r e v b r a s r e u m a t o l . 2017;57(1):85–87
w w w . r e u m a t o l o g i a . c o m . b r
REVISTA
BRASILEIRA
DE
REUMATOLOGIA
Case
report
Intracardiac
thrombosis
in
Behc¸et’s
disease:
a
life
threatening
event
Trombose
intracardíaca
na
doenc¸a
de
Behc¸et:
evento
com
risco
de
vida
Pedro
Madureira
a,b,∗,
Mariana
Rodrigues
c,
Edite
Serrano
d,
Artur
Bonito
Vítor
c,
Iva
Brito
a,b,caCentroHospitalardeSãoJoão,Servic¸odeReumatologia,Porto,Portugal
bFaculdadedeMedicinadoPorto,DepartamentodeReumatologia,Porto,Portugal
cCentroHospitalardeSãoJoão,Porto,DepartamentodePediatria,Porto,Portugal
dCentroHospitalardeSãoJoão,CardiologiaPediátrica,Porto,Portugal
a
r
t
i
c
l
e
i
n
f
o
Articlehistory:
Received31July2014 Accepted9November2014 Availableonline24January2015
Introduction
Behc¸et’sDisease (BD)is amultisystemicinflammatory dis-ease of unknown etiology. Although previously classified amongthesystemicvasculitides,recentclinical, immunolog-icalandgeneticinvestigationsledtoitsclassificationwithin theautoinflammatorydisorders,1eventhoughthis
classifica-tionisfarfromconsensualordefinitive.2,3
It is characterizedby recurrent oral and genital ulcers, uveitis,arthritisandskinlesionssuchaserythemanodosum or pseudofolliculitis.4 In more severe cases it may also
course with gastrointestinal, pulmonary, neurological and cardiovascular manifestations.5 Cardiac manifestations are
estimatedtobepresent in 1–6%6 ofpatients withBD, and
include acute myocardial infarction, conduction system disorders, valvular diseases, pericarditis, endomyocardial fibrosis, coronary arteritis and intracardiac thrombosis.5–7
∗ Correspondingauthor.
E-mail:pmsmadureira@gmail.com(P.Madureira).
Intracardiac thrombosisprevalence isuncommon, and the evidenceforitstreatmentislacking.6
Case
report
Theauthorsreportthecaseofamalepatient,14yearsold, with a previous history of recurrent oral ulcers, attention deficithyperactivitydisorderandasthma.
ThepatientwasadmittedtothePediatricwardofour hos-pitalwithfever,oralulcersandredeyethatstarted2weeks previously,andcomplicatedlaterwithcoughandright tho-racic pain. Suspecting pulmonary infection he was started onazithromycinfor5days,butthesymptomskept worsen-ing withincreasingfeverspikesandthe onsetoferythema nodosumandpseudofolliculitislesionsonhisrightleg.The pulmonaryx-ray showeda rightparacardiac consolidation,
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rbre.2014.11.002
86
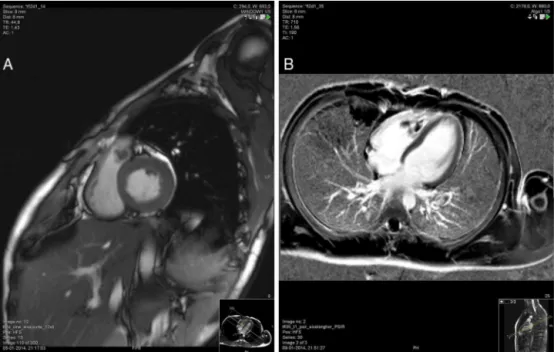
r e v b r a s r e u m a t o l . 2017;57(1):85–87Fig.1–Contrast-enhancedcardiacMRIwiththrombivisibleintherightventricleoutflowtract(A),andintherightventricle (B).
andthepatientwasthenstartedonampicillin.Despitethe improvementoftherespiratorysymptoms,thepatient main-tained daily fever spikes and 3 genital ulcers were then noticed.Infectiousagentswereexcludedandtheautoimmune labtestpanelwasnegativeforANA,anti-cardiolipins, circu-latingimmunecomplexesandANCA.Theechocardiography wasnormalatthattime.
The suggestive clinical picture allied to a positive HLA B51determinationandpathergytestallowedthediagnosisof BD.Hewasstartedoncolchicine1mg/dayandprednisolone 20mg/daywithresolutionofthesymptoms.
Three weeks later on a routine echocardiography a 9x21mmmassadjacenttotheleftcuspofthepulmonaryvalve wasdetected.Onphysicalexaminationasoftsystolic mur-murwasheardonupperleftsternaledge.Onthesuspicion ofendocarditisprednisolonedosewasreducedto10mg/day andthepatientwas startedonamoxicillin/clavulanateand gentamicin.Despitetheantibioticsarecurrentfeverwithnew oralulcersappeared3daysaftertheadmission, andserial cardiacultrasoundskeptshowingthecardiacmass.Blood cul-tureswerenegative.Fourweeksafterthehospitaladmission anewechocardiographyshowed2newlesionsontheright ventricle.Giventheabsenceofresponsetothetreatment,a contrast-enhancedcardiacmagneticresonanceimaging(MRI) wasperformed(Fig.1),showingseveralintracardiacthrombi ontherightventriclewithanoverall4cmlongitudinalsizeand anotheroneonthe rightventricle outflowtract,protruding tothepulmonarytrunk.Therewerealsosignsofpulmonary thromboembolism on segmentalbranches ofinferior lobar arteries, 2 occlusive thrombi on the right internal jugular vein,severestenosisoftherightbrachiocephalicveinanda non-occlusivethrombusofthesuperiorvenacava.Low molec-ularweightheparinwasimmediatelystartedandthepatient wassubmittedtocardiacsurgeryforexcisionofthe intrac-ardiacthrombi.Histologicalexaminationofthelesionswas
suggestive ofachronicinflammatoryprocesswith myocar-dialinvolvement,withoutevidenceofinfectiousorneoplastic disease.
