RevBrasAnestesiol.2017;67(2):214---216
REVISTA
BRASILEIRA
DE
ANESTESIOLOGIA
PublicaçãoOficialdaSociedadeBrasileiradeAnestesiologiawww.sba.com.br
CLINICAL
INFORMATION
Paratracheal
cyst
rupture:
a
differential
diagnosis
for
tracheal
rupture
Joana
Marques
∗,
Ana
Rita
Henriques,
Luisa
Azevedo,
Daniela
Chalo,
Adelina
Almeida
CentroHospitalarBaixoVouga,DepartamentodeAnestesiologia,Aveiro,Portugal
Received21June2014;accepted21July2014 Availableonline28October2014
KEYWORDS
Trachealrupture; Paratrachealcyst; Anesthetic complications
Abstract Tracheobronchialruptureisararebutpotentiallylife-threateningcomplication com-monlycausedbyneckandchesttrauma.Iatrogenictracheobronchialrupturecanbecausedby intubation,tracheostomy,bronchoscopybutalsolinkedtopre-existingprimarydiseases. Para-trachealaircysts,infrequentlydescribedinliterature,seemtobeassociatedwithobstructive lungdiseaseandweaknessesinrightposteriorlateralwallofthetrachea.Wereportacaseof aparatrachealaircystruptureinaprevioushealthypatient.
©2014SociedadeBrasileiradeAnestesiologia.PublishedbyElsevierEditoraLtda.Thisisan openaccessarticleundertheCCBY-NC-NDlicense( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
PALAVRAS-CHAVE
Rupturatraqueal; Cistoparatraqueal; Complicac¸ões anestésicas
Rupturadecistoparatraqueal:umdiagnósticodiferencialpararupturatraqueal
Resumo A ruptura traqueobrônquica (RTB) é uma complicac¸ão rara, mas potencialmente fatalcomumentecausadaportraumadepescoc¸oetórax.ARTBiatrogênicapodesercausada porintubac¸ão,traqueostomia,broncoscopia,mastambémpodeestarrelacionadaadoenc¸as primárias pré-existentes.Os cistosaéreos paratraqueais,raramentedescritos naliteratura, parecemestarassociadosàdoenc¸apulmonarobstrutiva efraquezadaparedeposterolateral direitadatraqueia.Relatamosocasodeumarupturadecistoaéreoparatraquealempaciente previamentesaudável.
©2014SociedadeBrasileiradeAnestesiologia.PublicadoporElsevierEditoraLtda.Este ´eum artigoOpen Accesssobumalicenc¸aCCBY-NC-ND( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
∗Correspondingauthor.
E-mail:joanalbm@gmail.com(J.Marques).
Introduction
Tracheobronchialrupture(TBR)isararebutpotentially life-threateningcomplicationcommonlyfoundinneckandchest trauma,but alsolinkedtopre-existingprimarypulmonary
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bjane.2014.07.014
Paratrachealcystrupture:adifferentialdiagnosisfortrachealrupture 215
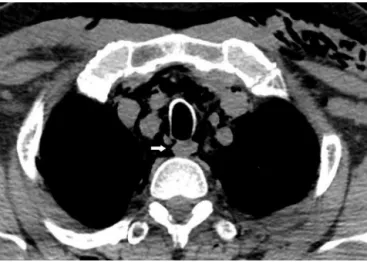
Figure1 Paratrachealcystrupture.
diseases.1 Orotrachealintubation,tracheostomyand bron-choscopyarealsopossibleiatrogeniccauses.2
Paratrachealaircystsarepoorlydescribedinliterature andonlyfoundinsmallserieswithfewpatientsorisolated casesinradiologicliterature.
Patientgaveconsenttopublicationofthedetails.
Case
description
Wepresentacasereportofatrachealruptureinapatient withclinicalsignsandCTfindingsofaparatrachealaircyst (Figs.1and2).
A 55-year-old man, ASA physical status II, underwent elective transoral laser microsurgery for Reincke’s edema treatment.Hehadnodiagnosisofpulmonarydiseasebesides chronictabagism.Nosignsofdifficultintubation.
Afterintravenousanesthesiainduction(remifentanil per-fusion,propofolandrocuronium),thepatientwasintubated with 5.0mm Laser-Flex® tracheal tube and registered a
Cormarck-LehanelaryngoscopygradeII.Immediatelyafter intubation, ETCO2 was not detected and a desaturation
occurred,whichjustifiedreplacementofthetube,although visually there was no doubt of tracheal intubation. Sec-ond attempt was tried and the same occurred. By the third attempt, performed withthe sametube, intubation
Figure2 Paratrachealcystrupture1.
wassuccessfully confirmed by capnography and ausculta-tion. About ten minutes later, peak inspiratory pressure increased to 39cm H2O and ETCO2 to 53mmHg, SpO2
droppedto89%andpulmonaryauscultationrevealedaudible rhonchi bilaterally. Hydrocortisone (100mg) and amino-phylin(240mg)wereadministeredandinspiredfractionof O2wasincreasedto70%.Parametersreturnedtonormalin
5min.
After 60min of surgery, extubation was performed without complications. On the second postoperative day, patient developed severe cervical and thoracic subcuta-neousemphysemawithoutrespiratoryinsufficiency.
CTrevealedapneumomediastinumwithaposterolateral trachealfocaldiscontinuitydefectwith1mmlong,located 2.5cmabovecarinawhichopenedininspirationwithahigh suspicionofbeingatrachealcystrupture,confirmedby car-diothoracicsurgeon.
Discussion
Paratrachealaircystscanbepresentinapproximately3.7% ofthepopulation.3Somereportssuggestanassociationwith obstructivelungdiseaseandemphysema,duetoweakness in the right lateral posterior wall of trachea, at the tho-racicinletlevel,becauseofincreasedexpiratorypressures inthesetypeof patients,3but therearealsostudiesthat didnotfindanyrelationshipbetweenthem.4
The term paratracheal cyst is very unspecific for an aircollection.Apparentlytheyarenothing morethan tra-chealdiverticula,linedbyciliatedcolumnarepithelia,some of them with one or multiple narrow connections to the trachea.3 Probablybecause of theincreased resolution in CTscanning,theincidenceofcommunicationswithtrachea variesfrom8%to35%.3,4Trachealright-sidedparatracheal aircystsmaybeunilocularormultilocular.
Diagnosis of paratracheal air cyst rupture is based on high clinical suspicion, thanks to the appearance of suggestive clinical signs and symptoms like subcutaneous emphysema, respiratory insufficiency, pneumothorax and hemoptysis.
Treatment of choice has been conservative or surgi-cal repair, depending on the lesion size and location. Nonsurgical treatment is advisable in small (<2cm) and uncomplicatedcases.5
Withthis case report, we intendto referparatracheal cystsasapossiblecausefortrachealrupture,infrequently describedinliteraturebutnotsouncommoninpopulation.
Conflicts
of
interest
Theauthorsdeclarenoconflictsofinterest.
References
1.RohJL,LeeJH.Spontaneoustrachealruptureaftersevere cough-ingina7-year-oldboy.Pediatrics.2006;118:e224---7.
216 J.Marquesetal.
3.GooJM,ImJG,AhnJM.Rightparatrachealaircystsinthe tho-racicinlet:clinicalandradiologicsignificance.AmJRoentgenol. 1999;173:65---70.
4.ButerbaughJE,ErlyWK.Paratrachealaircysts:acommon find-ingonroutineCTexaminationsofthecervicalspineandneck
thaymaymimicpneumomediastinuminpatientswithtraumatic injuries.AmJNeuroradiol.2008;29:1218---21.