsolidated cortices and presenceof bonecallus and fracture line.17,18 Basedontheseparameters,Kooistraetal.2developeda radio-graphic scaletodetermine theconsolidationoftibialshaft fractures, the RUST scale. Using the presence of callus in eachcortex,associatedwiththepresenceofafractureline, the hypothesis that the RUST scale would present greater validity and reliability than other proposed systems was raised.
TheRUSTscale assessesthefracture unequivocally and completely.Itpresentssomeadvantageswhencomparedwith other methods,amongwhichstandsoutthe factthateach cortexisevaluatedseparately,makingthescalemorereliable, sinceeachindividualcortexcontributestothefinalscore.This classificationiseasytoapply,withhighinter- and intraob-serveragreement.2,10,17–19
Whelanetal.10 assessedthe reproducibilityoftheRUST scale when using radiographs of 45 patients treated with locked intramedullary nails. They observed a correlation among all evaluators (ICC: 0.86,95% CI: 0.79 to0.91), with a trendtoward greater reliabilityfor traumatologistswhen comparedwithorthopedicsurgeonsand residents,aresult similar to thatfound inthe present study.Ali et al.18 cor-roborated these results when assessing the reproducibility betweenorthopedicsurgeonsandradiologists.When evalu-atingradiographswithconservativetreatmentforfractures ofthetibia,theyobservedasignificantinterobserver correla-tionship.Macrietal.17observedaninterobserveragreement, assessedbyICC,of0.93(95%CI:0.89to0.96).
Theabilitytobearweightonthefracturedlimbisdirectly related tothe bone consolidationphase. Thisinability can causechangesingait;therefore,gaitpatternmaybea prac-ticalwayofmonitoringfracturehealing.Astrongassociation betweengaitpatternandRUSTscorehasbeenobserved.17
Conclusion
ThepresentstudyconfirmedthattheRUSTscorefeaturesa highdegreeofreliabilityandcompliance.Asthereisnogold standardradiographicclassificationtoevaluatethe healing oftibialfractures,theauthors suggest thatthis isauseful functionaltool,butmoreresearchrelatingtheradiographic findingsonclinicalexaminationisneededtoestablishitas anessentialtoolindailypractice.
Conflicts
of
interest
Theauthorsdeclarenoconflictsofinterest.
r
e
f
e
r
e
n
c
e
s
1. Court-BrownCM,RimmerS,PrakashU,McQueenMM.The epidemiologyofopenlongbonefractures.Injury.
1998;29(7):529–34.
2. KooistraBW,DijkmanBG,BusseJW,SpragueS,Schemitsch EH,BhandariM.Theradiographicunionscaleintibial fractures:reliabilityandvalidity.JOrthopTrauma.2010;24 Suppl.3:S81–6.
3. ChuaW,MurphyD,SiowW,KagdaF,ThambiahJ. Epidemiologicalanalysisofoutcomesin323opentibial diaphysealfractures:anine-yearexperience.SingaporeMed J.2012;53(6):385–9.
4. KojimaKE,FerreiraRV.Fraturasdadiáfisedatíbia.RevBras Ortop.2011;46(2):130–5.
5. WhelanDB,BhandariM,McKeeMD,GuyattGH,KrederHJ, StephenD,etal.Interobserverandintraobservervariationin theassessmentofthehealingoftibialfracturesafter intramedullaryfixation.JBoneJointSurgBr.2002;84:15–8. 6. ZeckeyC,MommsenP,AndruszkowH,MackeC,FrinkM,
StübigT,etal.Theasepticfemoralandtibialshaftnon-union inhealthypatients–ananalysisofthehealth-relatedquality oflifeandthesocioeconomicoutcome.OpenOrthopJ. 2011;5:193–7.
7.DijkimanBG,SpragueS,SchemitschEH,BhandariM.Whenis afracturehealed?Radiographicandclinicalcriteriarevisited. JOrthopTrauma.2010;24Suppl.3:S76–80.
8.AntonovaE,KimLeT,BurgeR,MershonJ.Tibiashaft fractures:costlyburdenofnonunions.BMCMusculoskelet Disord.2013;14:42.
9.DavisBJ,RobertsPJ,MoorcroftCI,BrownMF,ThomasPB, WadeRH.Reliabilityofradiographsindefiningunionof internallyfixedfractures.Injury.2004;35(6):557–61. 10.WhelanDB,BhandariM,StephenD,KrederH,McKeeMD,
ZderoR,etal.Developmentoftheradiographicunionscore fortibialfracturesfortheassessmentoftibialfracture healingafterintramedullaryfixation.JTrauma.2010;68(3): 629–32.
11.PhillipsAM.Overviewofthefracturehealingcascade.Injury. 2005;36Suppl.3:S5–7.
12.BhandariM,GuyattGH,SwiontkowskiMF,TornettaP3rd, SpragueS,SchemitschEH.Alackofconsensusinthe assessmentoffracturehealingamongorthopaedicsurgeons. JOrthopTrauma.2002;16(8):562–6.
13.CorralesLA,MorshedS,BhandariM,MiclauT3rd.Variability intheassessmentoffracture-healinginorthopaedictrauma studies.JBoneJointSurgAm.2008;90(9):1862–8.
14.HungriaJOS,MercadanteMT.Fraturaexpostadadiáfiseda tíbia–Tratamentocomosteossínteseintramedularapós estabilizac¸ãoprovisóriacomfixadorexternonãotransfixante. RevBrasOrtop.2013;48(6):82–90.
15.PanjabiMM,WalterSD,KarudaM,WhiteAA,LawsonJP. Correlationsofradiographicanalysisofhealingfractureswith strength:astatisticalanalysisofexperimentalosteotomies.J OrthopRes.1985;3(2):212–8.
16.FreedmanEL,JohnsonEE.Radiographicanalysisoftibial fracturemalalignmentfollowingintramedullarynailing.Clin OrthopRelatRes.1995;(315):25–33.
17.MacriF,MarquesLF,BackerRC,SantosMJ,BelangeroWD. Validationofastandardisedgaitscoretopredictthehealing oftibialfractures.JBoneJointSurgBr.2012;94(4):544–8. 18.AliS,SinghA,AgarwalA,PariharA,MahdiAA,SrivastavaRN.
ReliabilityoftheRUSTscorefortheassessmentofunionin simplediaphysealtibialfractures.IJBR.2014;5(5):333–5. 19.C¸ekicE,AliciE,YesilM.Reliabilityoftheradiographicunion