With the exclusion of infection and neoplasia, it was assumed that the intracardiac masses were secondary to heart involvementbyBD. Prednisolonedose wasincreased to 1mg/kg/day and monthly cyclophosphamide pulses (500mg/m2), and oral anticoagulation with warfarin, were
started.Thepatientdidnothavenewfeverspikesandtheoral and genitalulcersresolved.Contrast-enhancedcardiacMRI performed4monthslatershowedacomplete resolutionof theintracardiac,pulmonaryandsuperiorvenacava thrombo-sis,withresidualthrombusseenontherightinternaljugular veinandtherightbrachiocephalicvein.
Discussion
Theauthorspresentararecaseofanadolescentwitharecent diagnosisofBDthatisadmittedwithintracardiacthrombosis, superior vena cava syndrome and pulmonary thromboem-bolism.Thepatientwassubmittedtosurgerytoexcise the lesionsandhasbeentreatedwithcyclophosphamide, pred-nisoloneandcolchicineachievingcompleteremission.Toour knowledgethereisonlyoneotherreportedcaseofintracardiac thrombosisonanadolescentwithBD.8
CardiacinvolvementinBehc¸et’sDiseaseisanuncommon manifestationwithmajorimplicationsonthedisease progno-sis.OnarecentliteraturereviewbyGeriandcolleaguesthere wereonly22casesofintracardiacthrombosisreportedfrom 1992to2010;mostofthe casesoccurred inmenand were limitedtotherightventricleandatrium.6The5-yearsurvival
r e v b r a s r e u m a t o l . 2017;57(1):85–87
87
Wecurrentlyknowtheimportantroleofboththeinnate andadaptiveimmunesystemsinthediseasepathogenesis,2
but the pathophysiology of the thrombotic predisposition amongthesepatientsarestillmainlyunknown.Several mech-anisms have been proposed, such as endothelial lesions, increasedlevelsofprothromboticfactorsandimmune com-plexesdepositioninthebloodvessel.9
Inthepresenceofintracardiaclesionsitisimportantto excludeother diagnoses,such as endocarditis and cardiac tumor,inorder toassumeheart involvementbyBDasthe causeofthelesions.Althoughtransthoracicechocardiography isanexcellentimagingmodalitytoscreenandevaluate intrac-ardiaclesions,insomecases,suchastheonepresented,it lackssensitivityonidentifyingandcharacterizingthethrombi whencomparedtocardiacMRI.1,10
Theevidenceforthetreatmentofintracardiac thrombo-sisin BDis based on casereports or case series available intheliterature,andcurrentlythereisnoconsensusonthe mosteffectiveapproach.Mostofthecasesreportedhavebeen treatedwithacombinationofanticoagulantand immunosup-pressiveagents (azathioprineor cyclophosphamide),which seems to beassociated withhigher rates of remission.6 It
shouldbenotedthatinthepresenceofaneurysmofthe pul-monaryarteryanticoagulantagentsshouldbeavoidedorused withcaution,astheyare associatedwith increasedriskof severehemoptysis.1,9Cardiacsurgeryshouldbeconsideredon
thecasesofextensiveorrecurrentthrombosisdespitemedical treatment,orwhenitisassociatedwithcardiaccongestion.9
Conflicts
of
interest
Theauthorsdeclarenoconflictsofinterest.
r
e
f
e
r
e
n
c
e
s
1.CoccoG,GasparyanAY.Behcet’sdisease:aninsightfroma cardiologist’spointofview.OpenCardiovascMedJ. 2010;4:63–70.
2.DireskeneliH.Autoimmunityvsautoinflammationin Behcet’sdisease:doweoversimplifyacomplexdisorder? Rheumatology(Oxford).2006;45:1461–5.
3.YaziciH,UgurluS,SeyahiE.Behcet’ssyndrome:isitone condition?ClinRevAllergyImmunol.2012;43:275–80.
4.DoganSM,BirdaneA,KorkmazC,AtaN,TimuralpB.Right ventricularthrombuswithBehcet’ssyndrome:successful treatmentwithwarfarinandimmunosuppressiveagents.Tex HeartInstJ.2007;34:360–2.
5.JagadeeshLY,WajedJ,SangleSR,Carr-WhiteG,D’CruzDP. CardiaccomplicationsofBehcet’sdisease.ClinRheumatol. 2014;33:1185–7.
6.GeriG,WechslerB,ThiHuongduL,IsnardR,PietteJC, AmouraZ,etal.SpectrumofcardiaclesionsinBehcet’s disease:aseriesof52patientsandreviewoftheliterature. Medicine(Baltimore).2012;91:25–34.
7.MarzbanM,MandegarMH,KarimiA,AbbasiK,MovahediN, NavabiMA,etal.Cardiacandgreatvesselinvolvementin Behcet’sdisease.JCardSurg.2008;23:765–8.
8.VivanteA,BujanoverY,JacobsonJ,PadehS,BerkunY. Intracardiacthrombusandpulmonaryaneurysmsinan adolescentwithBehcet’sdisease.RheumatolInt. 2009;29:575–7.
9.LoualiFE,TamdyA,SoufianiA,OukerrajL,OmariD, BounjoumF,etal.Cardiacthrombosisasamanifestationof Behcet’ssyndrome.TexHeartInstJ.2010;37:568–71.